
TextbooK Molecular Biology,by Robert F.Weaver Molecular Molecular Biology Biology 分子生物晋 Fourth Editio (上册) Robert F.Weaver the 4th edition 2008 It is particularly strong on experimental detail. http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072995246/ www.mhhe.com/weaver4
Textbook Molecular Biology, by Robert F. Weaver It is particularly strong on experimental detail. http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072995246/ www.mhhe.com/weaver4 the 1st edition 1999 the 2nd edition 2002 the 3rd edition the 42005 th edition 2008

Contents Focus on Part I Introduction Gene conception Chapter 1:A Brief History Part ThaptethodbdmMeldaulut Biologynes Methods CHaapftoB:Wolentlad adtininoNetholanction Part9益盘ying Gemes ad Geme Activi女 Chapter 6:The Mechanism of Transcription in bteogma Chapter 7:Qperons:Fine Control of Prokaryotic Transcription Part In泡P闲3抽969 tic Trans(电o法则】 Chapter 10DSukPrxotimnBiNerRolkunstasesalalThnir Promoters Part Vharsin guhayoeryofes Transcription Activators in Eukaryotes Cept城4i3$阳SArPEegeesin服tsp欺on Transcription。 Part pranslaforenger RNA Processing II:Capping and Polyadenylation Chaf解qFe8ahA6F9份ofBnitiation L狂恋常m Part VhertendmesA Rspiretiomnd sf hapter 2 Homologous, ecombination 药:6A0eom
Contents Part I Introduction Chapter 20: DNA Replication I: Basic Mechanism and Enzymology Chapter 21: DNA Replication II: Detailed Mechanism Chapter 22: Homologous Recombination Chapter 23: Transposition Part II Methods in Molecular Biology Chapter 6: The Mechanism of Transcription in Prokaryotes Chapter 7: Operons: Fine Control of Prokaryotic Transcription Chapter 8: Major Shifts in Prokaryotic Transcription Chapter 9: DNA-Protein Interactions in Prokaryotes Part III Transcription in Bacteria Chapter 10: Eukaryotic RNA Polymerases and Their Promoters Chapter 11: General Transcription Factors in Eukaryotes Chapter 12: Transcription Activators in Eukaryotes Chapter 13: Chromatin Structure and Its Effects on Transcription Part IV Transcription in Eukaryotes Part V Posttranscriptional Events Chapter 17: The Mechanism of Translation I: Initiation Chapter 18: The Mechanism of Translation II: Elongation and Termination Chapter 19: Ribosomes and Transfer RNA Chapter 24: Genomics and Proteomics Part VI Translation Part VII DNA Replication, Recombination, and Transposition Part VIII Genomes Chapter 1: A Brief History Chapter 2: The Molecular Nature of Genes Chapter 4: Molecular Cloning Methods Chapter 3: An Introduction to Gene Function Chapter 5: Molecular Tools for Studying Genes and Gene Activity Chapter 14: Messenger RNA Processing I: Splicing Chapter 15: Messenger RNA Processing II: Capping and Polyadenylation Chapter 16: Other RNA Processing Events Gene conception Methods Central Dogma (中心法则) -omics and bioinformatics Focus on
What is molecular biology? √Molecular biology The attempt to understand biological phenomena in molecular terms The study of gene structure and function at the molecular level the experimental strategy and the data that led to the conclusions,rather than just the conclusions themselves. Molecular biology is a melding of aspects of genetics and biochemistry
✓ Molecular biology – The attempt to understand biological phenomena in molecular terms – The study of gene structure and function at the molecular level – the experimental strategy and the data that led to the conclusions, rather than just the conclusions themselves. ✓ Molecular biology is a melding of aspects of genetics and biochemistry What is molecular biology?
