
有限元理论与建模方法 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 第八章 热分析有限元法 FEM of Thermal Analysis When:high temperature 昵图uuuu.nipic.com Byh yaaabb6N6.20130513144734177 电子料技大学机械与电气工程学院 2020,10
有限元理论与建模方法 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 2020,10 第八章 热分析有限元法 FEM of Thermal Analysis When: high temperature

有限元理论与建模方法 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 热分析的目的: 1.温度场计算 温度分布Temperature distribution 热流FIux 2.热力耦合分析 热变形Thermal deformation 热应力Thermal stress 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 2020,10
有限元理论与建模方法 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 2020,10 热分析的目的: 热变形 Thermal deformation 热应力 Thermal stress 1. 温度场计算 2. 热力耦合分析 温度分布 Temperature distribution 热流 Flux

有限理论与建模方法 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 第一节热传导方程及热边界条件 传热学 第二节热分析有限元法的一般步骤 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 2020,10
有限元理论与建模方法 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 2020,10 第一节 热传导方程及热边界条件 第二节 热分析有限元法的一般步骤 传热学

有限元理论与建模方法 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 第一节热传导方程及热边界条件 1.Equation of heat conduction Conduction(传导) Heat transfer Convection(对流) 、Radiation(辐射) 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 2020,10
有限元理论与建模方法 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 2020,10 第一节 热传导方程及热边界条件 1. Equation of heat conduction Heat transfer Conduction(传导) Convection(对流) Radiation(辐射)
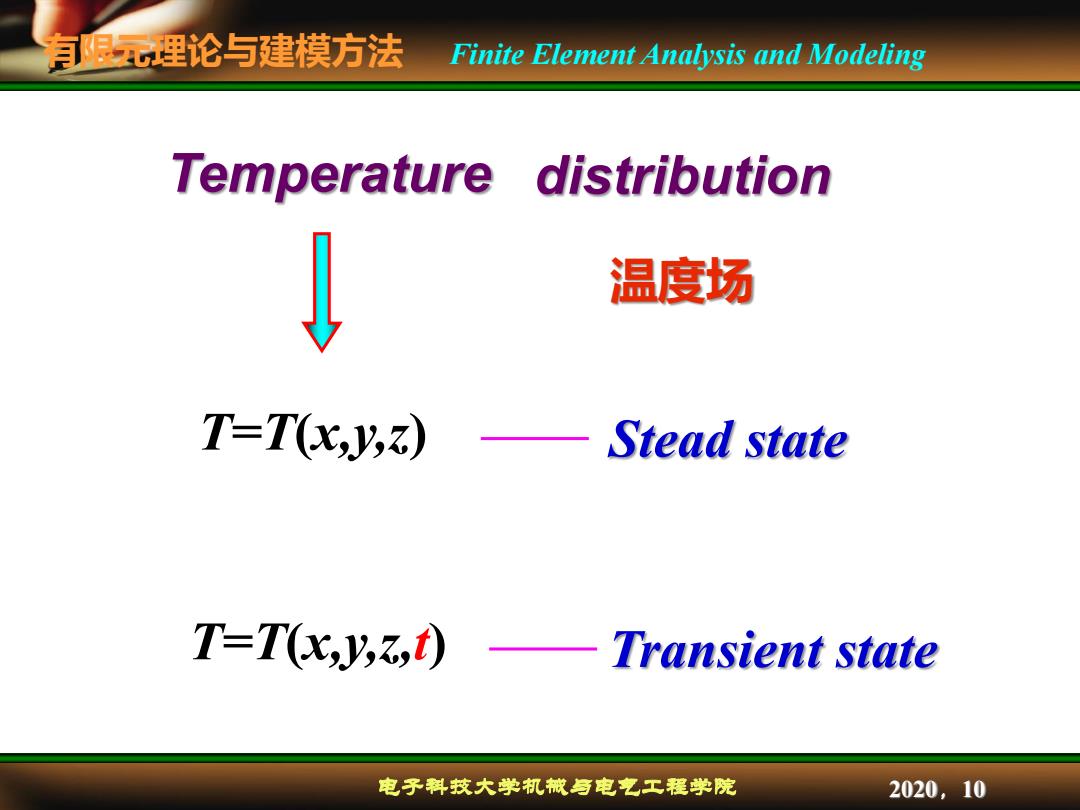
有限理论与建模方法 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling Temperature distribution ↓ 温度场 T-T(x,y, -Stead state T-T(x,y,3,t)-Transient state 电子料技大学机械与电克工程学院 2020,10
有限元理论与建模方法 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 2020,10 T=T(x,y,z,t) Temperature Stead state Transient state T=T(x,y,z) distribution 温度场

