
计算机问题求解一论题3-8 单源最短通路算法 2022年11月2日
计算机问题求解 – 论题3-8 - 单源最短通路算法 2022年11月2日

什么是最短通路问题: In a shortest-paths problem,we are given a weighted,directed graph G=(V,E),with weight function w:ER mapping edges to real-valued weights.The weight w(p)of path p=(vo.v1...v)is the sum of the weights of its constituent edges: 问题1: k w(p)=w(-1,). 输入是什么?输出是 i=1 什么? We define the shortest-path weight 8(u,v)from u to v by min()ithere isa pathfrom o otherwise A shortest path from vertex u to vertex v is then defined as any path p with weight w(p)=8u,)
什么是最短通路问题?

问题2 单源最短略问题的解必定是一棵树? A shortest-paths tree rooted at s is a directed subgraph G'=(V',E), where V'C V and E'C E,such that 1.V'is the set of vertices reachable from s in G, 2.G'forms a rooted tree with root s,and 3.for all vV,the unique simple path froms to v in G'is a shortest path froms to v in G. 由.T决定的 Vπ={v∈V:w.π≠NTL}U{s}· 最短路径树: E元={v.π,v)∈E:v∈Vπ-{s}
由.π决定的 最短路径树:

单源最短路问题具有最佳子结构性 Lemma 24.1 (Subpaths of shortest paths are shortest paths) Given a weighted,directed graph G=(V.E)with weight function w:E->R, let p =(vo,v1,....vk)be a shortest path from vertex vo to vertex vk and,for any i and j such that0≤i≤j≤k,let Pij=(i,vi+l,,vi)be the subpath of p from vertex vi to vertex vj.Then,Pij is a shortest path from vi to vj. Proof If we decompose path p into vv,then we have that w(p)=w(Poi)+w(Pij)+w(pik).Now,assume that there is a path p;from vi to with weight w(p(.Then,is a path from v to vk whose weight w(poi)+w(p)+w(pjk)is less than w(p),which contradicts the assumption that p is a shortest path from vo to vk
单源最短路问题具有最佳子结构性
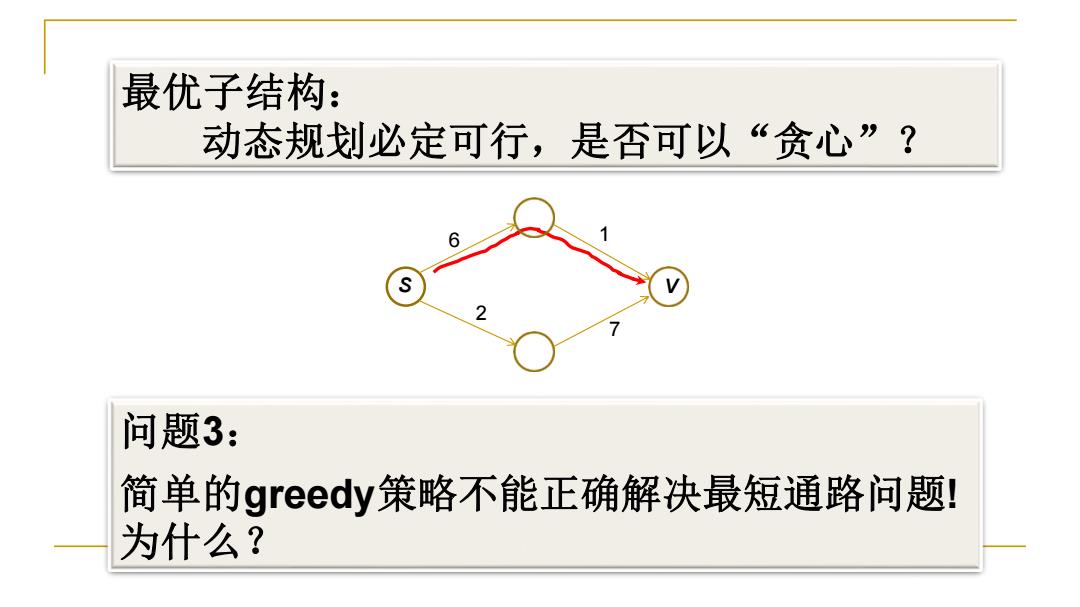
最优子结构: 动态规划必定可行,是否可以“贪心”? 问题3: 简单的greedy策略不能正确解决最短通路问题! 为什么?
s 2 6 1 7 v 问题3: 简单的greedy策略不能正确解决最短通路问题! 为什么? 最优子结构: 动态规划必定可行,是否可以“贪心”?

问题5: 在本章中介绍的算法基本思路 是一样的,那是什么? Bellman-Ford算法、DAG算法、Dijkstra算法 松弛+有序的松弛
Bellman-Ford算法、DAG算法、Dijkstra算法 松弛+有序的松弛

问题6: Relax到底在干什么? 为什么它会是最短路算法的核心?

