国上海支大学 西+口 LECTURE 8 ME371ME337 DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Power Screws Covered: 11-1 and 11-2 in Mechanical Engineering Design 圆上泽大些 Lectures Power/Energy Conversion Power/Energy (Electrical Motors) Transmission (Gears,Cam,Linkage, Belt Drives, Rower Screws) Joints Transmission (Fasteners Support Connectors (Bearings) Structura Support (Frames) Tools Statics,Dynamics, Stress Analysis,etc. 1
1 Power Screws LECTURE 8 Covered: 11-1 and 11-2 in Mechanical Engineering Design ME371/ME337 DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Lectures Power/Energy Conversion (Electrical Motors) Transmission Support (Bearings) Joints (Fasteners, Connectors) Structural Support (Frames) Tools Statics, Dynamics, Stress Analysis, etc. Power/Energy Transmission (Gears, Cam, Linkage, Belt Drives, Power Screws)

圆上清支大学 OUTLINE Power Screw Introduction © Basic Terminology ©Torque Loading ©Other issues 圈上泽夫道大学 Power Screw Principles The screw thread is one of the most important inventions ever made Power screw using the principle of a screw thread and its mating nut Used to convert rotation to linear motion in actuators,machines(Lead screws)and jacks,etc. Transmit power,exert the necessary force to move a machine element along a desired path. Capable of very large mechanical advantages,can lift or- move large loads,the speed is often slow. 2
2 OUTLINE Power Screw Introduction Basic Terminology Torque Loading Other issues The screw thread is one of the most important inventions ever made Power screw using the principle of a screw thread and its mating nut Used to convert rotation to linear motion in actuators, machines (Lead screws) and jacks, etc. Transmit power, exert the necessary force to move a machine element along a desired path. Capable of very large mechanical advantages, can lift or move large loads, the speed is often slow. Power Screw Principles

圆上泽文大学 Applications 1 ▣Power screws >Either screw can move,as in a jack or >Nut can move,as in a positioning device. Head servomotor Lever coupling Sq.threaded rod lead screw nut 圆上清支大华 Applications 1 3
3 Applications 1 Power screws Either screw can move, as in a jack or Nut can move, as in a positioning device. Applications 1

国 上海文通大学 Lead Screw(传导螺杆) ▣Lead screw Lead screws are essentially accurate screws used to move a nut attached to a load,and they have been used for centuries to convert rotary motion into linear motion Lead screws are commonly used on manual economy machine tools > Efficiency in a lead screw system may be 30-50% © 上海充廷大学 Ball Screws(滚珠螺旋) Ball screw is similar in function to lead screw.Sliding contact between the screw and nut is replaced by rolling contact using recirculating spherical balls,reduce the thread friction.do not suffer from the stick-slip characteristics of sliding joints Leads to higher efficiency,may have 95%efficiency >However,not self-locking. >Have a more limited fatigue life,but have very high load nitonis capacity 4
