
CHARLESK.ALEXANDERMATTHEWNO.SADIKUELECTRICCIRCUITS
PrefaceIntroduction中Place of Electrical Circuits in Modern TechnologyThe design of the circuits has 2 main objectives1) To gather, store, process, transport, and present information2)To distribute and convert energy between various formsThe study of circuits provides afoundation for areas of electricaengineering suchas:.Communicationsystem·Electromagnetic.Computersystem·Power systems.Control system·Signal processing·Electronics
Preface • Place of Electrical Circuits in Modern Technology Introduction The design of the circuits has 2 main objectives: 1) To gather, store, process, transport, and present information. 2) To distribute and convert energy between various forms. The study of circuits provides a foundation for areas of electrical engineering such as: • Communication system •Computer system •Control system •Electronics •Electromagnetic •Power systems •Signal processing
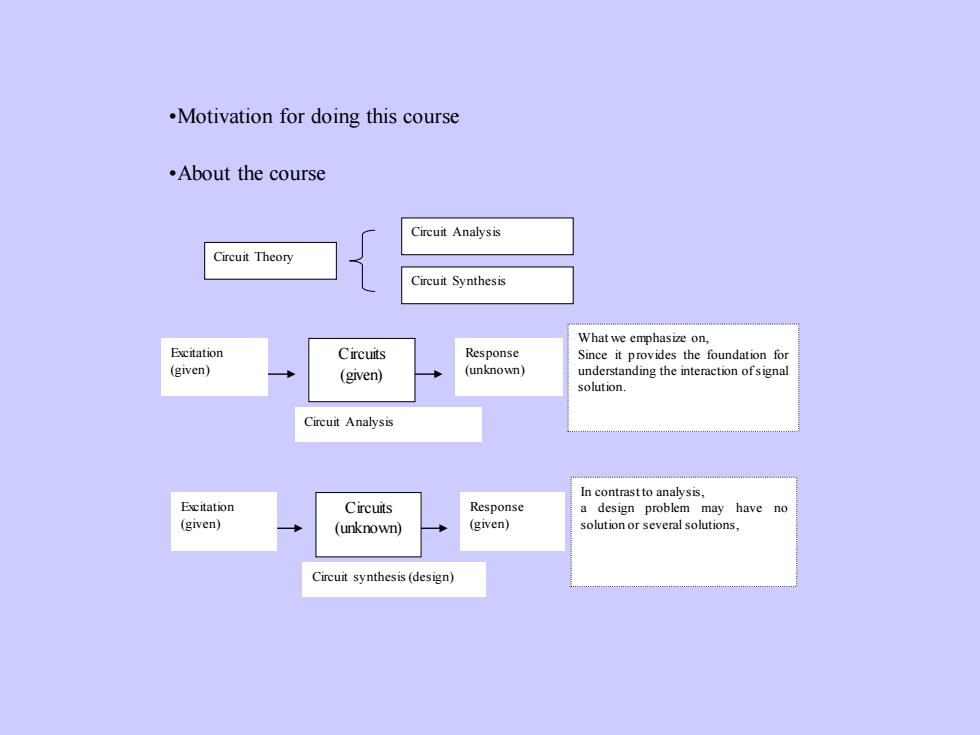
·Motivation for doing this course·About the courseCircuit AnalysisCircuit TheoryCircuit SvnthesisWhat we emphasize on,ExcitationCircuitsResponseSince it provides the foundation for(given)(unknown)understanding the interaction ofsignal(given)solution.Circuit AnalysisIn contrastto analysis,ExcitationCircuitsResponsehavenoadesign problem may(given)(given)solutionorseveral solutions,(unknown)Circuit synthesis (design)
•Motivation for doing this course •About the course Circuit Theory Circuit Analysis Circuit Synthesis Circuits (given) Excitation (given) Response (unknown) Circuit Analysis What we emphasize on, Since it provides the foundation for understanding the interaction of signal solution. Circuits (unknown) Excitation (given) Response (given) Circuit synthesis (design) In contrast to analysis, a design problem may have no solution or severalsolutions
