
Oral physiology Oral Function ZHANG LEI School of Dentistry,Tongji University 1902
Oral physiology Oral Function ZHANG LEI School of Dentistry, Tongji University
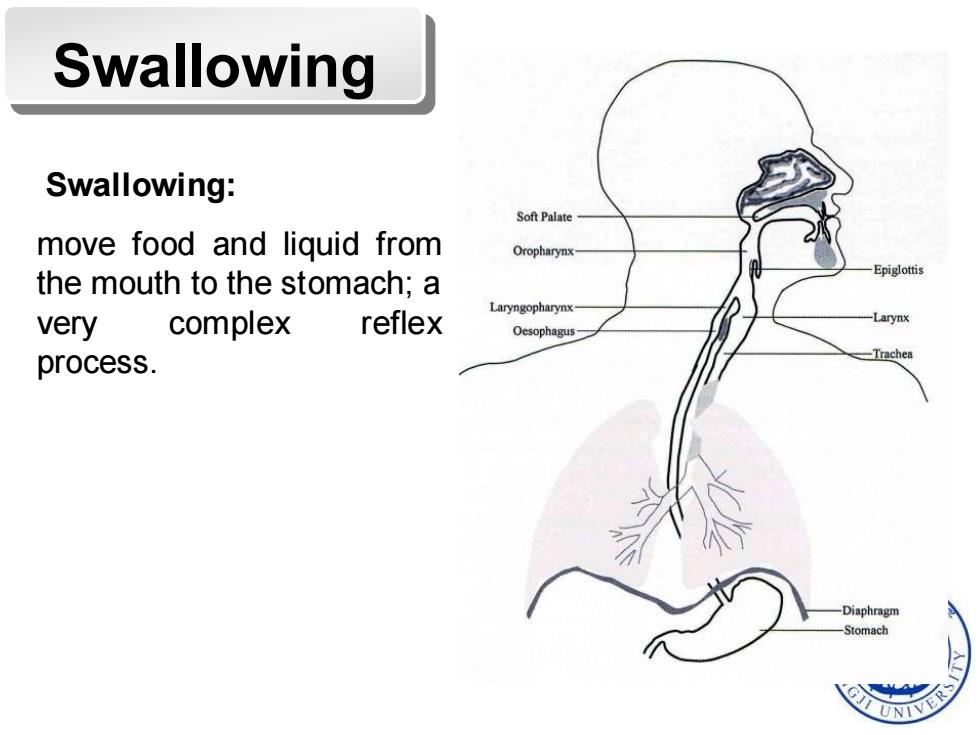
Swallowing Swallowing: Soft Palate move food and liquid from Oropharynx the mouth to the stomach;a Laryngopharynx very complex reflex Oesophagus process. -Diaphragn tomach
Swallowing Swallowing: move food and liquid from the mouth to the stomach; a very complex reflex process

Process of swallowing I.Oral preparatory phase: the food is chewed and mixed with saliva to form a moist,cohesive bolus ready to be swallowed. Il.Pharyngeal phase: When the food bolus comes into contact with the mucosa of the pharynx and larynx,it activates mucosal mechanoreceptors, hence activate many muscles that are involved in swallowing.The next event in this complex sequence of events is the inhibition of respiration. Ill.Oesophageal phase: 190 Once in the oesophagus,the food bolus is propelled towards stomach by peristalsis(partly controlled by the vagus nerve)
I. Oral preparatory phase: the food is chewed and mixed with saliva to form a moist, cohesive bolus ready to be swallowed. II. Pharyngeal phase: When the food bolus comes into contact with the mucosa of the pharynx and larynx , it activates mucosal mechanoreceptors, hence activate many muscles that are involved in swallowing. The next event in this complex sequence of events is the inhibition of respiration. III. Oesophageal phase: Once in the oesophagus, the food bolus is propelled towards the stomach by peristalsis (partly controlled by the vagus nerve) Process of swallowing

