
NANJING UNIVERSITY Transition System Lei Bu bulei@nju.edu.cn
Lei Bu bulei@nju.edu.cn Transition System
效绵县 Definitions and notations Reactive System The intuition is that a transition system consists of a set of possible states for the system and a set of transitions or state changes which the system c can effect. When a state change is the result of an external event or of an action made by the system,then that transition is labeled with that event or action. Particular states or transitions in a transition system can be distinguished
Definitions and notations ◼ Reactive System ◼ The intuition is that a transition system consists of a set of possible states for the system and a set of transitions - or state changes - which the system can effect. ◼ When a state change is the result of an external event or of an action made by the system, then that transition is labeled with that event or action. ◼ Particular states or transitions in a transition system can be distinguished
效绵鼎 model to describe the behavior of systems digraphs where nodes represent states,and edges model transitions state: the current color of a traffic light the current values of all program variables the program counter 0 the value of register and output transition:("state change") o a switch from one color to another the execution of a program statement the change of the registers and output bits for a new input
◼ model to describe the behavior of systems ◼ digraphs where nodes represent states, and edges model transitions ◼ state: the current color of a traffic light the current values of all program variables + the program counter the value of register and output ◼ transition: (“state change”) a switch from one color to another the execution of a program statement the change of the registers and output bits for a new input
