
Typhoid Fever and Paratyphoid Fever Yuan Zhe The first Affiliated Hospital Chongqing Medical University
Typhoid Fever and Paratyphoid Fever Yuan Zhe The first Affiliated Hospital Chongqing Medical University

Typhoid and Paratyphoid Definition ■Complications Etiology Diagnosis and ·Pathogenesis differential diagnosis ■Epidemiology Prognosis Clinical Treatment manifestations Preventions The laboratory and Paratyphoid Fever other examinations
Typhoid and Paratyphoid ◼ Definition ◼ Etiology ◼ Pathogenesis ◼ Epidemiology ◼ Clinical manifestations ◼ The laboratory and other examinations ◼ Complications ◼ Diagnosis and differential diagnosis ◼ Prognosis ◼ Treatment ◼ Preventions ◼ Paratyphoid Fever

Definition of Typhoid fever Acute enteric infectious disease caused by Salmonella typhi(S.Typhi). prolonged fever,Relative bradycardia,apathetic facial expressions,roseola,splenomegaly,hepatomegaly, leukopenia. intestinal perforation,intestinal hemorrhage
Definition of Typhoid fever ◼ Acute enteric infectious disease ◼ caused by Salmonella typhi (S.Typhi). ◼ prolonged fever, Relative bradycardia, apathetic facial expressions, roseola, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, leukopenia. ◼ intestinal perforation, intestinal hemorrhage

Etiology Serotype:D group of Salmonella Gram-negative rod non-spore flagella Culture characteristics
Etiology Serotype: D group of Salmonella Gram-negative rod non-spore flagella Culture characteristics

Antigens:located in the cell capsule H(flagellar antigen). O(Somatic or cell wall antigen). Vi (polysaccharide virulence) “widel test
◼ Antigens: located in the cell capsule H (flagellar antigen). O (Somatic or cell wall antigen). Vi (polysaccharide virulence) “widel test

A schematic diagram of a single Salmonella typhi cell showing the locations of the H (flagellar),0 (somatic),and Vi (K envelope)antigens
A schematic diagram of a single Salmonella typhi cell showing the locations of the H (flagellar), 0 (somatic), and Vi (K envelope) antigens

■Endotoxin ■A variety of plasmids Resistance:Live 2-3 weeks in water.1-2 months in stool.Die out quickly in summer Resistance to drying and cooling
◼ Endotoxin ◼ A variety of plasmids ◼ Resistance: Live 2-3 weeks in water. 1-2 months in stool. Die out quickly in summer Resistance to drying and cooling

Epidemiology continues to be a global health problem ■ areas with a high incidence include Asia,Africa and Latin America affects about 6000000 people with more than 600000 deaths a year.80%in Asia. sporadic occur usually,sometimes have epidemic outbreaks
Epidemiology ◼ continues to be a global health problem ◼ areas with a high incidence include Asia, Africa and Latin America ◼ affects about 6000000 people with more than 600000 deaths a year. 80% in Asia . ◼ sporadic occur usually, sometimes have epidemic outbreaks
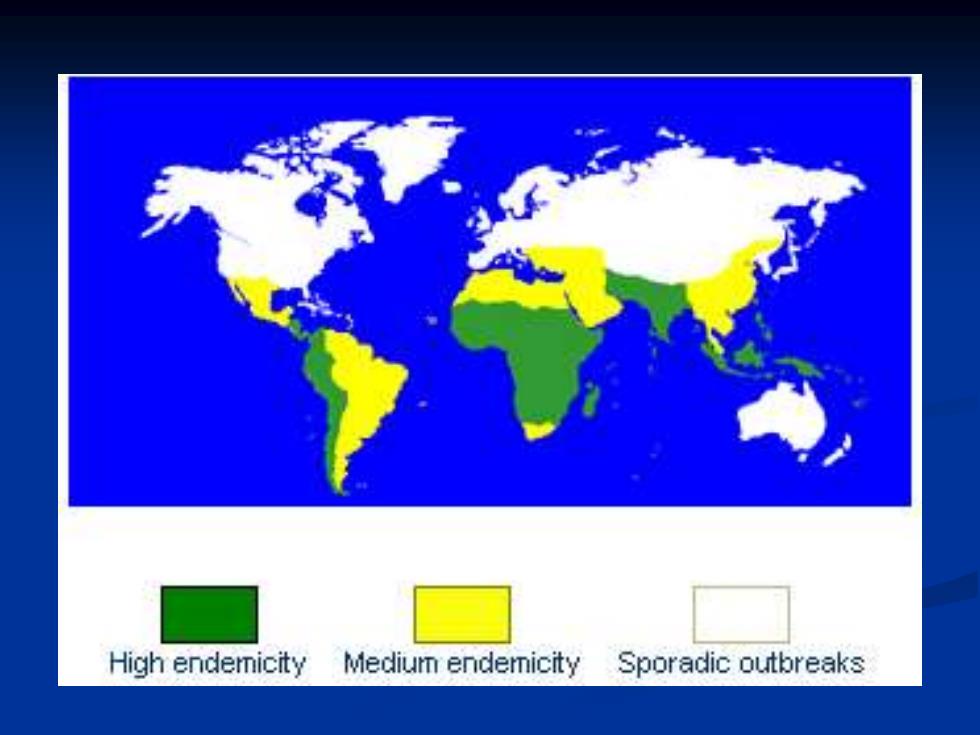
High endemicity Medium endemicity Sporadic outbreaks

Source of infection Cases and chronic carriers Cases discharge from incubation,more in 2~4 weeks after onset,a few (about 2~5%)last longer than 3 months chronic carrier Typhoid Mary
Source of infection Cases and chronic carriers Cases discharge from incubation, more in 2~4 weeks after onset, a few (about 2~5%) last longer than 3 months chronic carrier Typhoid Mary