
Chapter two Structure of Genome nate图 thehuman genome
1 Chapter two Structure of Genome
Contents Part 1 Concepts of gene and genome Part 2 Structural features of virus genome Part 3 Structural features of prokaryotic genome Part 4 Structural features of eukaryotic genome Part 5 Features of some commonly used model organisms 2
2 Contents Part 1 Concepts of gene and genome Part 2 Structural features of virus genome Part 3 Structural features of prokaryotic genome Part 4 Structural features of eukaryotic genome Part 5 Features of some commonly used model organisms

Key points Concepts of gene and genome, C value and C value paradox, Splitting gene (intron and exon),satellite DNA, Features of prokaryotic eukaryotic genomes, Features of model organisms. 3
3 Key points: Concepts of gene and genome, C value and C value paradox, Splitting gene (intron and exon), satellite DNA, Features of prokaryotic & eukaryotic genomes, Features of model organisms
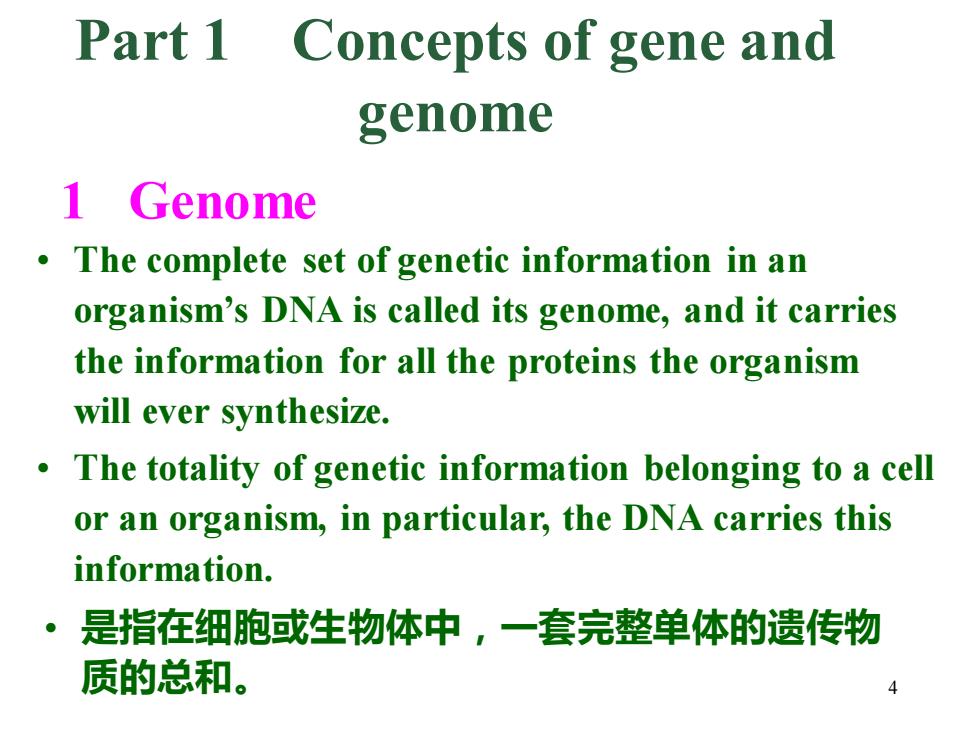
Part 1 Concepts of gene and genome 1 Genome The complete set of genetic information in an organism's DNA is called its genome,and it carries the information for all the proteins the organism will ever synthesize. The totality of genetic information belonging to a cell or an organism,in particular,the DNA carries this information. 。 是指在细胞或生物体中,一套完整单体的遗传物 质的总和
4 1 Genome • The totality of genetic information belonging to a cell or an organism, in particular, the DNA carries this information. Part 1 Concepts of gene and genome • 是指在细胞或生物体中,一套完整单体的遗传物 质的总和。 • The complete set of genetic information in an organism’s DNA is called its genome, and it carries the information for all the proteins the organism will ever synthesize

There are 22 autosomes in human,and X and Y sex chromosomes the so-called nuclear genome )as well as the genetic material containing in mitochondria. 5
5 There are 22 autosomes in human, and X and Y sex chromosomes(the so-called nuclear genome), as well as the genetic material containing in mitochondria

◆ Human chromosomes 3 4 5 = 9 10 11 13 14 15 15 17 10 双 电 21 6
6 Human chromosomes

