图 上海久通大学 h人口 LECTURE 12-I ME371/ME337 DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Gear design Covered Cha5 and Cha6 in Design of Machinery 图上涤夫廷大学 Outline Failure types of gears ▣Forces on Gears Fundamental theories for gearing strength Design of gear transmission 1
1 Gear design LECTURE 12-III ME371/ME337 DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Covered Cha5 and Cha6 in Design of Machinery Outline Failure types of gears Forces on Gears Fundamental theories for gearing strength Design of gear transmission

公 上海通大学 Failure types of gears ▣Tooth fracture due to bending stresses (either Light scuffing static or under fatigue cyclic load)轮齿断裂 国上清通大学 Failure types of gears ▣Pitting点蚀 Occurs at dedendum near pitch circle 2
2 Failure types of gears Tooth fracture due to bending stresses (either static or under fatigue cyclic load) 轮齿断裂 Occurs at dedendum near pitch circle Pitting点蚀 Failure types of gears

图 上海久通大学 Failure types of gears 口Scuffing damage(齿面胶合) occurs on gear teeth if they are operated with an inadequate lubricant film between the teeth.High surface temperatures then arise from the frictional heating and local welding and surface dragging and scoring tend to occur. 国上清通大学 Failure types of gears ▣surface wear(齿面磨损) When hard abrasive material is present in the lubricant the teeth may show embedding damage or abrasive scoring sometimes leading to major surface wear 3
3 occurs on gear teeth if they are operated with an inadequate lubricant film between the teeth. High surface temperatures then arise from the frictional heating and local welding and surface dragging and scoring tend to occur. Failure types of gears Scuffing damage(齿面胶合) When hard abrasive material is present in the lubricant the teeth may show embedding damage or abrasive scoring sometimes leading to major surface wear Failure types of gears surface wear (齿面磨损)

公 上游充通大学 Failure types of gears ▣Teeth deformed When unhardened teeth are subjected to very high loads,and particularly shock loads,the surfaces of the teeth can become deformed.so that the surface material is squeezed out at the