Resistance circuits analysisThe course includes 3 parts:Dynamic circuits analysisSinusoidal steady state·Reference Books1)FundamentalsofElectricCircuitsCharlesKAlexanderMatthewNOSadiku清华大学出版社2)TheAnalysis and DesignofLinear CircuitsRoland E.Thomas,Albert J.Rosa2nd ed3)Electrical Engineering Principles and Applications Allan R.Hambley---2nd ed4)电路分析基础李瀚荪第三版5)电路邱关源第四版6)ElectricCircuitsJosephEdminister,MahmoodNahvi-----3rded
Resistance circuits analysis Dynamic circuits analysis Sinusoidal steady state The course includes 3 parts: •Reference Books 1)Fundamentals of Electric Circuits Charles K Alexander, Matthew N O Sadiku 清华大学出 版社 2)The Analysis and Design of Linear Circuits Roland E.Thomas, Albert J.Rosa—2 nd ed 3) Electrical Engineering Principles and Applications Allan R.Hambley -2 nd ed 4) 电路分析基础 李瀚荪 第三版 5) 电路 邱关源 第四版 6) Electric Circuits Joseph Edminister, Mahmood Nahvi -3 rd ed

Chapter 1Fundamental Knowledge
Chapter 1 Fundamental Knowledge
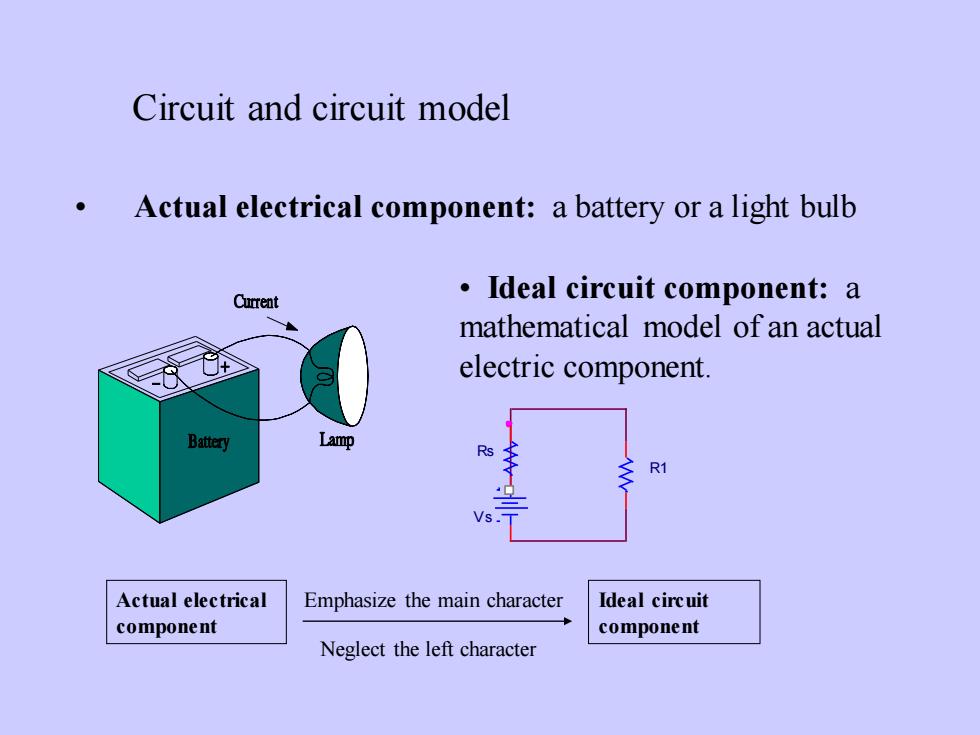
Circuit and circuit modelActual electrical component: a battery or a light bulb.Ideal circuit component:aCurrentmathematical model of an actualelectriccomponent.LampBatteryRsARTVsIdeal circuitActualelectricalEmphasizethemaincharactercomponentcomponentNeglecttheleftcharacter
Circuit and circuit model • Actual electrical component: a battery or a light bulb Actual electrical component Ideal circuit component Emphasize the main character Neglect the left character • Ideal circuit component: a mathematical model of an actual electric component. R1 V s Rs
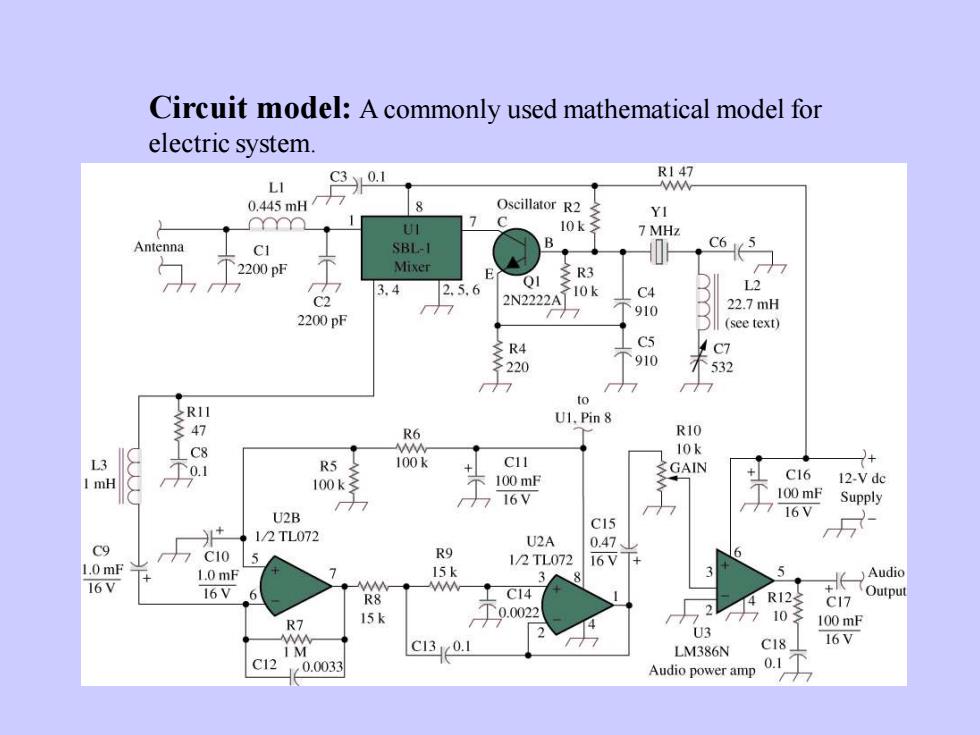
