
圆上清支大学 e+口 LECTURE 1 ME371/ME337 DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Introduction to Design Covered:ch1 in Mechanical Engineering Design ch1 in Design of Machinery 圈上泽夫道大学 OUTLINE The world of MACHINES MECHANISMS Basic concepts and definitions What is ENGINEERING DESIGN? ▣Standards and Codes ▣Units Some examples of ancient and modern machines 1
1 Introduction to Design LECTURE 1 Covered : ch1 in Mechanical Engineering Design ch1 in Design of Machinery ME371/ME337 DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING OUTLINE The world of MACHINES & MECHANISMS Basic concepts and definitions What is ENGINEERING DESIGN? Standards and Codes Units Some examples of ancient and modern machines

圆上泽文大学 Video Tesla factory 圈上泽充大学 The world of MECHANISMS Aircraft radial engine Elliptic compass Sewing machine Malta cross movement(1880) 2
2 Video Tesla factory The world of MECHANISMS Aircraft radial engine Elliptic compass Sewing machine Malta cross movement(1880)
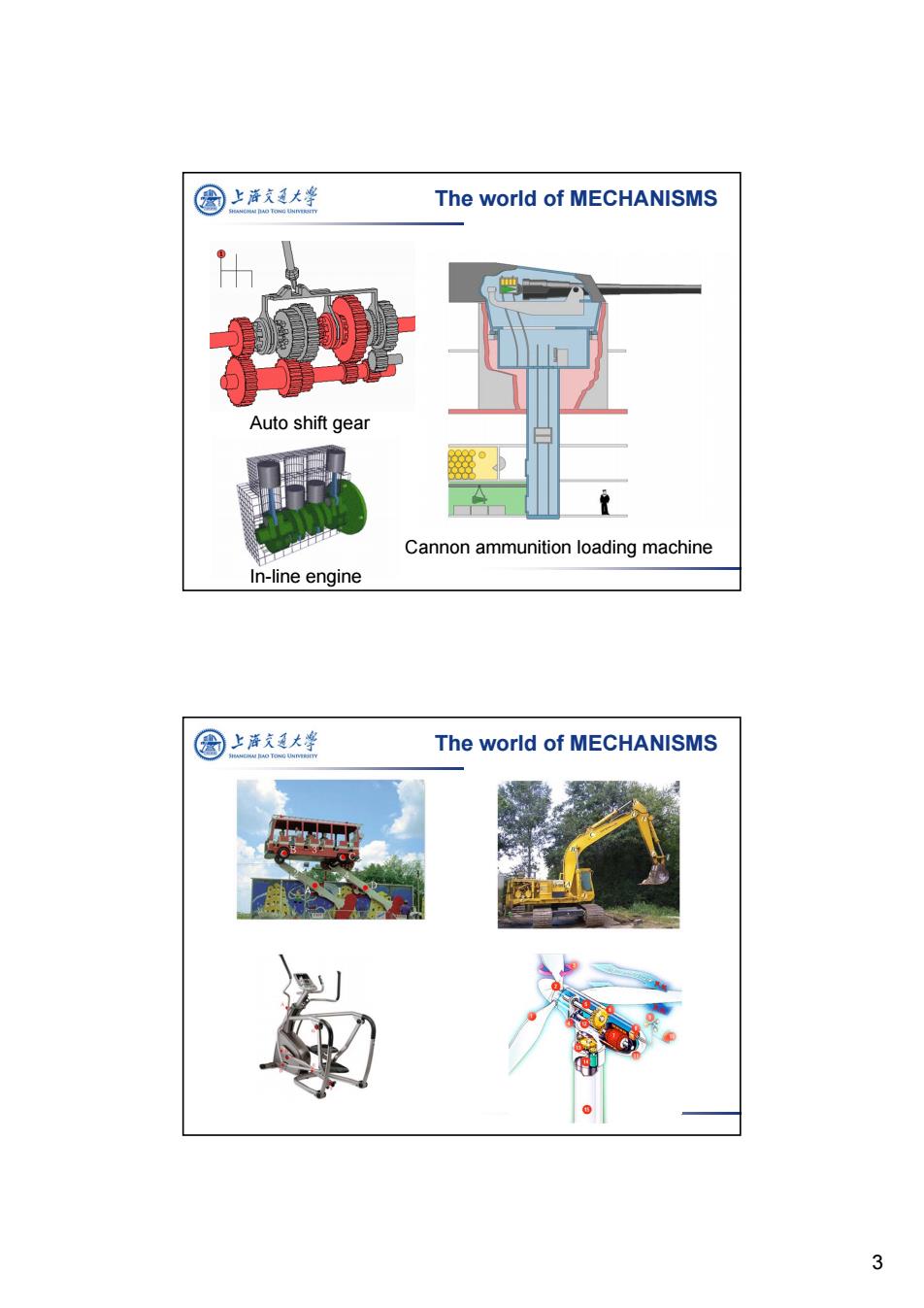
圈上泽文通大华 The world of MECHANISMS h Auto shift gear Cannon ammunition loading machine In-line engine 圆上清支大学 The world of MECHANISMS 3
3 Auto shift gear Cannon ammunition loading machine In-line engine The world of MECHANISMS The world of MECHANISMS

圈上海克通大华 The world of MECHANISMS hour wheel whe entre whee 2007 圆上泽夫通大学 Humanoid head @【3a Bio-mechanical 4
4 The world of MECHANISMS Humanoid head Bio-mechanical

图上涤支大峰 OUTLINE The world of MACHINES MECHANISMS Basic concepts and definitions What is ENGINEERING DESIGN? ▣Standards and Codes ▣Units Some examples of ancient and modern machines 国 上潘充通大学 Basic concepts and definitions Machine(机器):a combination of resistant bodies arranged to compel the