
图 上酒短大峰 色a人口 LECTURE 12-I ME371/ME337 DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Gear train Covered Cha9 in Design of Machinery SHAN 手柄 齿轮1 磁铁 齿轮2 齿轮4 线轮 ·LEDT 齿轮3 1
1 Gear train LECTURE 12-II ME371/ME337 DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Covered Cha9 in Design of Machinery
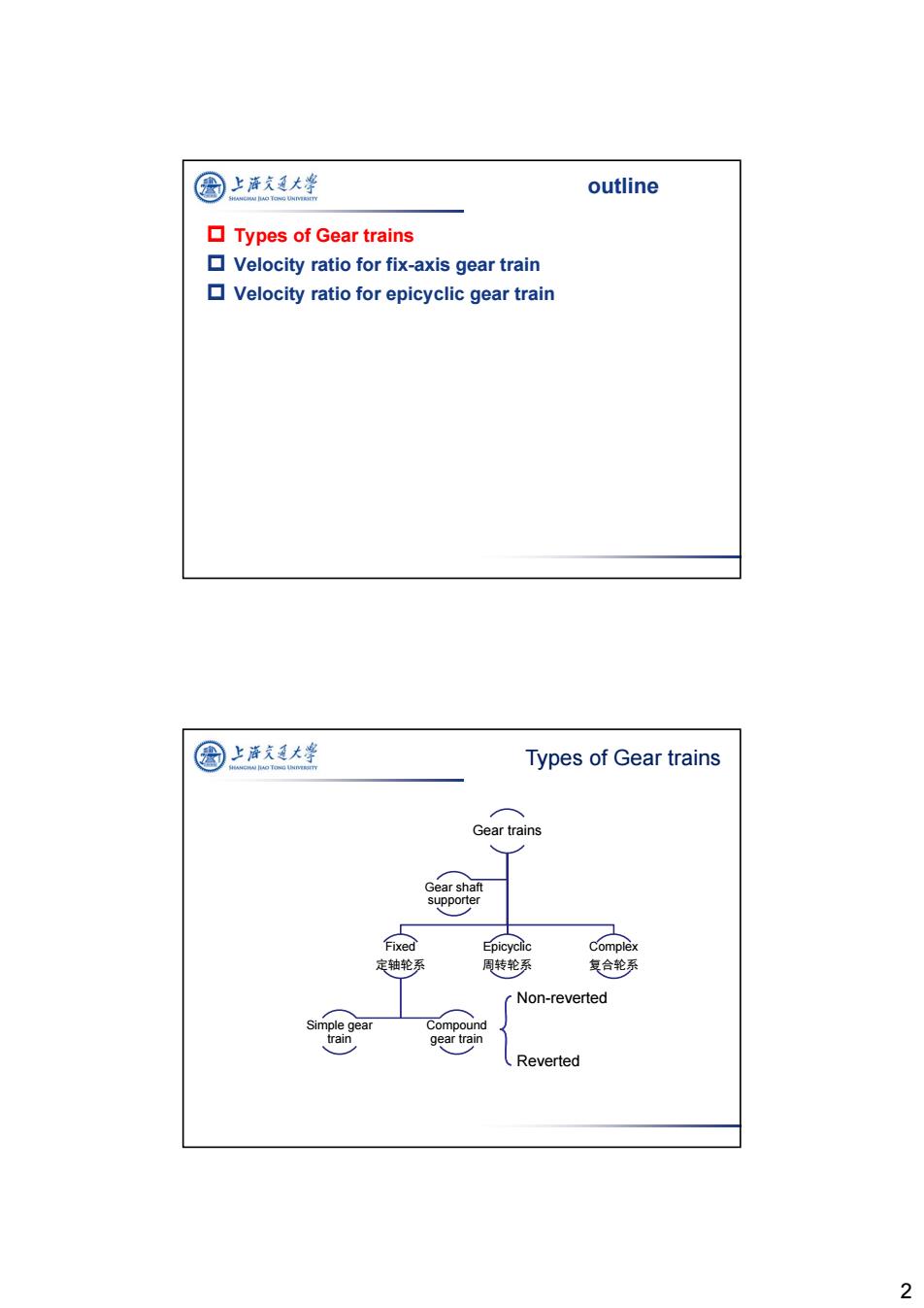
图 上海久通大学 outline ▣Types of Gear trains Velocity ratio for fix-axis gear train Velocity ratio for epicyclic gear train 圆上泽支大学 Types of Gear trains Gear trains Gear shaft supporter Fixed Epicyclic Complex 定轴轮系 周转轮系 复合轮系 Non-reverted Simple gear Compound train gear train Reverted 2