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. Molecular Biology Chapter 1:A Brief History Holt Studios International (Nigel Cattlin)/Photo Researchers,Inc
Molecular Biology Chapter 1: A Brief History
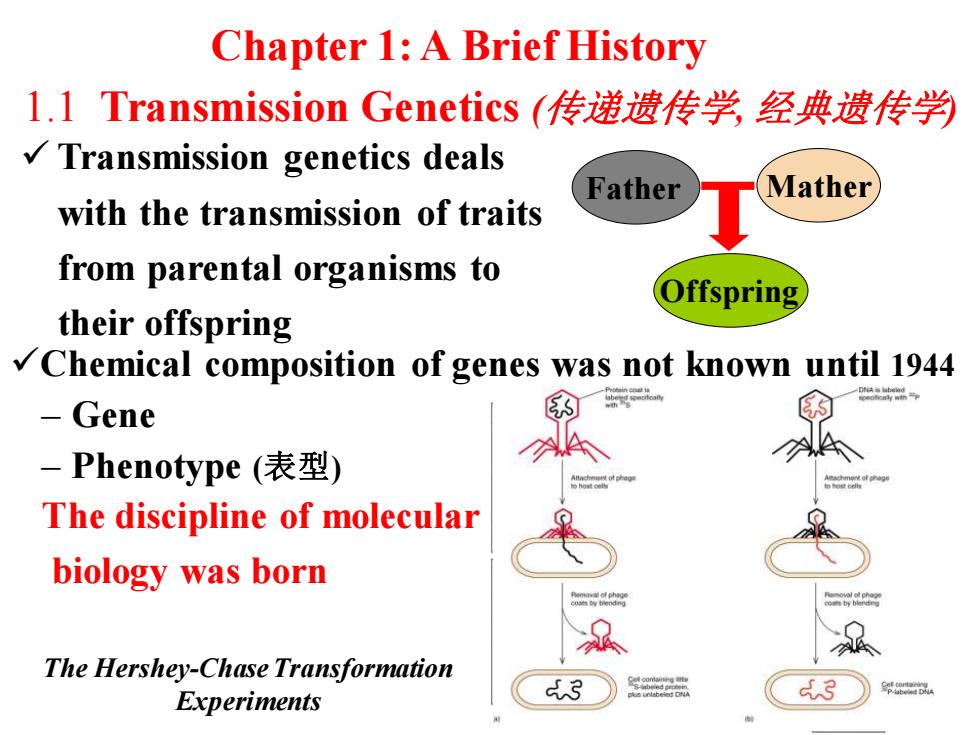
Chapter 1:A Brief History 1.1 Transmission Genetics(传递遗传学经典遗传学 Transmission genetics deals Father Mather with the transmission of traits from parental organisms to Offspring their offspring Chemical composition of genes was not known until 1944 Gene -Phenotype(表型) The discipline of molecular biology was born w g The Hershey-Chase Transformation Experiments 3 二品 3 邹a
1.1 Transmission Genetics (传递遗传学, 经典遗传学) ✓ Transmission genetics deals with the transmission of traits from parental organisms to their offspring Father Mather Offspring ✓Chemical composition of genes was not known until 1944 – Gene – Phenotype (表型) The discipline of molecular biology was born Griffith’s Transformation Experiments The Hershey-Chase Transformation Experiments Chapter 1: A Brief History
Mendel's Laws of Inheritance (孟德尔遗传定律) A gene can exist in different forms called alleles(等位基因) √One allele can be dominant(显性)over the other,recessive(隐性)allele The first filial generation (F)contains offspring of the original parents If each parent carries two copies of a gene, the parents are diploid(双倍体)for that gene
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance (孟德尔遗传定律) ✓One allele can be dominant (显性) over the other, recessive (隐性) allele ✓The first filial generation (F1 ) contains offspring of the original parents ✓If each parent carries two copies of a gene, the parents are diploid (双倍体) for that gene ✓A gene can exist in different forms called alleles (等位基因)
Mendel's Gene Transmission √Sex cells,or gametes(配子)are haploid(单倍体), containing only 1 copy of each gene. √Parents are homozygotes(纯和体),having2 copies of one allele,it produce gametes having only one allele. √Heterozygotes(杂合体)have one copy of each allele,it produce gametes having either allele,its characteristic is dictated by the dominant allele.The recessive allele is not lost;it can still exert its influence when paired with another recessive allele in a homozygote