mechanical forces of nature to do work accompanied by determinate motion © Machines are mechanical devices used to alter,transmit and direct forces to accomplish a specific objective,(to do work,to achieve some certain application functions. ©Features: >Combination of bodies >Specific motion >Do specific work(for classification 5
5 OUTLINE The world of MACHINES & MECHANISMS Basic concepts and definitions What is ENGINEERING DESIGN? Standards and Codes Units Some examples of ancient and modern machines Machine(机器): a combination of resistant bodies arranged to compel the mechanical forces of nature to do work accompanied by determinate motion Machines are mechanical devices used to alter, transmit and direct forces to accomplish a specific objective, (to do work, to achieve some certain application functions. ) Features: Combination of bodies Specific motion Do specific work (for classification ) Basic concepts and definitions

圆上清支大学 Machinery classification Power machine:to convert mechanical energy >Other kinds of power->mechanical energy such as steamer,internal-combustion engine,motor; >Mechanical energy->other kinds of power such as air compressor 圆上泽充大学 Machine classification Machining machinery:change the dimension /Geometry/function/state of processing object such as lathe,milling machine,packing machine 6
6 Power machine: to convert mechanical energy Other kinds of power mechanical energy such as steamer, internal-combustion engine, motor; Mechanical energy other kinds of power such as air compressor Machinery classification Machining machinery: change the dimension /Geometry/function/state of processing object such as lathe, milling machine, packing machine Machine classification

