第3章 微生物的 结构与功能
第3章 微生物的 结构与功能
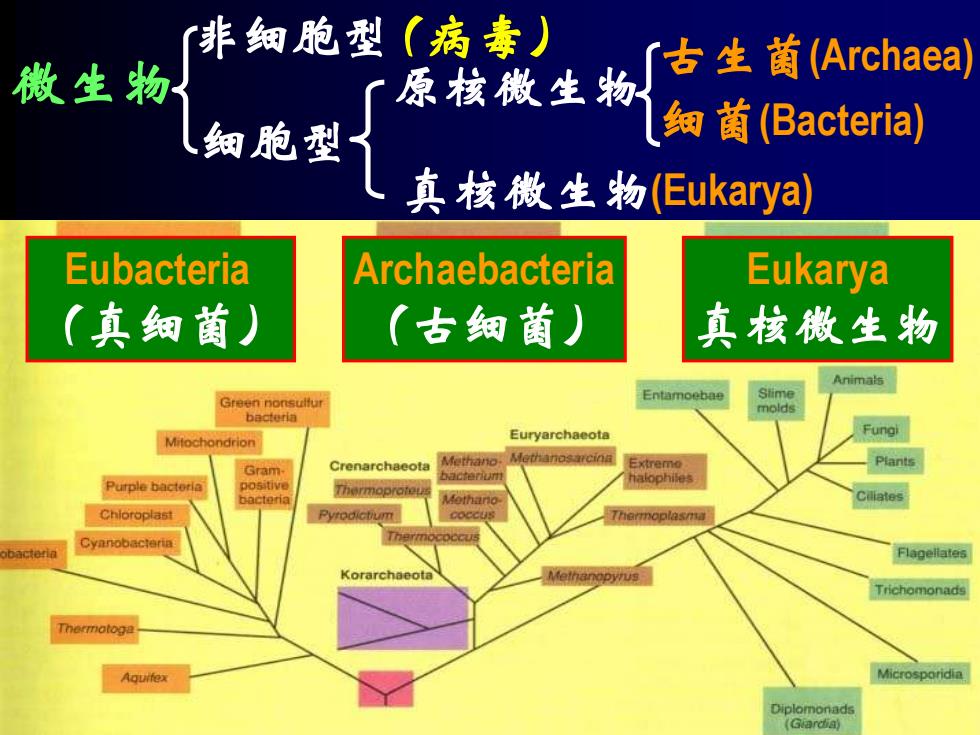
非细胞型(病毒) 微生物 古生菌(Archaea) 原核微生物 人细胞型 知菌(Bacteria) 真核微生物(Eukarya) Eubacteria Archaebacteria Eukarya (真细菌) (古细菌) 真核微生物 Animals Green nonsulfur Entamoebae Slime molds bacteria Euryarchaeota Fungi Mitochondrion Methano Gram- Crenarchaeota E右emo othano Chioroplast Flagellates Korarchaeota Trichamonads Thermotoga Diplomonads (Giardia)
微生物 (病毒) 古生菌(Archaea) 细菌(Bacteria) 真菌(酵母、霉菌、蕈菌等)、 单细胞藻类、 原生动物等 非细胞型 细胞型 原核微生物 真核微生物(Eukarya) 又称真细菌(eubacteria),包括:普通细菌、放 线菌、蓝细菌、枝原体、立克次氏体和衣原 体等 古生菌在进化谱系上与真细菌及真核生物 相互并列,且与后者关系更近,而其细胞构 造却与真细菌较为接近,同属于原核生物。 