2 outline Types of Gear trains Velocity ratio for fix-axis gear train Velocity ratio for epicyclic gear train Types of Gear trains Gear trains Fixed 定轴轮系 Compound gear train Simple gear train Epicyclic 周转轮系 Complex 复合轮系 Gear shaft supporter Non-reverted Reverted
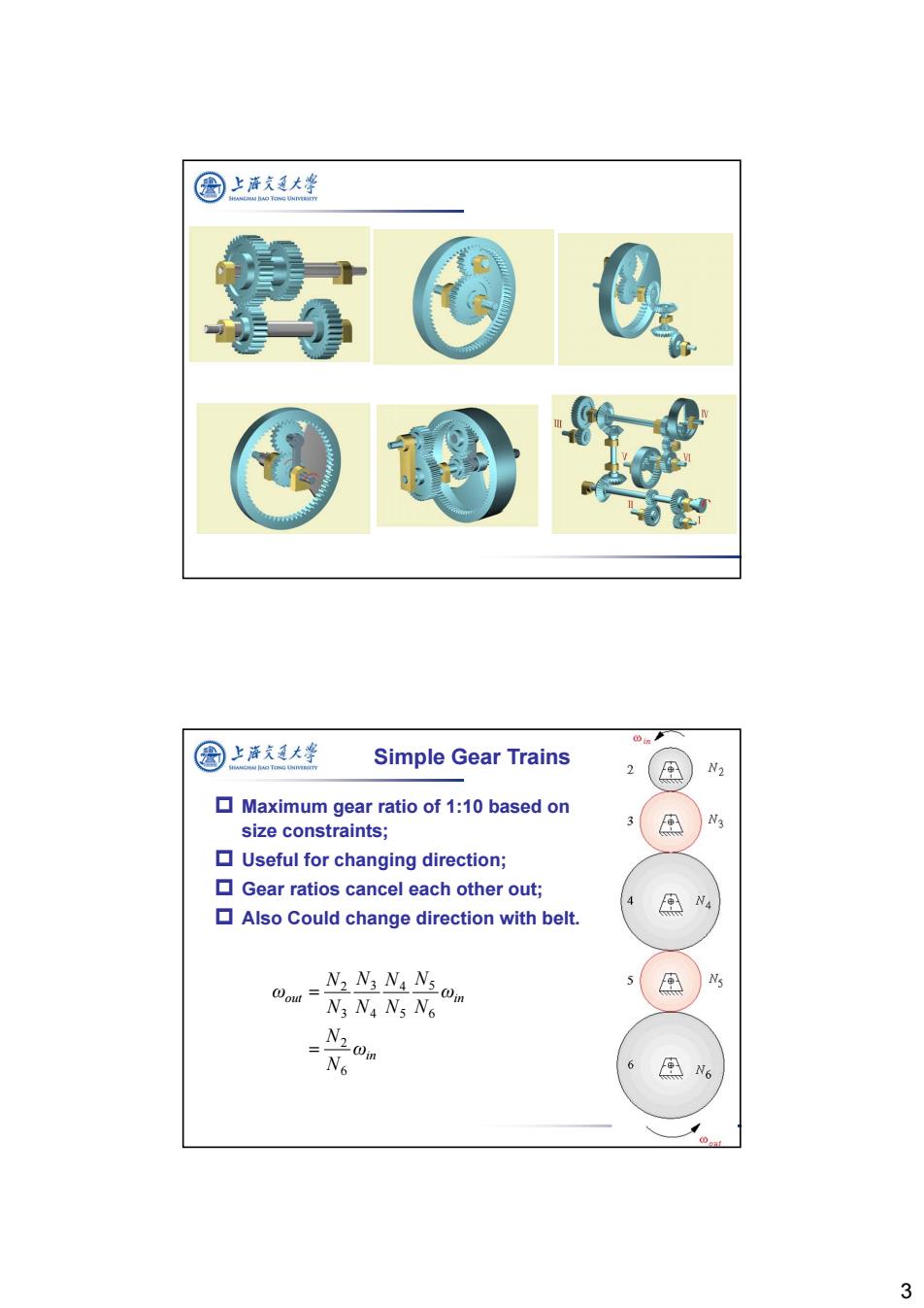
图 上游久通大学 in 圆上泽支大学 Simple Gear Trains N2 Maximum gear ratio of 1:10 based on size constraints; A N3 Useful for changing direction; Gear ratios cancel each other out; NA Also Could change direction with belt. 5 @out Nz N.NaN5m A N3 N4 Ns N6 N2Om 2N6 6 食N6 3
3 Simple Gear Trains Maximum gear ratio of 1:10 based on size constraints; Useful for changing direction; Gear ratios cancel each other out; Also Could change direction with belt. in out in ω N N ω N N N N N N N N ω 6 2 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2