ends and towards the tips of the teeth(塑性变形) 图上涤夫廷大学 Outline Failure types of gears ▣Forces on Gears Fundamental theories for gearing strength Design of gear transmission 4
4 When unhardened teeth are subjected to very high loads, and particularly shock loads, the surfaces of the teeth can become deformed, so that the surface material is squeezed out at the ends and towards the tips of the teeth (塑性变形) Failure types of gears Teeth deformed Outline Failure types of gears Forces on Gears Fundamental theories for gearing strength Design of gear transmission
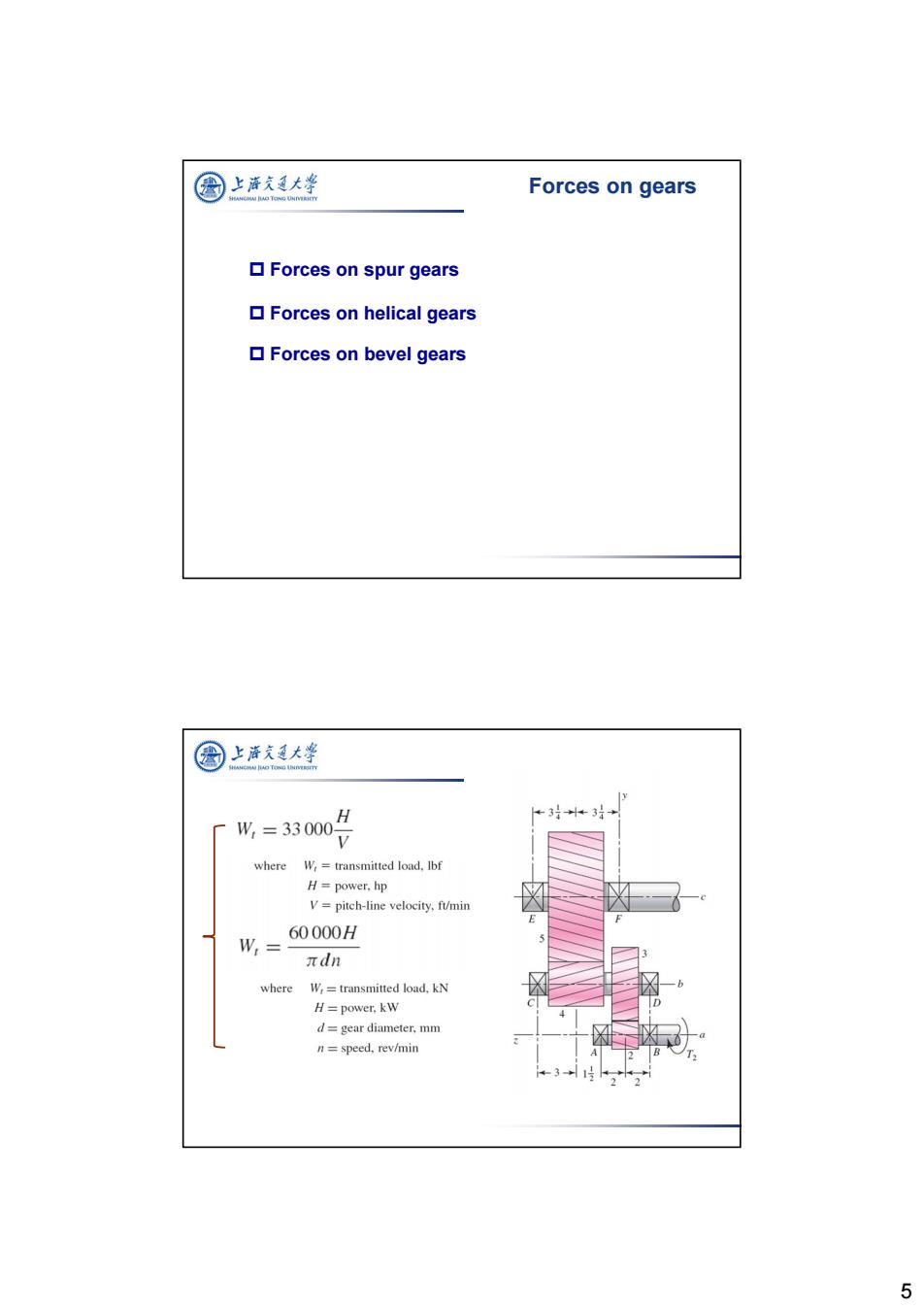
公 上酒我廷大峰 Forces on gears ▣Forces on spur gears Forces on helical gears ▣Forces on bevel gears 圆上游夫大学 H +3+31+ W,=33000 P where W,=transmitted load.Ibf H=power.hp V=pitch-line velocity,ft/min 60000H W,= πdn where W,transmitted load,kN H=power.kW d=gear diameter,mm n=speed,rev/min 31 5
5 Forces on spur gears Forces on helical gears Forces on bevel gears Forces on gears
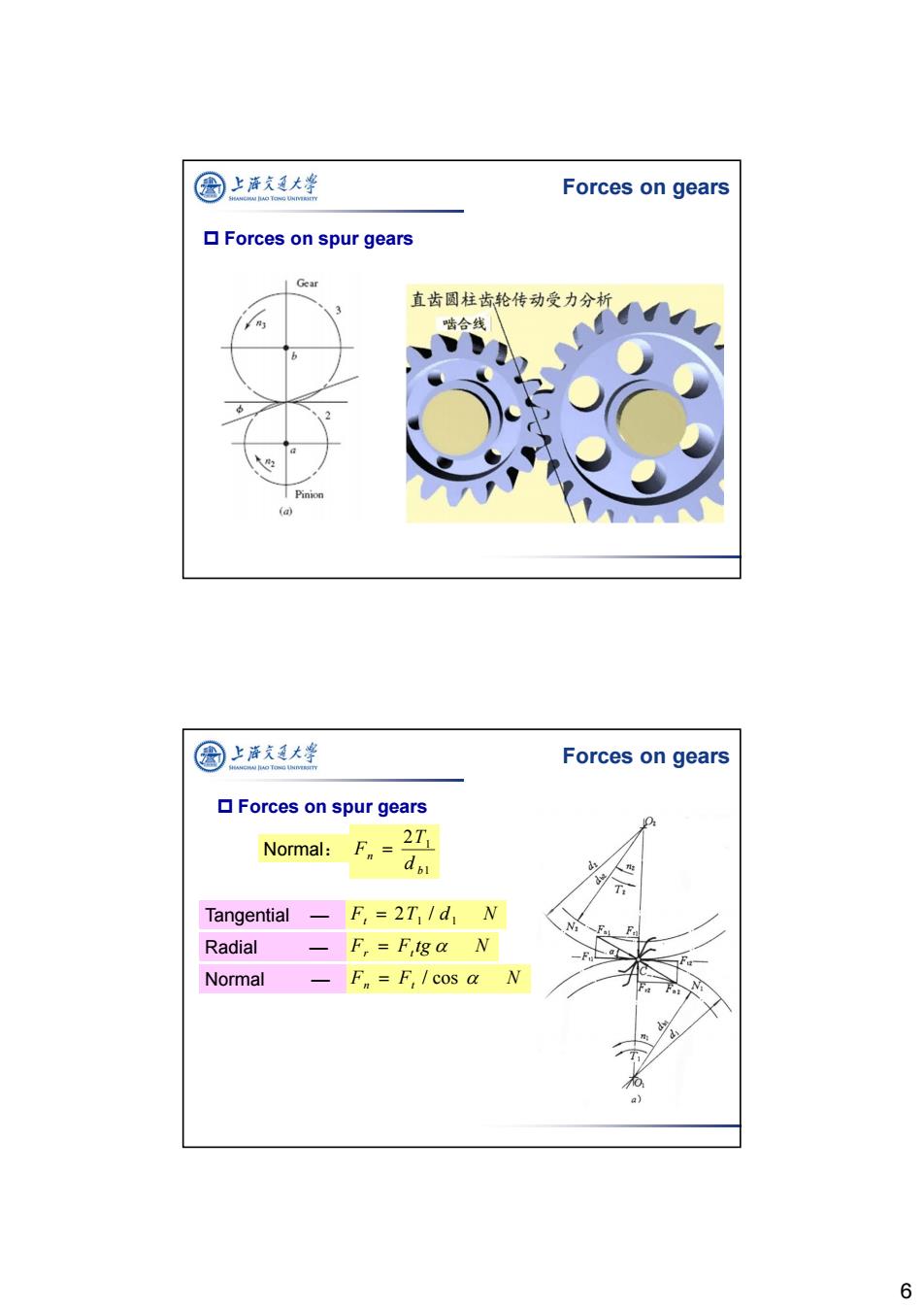
