
上泽文通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 12-1 Microbial Genomics Chapter 12 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS A●NV ■■■ Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn
1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 12-1 Microbial Genomics Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn Chapter 12 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS
Genetic elements in bacteria Genetic elements:structures containing genetic material ·Chromosome Plasmid ·transposon Chen Feng,Lecture of Microbiology
Chen Feng, Lecture of Microbiology Genetic elements in bacteria Genetic elements: structures containing genetic material • Chromosome • Plasmid • transposon

I.Genomes and Genomics 11.1 Introduction to Genomics Genome Entire complement of genetic information Includes genes,regulatory sequences,and noncoding DNA 圈Genomics o Discipline of mapping,sequencing,analyzing,and comparing genomes Chen Feng,Lecture of Microbiology
Chen Feng, Lecture of Microbiology 11.1 Introduction to Genomics Genome • Entire complement of genetic information • Includes genes, regulatory sequences, and noncoding DNA Genomics • Discipline of mapping, sequencing, analyzing, and comparing genomes I. Genomes and Genomics
Genomics基因组学 Genomics is the study of the molecular organization of genomes,their information content,and the gene products they encode. Genomics can divided into at least three areas: Structural genomics:is the study of the physical nature of genomes.结构基因组学 Functional genomics:is concerned with the way in which the genome functions.功能基因组学 Comparative genomics:genomes from different organisms are compared to look for significant differences and similarities.比较基因组学 Chen Feng,Lecture of Microbiology
Chen Feng, Lecture of Microbiology Genomics基因组学 Genomics : is the study of the molecular organization of genomes, their information content, and the gene products they encode. Genomics can divided into at least three areas: Structural genomics: is the study of the physical nature of genomes. 结构基因组学 Functional genomics: is concerned with the way in which the genome functions. 功能基因组学 Comparative genomics: genomes from different organisms are compared to look for significant differences and similarities.比较基因组学
