
Molecu oay Course CHAPTER 4:DNA damage and repair(DNA损伤与修复) Help l!my DNA is broken eaclng hours
CHAPTER 4: DNA damage and repair(DNA损伤与修复) •Molecular Biology Course 4 teaching hours
The consequence of high rates of mutation ■ Mutation in germ cell(生殖细胞)would destroy the species ■Mutation in somatic cell(体细胞)would destroy the individual. Maintenance of the correctness of the DNA sequence is definitely crucial for living organisms
The consequence of high rates of mutation ◼ Mutation in germ cell (生殖细胞) would destroy the species ◼ Mutation in somatic cell (体细胞) would destroy the individual. Maintenance of the correctness of the DNA sequence is definitely crucial for living organisms

Two important sources for mutation (unavoidable) ■ Inaccuracy in DNA replication-Errors (错误) ■( Chemical and radiant damage to the genetic material (environment)
Two important sources for mutation (unavoidable) ◼ Inaccuracy in DNA replication- Errors (错误) ◼ Chemical and radiant damage to the genetic material (environment)

Out ine: Section 1:The types and causes of DNA damage(DNA损伤的类型及原因) Section 2:The repair mechanisms c of DNA damage(DNA损伤的修复机制)
Outline: Section 1:The types and causes of DNA damage (DNA损伤的类型及原因) Section 2: The repair mechanisms of DNA damage (DNA损伤的修复机制)

■Key points(重点掌握): The types and causes of DNA damage (DNA损伤的类型及原因) The repair mechanisms of DNA damage (DNA损伤的修复机制)
◼ Key points (重点掌握): The types and causes of DNA damage (DNA损伤的类型及原因) The repair mechanisms of DNA damage (DNA损伤的修复机制)

Section 1: The types and causes of DNA damage
Section 1: The types and causes of DNA damage

1.1 DNA undergoes damage spontaneously (自发的)from hydrolysis(水解)and deamination(脱氨基) Resulted from the action of water
1.1 DNA undergoes damage spontaneously (自发的) from hydrolysis (水解) and deamination (脱氨基) Resulted from the action of water
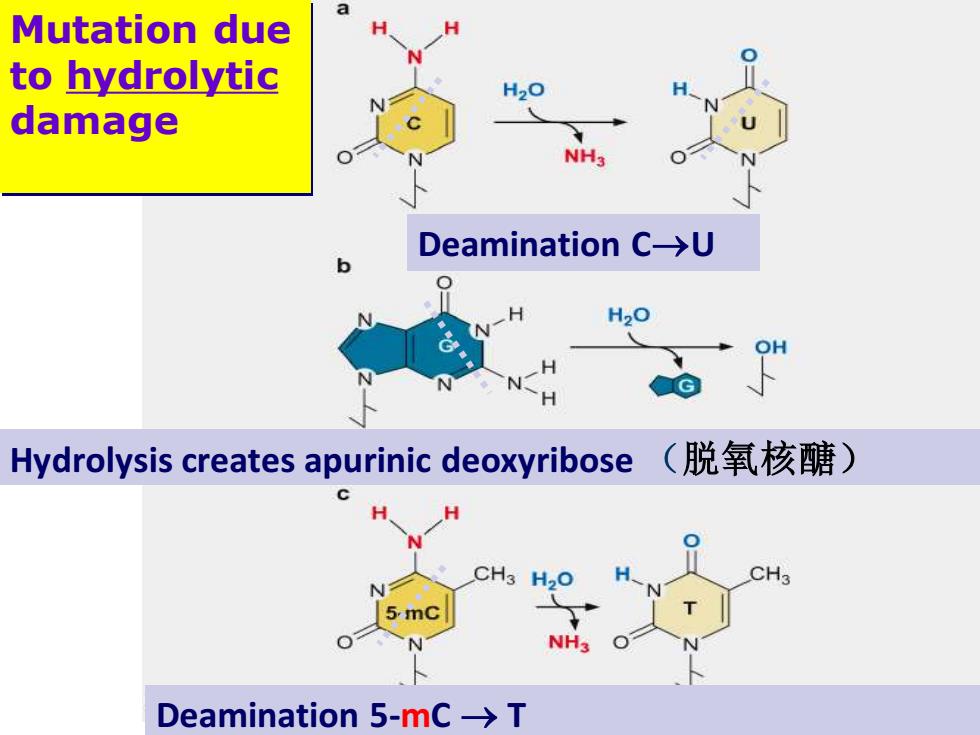
Mutation due to hydrolytic damage N Deamination C-→U H2O or Hydrolysis creates apurinic deoxyribose(脱氧核醣) CH3 I N 5mC NH Deamination5-mc→T
Mutation due to hydrolytic damage Deamination C→U Hydrolysis creates apurinic deoxyribose (脱氧核醣) Deamination 5-mC → T