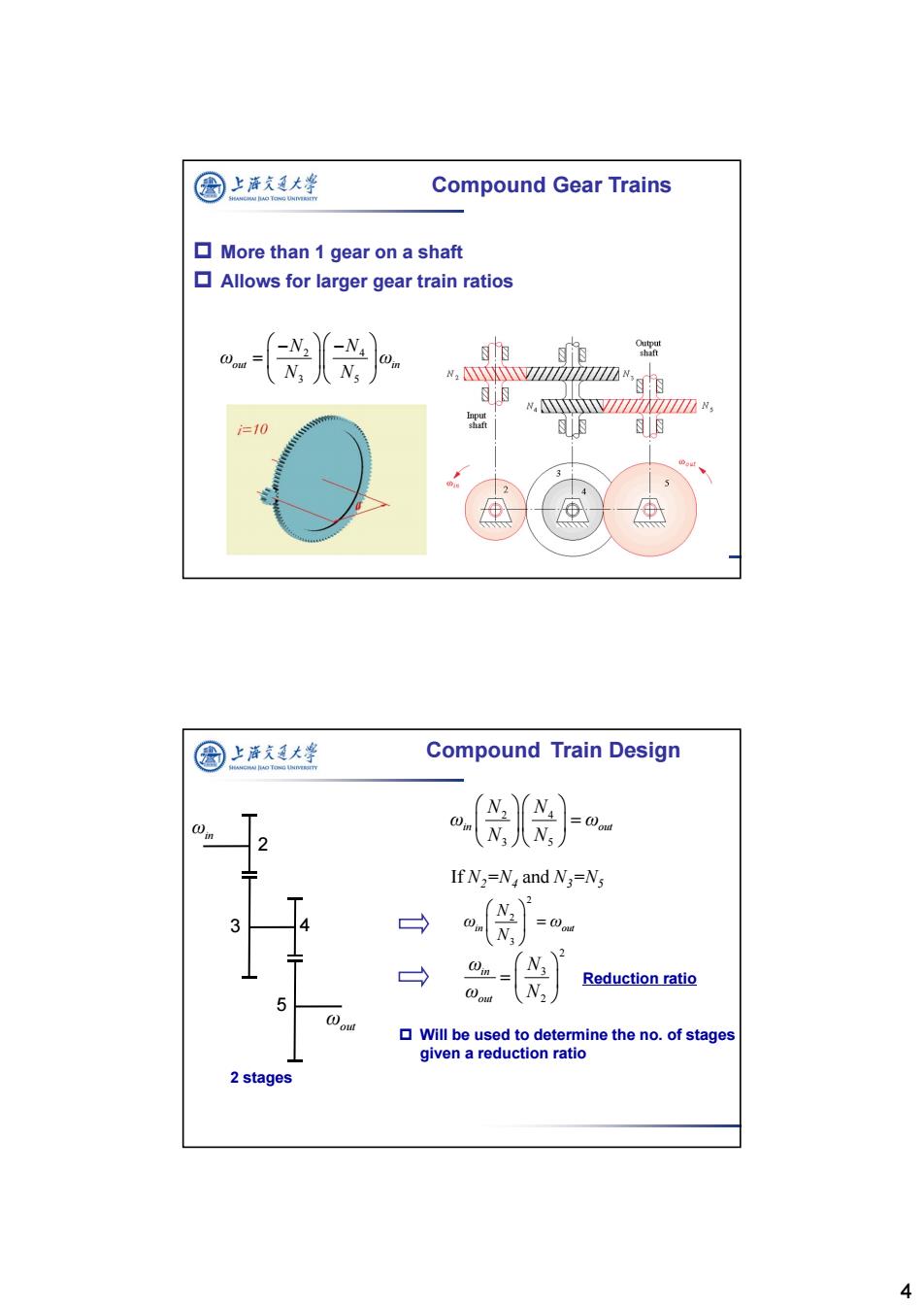
国 上酒短大峰 Compound Gear Trains More than 1 gear on a shaft Allows for larger gear train ratios o ,Yiim"ge 的.Vi☑%, 10 明 的 5 4 ⊕ 圆上泽支大学 Compound Train Design @u 2 ) If N2=N,and N3=Ns 3 4 → → 0n= Reduction ratio 5 ou Will be used to determine the no.of stages given a reduction ratio 2 stages 4
4 Compound Gear Trains More than 1 gear on a shaft Allows for larger gear train ratios 2 4 3 5 out in N N ω ω N N Compound Train Design ωin ωout 2 3 4 5 2 4 3 5 in out N N ω ω N N If N2=N4 and N3=N5 2 2 3 in out N ω ω N 2 3 2 in out ω N ω N Reduction ratio 2 stages Will be used to determine the no. of stages given a reduction ratio
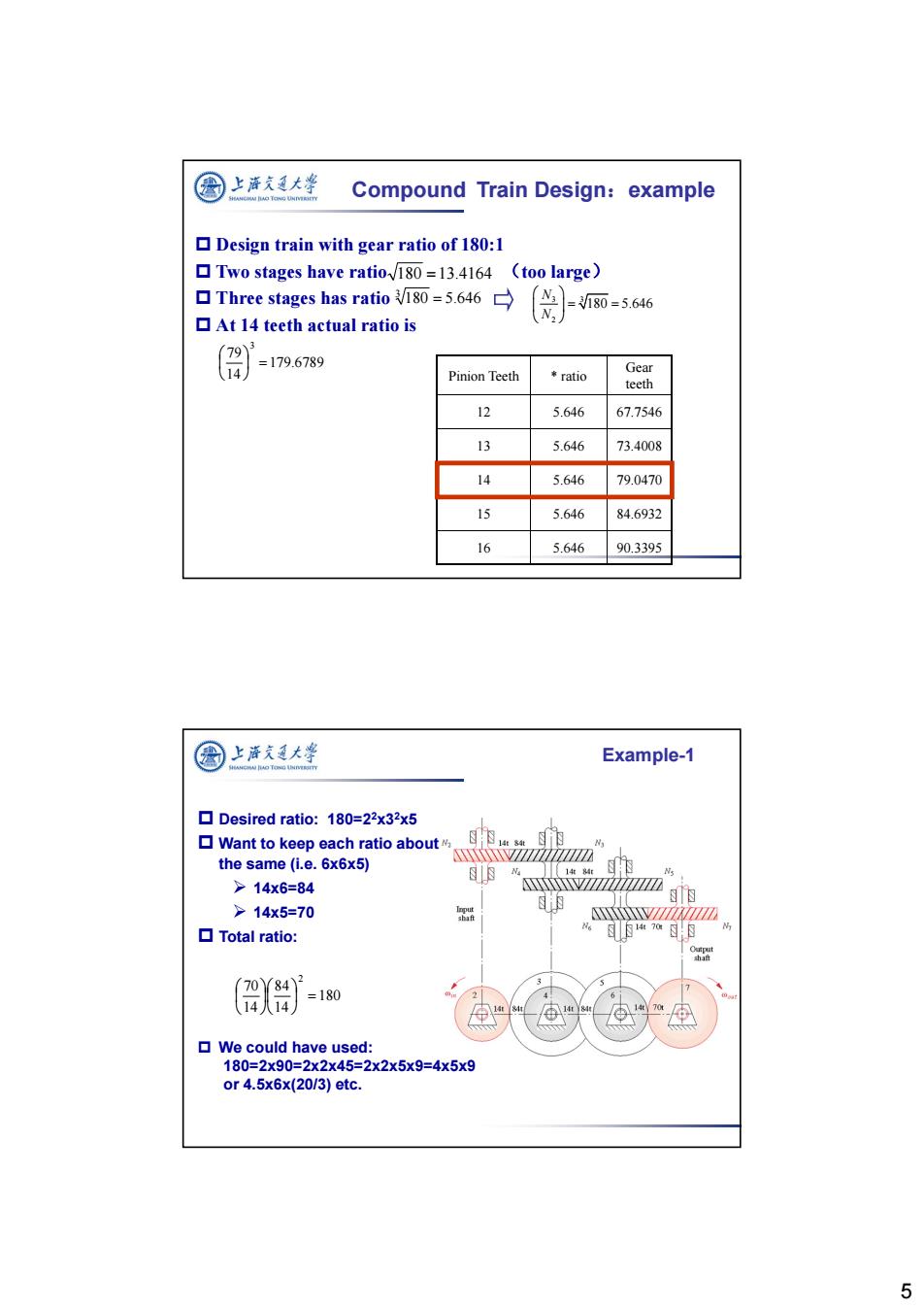