Mendel’s Gene Transmission ✓ Sex cells, or gametes (配子) are haploid (单倍体) , containing only 1 copy of each gene. ✓ Parents are homozygotes (纯和体) , having 2 copies of one allele, it produce gametes having only one allele. ✓ Heterozygotes (杂合体) have one copy of each allele, it produce gametes having either allele, its characteristic is dictated by the dominant allele. The recessive allele is not lost; it can still exert its influence when paired with another recessive allele in a homozygote
Where is the inheritance particulate (gene/allele) 72)777722 Chromosome Gregor Mendel 1822-1884 Theory of particulate inheritance Law of segregation(分离定律) Law of independent assortment(自由组合定律)
Gregor Mendel 1822-1884 Theory of particulate inheritance Law of segregation(分离定律 ) Law of independent assortment(自由组合定律 ) Where is the inheritance particulate(gene/allele) ????????? Chromosome

1900 Mendel's Laws of Inheritance had been confirmed by Hug0 de vires1848-1935荷兰阿姆斯特丹大学 Erich von Tchermark1871-1962德国±宾根大学 Carl C0 rrens1864-1933奥地利维也纳农业大学
1900 Hugo de vires 1848-1935 荷兰 阿姆斯特丹大学 Erich von Tchermark 1871-1962 德国 土宾根大学 Carl Correns 1864-1933 奥地利 维也纳农业大学 Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance had been confirmed by
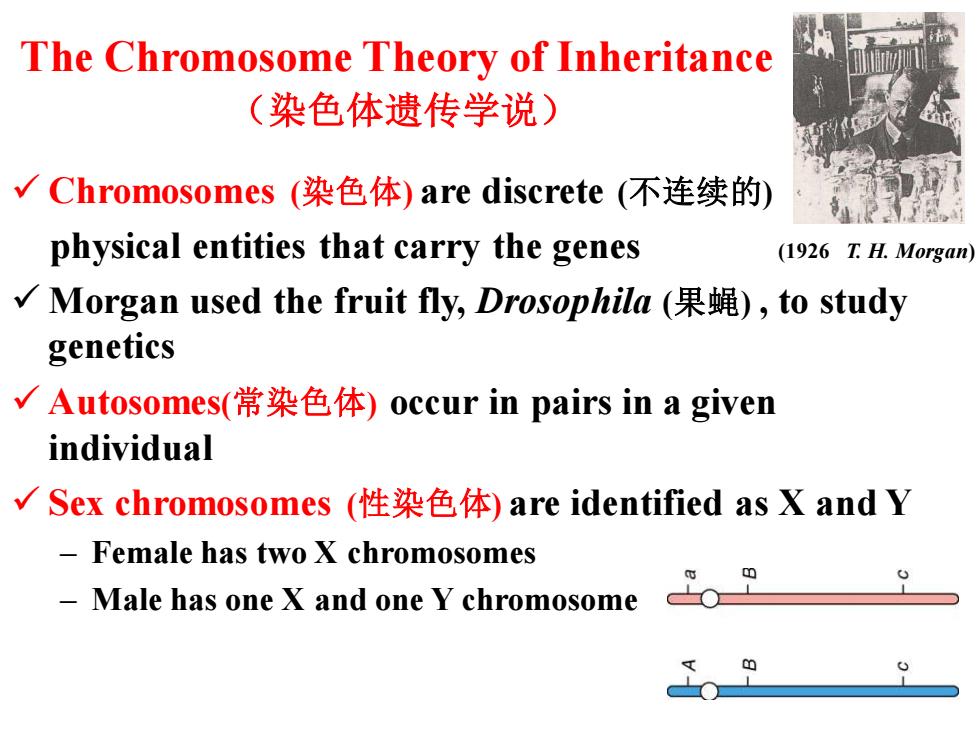
The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance (染色体遗传学说) √Chromosomes(染色体)are discrete(不连续的) physical entities that carry the genes (1926 T.H.Morgan) √Morgan used the fruit fly,Drosophila(果蝇),to study genetics √Autosomes(常染色体)occur in pairs in a given individual √Sex chromosomes(性染色体)are identified as X and Y Female has two X chromosomes Male has one X and one Y chromosome
The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance (染色体遗传学说) ✓ Chromosomes (染色体) are discrete (不连续的) physical entities that carry the genes ✓ Morgan used the fruit fly, Drosophila (果蝇) , to study genetics ✓ Autosomes(常染色体) occur in pairs in a given individual ✓ Sex chromosomes (性染色体) are identified as X and Y – Female has two X chromosomes – Male has one X and one Y chromosome (1926 T. H. Morgan)