公 上海久通大学 Forces on gears ▣Forces on spur gears Gear 直齿圆柱齿轮传动受力分析 啮合线 nion (a 图上涤夫廷大学 Forces on gears ▣Forces on spur gears Normal: Fn二 2T1 di 7 Tangential F,=2T Id N Radial F,F tga N Normal F=F,/cos a a) 6
6 Forces on gears Forces on spur gears Normal: Tangential — 1 1 2 b n d T F Ft 2T1 / d1 N Radial — Fr Ft tg N Normal — Fn Ft / cos N Forces on gears Forces on spur gears
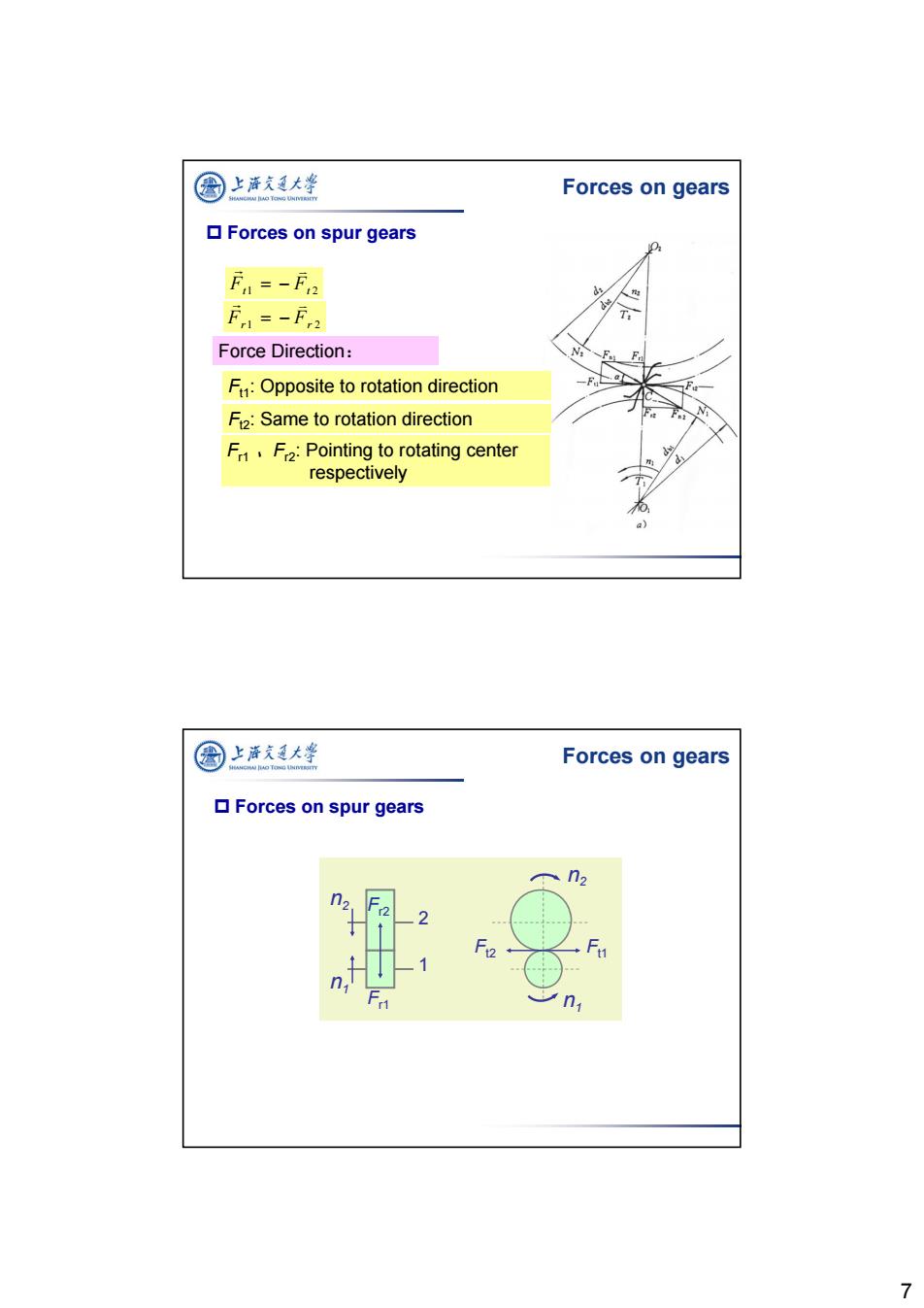
公 上酒短大峰 Forces on gears ▣Forces on spur gears =-f2 F=-F2 T. Force Direction: F:Opposite to rotation direction F2:Same to rotation direction F,F2:Pointing to rotating center respectively q) 圆上泽支大学 Forces on gears ▣Forces on spur gears n 7
7 Ft1 Ft 2 Fr 1 Fr 2 Force Direction: Ft1: Opposite to rotation direction Ft2: Same to rotation direction Fr1 、Fr2: Pointing to rotating center respectively Forces on gears Forces on spur gears 2 1 n2 n1 Fr2 Fr1 Ft2 Ft1 n1 n2 Forces on gears Forces on spur gears
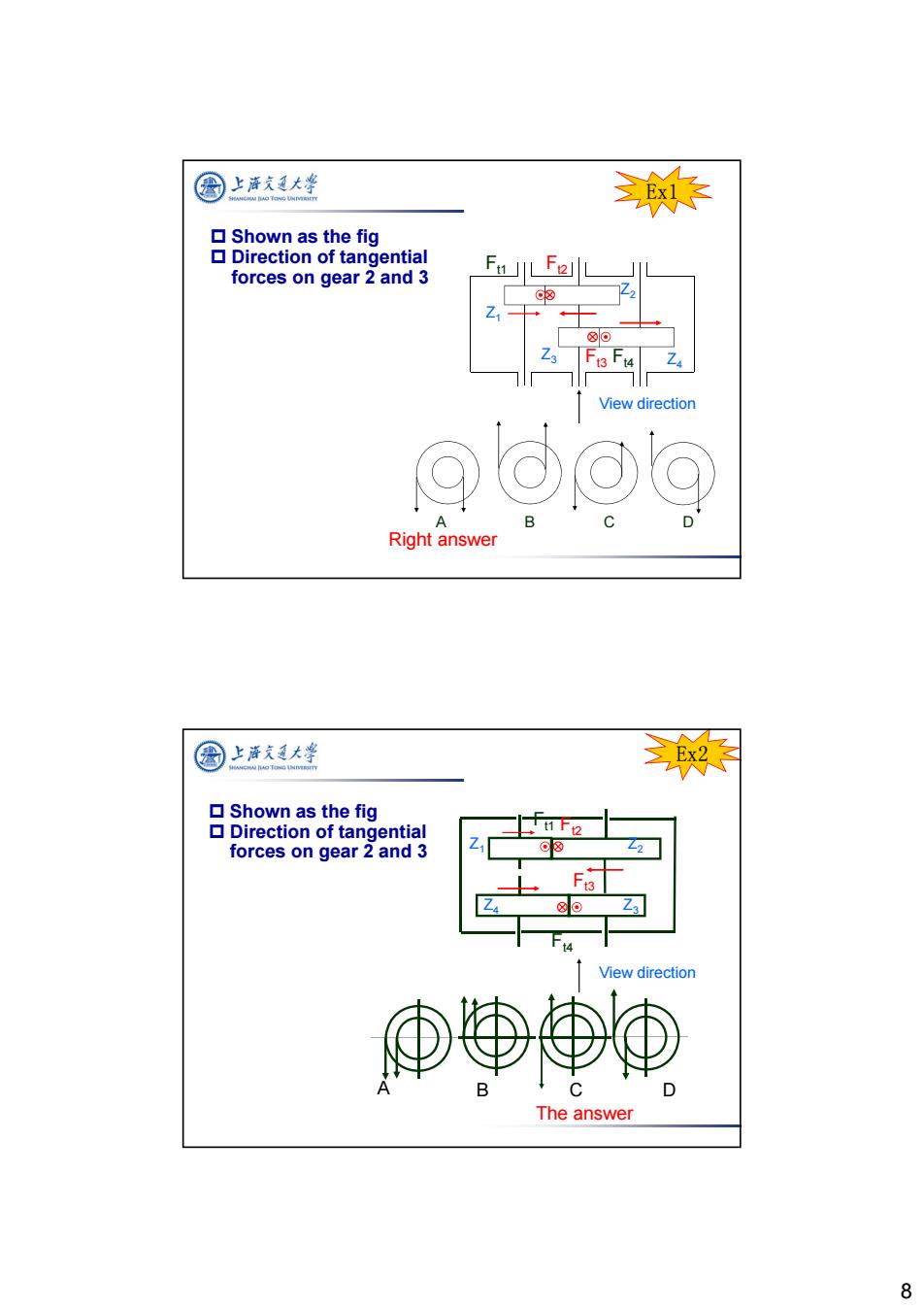
图 上海通大学 染 ▣Shown as the fig Direction of tangential forces on gear 2 and 3 ⊙8 Z 80 View direction Right answer 圆上泽支大学 ▣Shown as the fig Direction of tangential nF2 forces on gear 2 and 3 ⊙8 ⑧ View direction The answer 8