11.1 Introduction to Genomics >2,000 prokaryotic genomes sequenced or in progress RNA virus MS2 ·First genome sequenced in1976第一个被测出全基因 组的物种 ·3,569bp Haemophilus influenza流感嗜血杆菌 ·First cellular genome sequenced in1995第一个被测 出全基因组的细胞生物 ·1,830,137bp Chen Feng,Lecture of Microbiology
Chen Feng, Lecture of Microbiology 11.1 Introduction to Genomics >2,000 prokaryotic genomes sequenced or in progress RNA virus MS2 • First genome sequenced in 1976 第一个被测出全基因 组的物种 • 3,569 bp Haemophilus influenza流感嗜血杆菌 • First cellular genome sequenced in 1995 第一个被测 出全基因组的细胞生物 • 1,830,137 bp
11.2 Sequencing and Annotating Genomes Sequencing:determining the precise order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule @Sanger dideoxy method桑格双脱氧测序方法 Invented by Nobel Prize winner Fred Sanger Dideoxy analogs of dNTPs used in conjunction with dNTPs Analog prevents further extension of DNA chain Bases are labeled with radioactivity Gel electrophoresis is then performed on products Chen Feng,Lecture of Microbiology
Chen Feng, Lecture of Microbiology 11.2 Sequencing and Annotating Genomes Sequencing: determining the precise order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule Sanger dideoxy method 桑格双脱氧测序方法 • Invented by Nobel Prize winner Fred Sanger • Dideoxy analogs of dNTPs used in conjunction with dNTPs • Analog prevents further extension of DNA chain • Bases are labeled with radioactivity • Gel electrophoresis is then performed on products
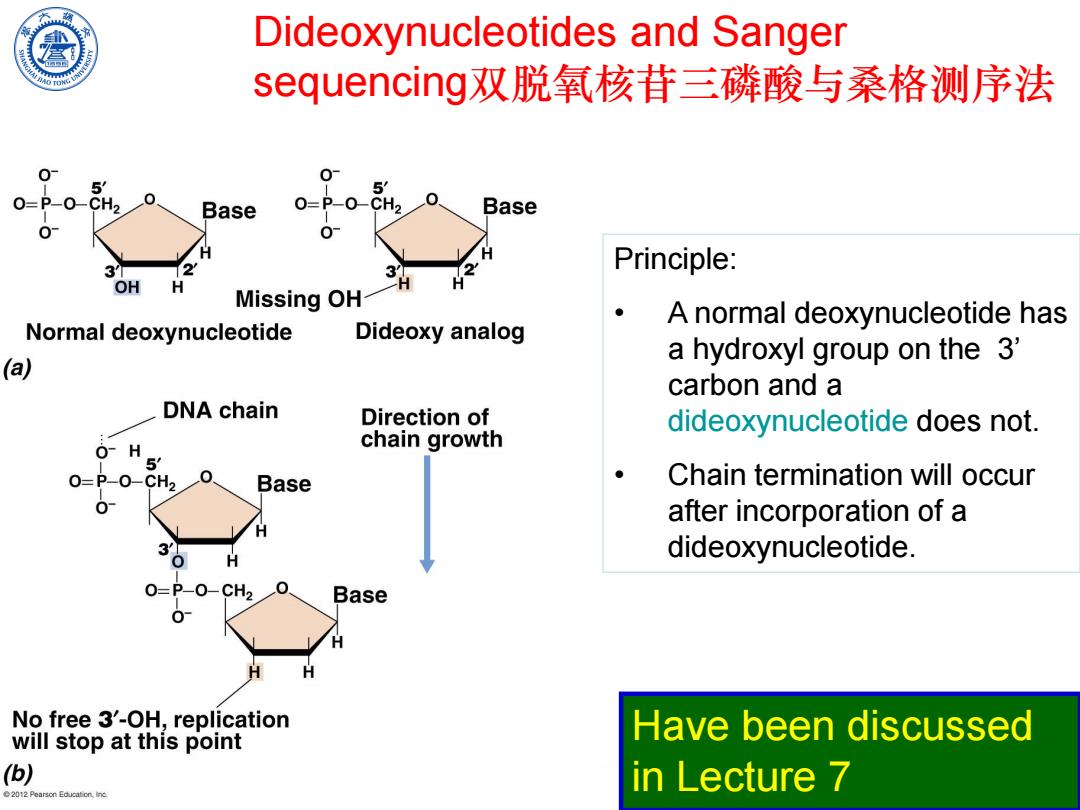
Dideoxynucleotides and Sanger sequencing双脱氧核苷三磷酸与桑格测序法 5 CH2 Base O=P-O-CH2 Base 0 3 Principle: OH H Missing OH- A normal deoxynucleotide has Normal deoxynucleotide Dideoxy analog (a) a hydroxyl group on the 3' carbon and a DNA chain Direction of dideoxynucleotide does not. O-H chain growth 5 0=P-0-CH20 Base Chain termination will occur 0 after incorporation of a dideoxynucleotide. P-O-CH2 Base No free 3'-OH,replication will stop at this point Have been discussed (b) in Lecture 7 2012 Pearson Educaton,ine