Circuit model: A commonly used mathematical model forelectric systemR147.0.1C3L18OscillatorR20.445mHYI17C10kUI7MHzBCeTAntennaSBL-1C1Mixer2200pF≥R3EQIL23,42.5,6>10kC42N2222AC222.7mH9102200pF(see text)C5LC7≥R4910532220to>R11U.Pin8W47R10.R610kC82+C11100kL3R5>GAINT0.1C1612-Vdc100mF1mH100k100mFSupply716V16VU2BC151/2TL072U2A0.47C9R9C10512TL07216V1.0mF15k7AudioL.OmF316VOutput16VC146R12R8C170.00221015k100mFR7U316VC18C130.1LM386NiM0.1C120.0033Audiopoweramp
Circuit model: A commonly used mathematical model for electric system
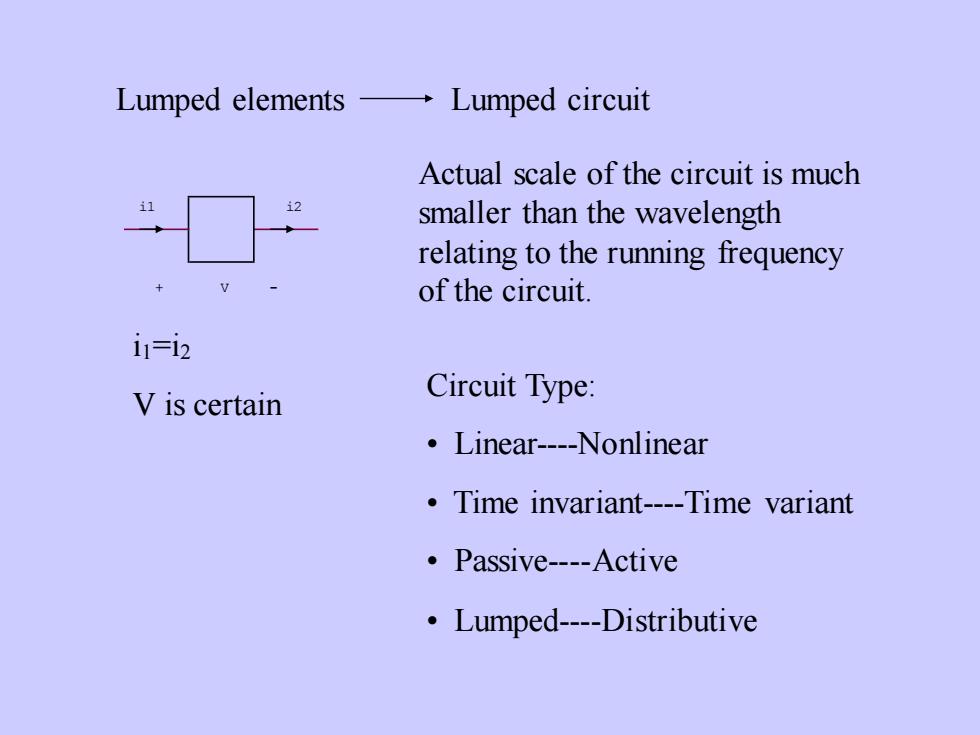
Lumped elements → Lumped circuitActual scale of the circuit is muchi2i1smaller than the wavelengthrelating to the running frequencyVof the circuit.ii=i2Circuit Type:V is certain. Linear----Nonlinear? Time invariant----Time variant.Passive----ActiveLumped----Distributive
Lumped elements Lumped circuit i2 + V - i1 i1=i2 V is certain Actual scale of the circuit is much smaller than the wavelength relating to the running frequency of the circuit. Circuit Type: • Linear-Nonlinear • Time invariant-Time variant • Passive-Active • Lumped-Distributive

Circuit VariablesElectric current is the time rate ofchange of charge,measured inamperes (A)dq1dtA direct current (DC) is a current thatremains constant with time. (I)SortAn alternating current (AC) is a current that variessinusoidally with time
Circuit Variables dt dq i = n Electric current is the time rate of change of charge, measured in amperes (A). A direct current (DC) is a current that remains constant with time. (I) An alternating current (AC) is a current that varies sinusoidally with time. Sort

Reference directioni>0 means the real direction issame to the reference directioni <0 means the real direction isopposite to the reference direction5A-5A(b)(a)
Reference direction i i >0 means the real direction is same to the reference direction i <0 means the real direction is opposite to the reference direction