8 Shown as the fig Direction of tangential forces on gear 2 and 3 Right answer Ex1 View direction Z1 Z4 Z2 Z3 A BCD Ft1 Ft2 Ft3 Ft4 The answer Ex2 Z4 Z3 Z1 Z2 Ft2 Ft1 Ft4 Ft3 A BCD Shown as the fig Direction of tangential forces on gear 2 and 3 View direction
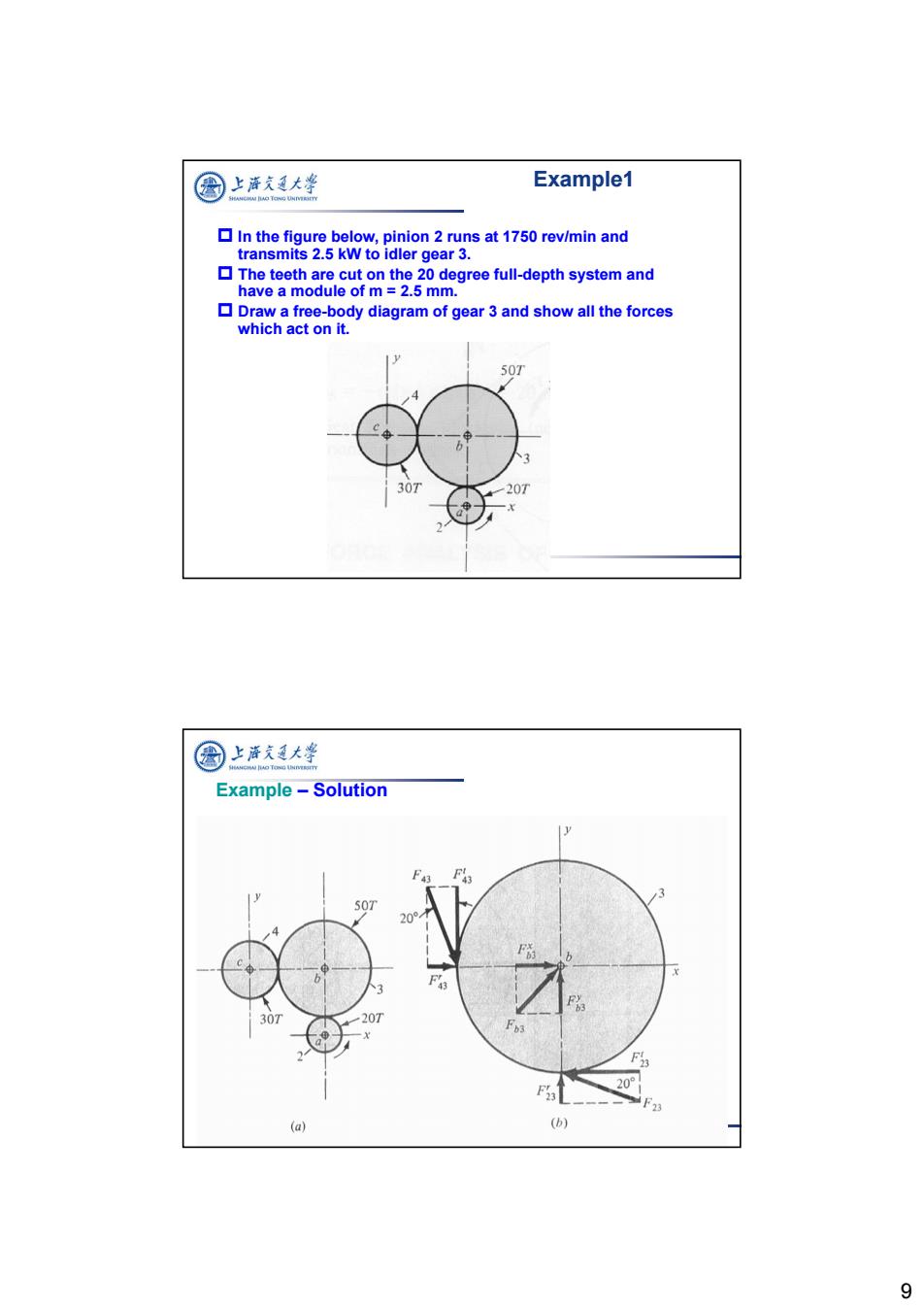
图 上海通大学 Example1 In the figure below,pinion 2 runs at 1750 rev/min and transmits 2.5 kW to idler gear 3. The teeth are cut on the 20 degree full-depth system and have a module of m=2.5 mm. Draw a free-body diagram of gear 3 and show all the forces which act on it. 50T 30T 201 圈上充通大学 Example -Solution y F43 Fs 3 50T 20° F 30 20T Fb3 20° (a) (b) 9
9 Example1 In the figure below, pinion 2 runs at 1750 rev/min and transmits 2.5 kW to idler gear 3. The teeth are cut on the 20 degree full-depth system and have a module of m = 2.5 mm. Draw a free-body diagram of gear 3 and show all the forces which act on it. Example – Solution

