
CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 21 DNA Replication II Detailed Mechanism Cal Harley/Geron Corporation Peter Rabinovitch,Univ.of Washington
Chapter 21 DNA ReplicationⅡ: Detailed Mechanism

2 1.1 Speed of Replication
2 1.1 Speed of Replication

measure the rate of fork movement in vitro Primosome assembly site 00 Pol IlI holoenzyme +SSB a To create a synthetic circular template for rolling circle replication,This template contained a 32p-labeled tailed. At 10 sec intervals,they removed the labeled product DNAs and measured their lengths by electrophoresis
To create a synthetic circular template for rolling circle replication,This template contained a 32p-labeled tailed. At 10 sec intervals, they removed the labeled product DNAs and measured their lengths by electrophoresis. measure the rate of fork movement in vitro

Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies.Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. (a) (b) (c) 1234567891011 1234567891011 他 50 2 431 9 7395 37.7 器8 16.2 162 21.5 30 162 16.2 10.8 108 20 108 108 Tailed form ll 1111I11 54 1020304050607080 Tailed Time (sec) form ll 54 -54 polⅢholoenzyme plus:(a)the preprimosomal proteins((前引发 体蛋白)(the primosomal proteins minus DnaG);or(b)DnaB alone.about 730 nt/sec
pol III holoenzyme plus: (a) the preprimosomal proteins(前引发 体蛋白) (the primosomal proteins minus DnaG); or (b) DnaB alone. about 730 nt/sec

Processivity(持续性):the ability of the enzyme to stick to its job a long time without falling off and having to reinitiate
Processivity(持续性): the ability of the enzyme to stick to its job a long time without falling off and having to reinitiate.

小结 聚合酶II全酶在体外合成DNA的速率大约 是730nt/sec,稍慢于在体内观测到的1000 nt/sec。该酶在体内和体外都具有高度持 续性
聚合酶III全酶在体外合成DNA的速率大约 是730 nt/sec,稍慢于在体内观测到的1000 nt/sec。该酶在体内和体外都具有高度持 续性。 小结
21.2 Initiation(起始) Initiation of DNA replication means primer synthesis.Different organisms use different mechanisms to make primers;even different phages that infect E.coli(coliphages)use quite different primer synthesis strategies. Priming(引发)lnE.coli M13 phage use the host RNA polymerase as its primase(primer-synthesizing enzyme).But E.coli and its other phages employ a primase called DnaG,which is the product of the E.coli dnaG gene.E.coli and most of its phages need at least one more protein (DnaB,the product of the E.coli dnaB gene)to form primers,at least on the lagging strand
2 1.2 Initiation(起始) Initiation of DNA replication means primer synthesis.Different organisms use different mechanisms to make primers;even different phages that infect E.coli(coliphages)use quite different primer synthesis strategies. Priming(引发)ln E.coIi M13 phage use the host RNA polymerase as its primase(primer-synthesizing enzyme).But E.coli and its other phages employ a primase called DnaG,which is the product of the E.coli dnaG gene. E.coli and most of its phages need at least one more protein (DnaB,the product of the E.coli dnaB gene)to form primers,at least on the lagging strand.

DX174 phage DNA replication Kornberg and colleagues found that three proteins: DnaG(the primase),DnaB,and pol III holoenzyme were required in this assay.Thus,DnaG and DnaB were apparently needed for primer ynthesis. primosome(引发体)to refer to the collection of proteins needed to make primers for a given replicating DNA.Usually this is just two proteins,DnaG and DnaB,although other proteins may be needed to assemble the primosome
ΦX174 phage DNA replication Kornberg and colleagues found that three proteins: DnaG(the primase),DnaB,and pol III holoenzyme were required in this assay.Thus,DnaG and DnaB were apparently needed for primer ynthesis. primosome (引发体)to refer to the collection of proteins needed to make primers for a given replicating DNA.Usually this is just two proteins,DnaG and DnaB,although other proteins may be needed to assemble the primosome

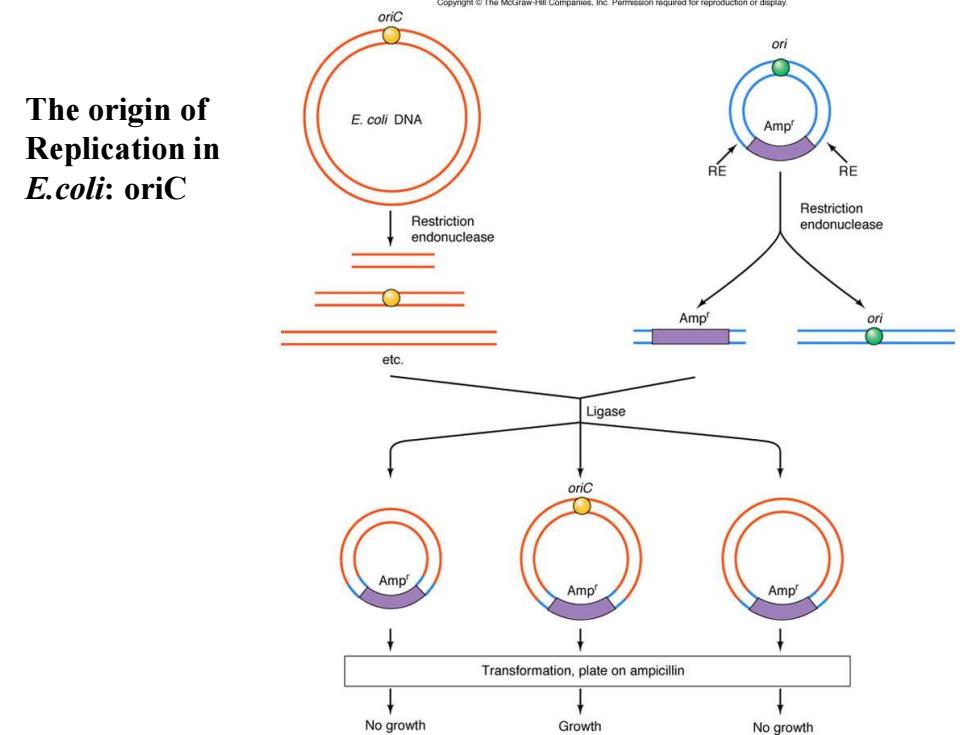
The origin(复制起点)of Replication in E.coli Origin:a DNA site at which DNA replication begins and which is essential for proper replication to occur. how do we know how much of the DNA around the initiation site is essential for replication to begin? One way is to clone a DNA fragment,Including the initiation site into a plasmid that lacks its own origin of replication but has an antibiotic resistance gene.Then we can select for autonomously replicating plasmids with the antibiotic
The origin (复制起点)of Replication in E.coli Origin:a DNA site at which DNA replication begins and which is essential for proper replication to occur. how do we know how much of the DNA around the initiation site is essential for replication to begin? One way is to clone a DNA fragment,Including the initiation site into a plasmid that lacks its own origin of replication but has an antibiotic resistance gene.Then we can select for autonomously replicating plasmids with the antibiotic.
oric The origin of E.coli DNA Amp' Replication in RE E.coli:oriC Restriction Restriction endonuclease endonuclease Amp etc Ligase Amp Amp Transformation,plate on ampicillin No growth Growth No growth
The origin of Replication in E.coli: oriC