圆上泽文大学 Machine classification Transportation machinery:transfer object and man,such as automobile,plane,crane etc. 圆上清支大华 Machine classification Information machine:to process information such as print,copy,drawing machine. 7
7 Transportation machinery: transfer object and man, such as automobile, plane, crane etc. Machine classification Information machine: to process information such as print, copy, drawing machine. Machine classification
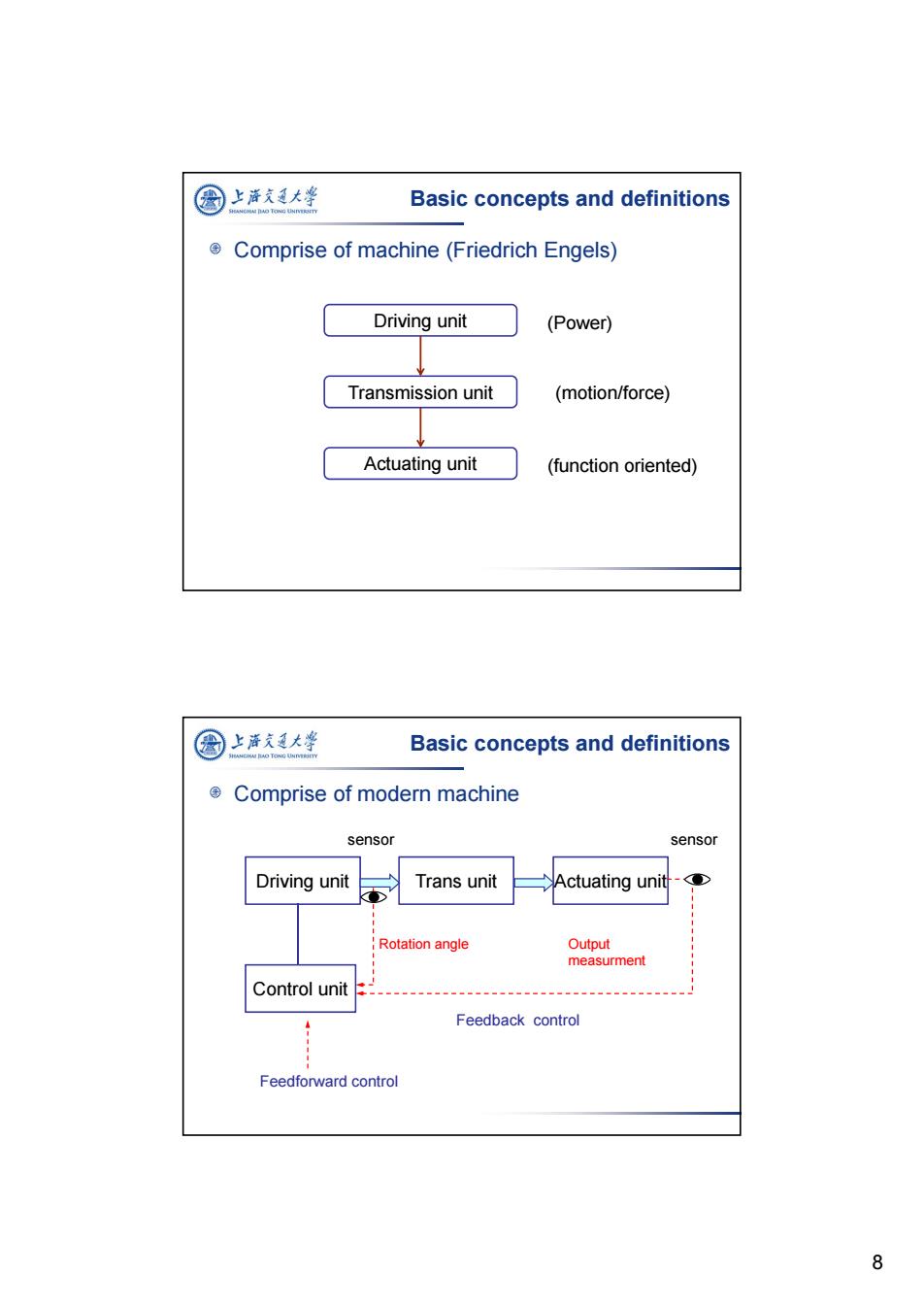
圈上海文通大华 Basic concepts and definitions Comprise of machine(Friedrich Engels) Driving unit (Power) Transmission unit (motion/force) Actuating unit (function oriented) 圆上泽夫道大学 Basic concepts and definitions Comprise of modern machine sensor sensor Driving unit Trans unit Actuating unit > Rotation angle Output measurment Control unit 4 Feedback control Feedforward control 8
8 Comprise of machine (Friedrich Engels) Basic concepts and definitions Driving unit Transmission unit Actuating unit (Power) (function oriented) (motion/force) Comprise of modern machine Basic concepts and definitions Driving unit Trans unit Actuating unit Control unit Rotation angle Output measurment Feedforward control sensor sensor Feedback control

圆上泽文大学 Basic concepts and definitions Mechanism(机构):a kinematic chain in which at lease one link has been"grounded",or attached,to the frame of reference(which itself may be in motion);the links in the kinematic chain move upon each other with definite relative motion. ⑧Kinematic Chain(运动链):an assembly of links and joints.(Interconnected in a way to provide a controlled output motion in response to a supplied input motion.) 圈上泽充大学 Basic concepts and definitions Engine Rear Wheel Transmission s Control system ower system Executive syste Augxiary system 9