Speech Speech denote the peripheral processes that are needed to produce spoken language,it is a motor activity and consequently can be mapped onto anatomical structures of the articulatory tract. 1907
Speech Speech denote the peripheral processes that are needed to produce spoken language, it is a motor activity and consequently can be mapped onto anatomical structures of the articulatory tract

Functional subsystems of motor speech I.Respiration: Il.Phonation (sound production): Ill.Resonance: IV.Articulation: 4907
I. Respiration: II. Phonation (sound production): III. Resonance: IV. Articulation: Functional subsystems of motor speech
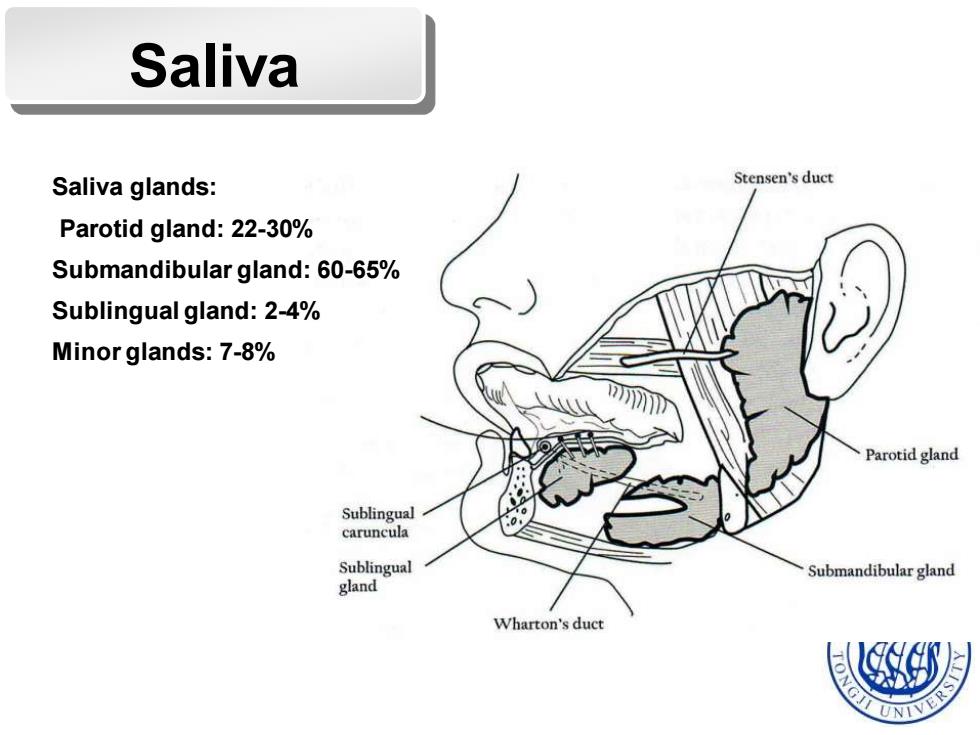
Saliva Saliva glands: Stensen's duct Parotid gland:22-30% Submandibular gland:60-65% Sublingual gland:2-4% Minor glands:7-8% Parotid gland Sublingual caruncula Sublingual Submandibular gland gland Wharton's duct
Saliva Saliva glands: Parotid gland: 22-30% Submandibular gland: 60-65% Sublingual gland: 2-4% Minor glands: 7-8%
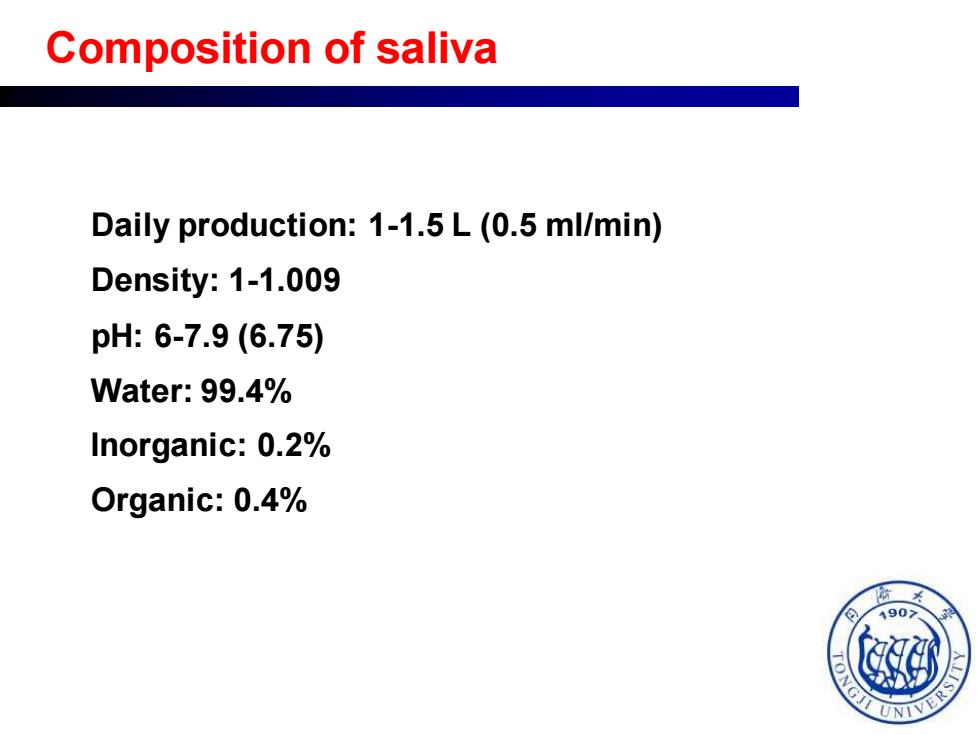
Composition of saliva Daily production:1-1.5 L (0.5 ml/min) Density:1-1.009 pH:6-7.9(6.75) Water:99.4% Inorganic:0.2% Organic:0.4% 4907 © G