国 上海久通大学 Compound Train Design:example Design train with gear ratio of 180:1 Two stages have ratio 180=13.4164 (too large) Three stages has ratio180=5.646 180=5.646 N, At 14 teeth actual ratio is =179.6789 Pinion Teeth *ratio Gear teeth 12 5.646 67.7546 13 5.646 73.4008 14 5.646 79.0470 15 5.646 84.6932 16 5.646 90.3395 图上涤夫廷大学 Example-1 Desired ratio:180=22x32x5 Want to keep each ratio about the same (i.e.6x6x5) wwww viziiMsiN 14t84 >14x6=84 >14x5=70 XZZZZ4ZZZZ ▣Total ratio: a (70/84)2 =180 14八14 ▣Ve could have used: 180=2x90=2x2x45=2x2x5x9=4x5x9 or4.5x6x(20/3)etc. 5
5 Design train with gear ratio of 180:1 Two stages have ratio (too large) Three stages has ratio At 14 teeth actual ratio is 180 13.4164 180 5.646 3 Pinion Teeth * ratio Gear teeth 12 5.646 67.7546 13 5.646 73.4008 14 5.646 79.0470 15 5.646 84.6932 16 5.646 90.3395 179.6789 14 79 3 3 3 2 180 5.646 N N Compound Train Design:example Desired ratio: 180=22x32x5 Want to keep each ratio about the same (i.e. 6x6x5) 14x6=84 14x5=70 Total ratio: 180 14 84 14 70 2 We could have used: 180=2x90=2x2x45=2x2x5x9=4x5x9 or 4.5x6x(20/3) etc. Example-1
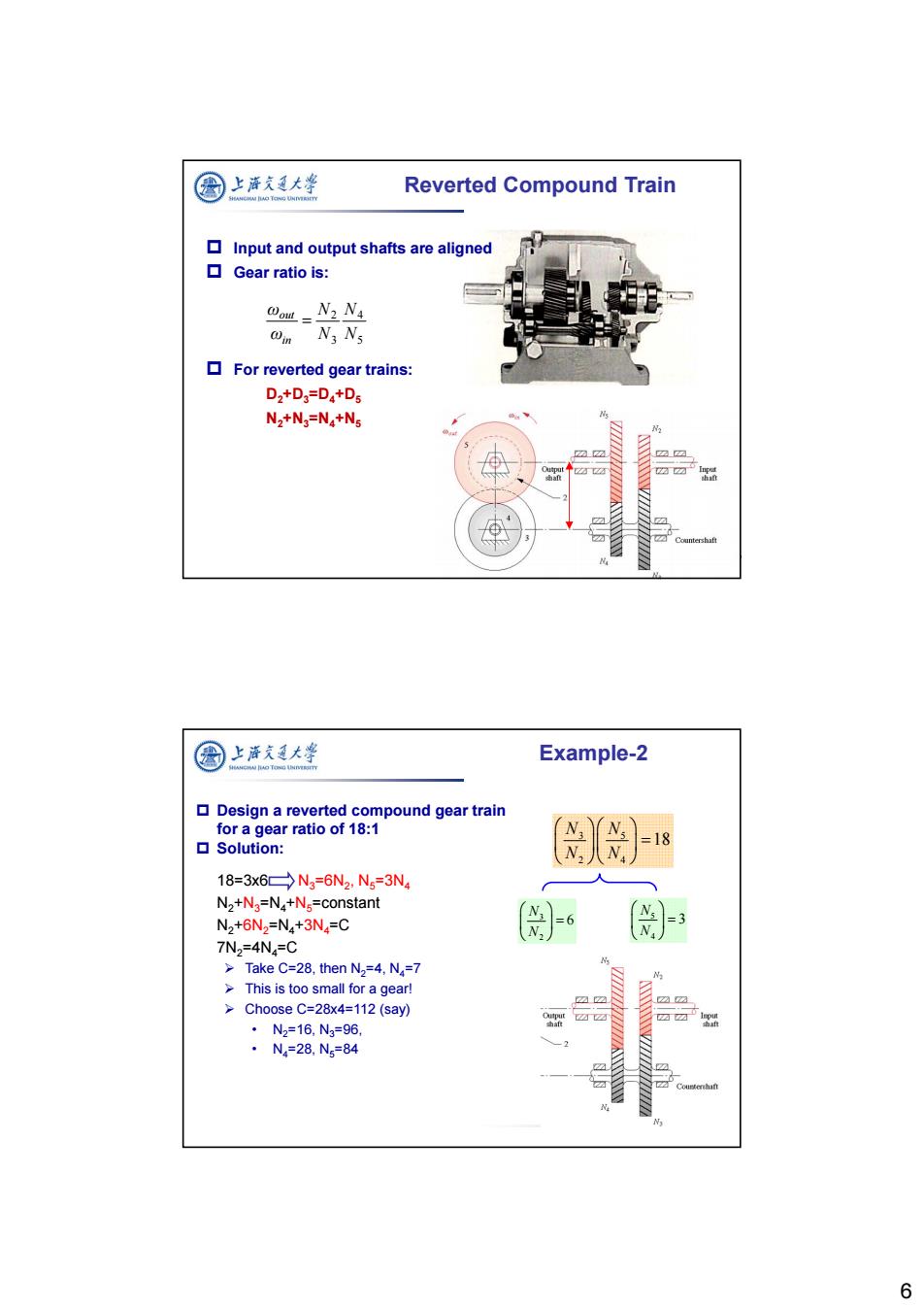
图 上酒短大峰 Reverted Compound Train I Input and output shafts are aligned ▣Gear ratio is: ou=N2 N @in N3 Ns For reverted gear trains: D2+D=Da+Ds N2+Ng=N4+N5 2☑ 图上涤夫廷大学 Example-2 Design a reverted compound gear train for a gear ratio of 18:1 口Solution: 18=3x6→N3=6N2,N5=3N4 