
计算机问题求解一论题3-4 -用于动态等价关系的数据结构 2022年09月28日
计算机问题求解 – 论题3-4 -用于动态等价关系的数据结构 2022年09月28日

问题1: 什么是等价关系? 它有什么应用意义?
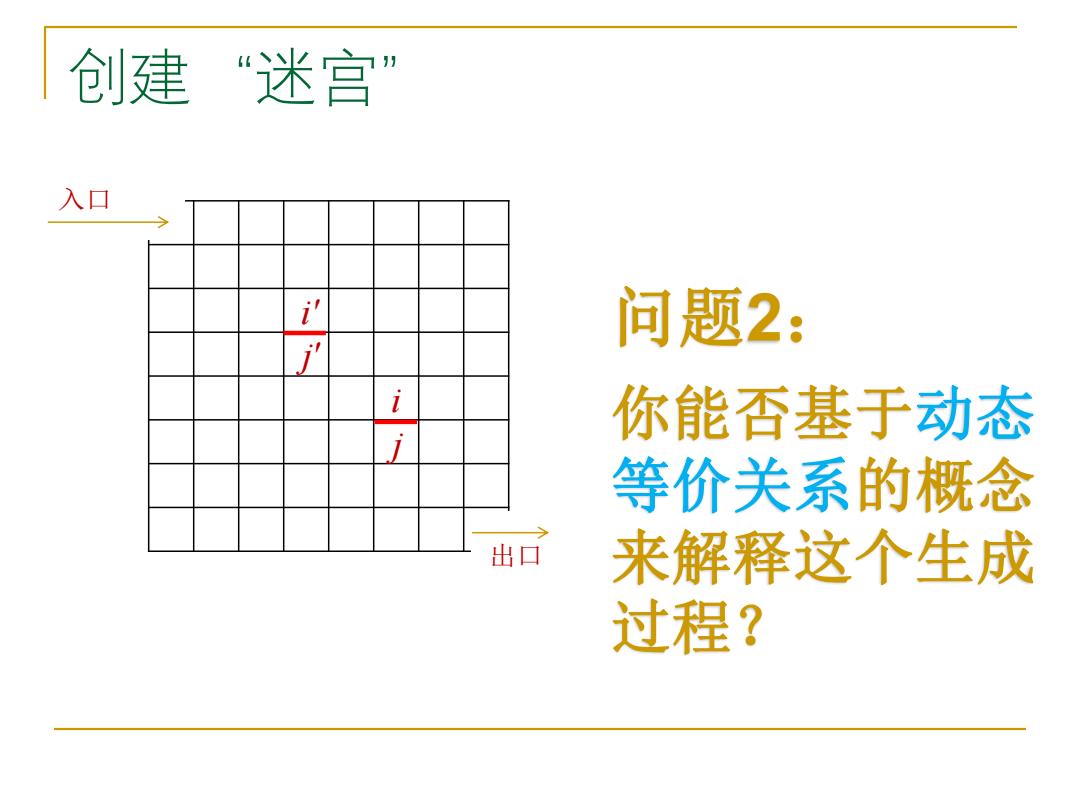
创建“迷宫” 入口 i' 问题2: ' 你能否基于动态 等价关系的概念 出口 来解释这个生成 过程?
创建“迷宫” 入口 出口 i j 问题2: 你能否基于动态 等价关系的概念 来解释这个生成 过程? i' j

问题3: 我们用什么数据结构实现 动态等价关系? 这个数据结构的基本操作 是什么?
问题3: 我们用什么数据结构实现 动态等价关系? 这个数据结构的基本操作 是什么?

ADT of disjoint-set MAKE-SET(x)creates a new set whose only member (and thus representative) is x.Since the sets are disjoint,we require that x not already be in some other set. UNION(x.y)unites the dynamic sets that contain x and y,say Sx and Sy,into a new set that is the union of these two sets.We assume that the two sets are dis- joint prior to the operation.The representative of the resulting set is any member of SxU Sy,although many implementations of UNION specifically choose the representative of either Sx or Sy as the new representative.Since we require the sets in the collection to be disjoint,conceptually we destroy sets Sx and Sy, removing them from the collection 8.In practice,we often absorb the elements of one of the sets into the other set. FIND-SET(x)returns a pointer to the representative of the (unique)set contain- ingx
ADT of disjoint-set

问题4: 什么是representative? 讨论数学与讨论数据结构 时它有什么差别?
representative

问题5: 讨论的不是一个算法, 而是一个数据结构. 所谓“时间复杂性分析 究竟是什么意思呢?
问题5: 讨论的不是一个算法, 而是一个数据结构. 所谓“时间复杂性分析” 究竟是什么意思呢?