有限理论与建模方法 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling Differential Equation of Heat Conduction 比热容 热传导系数(导热系数) 内部热源 x宫-,黑)+,+4 +P9 温度升高需 从三个方向传递 内部产生 要的热量 进来的热量 的热量 热平衡方程 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 2020,10
有限元理论与建模方法 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 2020,10 c T t x T x y T y z T z x y z qi Differential Equation of Heat Conduction 热平衡方程 比热容 热传导系数(导热系数) 温度升高需 要的热量 从三个方向传递 进来的热量 内部产生 的热量 内部热源
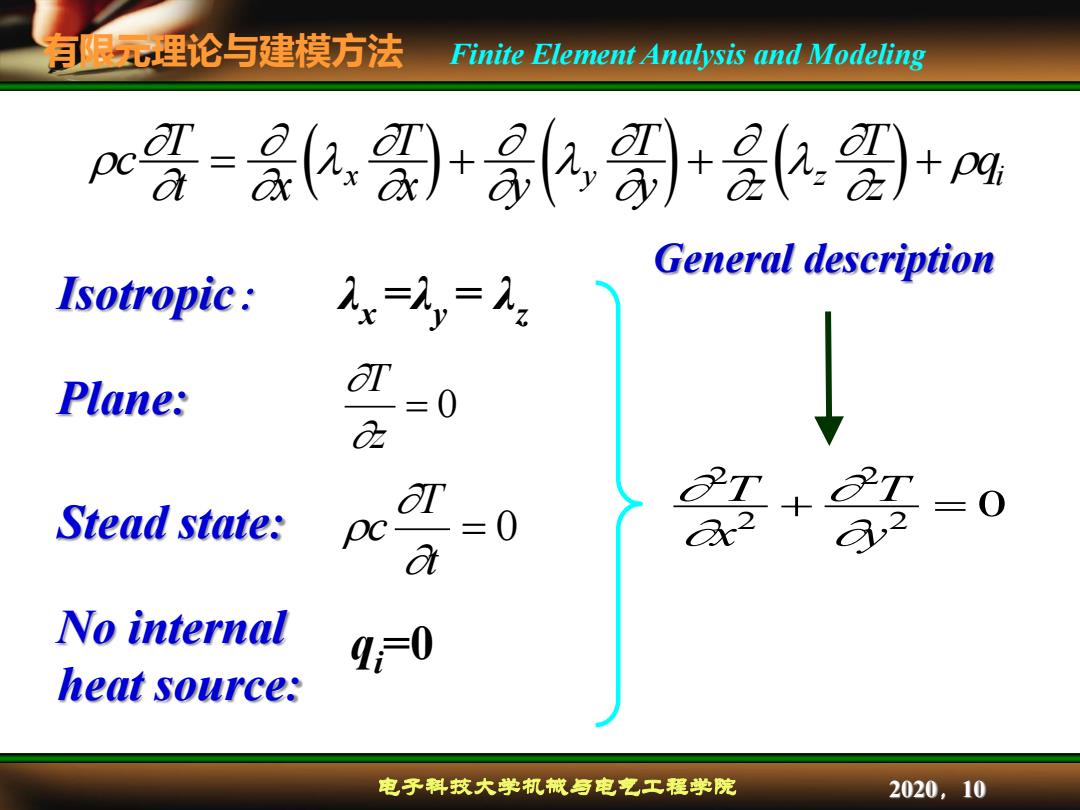
有限理论与建模方法 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling =.黑)+(,别+)+ General description Isotropic: x= =2 Plane: T 0 2 ar 子T Stead state: 0 a No internal heat source: 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 2020,10
有限元理论与建模方法 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 2020,10 c T t x T x y T y z T z x y z qi Isotropic: λx =λy = λz qi =0 0 z T 0 t T c Stead state: Plane: No internal heat source: 2 2 2 2 0 T x T y General description
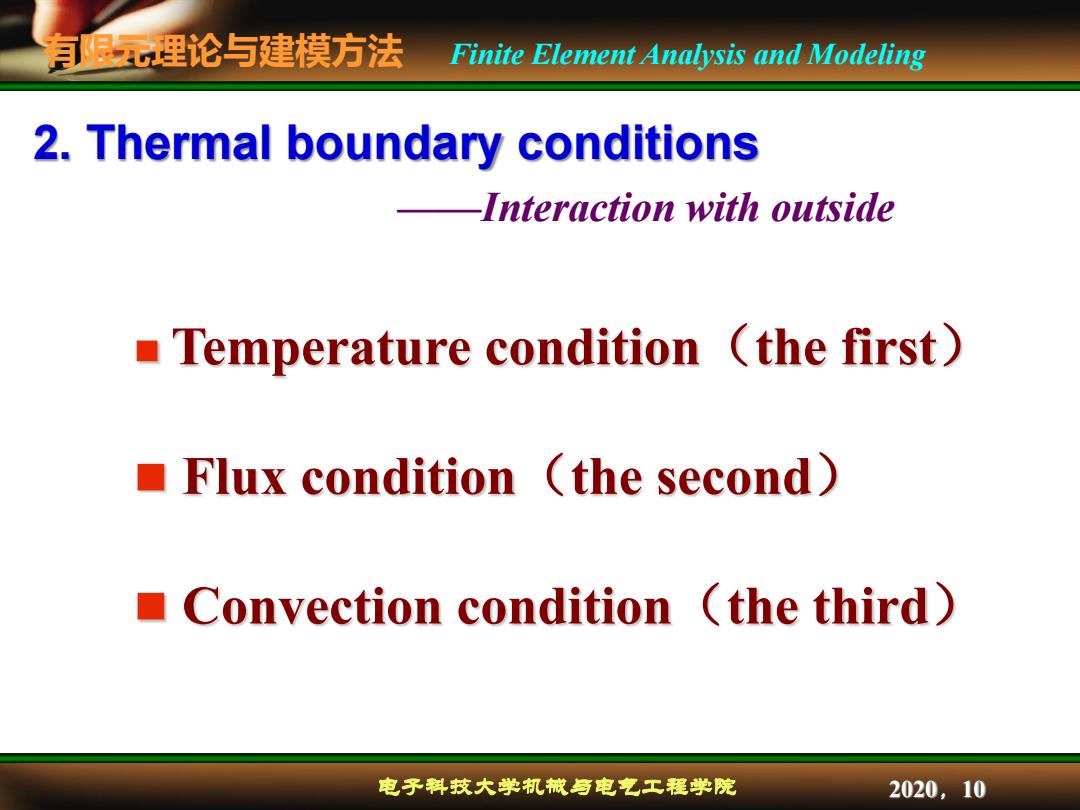
有限元理论与建摸方法 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 2.Thermal boundary conditions -Interaction with outside Temperature condition (the first) Flux condition (the second) Convection condition (the third) 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 2020,10