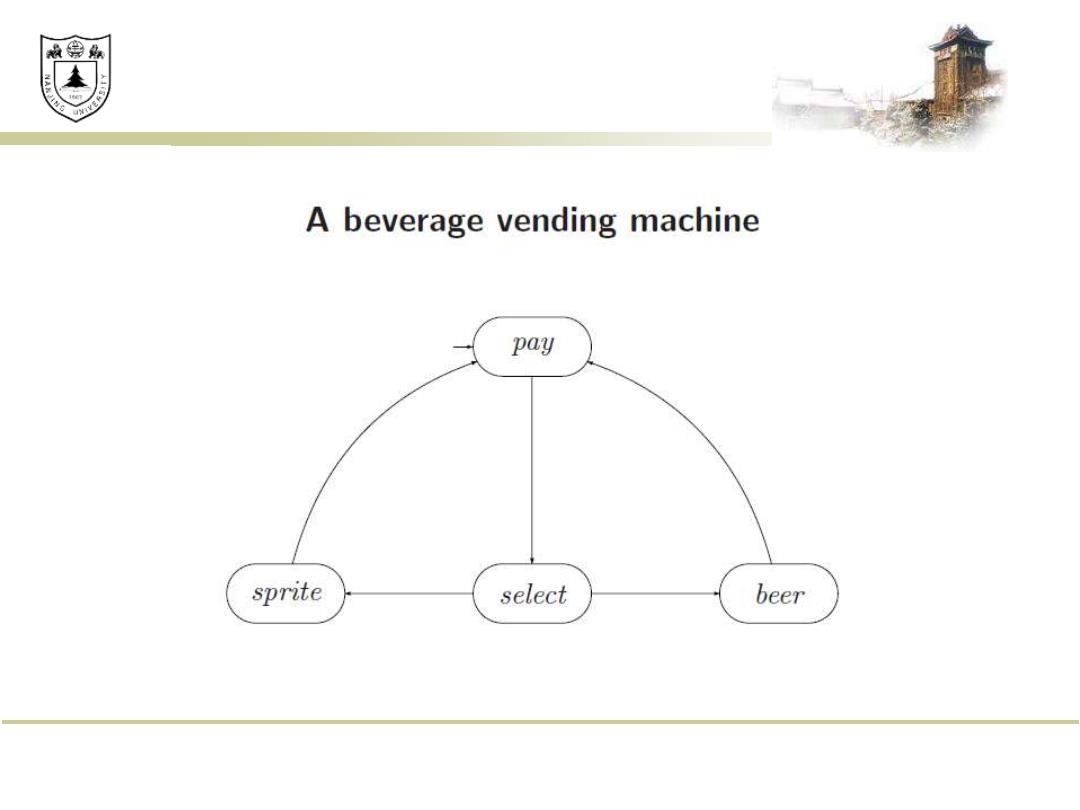
效绵鼎 A beverage vending machine pay sprite select beer
效绵鼎 Transition systems A transition systems is a tuple A= where o S is a finite or infinite set of states, So is initial location o Tis a finite or infinite set of transitions, a and B are two mapping from T to S which take each transition t in Tto the two states a(t)and B(t),respectively the source and the target of the transition t. A transition t with some source s and target s'is written t:S→S. Several transitions can have the same source and target. A transition system is finite if S and T are finite
Transition systems ◼ A transition systems is a tuple 𝒜 = where S is a finite or infinite set of states, 𝑆0 is initial location T is a finite or infinite set of transitions, 𝛼 and 𝛽 are two mapping from T to S which take each transition t in T to the two states 𝛼(𝑡) and 𝛽(𝑡), respectively the source and the target of the transition t. ◼ A transition t with some source s and target s’ is written t : s→s’. ◼ Several transitions can have the same source and target. ◼ A transition system is finite if S and T are finite
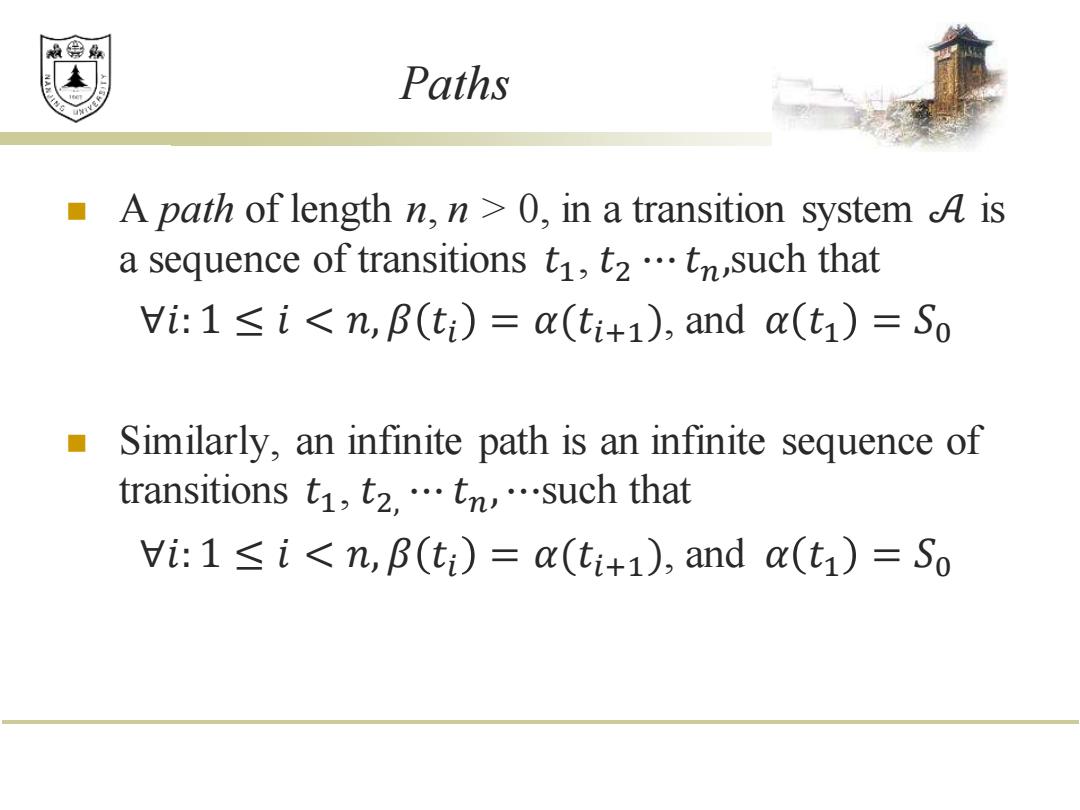
效绵鼎 Paths A path of length n,n>0,in a transition system A is a sequence of transitions ti,t2.tn,such that Vi:1<i<n,B(ti)=a(ti+1),and a(t)=So Similarly,an infinite path is an infinite sequence of transitions t,t2,…tn…such that Vi:1<i<n,B(ti)=a(ti+1),and a(t)=So
Paths ◼ A path of length n, n > 0, in a transition system 𝒜 is a sequence of transitions 𝑡1 , 𝑡2 ⋯ 𝑡𝑛,such that ∀𝑖: 1 ≤ 𝑖 < 𝑛, 𝛽 𝑡𝑖 = 𝛼(𝑡𝑖+1 ), and 𝛼 𝑡1 = 𝑆0 ◼ Similarly, an infinite path is an infinite sequence of transitions 𝑡1 , 𝑡2, ⋯ 𝑡𝑛, ⋯such that ∀𝑖: 1 ≤ 𝑖 < 𝑛, 𝛽 𝑡𝑖 = 𝛼(𝑡𝑖+1 ), and 𝛼 𝑡1 = 𝑆0