Eubacteria (真细菌) Archaebacteria (古细菌) Eukarya 真核微生物
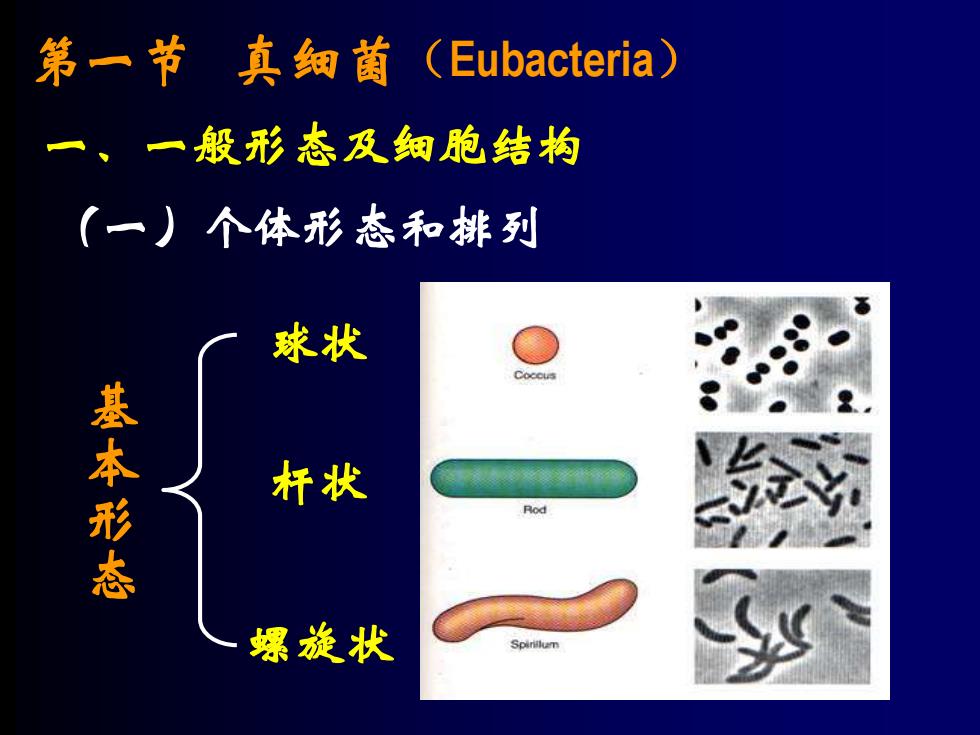
第一节真知酋(Eubacteria) 一、一般形态及细胞结构 (一)个体形态和排列 球状 基本形态 杆状 Rod 螺旋状
第一节 真细菌(Eubacteria) 一、一般形态及细胞结构 (一)个体形态和排列 球状 杆状 螺旋状 基 本 形 态
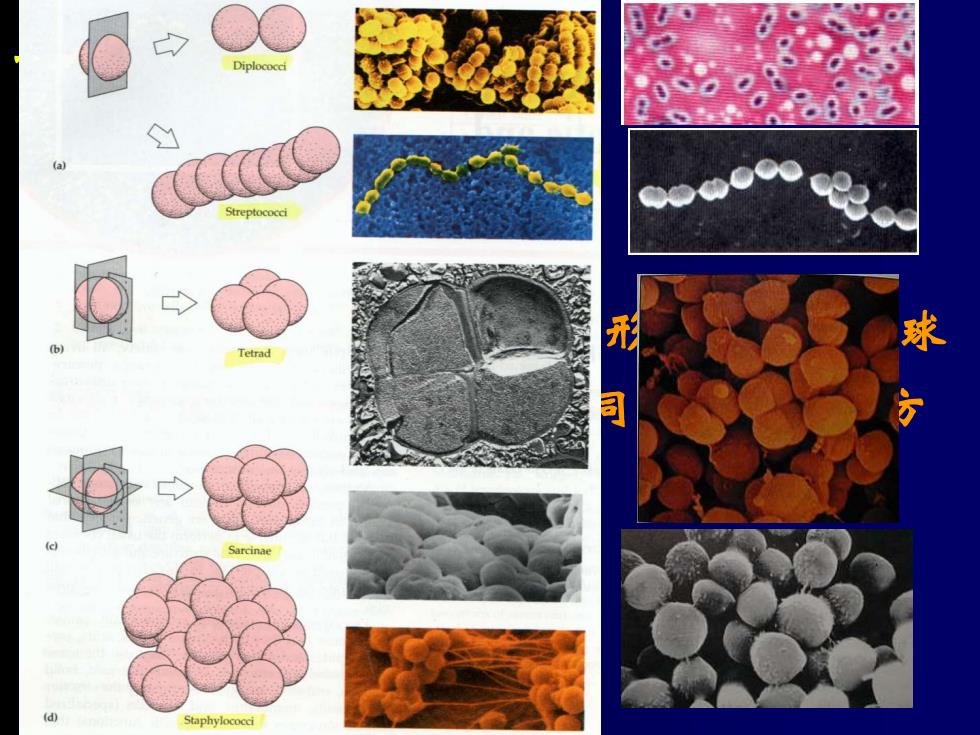
(a 形 球 Tetrad
一、一般形态及细胞结构 (一)个体形态和排列 1、球状 细胞个体呈球形或椭圆形,不同种的球 菌在细胞分裂时会形成不同的空间排列方 式,常被作为分类依据
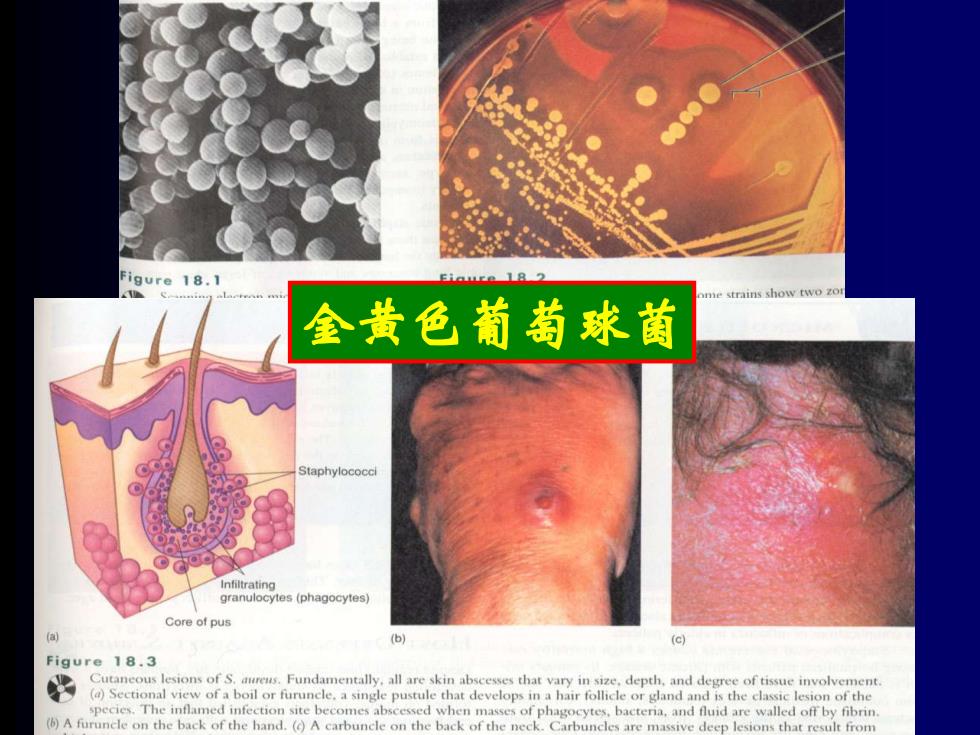
igure 18.1 18 ne strains show two zor 金黄色葡萄球菌 granulocytes(phagocytes) Core of pus 6 (c) Figure 18.3 Cutaneous lesions of S.aureus.Fundamentally.all