
Epidemic Cerebrospinal Meningitis Yuan Zhe MD Dept.Of Infectious Disease The First Affiliated Hospital Chongqing Medical University
Epidemic Cerebrospinal Meningitis Yuan Zhe MD Dept. Of Infectious Disease The First Affiliated Hospital Chongqing Medical University

DEFINITION 1.Epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis is acute infectious disease caused by meningococcus. 2.characteristics of ECM are fever, ■headache,vomiting, petechiae or ecchymosis and meningeal irritation signs.CSF is purulent
DEFINITION ◼ 1. Epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis is acute infectious disease caused by ◼ meningococcus. ◼ 2.characteristics of ECM are fever, ◼ headache, vomiting , petechiae or ecchymosis , and meningeal irritation signs. CSF is purulent

ETIOLOGY 1.Pathogen is Neisseria meningitidis (meningococcus);G diplococcus 2.Biological features: 2.1.The organism grow by incubation on blood,chocolate or trypticase soy agar in 5≈10%CO2,PH7.4~7.6; 2.2.The organism is susceptible to dry, heat chill and disinfectant;
ETIOLOGY ◼ 1.Pathogen is Neisseria meningitidis (meningococcus); G- diplococcus. ◼ 2.Biological features: ◼ 2.1.The organism grow by incubation ◼ on blood,chocolate or trypticase soy agar in 5~10%CO2,PH 7.4~7.6; ◼ 2.2.The organism is susceptible to dry, ◼ heat , chill and disinfectant;

ETIOLOGY 2.3.autolysis by autolysin in vitro; 3.The organism can be detected in patient's nasopharynx,blood,CSF, petechiae in skin; 4.Pathogenic factor:endotoxin
◼ 2.3. autolysis by autolysin in vitro; ◼ 3.The organism can be detected in patient’s nasopharynx, blood, CSF, petechiae in skin; ◼ 4.Pathogenic factor: endotoxin. ETIOLOGY

ETIOLOGY 5.Serogroups of meningoccus; ■13 serogroups and more than 20 serotypes found in the world; ■ most common serogroups: A B C group Group A is the most common in china
◼ 5.Serogroups of meningoccus; ◼ 13 serogroups and more than 20 serotypes found in the world; ◼ most common serogroups: ◼ A B C group ◼ Group A is the most common in china. ETIOLOGY

EPIDEMIOLOGY 1.Source of infection: patients and carriers; 2.The routes of transmission ■1)air borne 2)closed contact transmission 3.Susceptibility of population:universal susceptible ■ stable and persistent immunity
EPIDEMIOLOGY ◼ 1.Source of infection: ◼ patients and carriers; ◼ 2.The routes of transmission : ◼ 1) air borne ◼ 2) closed contact transmission : ◼ 3.Susceptibility of population: universal susceptible ◼ stable and persistent immunity