N2+N3=N4+Ns=constant N2+6N2=N4+3N4=C 7N2=4N4=C >Take C=28,then N2=4,N3=7 >This is too small for a gear! Choose C=28x4=112(say) ·N2=16,N3=96, ·N4=28.N3=84 6
6 Reverted Compound Train Input and output shafts are aligned Gear ratio is: For reverted gear trains: D2+D3=D4+D5 N2+N3=N4+N5 5 4 3 2 N N N N ω ω in out 3 5 2 4 18 N N N N Design a reverted compound gear train for a gear ratio of 18:1 Solution: 18=3x6 N3=6N2, N5=3N4 N2+N3=N4+N5=constant N2+6N2=N4+3N4=C 7N2=4N4=C Take C=28, then N2=4, N4=7 This is too small for a gear! Choose C=28x4=112 (say) • N2=16, N3=96, • N4=28, N5=84 3 2 6 N N 5 4 3 N N Example-2
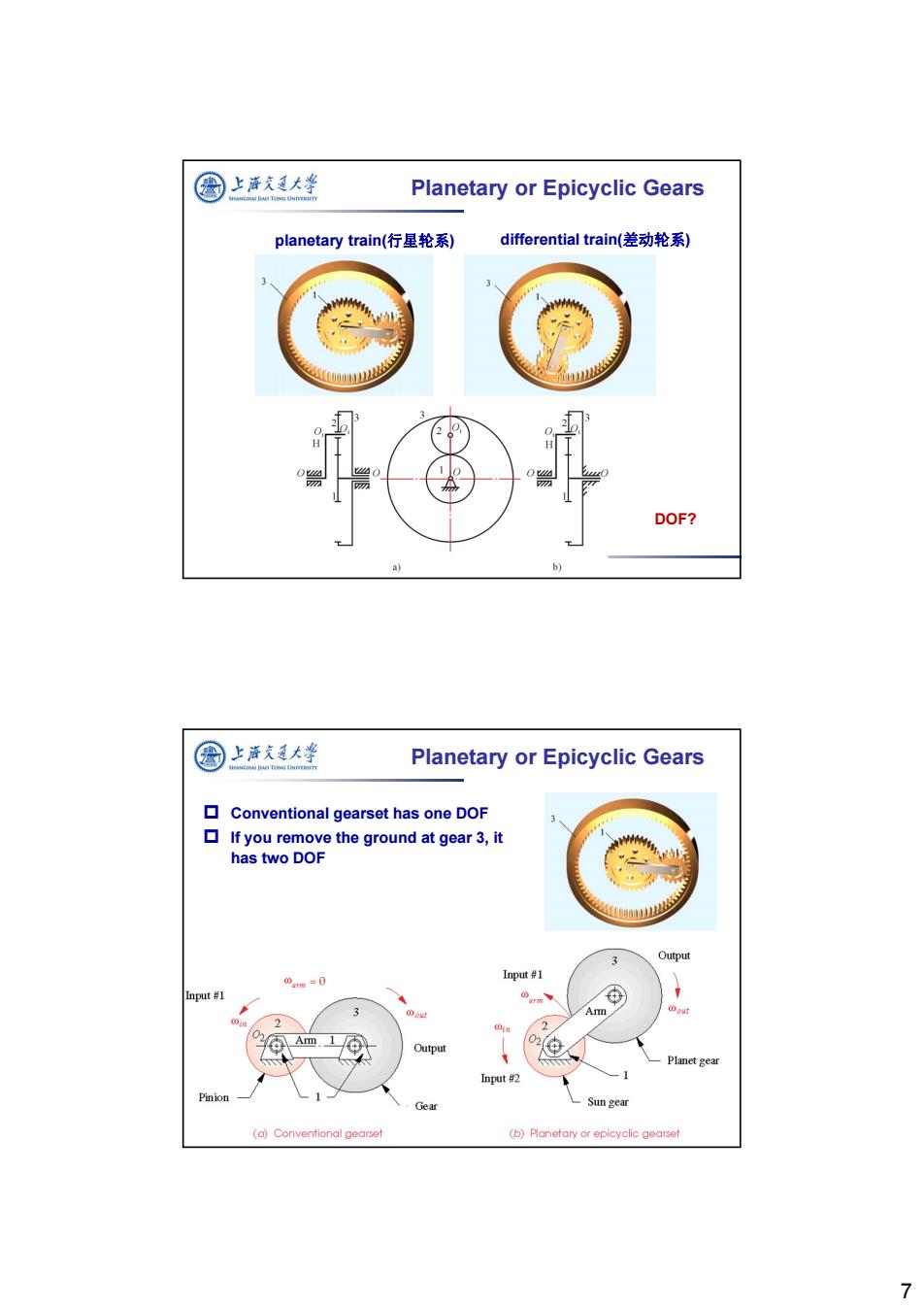