are skin abscesses that vary in size,depth,and degree of tissue involvement. bor furuncle.a single pustule that develops in a hair follicleord species.The inflamed infection site becomes abscessed when masses of phagocytes,bacteria,and fluid are walled off by fibrin. (A furuncle on the back of the hand.(A carbuncle on the back of the neck.Carbuncles are massive deep lesions that result from
金黄色葡萄球菌
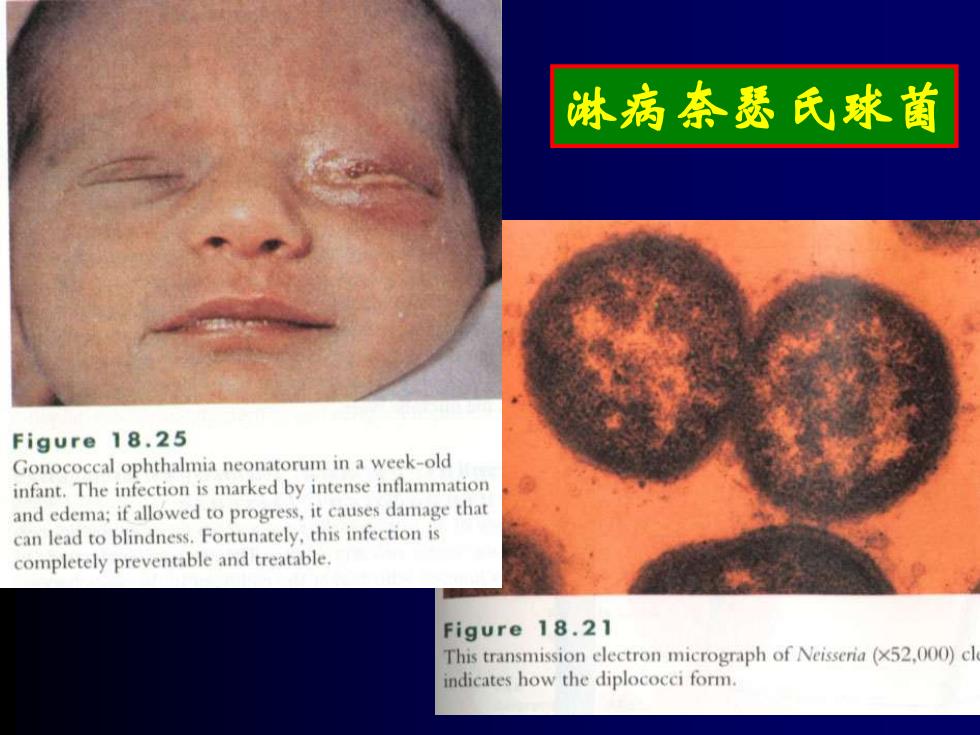
淋病奈瑟氏球菌 Figure 18.25 Gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum in a week-old infant.The infection