4 Lead Screw(传导螺杆) Lead screw Lead screws are essentially accurate screws used to move a nut attached to a load, and they have been used for centuries to convert rotary motion into linear motion Lead screws are commonly used on manual economy machine tools Efficiency in a lead screw system may be 30-50% Ball Screws(滚珠螺旋) Ball screw is similar in function to lead screw. Sliding contact between the screw and nut is replaced by rolling contact using recirculating spherical balls, reduce the thread friction, do not suffer from the stick-slip characteristics of sliding joints Leads to higher efficiency, may have 95% efficiency However, not self-locking. Have a more limited fatigue life, but have very high load capacity

圈上海充通大峰 Ball Screws(遠珠螺旋) Modern machine tools,automation equipment,and actuators on aircraft use ball screws for high precision,high efficiency, fast response,and smooth operation. Carriage Rotary Encoder AC Brushless Motor Flexible Coupling Rearing Housing Ballscrew Ballnut Support Bearings 5
5 Ball Screws(滚珠螺旋) Modern machine tools, automation equipment, and actuators on aircraft use ball screws for high precision, high efficiency, fast response, and smooth operation

图上活文通大华 Roller Screws(滚柱螺羡) 轨Housing n 圆上泽夫通大学 Other Applications 6
6 Roller Screws(滚柱螺旋) Other Applications
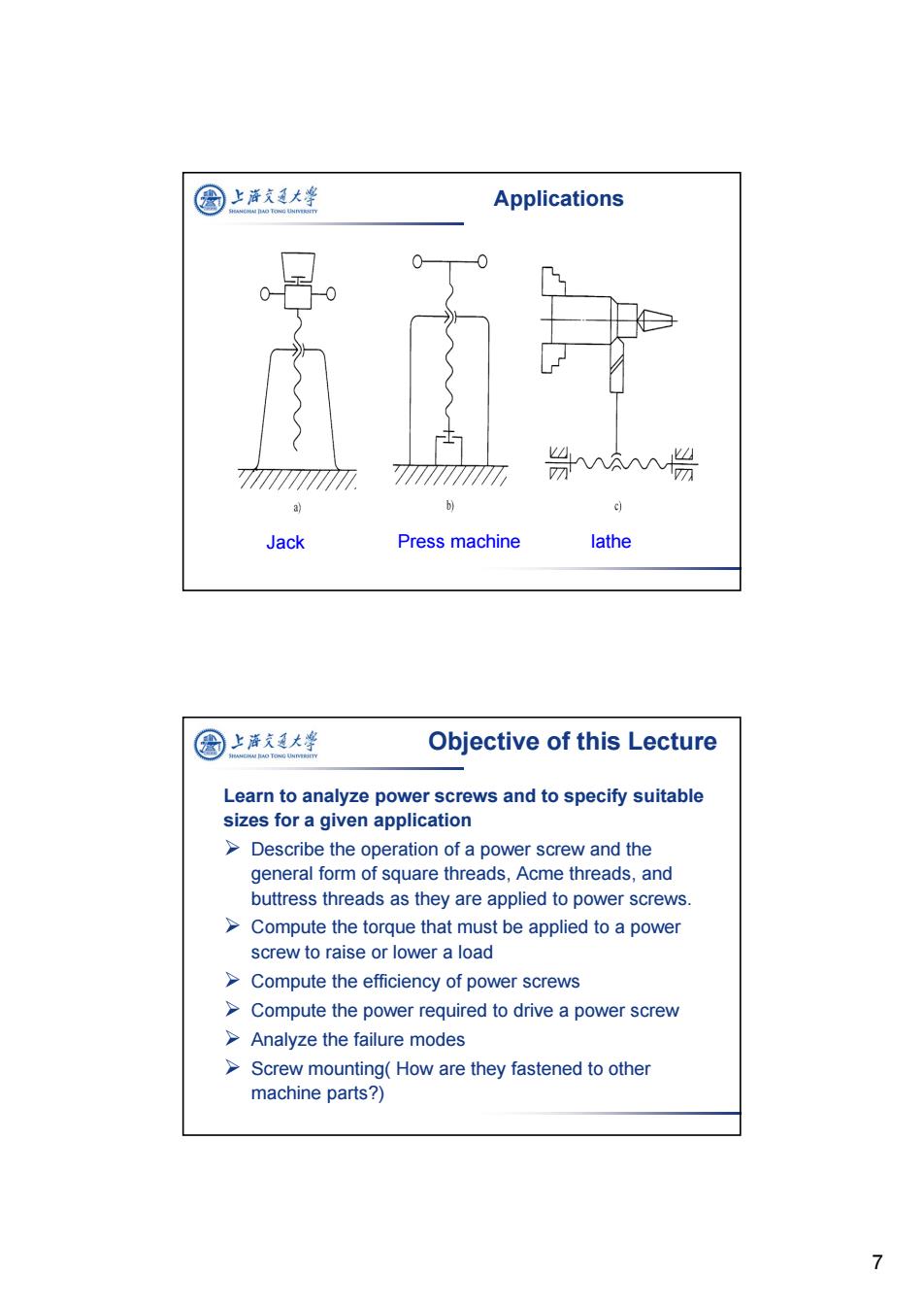
圆上海支通大峰 Applications 0 7 方 w a ) Jack Press machine lathe 上泽充通大学 Objective of this Lecture Learn to analyze power screws and to specify suitable sizes for a given application Describe the operation of a power screw and the general form of square threads,Acme threads,and buttress threads as they are applied to power screws. >Compute the torque that must be applied to a power screw to raise or lower a load Compute the efficiency of power screws >Compute the power required to drive a power screw >Analyze the failure modes Screw mounting(How are they fastened to other machine parts?) >
7 Applications Jack Press machine lathe Objective of this Lecture Learn to analyze power screws and to specify suitable sizes for a given application Describe the operation of a power screw and the general form of square threads, Acme threads, and buttress threads as they are applied to power screws. Compute the torque that must be applied to a power screw to raise or lower a load Compute the efficiency of power screws Compute the power required to drive a power screw Analyze the failure modes Screw mounting( How are they fastened to other machine parts?)