Running times of disjoint-set Throughout this chapter,we shall analyze the running times of disjoint-set data structures in terms of two parameters n,the number of MAKE-SET operations, and m,the total number of MAKE-SET,UNION,and FIND-SET operations.Since the sets are disjoint,each UNION operation reduces the number of sets by one. After n-1 UNION operations,therefore,only one set remains.The number of UNION operations is thus at most n-1.Note also that since the MAKE-SET operations are included in the total number of operations m,we have m >n.We assume that the n MAKE-SET operations are the first n operations performed
Running times of disjoint-set
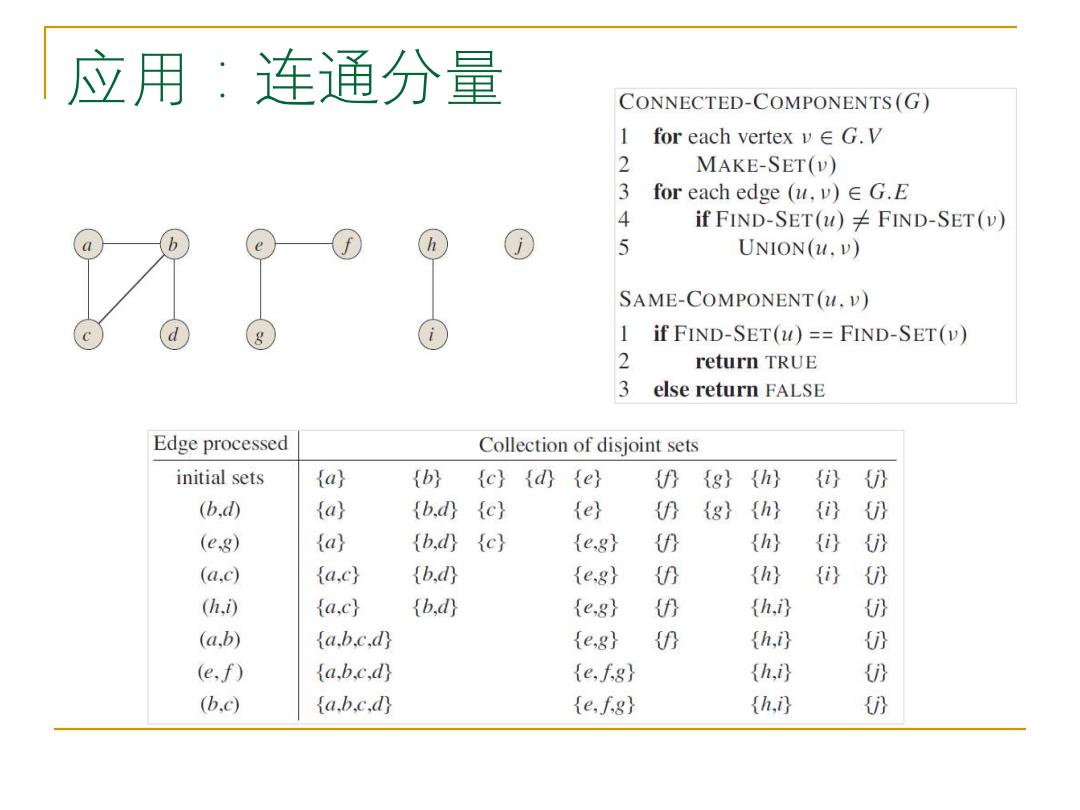
应用:连通分量 CONNECTED-COMPONENTS(G) 1 for each vertex v∈G.V 2 MAKE-SET(v) 3 for each edge (u,v)E G.E 4 if FIND-SET(u)FIND-SET(v) b ① 5 UNION(.V) SAME-COMPONENT(u.V) 1 if FIND-SET(u)==FIND-SET(v) 2 return TRUE 3 else return FALSE Edge processed Collection of disjoint sets initial sets La) {b) {c} Ad) {e} 价 {8} { 话 } (b,d0 La) {b,d) {c} {e} 仍 {g} (h) (0) 0 (eg) La) {b,d) {c} {e,8} 仍 th) {i) 仍 (a,c) {a,c} {b,d) {e,8} (h) (d} 仍 (h,i0 {a,c} (b,d) {e,8} 仍 {h,} } (a,b) a.b.c.dy {e,8} (h.i (e,f) a.b.c.dy e.fg) {h,i} 仍 (b,c) a.bc.dy {e,f8} (h,i }
应用:连通分量

Kruskal算法 7 d (a) 14 e (b) d (c) d e】 9 (g) (h) 10 Figure 23.4 The execution of Kruskal's algorithm on the graph from Figure 23.1.Shaded edges
Kruskal 算法