is marked by intense inflammation and edema;if allowed to progress,it causes damage that can lead to blindness.Fortunately,this infection is completely preventable and treatable. Figure 18.21 This transmission electron micrograph of Neisseria(x52,000)cl indicates how the diplococci form
淋病奈瑟氏球菌
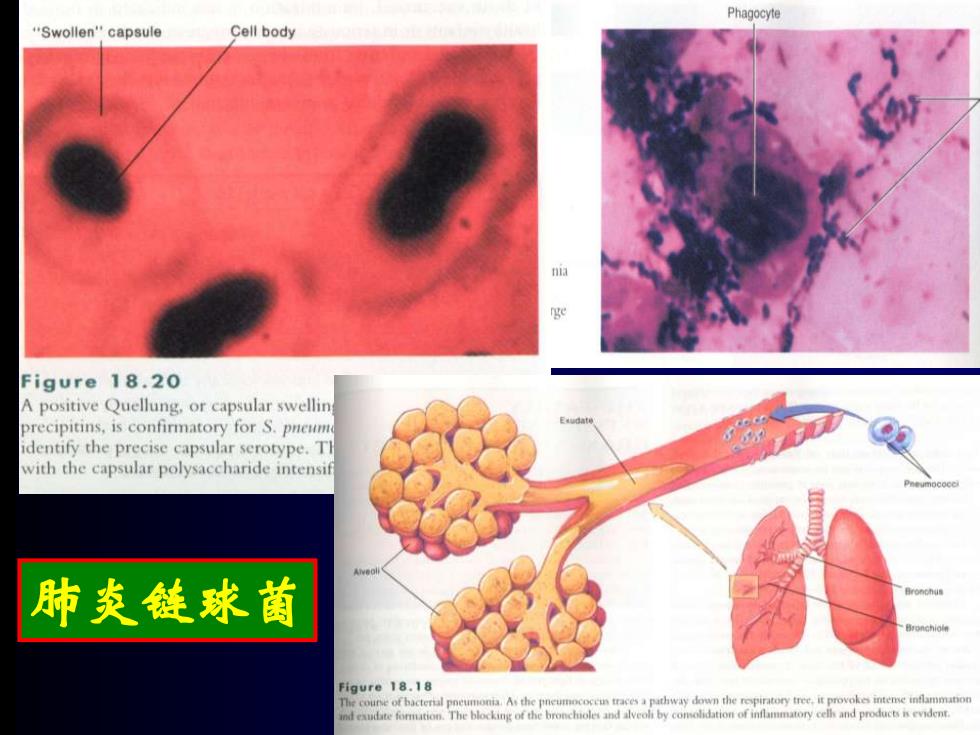
Phagocyte "Swollen"capsule Cell body a ge Figure 18.20 A positive Quellung,or capsular swellin precipitins,is confirmatory for S.pneum identify the precise capsular serotype.Tl with the capsular polysaccharide intensif 肺炎链球菌 