9 Mechanism(机构): a kinematic chain in which at lease one link has been “grounded”, or attached, to the frame of reference(which itself may be in motion); the links in the kinematic chain move upon each other with definite relative motion. Kinematic Chain(运动链): an assembly of links and joints. (Interconnected in a way to provide a controlled output motion in response to a supplied input motion.) Basic concepts and definitions Basic concepts and definitions Power system Transmission system Control system Executive system Augxiliary system
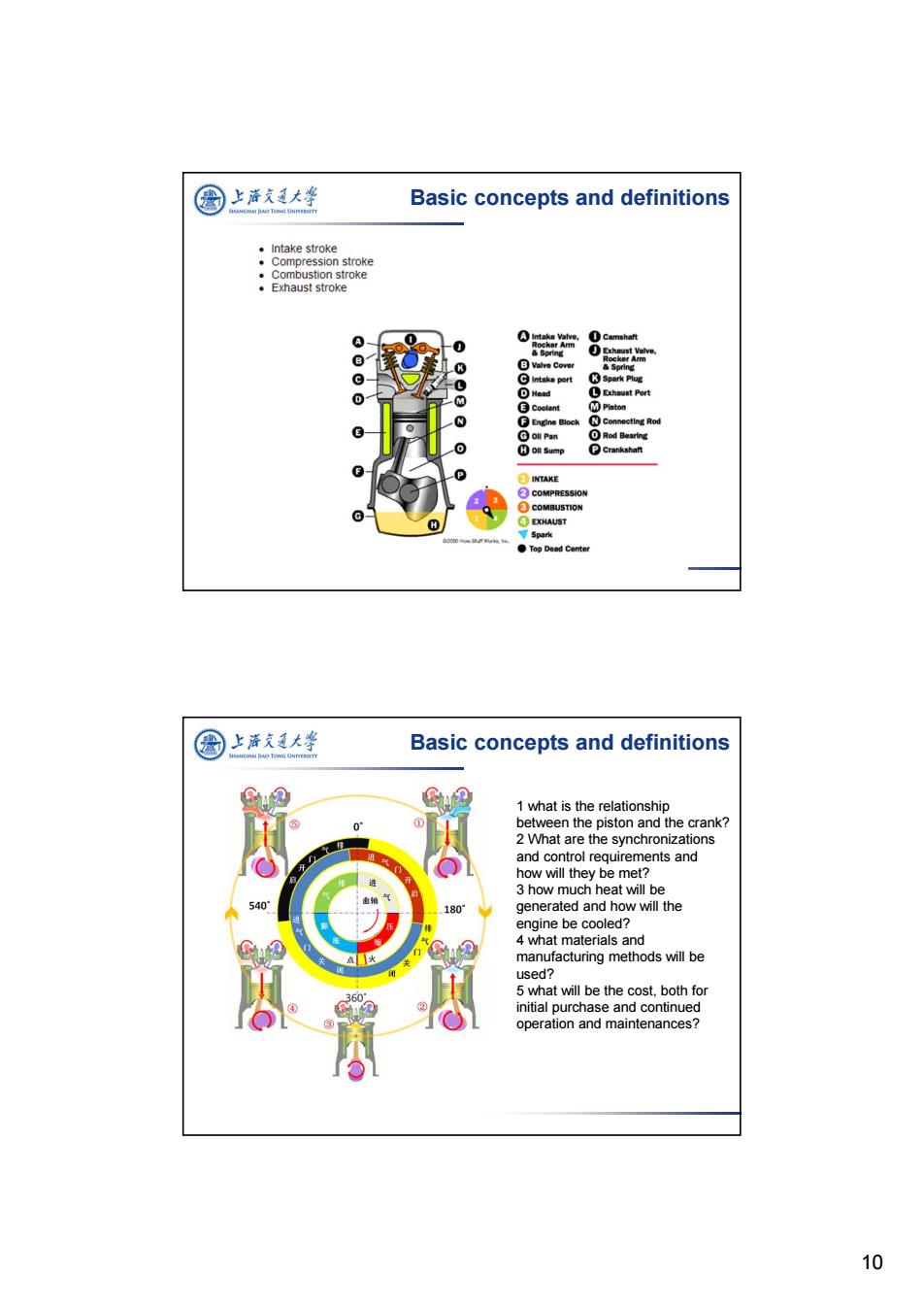
圈上海文通大华 Basic concepts and definitions ·Intake stroke ·Compression stroke : Combustion stroke Exhaust stroke 0 B Valve Cover intake port 3 Spark Plug ①Exhaust Port ⑧Connecting Rod oil Pan Rod Bearing Oll Sump INTAKE ②C MPRESSION COMBUSTION H EXHAUST Spark ●Top Dead Con © 上海充廷大学 Basic concepts and definitions G 1 what is the relationship 0 between the piston and the crank? 2 What are the synchronizations and control requirements and how will they be met? 3 how much heat will be 40 180 generated and how will the engine be cooled? 4 what materials and manufacturing methods will be used? 5 what will be the cost.both for initial purchase and continued operation and maintenances? 10
10 Basic concepts and definitions Basic concepts and definitions 1 what is the relationship between the piston and the crank? 2 What are the synchronizations and control requirements and how will they be met? 3 how much heat will be generated and how will the engine be cooled? 4 what materials and manufacturing methods will be used? 5 what will be the cost, both for initial purchase and continued operation and maintenances?