A global view ofour genome EVELYN FOX KELLER of the bene 基因世纪
7 A global view of our genome 基因世纪
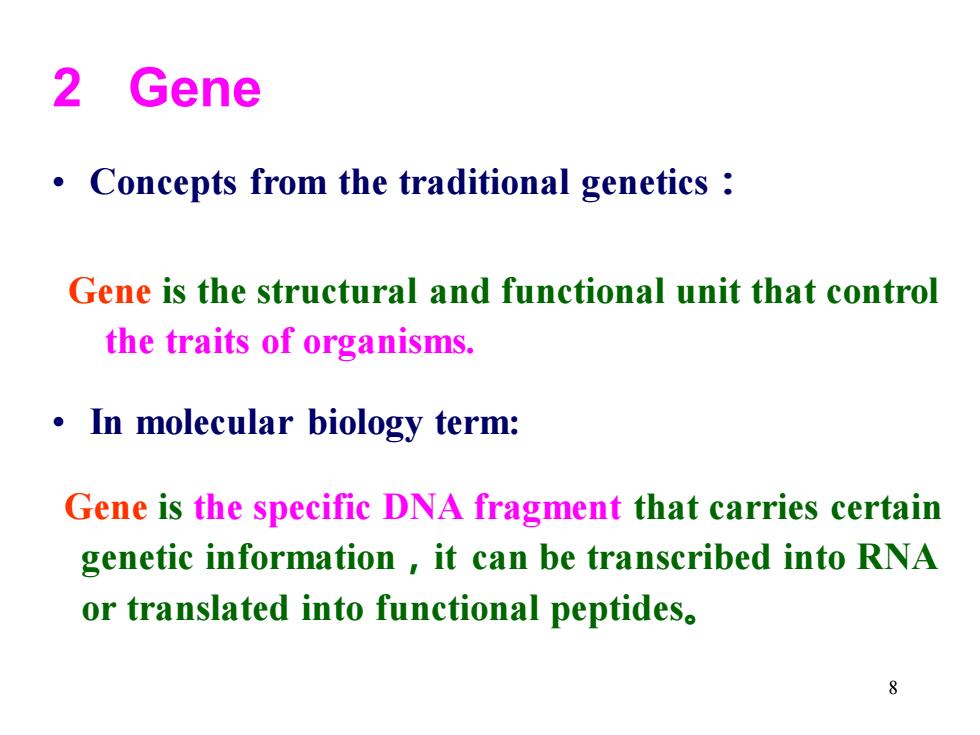
2 Gene Concepts from the traditional genetics Gene is the structural and functional unit that control the traits of organisms. In molecular biology term: Gene is the specific DNA fragment that carries certain genetic information it can be transcribed into RNA or translated into functional peptides. 8
8 2 Gene • Concepts from the traditional genetics: • In molecular biology term: Gene is the structural and functional unit that control the traits of organisms. Gene is the specific DNA fragment that carries certain genetic information,it can be transcribed into RNA or translated into functional peptides

·New concepts: A gene is the complete,essential nucleotide sequence that synthesized the functional peptides or RNA. The nucleotide sequence encoding protein or Gene RNA The regulatory sequences guarantee the transcription 5'un-translated region Non-coding intron region 3'un-translated region 9
9 • New concepts: A gene is the complete, essential nucleotide sequence that synthesized the functional peptides or RNA. The nucleotide sequence encoding protein or RNA The regulatory sequences guarantee the transcription Gene 5’ un-translated region intron 3’ un-translated region Non-coding region
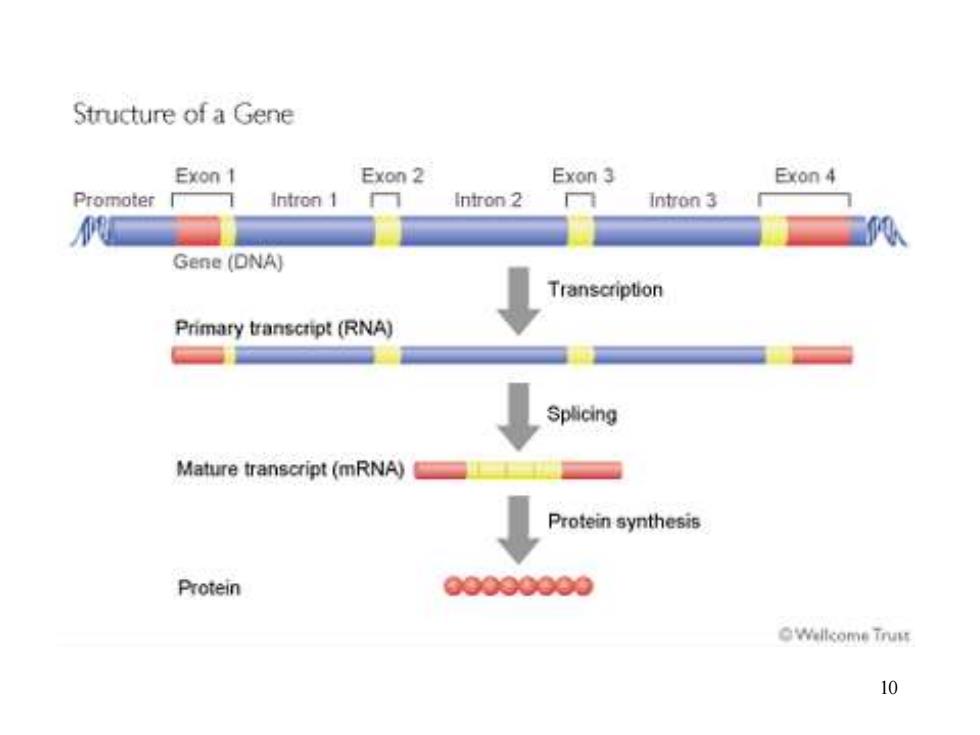
Structure of a Gene Exon 1 Exon 2 Exon 3 Exon 4 Promoter Intron 1 Intron 2 Intron 3 Gene (DNA) Transcription Primary transcript(RNA) Splicing Mature transcript(mRNA) Protein synthesis Protein 0309000 Wellcome Trust 10
10