Figure 18.18 The cou of bacteral A the pathway down the repiratory tree.it provokes inteme ind eaudte formation.The blocking of the broncholes and alveoh by comolidation of inflammatory celh and products is evident
肺炎链球菌
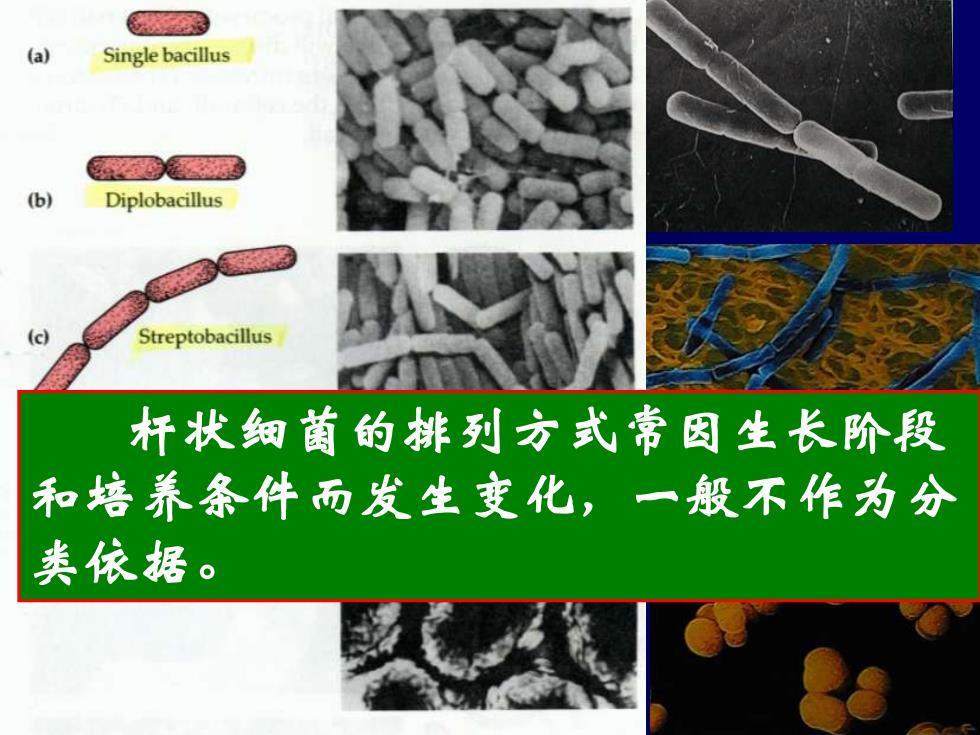
(a) Single bacillus (b) Diplobacillus (c) Streptobacillus 杆状细菌的排列方式常因生长阶段 和培养条件而发生变化,一殷不作为分 类依据
一、一般形态及细胞结构 (一)个体形态和排列 2、杆状 细胞呈杆状或圆柱形,一般其粗细(直 径)比较稳定,而长度则常因培养时间、培 养条件不同而有较大变化。 杆状细菌的排列方式常因生长阶段 和培养条件而发生变化,一般不作为分 类依据
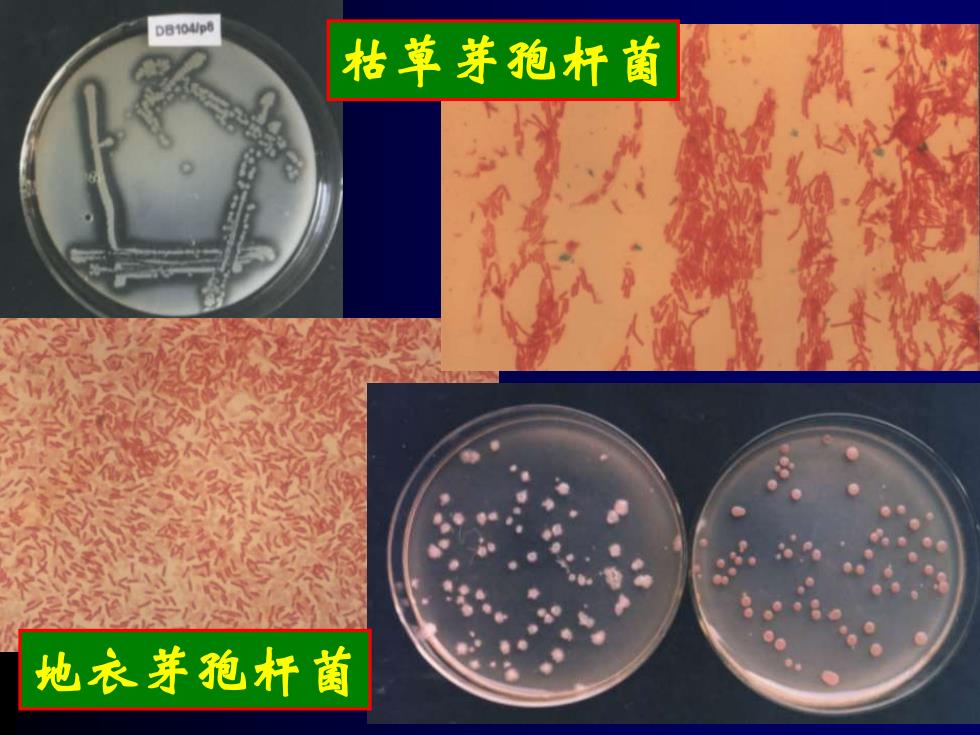
DB104/p 枯草芽孢杆菌 地衣芽孢杆菌
枯草芽孢杆菌 地衣芽孢杆菌
