Molecular Biology course chater 6 The Biosynthesis f Protein (Translation) chain of amino acids IRNA mRNA odo GG GUU 5 bosom
•Molecular Biology Course Chapter 6 The Biosynthesis of Protein (Translation)
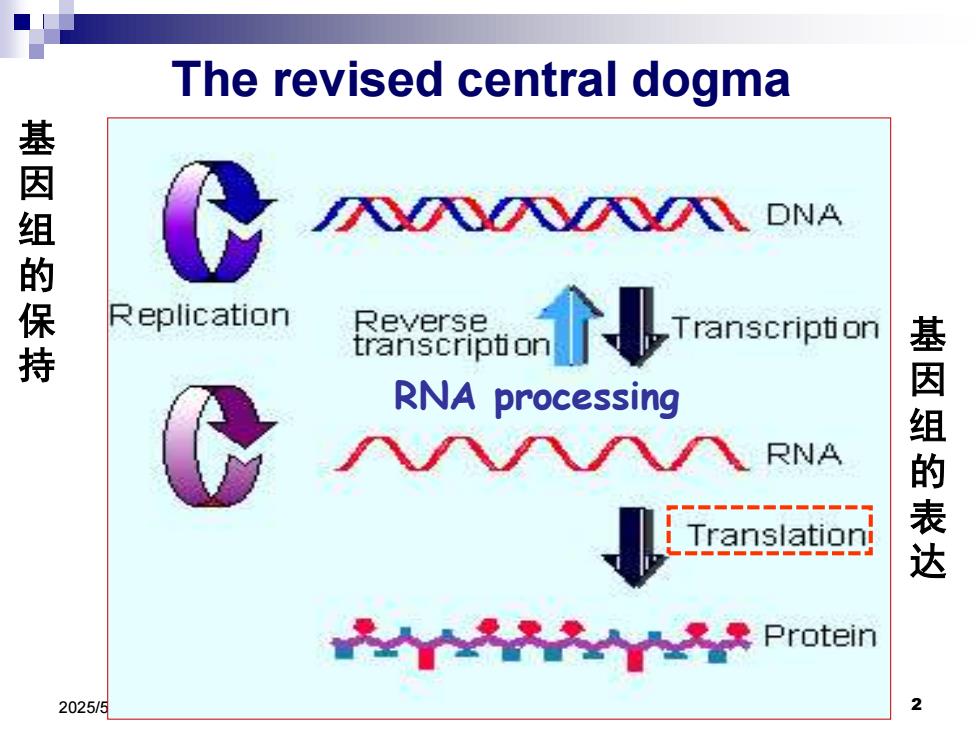
The revised central dogma 基因组的保持 N DNA Replication 閤部介↓ Reverse RNA processing 基因组 RNA 表达 Protein 2025/5
2025/5/15 2 The revised central dogma RNA processing 基 因 组 的 保 持 基 因 组 的 表 达