图上涤支大峰 OUTLINE Power Screw Introduction ©Basic Terminology ©Torque Loading ©Other issues 圆上海文大学 Basic Terminology 口Pitch,p(螺距) Maje dimteder >Distance between adjacent thread forms 一Pitch dumeter measured parallel to the thread axis. Mior diameler ▣Major Diameter,d(大径) >Largest diameter of a screw thread. ▣Minor Diameter,.d,(小径) >Smallest diameter of a screw thread 口Pitch Diameter,d,(中径) >The effective diameter of the screw Sometimes called the mean diameter,dm 8
8 OUTLINE Power Screw Introduction Basic Terminology Torque Loading Other issues Basic Terminology Pitch, p(螺距) Distance between adjacent thread forms measured parallel to the thread axis. Major Diameter, d(大径) Largest diameter of a screw thread. Minor Diameter, dr (小径) Smallest diameter of a screw thread Pitch Diameter, dp(中径) The effective diameter of the screw Sometimes called the mean diameter, dm
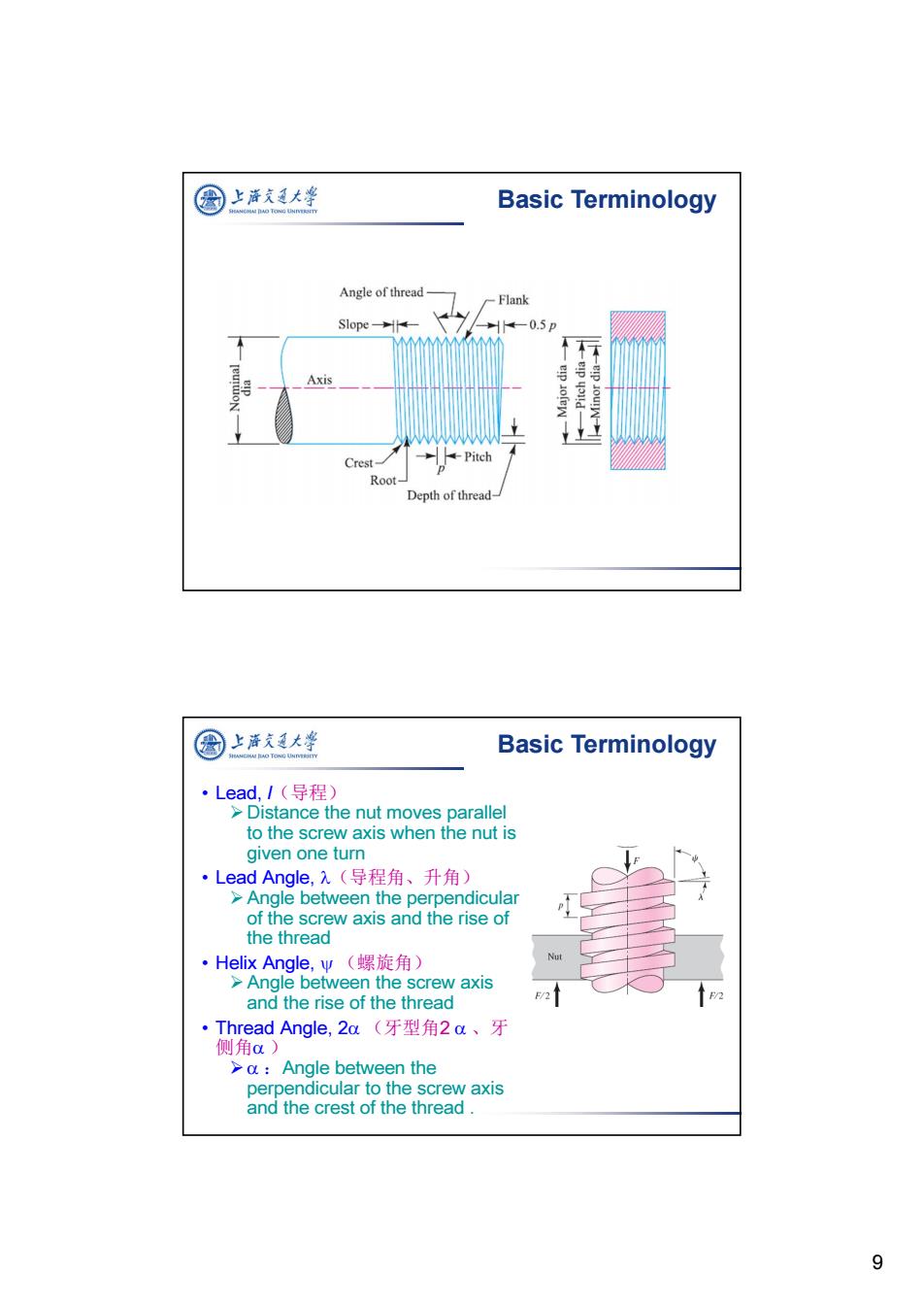
图上活文通大华 Basic Terminology Angle of thread -Flank Slope→- -0.5p Axis eip youd Crest- -Pitch Root- Depth of thread- 圈上泽支大学 Basic Terminology ·Lead,/(导程) >Distance the nut moves parallel to the screw axis when the nut is given one turn ·Lead Angle,,(导程角、升角) >Angle between the perpendicular of the screw axis and the rise of the thread ·Helix Angle,.w(螺旋角) >Angle between the screw axis and the rise of the thread F/2 ·Thread Angle,2a(牙型角2a、牙 侧角a) >a:Angle between the perpendicular to the screw axis and the crest of the thread. 9