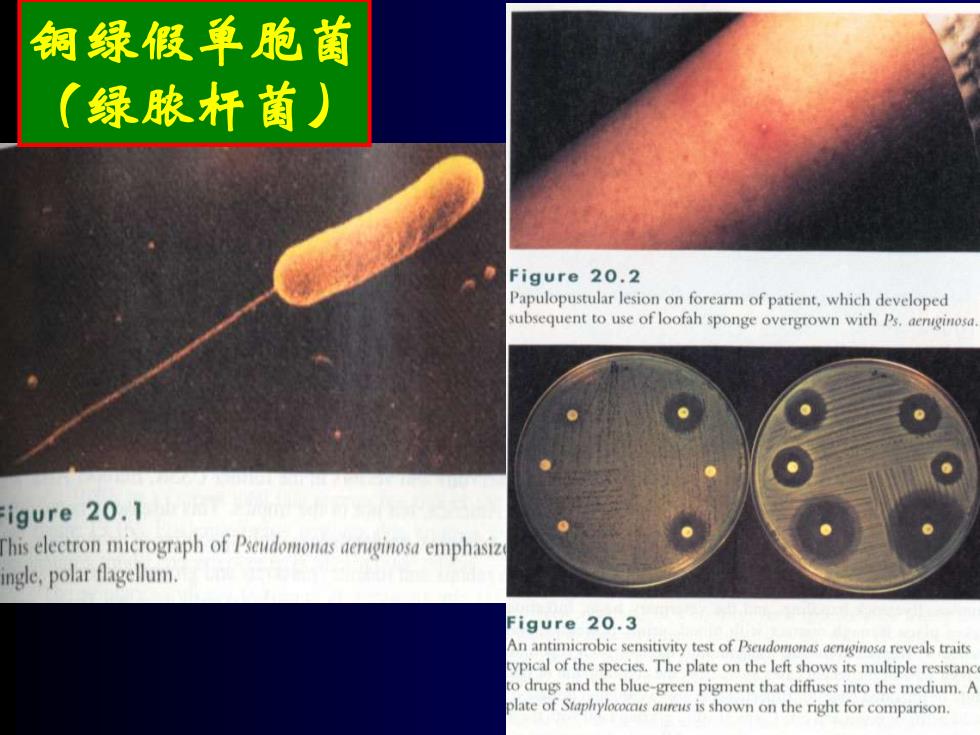
铜绿假单胞菌 (绿脓杆菌) Figure 20.2 Papulopustular lesion on forearm of patient,which developed subsequent to use of loofah sponge overgrown with Ps.aenginosa igure 20.1 This electron micrograph of Pudomonsn emphasiz ingle,polar flagellum. Figure 20.3 An antimicrobic sensitivity test of Pseudomonas aenginosa reveals traits ypical of the species.The plate on the left shows its multiple resistanc to drugs and the blue-green pigment that diffuses into the medium.A olate of Staphyloccs aureus is shown on the right for comparison
铜绿假单胞菌 (绿脓杆菌)