
Contents ◼ Introduction ◼ Part One Mechanisms in marine pollution ◼ Part two Topics in marine pollution ◼ Part three Measurement of biological response toxicity and water quality assessments ◼
Contents ◼ Introduction ◼ Part One Mechanisms in marine pollution ◼ Part two Topics in marine pollution ◼ Part three Measurement of biological response toxicity and water quality assessments ◼

Part two Topics in marine pollution ◼ Chap.2 Marine oxygen-demanded organic pollution ◼ Chap.3 Eutrophication and Red tide ◼ Chap.4 Oil pollution of the sea ◼ Chap.5 Marine synthetic organic pollution ◼ Chap.6 Heavy metal contamination in the sea ◼ Chap.7 Marine radioactivity pollution ◼ Chap.8 Marine heat pollution ◼ Chap.9 Other topics of marine polltion
Part two Topics in marine pollution ◼ Chap.2 Marine oxygen-demanded organic pollution ◼ Chap.3 Eutrophication and Red tide ◼ Chap.4 Oil pollution of the sea ◼ Chap.5 Marine synthetic organic pollution ◼ Chap.6 Heavy metal contamination in the sea ◼ Chap.7 Marine radioactivity pollution ◼ Chap.8 Marine heat pollution ◼ Chap.9 Other topics of marine polltion


Chap.3 Eutrophication and Red tide 3.1 What is Eutrophication? (definition) 3.2 Why Should We Be Concerned? (harmful effect) 3.3 The nutrient in the coastal seawater 3.4 Eutrophication in the coastal seawater 3.5 Red tide
Chap.3 Eutrophication and Red tide 3.1 What is Eutrophication? (definition) 3.2 Why Should We Be Concerned? (harmful effect) 3.3 The nutrient in the coastal seawater 3.4 Eutrophication in the coastal seawater 3.5 Red tide

What is Eutrophication? Eutrophication is a condition in an aquatic ecosystem where high nutrient concentrations stimulate blooms of algae (e.g., phytoplankton). -EPA
What is Eutrophication? Eutrophication is a condition in an aquatic ecosystem where high nutrient concentrations stimulate blooms of algae (e.g., phytoplankton). -EPA

The other definition "the enrichment of water by nutrients especially compounds of nitrogen and phosphorus, causing an accelerated growth of algae and higher forms of plant life to produce an undesirable disturbance to the balance of organisms and the quality of the water concerned.“ —— by the European Commission
The other definition "the enrichment of water by nutrients especially compounds of nitrogen and phosphorus, causing an accelerated growth of algae and higher forms of plant life to produce an undesirable disturbance to the balance of organisms and the quality of the water concerned.“ —— by the European Commission

Why Should We Be Concerned? Although eutrophication is a natural process in the aging of lakes and some estuaries, human activities can greatly accelerate eutrophication by increasing the rate at which nutrients and organic substances enter aquatic ecosystems from their surrounding watersheds
Why Should We Be Concerned? Although eutrophication is a natural process in the aging of lakes and some estuaries, human activities can greatly accelerate eutrophication by increasing the rate at which nutrients and organic substances enter aquatic ecosystems from their surrounding watersheds

Agricultural runoff, urban runoff, leaking septic systems, sewage discharges, eroded streambanks, and similar sources can increase the flow of nutrients and organic substances into aquatic systems. These substances can overstimulate the growth of algae, creating conditions that interfere with the recreational use of lakes and estuaries, and the health and diversity of indigenous fish, plant, and animal populations
Agricultural runoff, urban runoff, leaking septic systems, sewage discharges, eroded streambanks, and similar sources can increase the flow of nutrients and organic substances into aquatic systems. These substances can overstimulate the growth of algae, creating conditions that interfere with the recreational use of lakes and estuaries, and the health and diversity of indigenous fish, plant, and animal populations

Pollution From Agricultural Runoff
Pollution From Agricultural Runoff
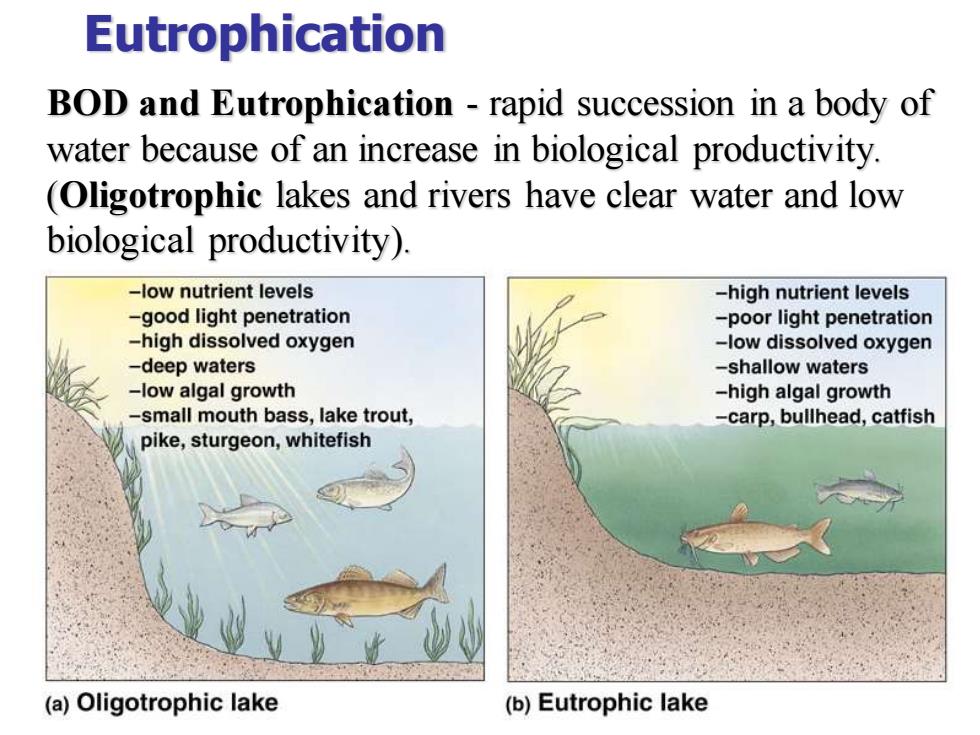
Eutrophication BOD and Eutrophication - rapid succession in a body of water because of an increase in biological productivity. (Oligotrophic lakes and rivers have clear water and low biological productivity)
Eutrophication BOD and Eutrophication - rapid succession in a body of water because of an increase in biological productivity. (Oligotrophic lakes and rivers have clear water and low biological productivity)