图 上海久通大学 Planetary or Epicyclic Gears planetary train(行星轮系) differential train(差动轮系) DOF? b) 国 上酒充通大学 Planetary or Epicyclic Gears ◇ Conventional gearset has one DOF If you remove the ground at gear 3,it has two DOF Output 0am=0 Input #1 Input #1 3 2 ou! out Am.1⑤ Output Planet gear Input #2 Pinion Gear Sun gear (o)Conventional gearset (b)Planetary or epicyclic gearset 7
7 planetary train(行星轮系) differential train(差动轮系) Planetary or Epicyclic Gears DOF? Planetary or Epicyclic Gears Conventional gearset has one DOF If you remove the ground at gear 3, it has two DOF
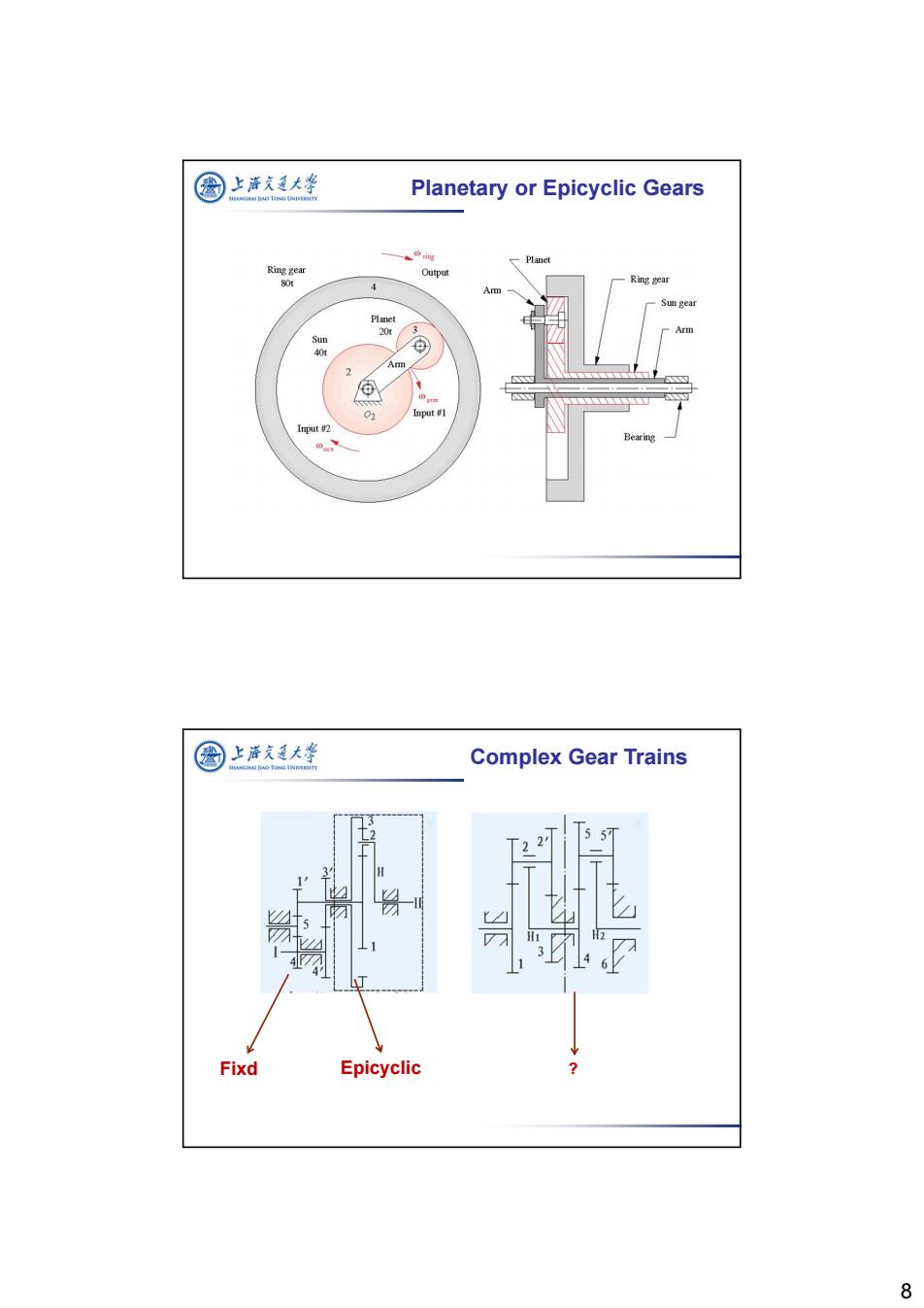
国 上酒短大峰 Planetary or Epicyclic Gears 0 ring Ring gear Output 80t Ring gear 4 Sun gear Arm 2 Am ® 02 Input Input 2 图上涤夫廷大学 Complex Gear Trains 57 3 Fixd Epicyclic 8