EPIDEMIOLOGY 4.Epidemiologic feature: (1).Season:November May high peak:March April (2).age:6 months to 2 years old
◼ 4.Epidemiologic feature: ◼ (1). Season: November - May ◼ high peak: March - April ◼ (2).age: 6 months to 2 years old EPIDEMIOLOGY
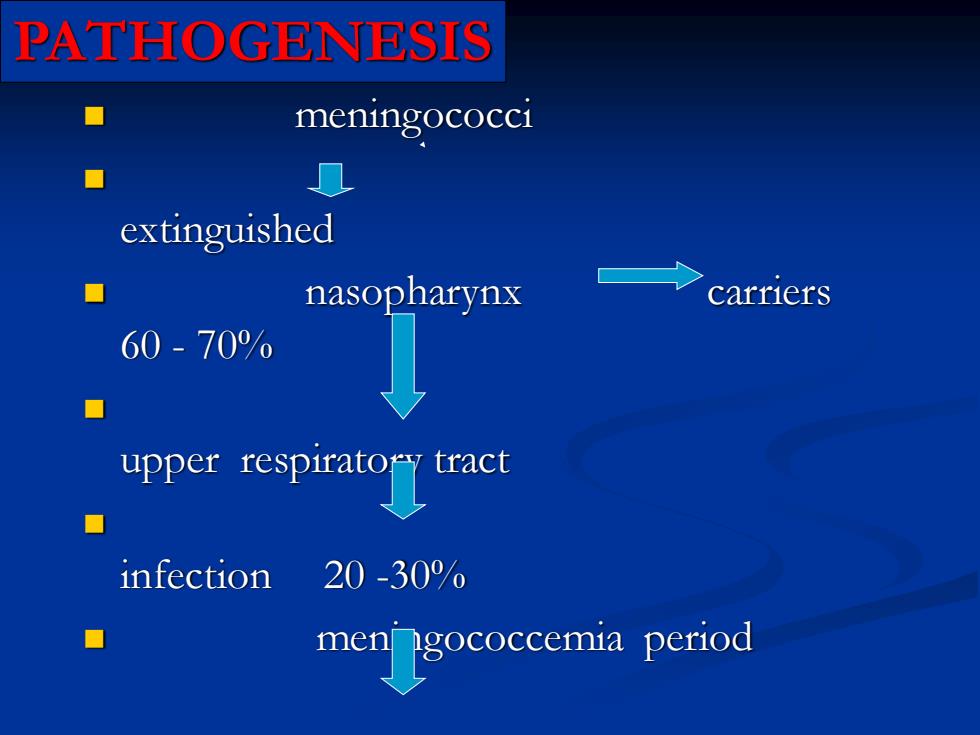
PATHOGENESIS meningococci extinguished nasopharynx carriers 60-700 upprespiratoract infection 20-30% period
PATHOGENESIS ◼ meningococci ◼ extinguished ◼ nasopharynx carriers 60 - 70% ◼ upper respiratory tract ◼ infection 20 -30% ◼ meningococcemia period septicemia
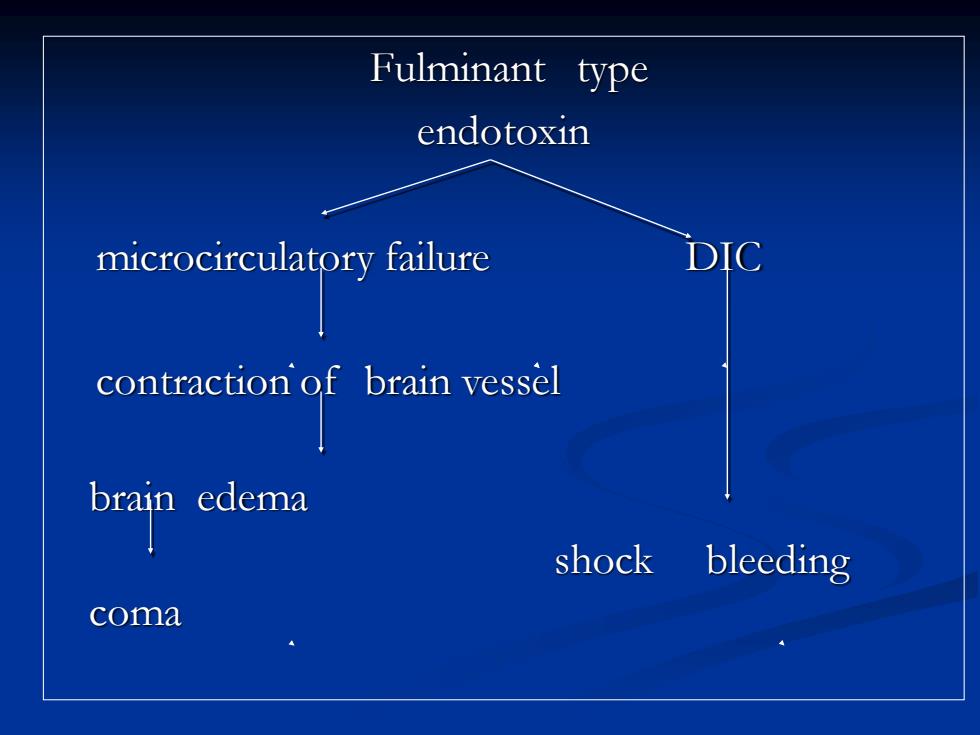
Fulminant type endotoxin microcirculatory failure DIC brain edema shock bleeding coma
Fulminant type endotoxin microcirculatory failure DIC contraction of brain vessel brain edema shock bleeding coma