What is translation? -It is the story about decoding the genetic information contained in messenger RNA(mRNA)into proteins. 2025/5/15 3
2025/5/15 3 What is translation? -It is the story about decoding the genetic information contained in messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins
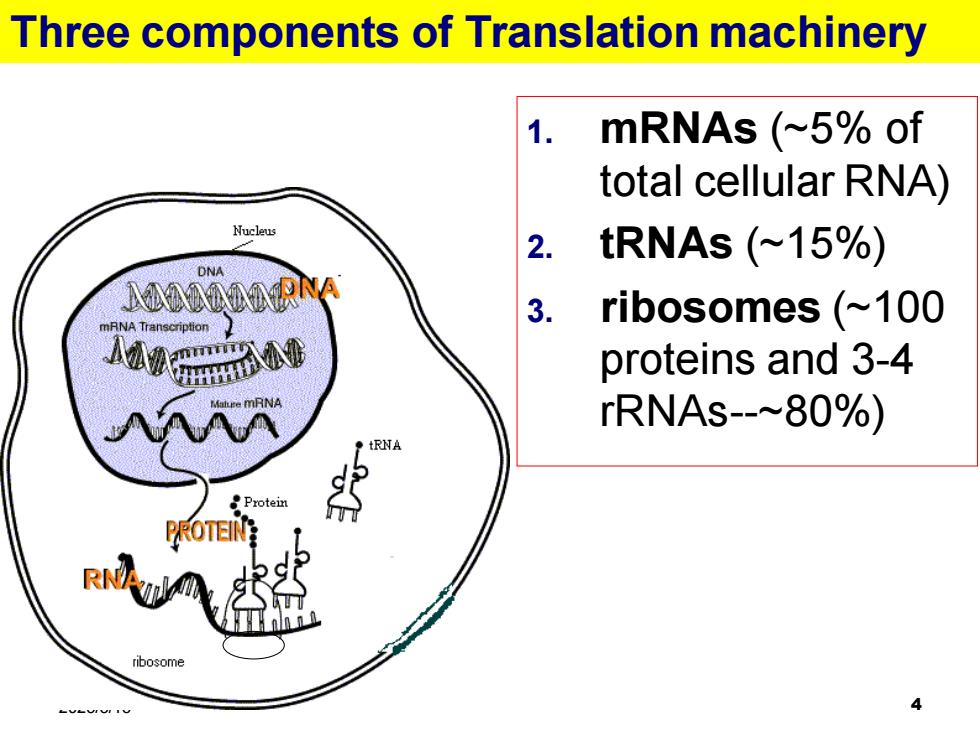
Three components of Translation machinery 1. mRNAs (~5%of total cellular RNA) Nucleus 2. tRNAS(~15%) DNA 3. ribosomes (~100 proteins and 3-4 rRNAS-~80%) Protein PROTEIN RN ribosome 4
2025/5/15 4 Three components of Translation machinery 1. mRNAs (~5% of total cellular RNA) 2. tRNAs (~15%) 3. ribosomes (~100 proteins and 3-4 rRNAs-~80%)

Translation extremely costs In rapid growing bacterial cells,protein synthesis consumes ■ 80%of the cell's energy 50%of the cell's dry weight Why? 2025/5/15 5
2025/5/15 5 Translation extremely costs In rapid growing bacterial cells, protein synthesis consumes ◼ 80% of the cell’s energy ◼ 50% of the cell’s dry weight Why?

The main challenges of translation The genetic information in mRNA cannot be recognized directly by amino acids. The genetic code has to be recognized by an adaptor(适配器)molecule (translator),and this adaptor has to accurately recruit the corresponding amino acid. 2025/5/15 6
2025/5/15 6 The main challenges of translation ◼ The genetic information in mRNA cannot be recognized directly by amino acids. ◼ The genetic code has to be recognized by an adaptor(适配器 ) molecule (translator), and this adaptor has to accurately recruit the corresponding amino acid
Outline ■ Section 1:mRNA and genetic code ■Section2:tRNA Section 3:the ribosome Section 4:translation process Section 5:protein translocation 2025/5/15
2025/5/15 7 Outline ◼ Section 1: mRNA and genetic code ◼ Section 2: tRNA ◼ Section 3: the ribosome ◼ Section 4: translation process ◼ Section 5: protein translocation

Key points of the chapter The structure and function of three components of the translation machinery. (重点) What is the degeneracy of genetic code? [重点]What are the benefits of the code universality?What is about the Wobble in the Anticodon? initiation,elongation and termination(具体 过程和翻译因子的作用注意起始阶段原核与真 核的不同,重点) Signal hypothesis 2025/5/15 8
2025/5/15 8 Key points of the chapter ◼ The structure and function of three components of the translation machinery. (重点) ◼ What is the degeneracy of genetic code? [重点] What are the benefits of the code universality? What is about the Wobble in the Anticodon? ◼ initiation, elongation and termination (具体 过程和翻译因子的作用-注意起始阶段原核与真 核的不同,重点) ◼ Signal hypothesis

Section 1:mRNA and genetic code Mature mRNA is direct template for protein biosynthesis. There are a lot of mRNA in a cell. The length of mRNA is different. The life of mRNA is the shortest in all RNA. 2025/5/15 9
2025/5/15 9 Mature mRNA is direct template for protein biosynthesis. There are a lot of mRNA in a cell. The length of mRNA is different. The life of mRNA is the shortest in all RNA. Section 1: mRNA and genetic code

Will all of the nucleotide sequence of a mRNA molecule be translated? io! 2025/5/15 10
2025/5/15 10 Will all of the nucleotide sequence of a mRNA molecule be translated?