图 上游充通大学 Example-Solution Pitch diameters of gears 2 and 3 are d2=N2m=20*2.5=50mm d3=N3m=50*2.5=125mm Transmitted load is W,=60×103×H=60x10'×25=0.546kN πd2n π×50×1750 Thus tangential force of gear 2 on gear 3 is F23=0.546 kN.Therefore Fr23=F23tan200=0.546*tan20°=0.199kN 国上清通大学 Example -Solution ▣Which implies that F23 F230.546 =0.581kN c0s20°c0s20° Gear 3 is an idler,and thus transmits no power or torque to its shaft. Thus tangential reaction of gear 4 on gear 3 is also equal to W,.Therefore Ft43=0.546kN F43=0.199kN F43=0.581kN 10
10 Example – Solution Pitch diameters of gears 2 and 3 are d2 = N2m = 202.5 = 50 mm d3 = N3m = 502.5 = 125 mm Transmitted load is Thus tangential force of gear 2 on gear 3 is Ft 23 = 0.546 kN. Therefore Fr 23 = Ft 23 tan 20o = 0.546tan 20o = 0.199 kN kN d n W H t 0.546 50 1750 60 10 60 10 2.5 3 2 3 Example – Solution Which implies that kN F F o o t 0.581 cos 20 0.546 cos 20 23 23 Gear 3 is an idler, and thus transmits no power or torque to its shaft. Thus tangential reaction of gear 4 on gear 3 is also equal to Wt . Therefore Ft 43 = 0.546 kN Fr 43 = 0.199 kN F43 = 0.581 kN