Chen Feng, Lecture of Microbiology Dideoxynucleotides and Sanger sequencing双脱氧核苷三磷酸与桑格测序法 Principle: • A normal deoxynucleotide has a hydroxyl group on the 3’ carbon and a dideoxynucleotide does not. • Chain termination will occur after incorporation of a dideoxynucleotide. Have been discussed in Lecture 7
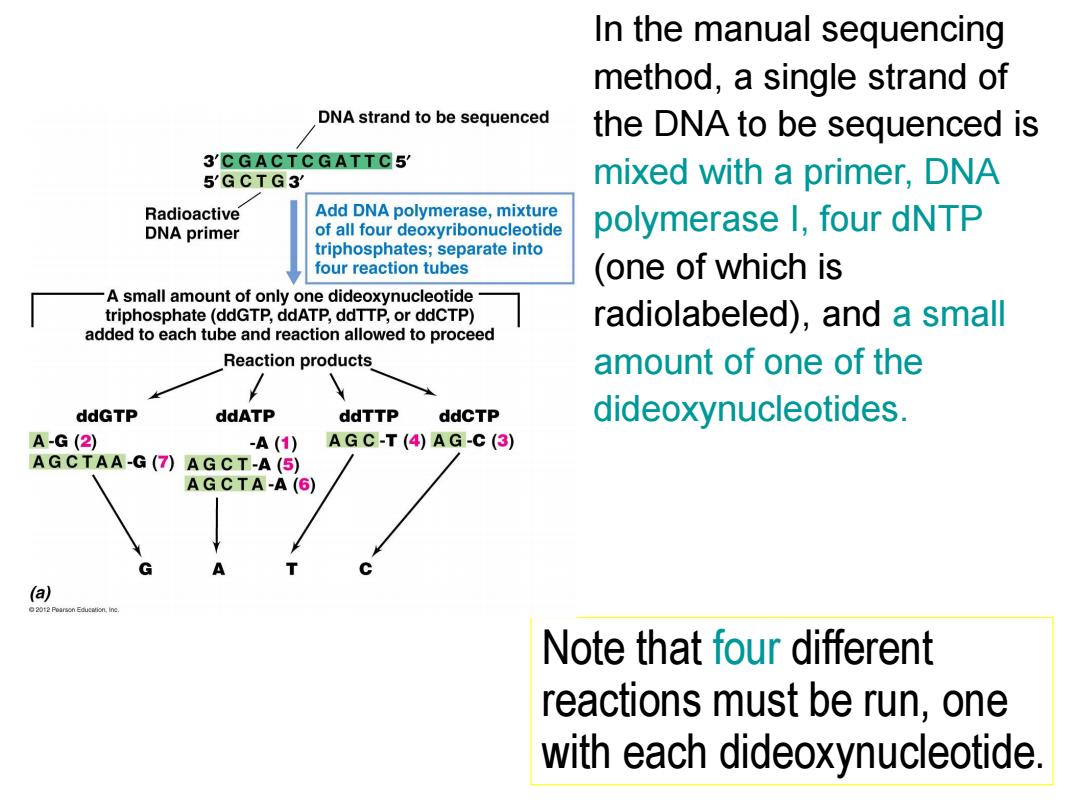
In the manual sequencing method,a single strand of DNA strand to be sequenced the DNA to be sequenced is 3'CGACTCGATTC5 5'GCTG3 mixed with a primer,DNA Radioactive Add DNA polymerase,mixture DNA primer of all four deoxyribonucleotide polymerase I,four dNTP triphosphates;separate into four reaction tubes (one of which is -A small amount of only one dideoxynucleotide triphosphate(ddGTP,ddATP,ddTTP,or ddCTP) radiolabeled),and a small added to each tube and reaction allowed to proceed Reaction products amount of one of the ddGTP ddATP ddTTP ddCTP dideoxynucleotides. A-G(2) -A(1) AGC-T(4)AG-C(3) AGCTAA-G(7)AGCT-A(5) AGCTA-A(6) A a 2012 Poarson,ine Note that four different reactions must be run,one with each dideoxynucleotide
In the manual sequencing method, a single strand of the DNA to be sequenced is mixed with a primer, DNA polymerase I, four dNTP (one of which is radiolabeled), and a small amount of one of the dideoxynucleotides. Note that four different reactions must be run, one with each dideoxynucleotide
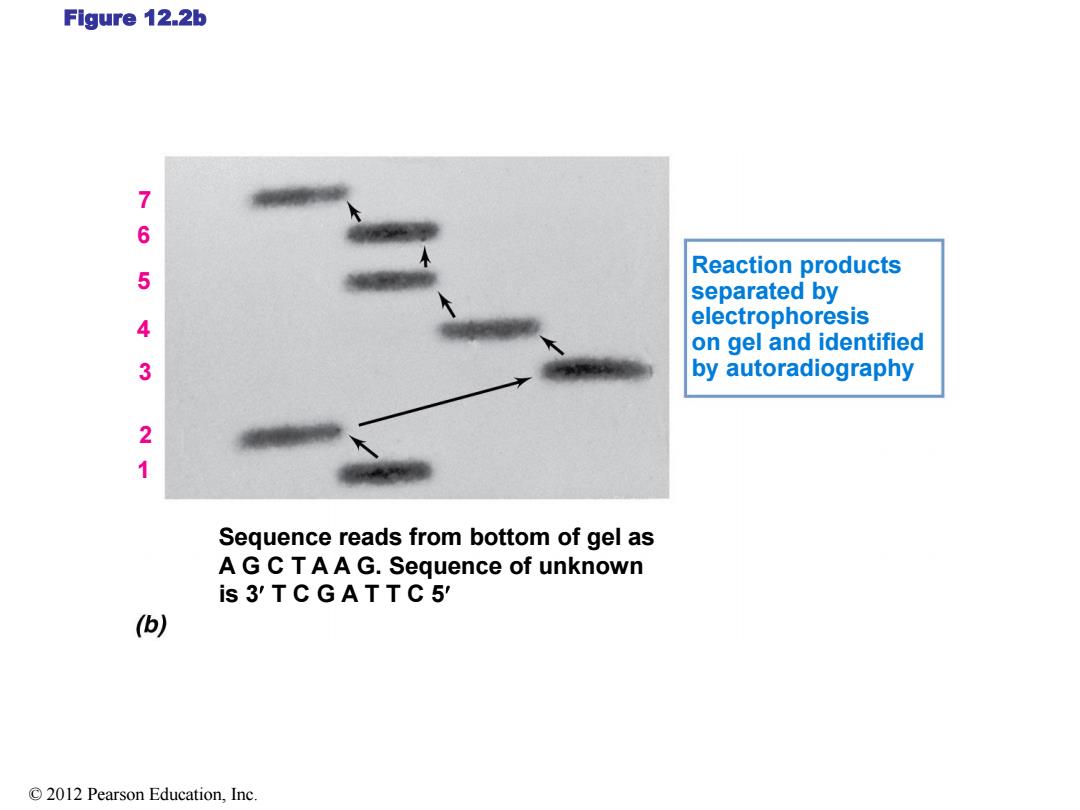
Figure 12.2b 7 6 Reaction products 5 separated by 4 electrophoresis on gel and identified 3 by autoradiography 2 1 Sequence reads from bottom of gel as A G C TAA G.Sequence of unknown is 3'TCGATTC5' () 2012 Pearson Education,Inc
Figure 12.2b Reaction products separated by electrophoresis on gel and identified by autoradiography 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Sequence reads from bottom of gel as A G C T A A G. Sequence of unknown is 3 T C G A T T C 5 © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc
automated DNA sequencing systems Large-scale sequencing projects have led to automated DNA sequencing systems . Based on Sanger method Radioactivity replaced by fluorescent dye Chen Feng,Lecture of Microbiology
Chen Feng, Lecture of Microbiology automated DNA sequencing systems Large-scale sequencing projects have led to automated DNA sequencing systems • Based on Sanger method • Radioactivity replaced by fluorescent dye