有限元理论与建模方法 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 2020,10 2. Thermal boundary conditions ——Interaction with outside Temperature condition(the first) Flux condition(the second) Convection condition(the third)
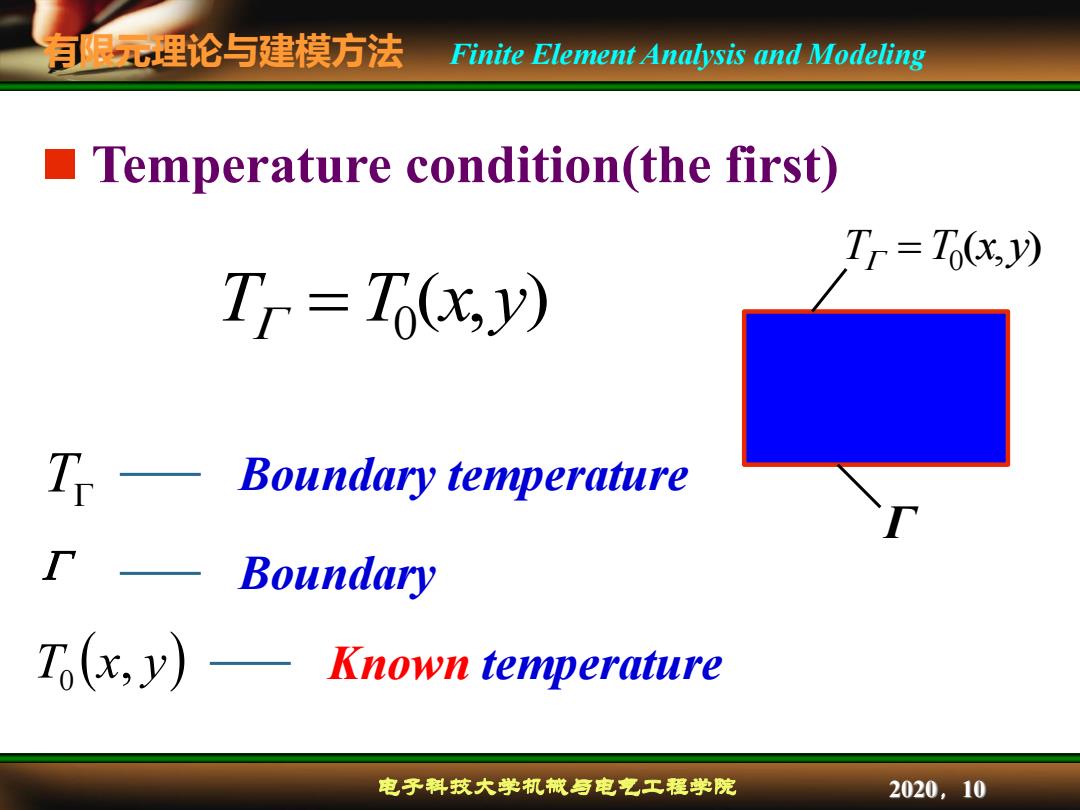
有限理论与建模方法 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling Temperature condition(the first) Tr=To(x,y) T=Ti(x,y) T Boundary temperature Boundary T(x,y)-Known temperature 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 2020,10
有限元理论与建模方法 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 2020,10 Temperature condition(the first) T T x y 0 , T T x, y 0 Boundary temperature Boundary Known temperature T T x y 0 , Γ

有限理论与建模方法 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling Flux condition(the second) 90 ),=% λ 热传导系数 40 —已知热流密度 分8 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 2020,10
有限元理论与建模方法 电子科技大学机械与电气工程学院 Finite Element Analysis and Modeling 2020,10 Flux condition(the second) T n q 0 —— 热传导系数 q0 —— 已知热流密度 Γ 0 q