Daily production: 1-1.5 L (0.5 ml/min) Density: 1-1.009 pH: 6-7.9 (6.75) Water: 99.4% Inorganic: 0.2% Organic: 0.4% Composition of saliva

Inorganic saliva composition Oral cavity Duct Acinus Interstitium HCO CI-K+Na+ Final saliva(mM) unstimulated stimulated Primary saliva(mM) Interstitium(mM) Na+ 3 45 Na146 Na+143 K 25 21 K 4 K+ 4 cI- 24 40 C102 C109 HCO 3 26 HCO28 HCO 28 Pco2 4.5 4.5(kPa) Pco2 6(kPa) Pco2 6 (kPa) pH 6.5 7.5 protein 2.0 2.5(mg/ml)
Inorganic saliva composition

Organic saliva composition Proteins: 1)Digestive enzymes: a-amylase:hydrolyses the a-1,4 glycosidic linkages of starch molecules Lipase:an enzyme able to break down dietary triglycerides. 2)Proteins with lubricating functions:Mucins(粘蛋白) 3)Calcium binding proteins::statherin(富酪蛋白) 4)Carbon dioxide hydration: Carbonic anhydrase:catalyse the reversible hydration of CO2.to carbonic acid. 5)Saliva proteins with antimicrobial functions: secretory IgA(slgA),mucins,lysozyme and lactoferrin(乳铁蛋白). 6)Growth factors in saliva: epidermal growth factor(EGF),Transforming growth factors(TGF-aand fibroblast growth factor(FGF)
Organic saliva composition Proteins: 1) Digestive enzymes: α-amylase: hydrolyses the α-1,4 glycosidic linkages of starch molecules Lipase: an enzyme able to break down dietary triglycerides. 2) Proteins with lubricating functions: Mucins(粘蛋白) 3) Calcium binding proteins: statherin(富酪蛋白) 4) Carbon dioxide hydration: Carbonic anhydrase: catalyse the reversible hydration of CO2 . to carbonic acid. 5) Saliva proteins with antimicrobial functions: secretory IgA (sIgA), mucins, lysozyme and lactoferrin(乳铁蛋白). 