Vertebrate(脊椎动物)DNA frequently contains5'- methyl cytosine(5'-甲基胞嘧啶)in place of cytosine as a result of the action of methyl transferase 转移酶),This modified base plays a role in the transcriptional silencing The presence of U and apurinic deoxyribose in DNA resulted from hydrolytic reactions is regarded as unnatural,thus is easily be recognized and repaired. Can 5-mC->T lesion be repaired? 5-mC->T mutations are hotspots for spontaneous mutations in vertebrates
The presence of U and apurinic deoxyribose in DNA resulted from hydrolytic reactions is regarded as unnatural, thus is easily be recognized and repaired. Can 5-mC → T lesion be repaired? Vertebrate(脊椎动物)DNA frequently contains 5’- methyl cytosine (5’-甲基胞嘧啶)in place of cytosine as a result of the action of methyl transferase (甲基 转移酶). This modified base plays a role in the transcriptional silencing . 5-mC → T mutations are hotspots for spontaneous mutations in vertebrates !
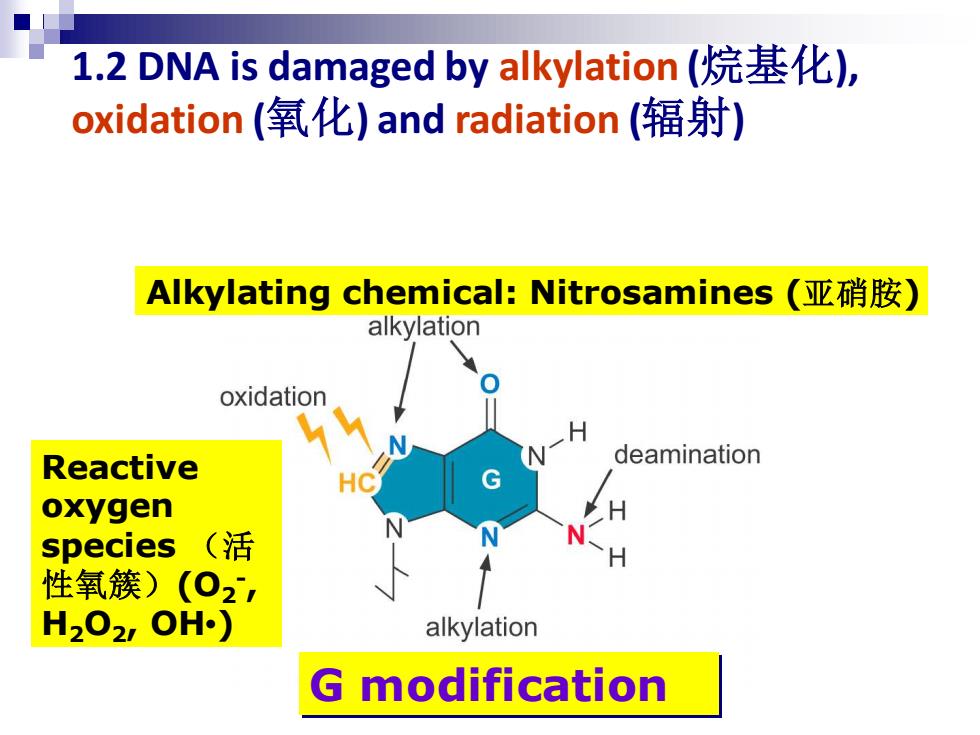
1.2 DNA is damaged by alkylation(烷基化), oxidation(氧化)and radiation(辐射) Alkylating chemical:Nitrosamines(亚硝胺) alkylation oxidation Reactive deamination G oxygen species(活 性氧簇)(02 H202,OH) alkylation modification
1.2 DNA is damaged by alkylation (烷基化), oxidation (氧化) and radiation (辐射) G modification Alkylating chemical: Nitrosamines (亚硝胺) Reactive oxygen species (活 性氧簇)(O2 - , H2O2, OH•)