从这个案例中,我们能够得到的启发: 令u.d是源点s到节点u的最短距离的预测,初始定义u.d=∞. u.d是&(s,u的上界,但不紧致 若节点u有一条有向边射入节点v,且此时u.d和v.d分别为5和9 v.d是否可以被紧致到一个更小的上界,比如7?
从这个案例中,我们能够得到的启发: 令u.d是源点s到节点u的最短距离的预测,初始定义u.d=∞. 若节点u有一条有向边射入节点v,且此时u.d和v.d分别为5和9 v.d是否可以被紧致到一个更小的上界,比如7? u.d是&(s,u)的上界,但不紧致
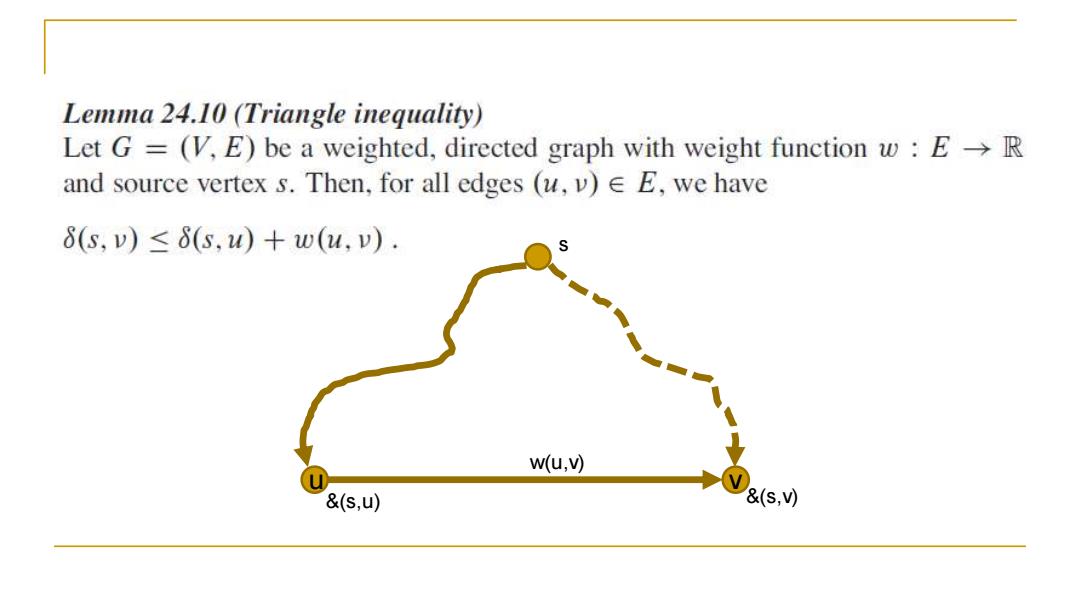
Lemma 24.10(Triangle inequality) Let G =(V,E)be a weighted,directed graph with weight function w E-R and source vertex s.Then,for all edges (u,v)EE,we have 8(s,v)≤6(s,u)+w(u,v). W(u,) &(S,U) &(s,)
s u v &(s,u) &(s,v) w(u,v)
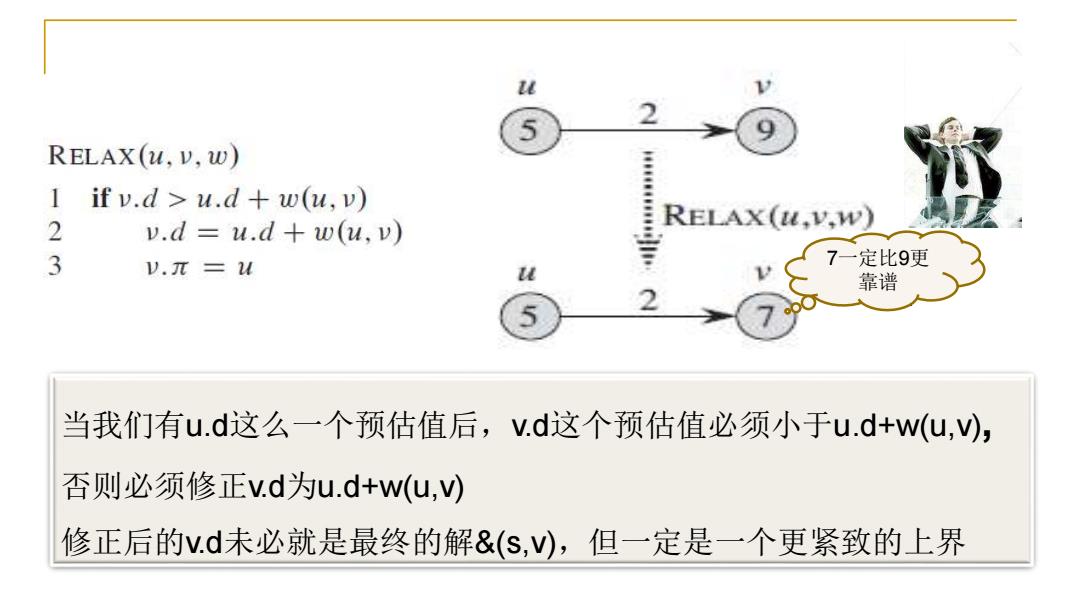
2 RELAX(u,v,w) 1 if v.d u.d+w(u,v) 2 v.d u.d+w(u,v) RELAX(u,v,W) 3 V.π=u 7一定比9更 u 靠谱 当我们有u.d这么一个预估值后,V.d这个预估值必须小于u.d+w(u,), 否则必须修正v.d为u.d+w(u,) 修正后的v.d未必就是最终的解&(S,V),但一定是一个更紧致的上界
s u v 当我们有u.d这么一个预估值后,v.d这个预估值必须小于u.d+w(u,v), 否则必须修正v.d为u.d+w(u,v) 修正后的v.d未必就是最终的解&(s,v),但一定是一个更紧致的上界 u.d v.d 7一定比9更 靠谱