6) Growth factors in saliva: epidermal growth factor (EGF) , Transforming growth factors (TGF-a and TGF-P) , fibroblast growth factor (FGF)
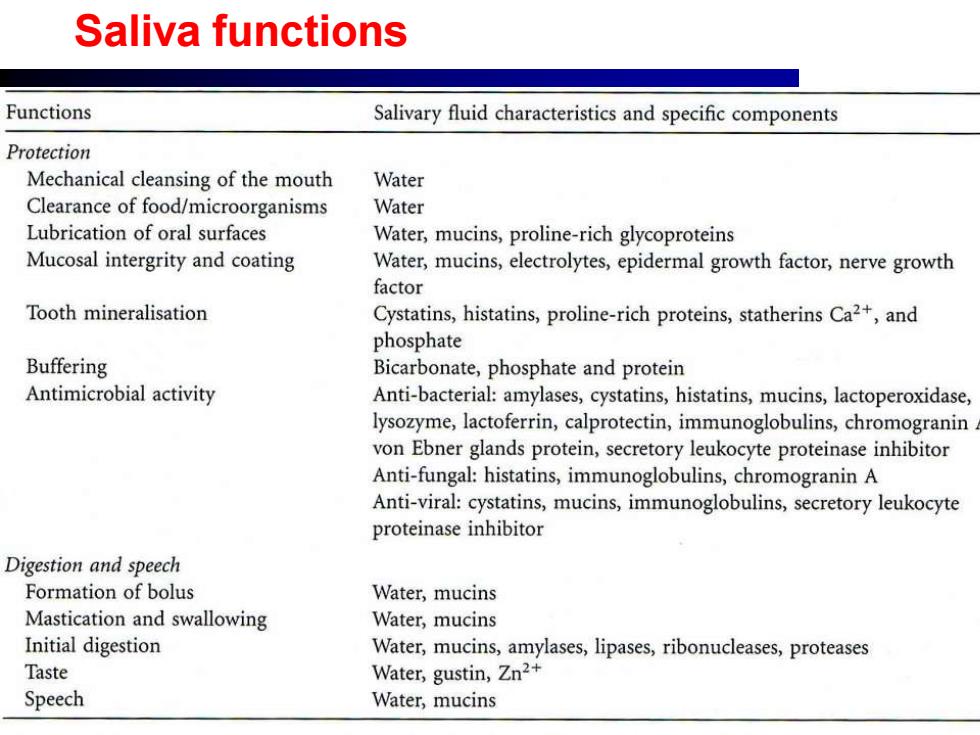
Saliva functions Functions Salivary fluid characteristics and specific components Protection Mechanical cleansing of the mouth Water Clearance of food/microorganisms Water Lubrication of oral surfaces Water,mucins,proline-rich glycoproteins Mucosal intergrity and coating Water,mucins,electrolytes,epidermal growth factor,nerve growth factor Tooth mineralisation Cystatins,histatins,proline-rich proteins,statherins Ca2+,and phosphate Buffering Bicarbonate,phosphate and protein Antimicrobial activity Anti-bacterial:amylases,cystatins,histatins,mucins,lactoperoxidase, lysozyme,lactoferrin,calprotectin,immunoglobulins,chromogranin von Ebner glands protein,secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor Anti-fungal:histatins,immunoglobulins,chromogranin A Anti-viral:cystatins,mucins,immunoglobulins,secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor Digestion and speech Formation of bolus Water,mucins Mastication and swallowing Water,mucins Initial digestion Water,mucins,amylases,lipases,ribonucleases,proteases Taste Water,gustin,Zn2+ Speech Water,mucins
Saliva functions