9 Basic Terminology • Lead, l(导程) Distance the nut moves parallel to the screw axis when the nut is given one turn • Lead Angle, (导程角、升角) Angle between the perpendicular of the screw axis and the rise of the thread • Helix Angle, (螺旋角) Angle between the screw axis and the rise of the thread • Thread Angle, 2 (牙型角2 、牙 侧角 ) :Angle between the perpendicular to the screw axis and the crest of the thread . Basic Terminology
圈上泽文通大华 Basic Terminology 口External Threads(外螺纹) >the threads on a screw ▣Internal Threads(内螺纹) >the threads on a nut 口Engagement Length,Le(旋合长度) >length over which the nut and the screw are engaged. 圈上大学Multiple Screw Threads(多线螺纹 Screws can be multiple-threaded by having two or more threads cut beside each other ▣Double-threaded screw(双线螺纹) >lead is equal to twice the pitch,/=2p ▣Triple-threaded screw(三线螺纹) >lead is equal to 3 times the pitch,/=3p Advantage of multiple threads:They have >Smaller thread height >Increased lead for fast advancement of nut. Standardized products all have single thread 10
10 External Threads(外螺纹) the threads on a screw Internal Threads(内螺纹) the threads on a nut Engagement Length, Le(旋合长度) length over which the nut and the screw are engaged. Basic Terminology Multiple Screw Threads(多线螺纹) Screws can be multiple-threaded by having two or more threads cut beside each other Double-threaded screw(双线螺纹) lead is equal to twice the pitch,l=2p Triple-threaded screw (三线螺纹) lead is equal to 3 times the pitch, l=3p Advantage of multiple threads: They have Smaller thread height Increased lead for fast advancement of nut. Standardized products all have single thread