
POPs Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) are chemical substances that persist in the environment, bioaccumulate through the food web, and pose a risk of causing adverse effects to human health and the environment. The "dirty dozen" includes: PCBs, aldrin, chlordane, DDT, dieldrin, endrin, heptachlor, hexachlorbenzene, mirex, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans, and toxaphene
POPs Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) are chemical substances that persist in the environment, bioaccumulate through the food web, and pose a risk of causing adverse effects to human health and the environment. The "dirty dozen" includes: PCBs, aldrin, chlordane, DDT, dieldrin, endrin, heptachlor, hexachlorbenzene, mirex, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans, and toxaphene
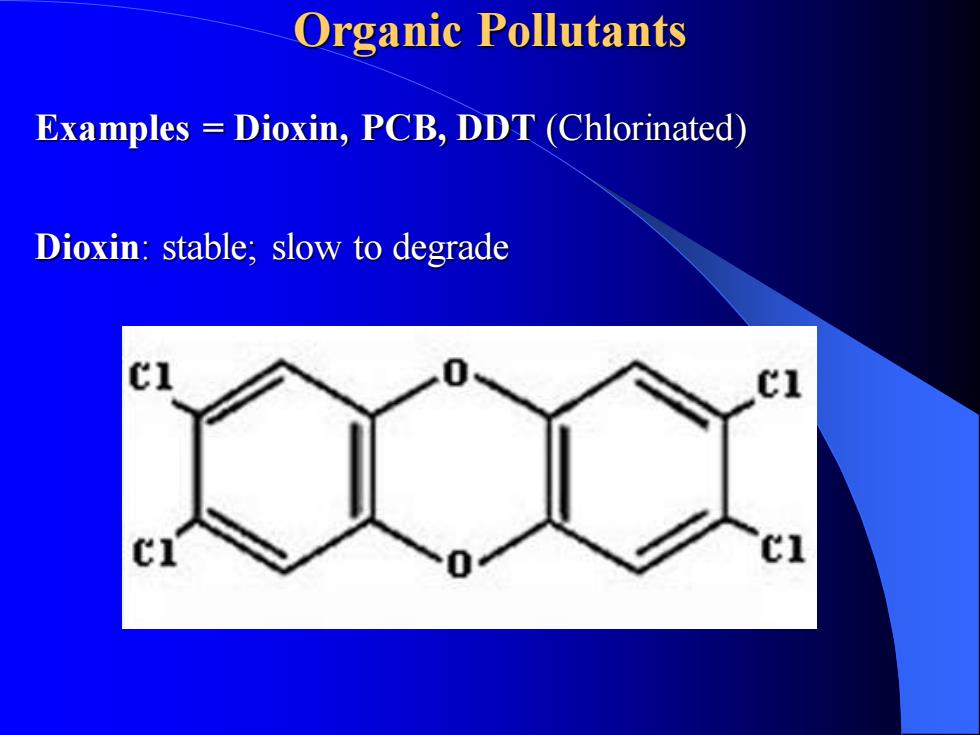
Organic Pollutants Examples = Dioxin, PCB, DDT (Chlorinated) Dioxin: stable; slow to degrade
Organic Pollutants Examples = Dioxin, PCB, DDT (Chlorinated) Dioxin: stable; slow to degrade

第9章 海洋合成有机化合物污染 9.1 海洋合成有机污染物概述 9.2 海洋有机氯农药污染 9.3 海洋多氯 9.4 海洋有机磷 9.5 海洋洗涤剂(磷)污染
第9章 海洋合成有机化合物污染 9.1 海洋合成有机污染物概述 9.2 海洋有机氯农药污染 9.3 海洋多氯 9.4 海洋有机磷 9.5 海洋洗涤剂(磷)污染

本节课需掌握的主要内容 ⚫ 9.1 海洋合成有机污染物概述 1. 主要的合成污染物种类、代表性物质及 其英文简写;
本节课需掌握的主要内容 ⚫ 9.1 海洋合成有机污染物概述 1. 主要的合成污染物种类、代表性物质及 其英文简写;

本节课需掌握的主要内容 ⚫ 9.2 海洋有机氯农药污染 1. P,P′- DDT的光分解反应、微生物降解 反应(脱氯、脱卤化氢作用)方程式, P52-53
本节课需掌握的主要内容 ⚫ 9.2 海洋有机氯农药污染 1. P,P′- DDT的光分解反应、微生物降解 反应(脱氯、脱卤化氢作用)方程式, P52-53

Pesticide Dilemma Because of the efficacy of DDT in checking malaria and other mosquito borne diseases (yellow fever, encephalitis), it is estimated that more than 75 million deaths have been averted
Pesticide Dilemma Because of the efficacy of DDT in checking malaria and other mosquito borne diseases (yellow fever, encephalitis), it is estimated that more than 75 million deaths have been averted

Pesticide Characteristics Pesticides are toxins used against organisms that interfere with human activities or welfare. Pesticides are grouped according to the pests they target – insecticides kill insects, herbicides kill plants, fungicides kill fungi, and rodenticides kill rats and mice. Agriculture uses ~85% of the almost 3 millions tons of pesticides used each year
Pesticide Characteristics Pesticides are toxins used against organisms that interfere with human activities or welfare. Pesticides are grouped according to the pests they target – insecticides kill insects, herbicides kill plants, fungicides kill fungi, and rodenticides kill rats and mice. Agriculture uses ~85% of the almost 3 millions tons of pesticides used each year

Pesticide Characteristics Many plant-derived pesticides (e.g., pyrethrin from chrysanthemums) or their derivatives are easily broken down by microorganisms and do not persist long in the environment. Most of the second generation man-made pesticides (e.g., DDT) are broad spectrum and slow to degrade (half-life 15 years in soil and as much as 150 years in aquatic environments)
Pesticide Characteristics Many plant-derived pesticides (e.g., pyrethrin from chrysanthemums) or their derivatives are easily broken down by microorganisms and do not persist long in the environment. Most of the second generation man-made pesticides (e.g., DDT) are broad spectrum and slow to degrade (half-life 15 years in soil and as much as 150 years in aquatic environments)

Pesticide Risks Pesticides can kill desirable organisms as well as pests. For example, broad spectrum insecticides may kill pollinators such as bees or lady bugs, which eat garden aphids. Pesticides enter the food network and through biological magnification may concentrate to toxin levels in secondary and tertiary consumers
Pesticide Risks Pesticides can kill desirable organisms as well as pests. For example, broad spectrum insecticides may kill pollinators such as bees or lady bugs, which eat garden aphids. Pesticides enter the food network and through biological magnification may concentrate to toxin levels in secondary and tertiary consumers

Pesticide Benefits Disease control - e.g., malaria caused by female Anopheles mosquitoes. Crop protection - reduce loss from competition with weeds, consumption by insects, and disease caused by fungi and bacteria. Part of reason for large numbers of agricultural pests is emphasis on monoculture in large tracts of land
Pesticide Benefits Disease control - e.g., malaria caused by female Anopheles mosquitoes. Crop protection - reduce loss from competition with weeds, consumption by insects, and disease caused by fungi and bacteria. Part of reason for large numbers of agricultural pests is emphasis on monoculture in large tracts of land