8 Planetary or Epicyclic Gears Complex Gear Trains Fixd Epicyclic ?
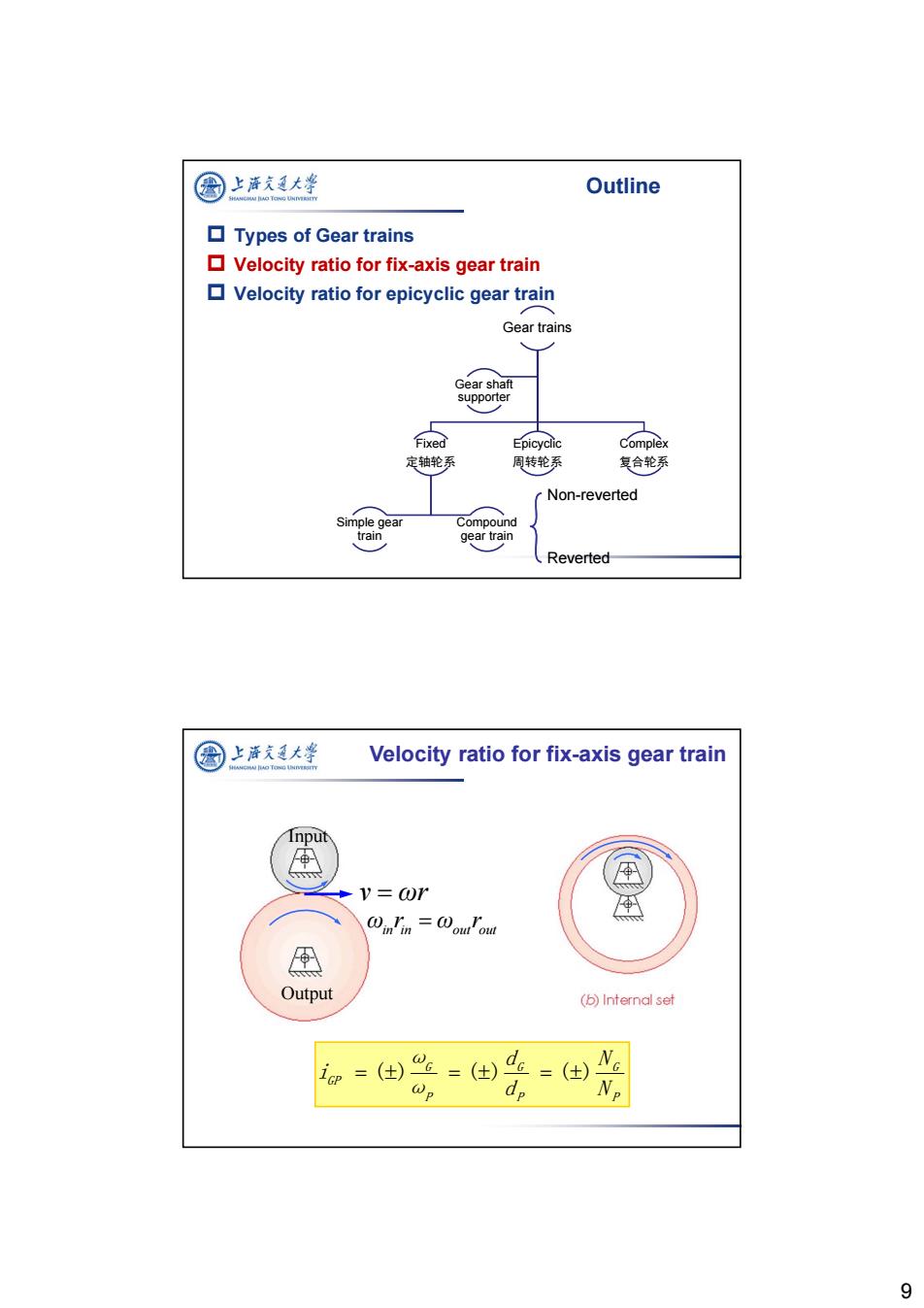
图 上海久通大学 Outline ▣Types of Gear trains Velocity ratio for fix-axis gear train Velocity ratio for epicyclic gear train Gear trains Gear shaft supporter Fixed Epicyclic Complex 定轴轮系 周转轮系 复合轮系 Non-reverted Simple gear Compound train gear train Reverted 圆上泽支大学 Velocity ratio for fix-axis gear train Input ⊕ v=@r @inin=ouou A Output (b)Internal set =() =(±) =(±) dp 9
9 Outline Types of Gear trains Velocity ratio for fix-axis gear train Velocity ratio for epicyclic gear train Gear trains Fixed 定轴轮系 Compound gear train Simple gear train Epicyclic 周转轮系 Complex 复合轮系 Gear shaft supporter Non-reverted Reverted v ωr ωin in out out r ω r Input Output P G P G P G GP N N d d ω ω i () () () Velocity ratio for fix-axis gear train

国 上海久通大学 Velocity ratio for fix-axis gear train 3 5= 0=? 05 M 3 3= N3 2 02 N 03 4 = 7 04 Ny = 05 N 1223i34i45= 0.02..-=is 0203040505 = N2NNNs 05 NNzNN 圆上泽支大学 Velocity ratio for fix-axis gear train Product of all b's Tooth Numbers Product of all a's Tooth Numbers i= N-N3NNs 3 NN2NsN. 4 Direction! 10
10 1 2' 3' 4 2 3 4 5 5 1 15 N N N N N N N N i 15 5 1 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 12 2'3 3 4 45 i i i i i ? 5 1 15 i 1 2 2 1 12 N N i 34 45 3 4 45 43 54 N N i i N N 2' 3 3 2 2'3 N N i Velocity ratio for fix-axis gear train Product of all Tooth Numbers Product of all Tooth Numbers a' s b' s iab 1 2' 3' 4 2 3 4 5 5 1 15 N N N N N N N N i Direction! Velocity ratio for fix-axis gear train