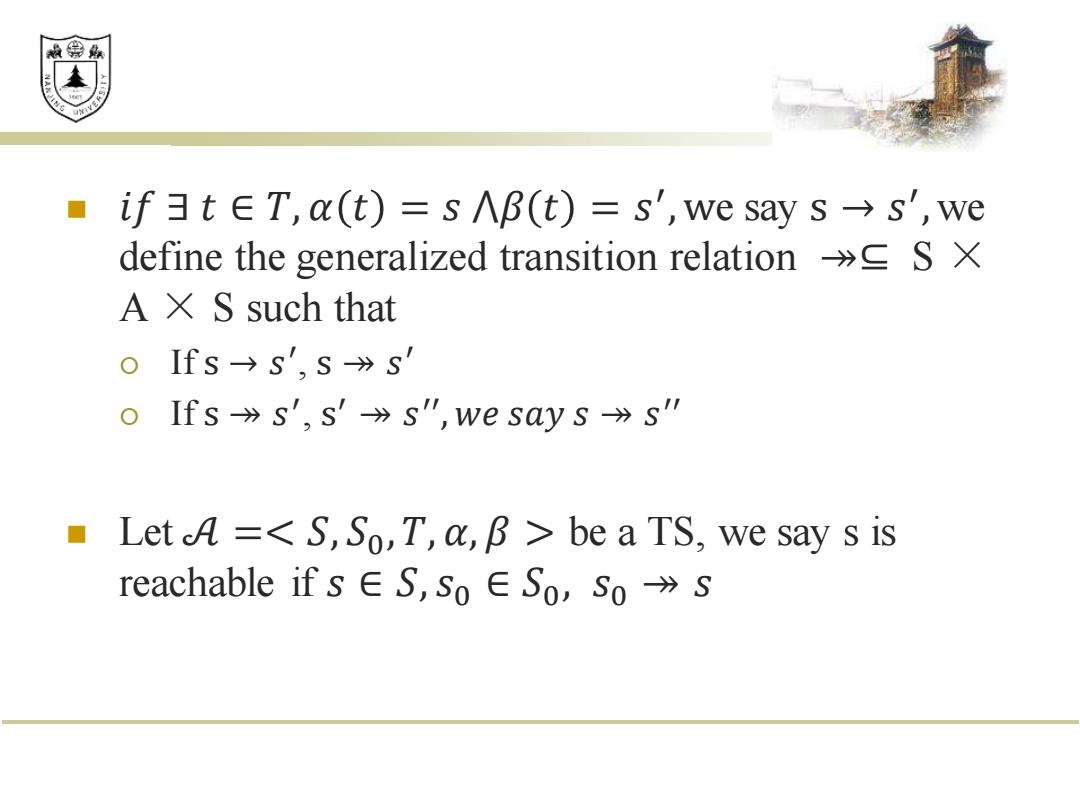
效绵鼎 if3tET,(t)=s∧B(t)=s',we say s→s',we define the generalized transition relation S X A X S such that 0IfS→s',S》s' Ifss',s'-》s",we say s》s" ■ Let A=<S,So,T,a,B be a TS,we say s is reachable if s∈S,So∈So,SoS
◼ 𝑖𝑓 ∃ 𝑡 ∈ 𝑇, 𝛼 𝑡 = 𝑠 ⋀𝛽 𝑡 = 𝑠 ′ ,we say s → 𝑠 ′ , we define the generalized transition relation ↠⊆ S × A × S such that If s → 𝑠 ′ , s ↠ 𝑠 ′ If s ↠ 𝑠 ′ , s ′ ↠ 𝑠 ′′ , 𝑤𝑒 𝑠𝑎𝑦 𝑠 ↠ 𝑠 ′′ ◼ Let 𝒜 = be a TS, we say s is reachable if 𝑠 ∈ 𝑆, 𝑠0 ∈ 𝑆0 , 𝑠0 ↠ 𝑠

效绵县 Let T be a transition system.A state s is a terminal state of T if there are no state s'such that s->s'. A state s is a deadlock state of T if s is reachable and terminal. 2 3
◼ Let T be a transition system. A state s is a terminal state of T if there are no state s’ such that s → 𝑠 ′ . ◼ A state s is a deadlock state of T if s is reachable and terminal

效绵鼎 Write T+for the set of finite paths and T for the set of infinite paths.The mappings a and B can be extended to T+by defining oa(ti...tn)=a(t),B(ti...tn)=B(tn) o A finite path c represents a finite evolution of a TS from state a(c)to B(c) Similarly,the mapping a is extended to T by defining a(t..)=a(t), 0 A infinite path c represents an infinite evolution of a TS from state a(c)
◼ Write 𝑇 + for the set of finite paths and 𝑇 𝜔 for the set of infinite paths. The mappings 𝛼 and 𝛽 can be extended to 𝑇 + by defining 𝛼 𝑡1 … 𝑡𝑛 = 𝛼 𝑡1 , 𝛽 𝑡1 … 𝑡𝑛 = 𝛽(𝑡𝑛) A finite path 𝑐 represents a finite evolution of a TS from state 𝛼 𝑐 to 𝛽 𝑐 ◼ Similarly, the mapping 𝛼 is extended to 𝑇 𝜔 by defining 𝛼 𝑡1 … = 𝛼 𝑡1 , A infinite path 𝑐 represents an infinite evolution of a TS from state 𝛼 𝑐
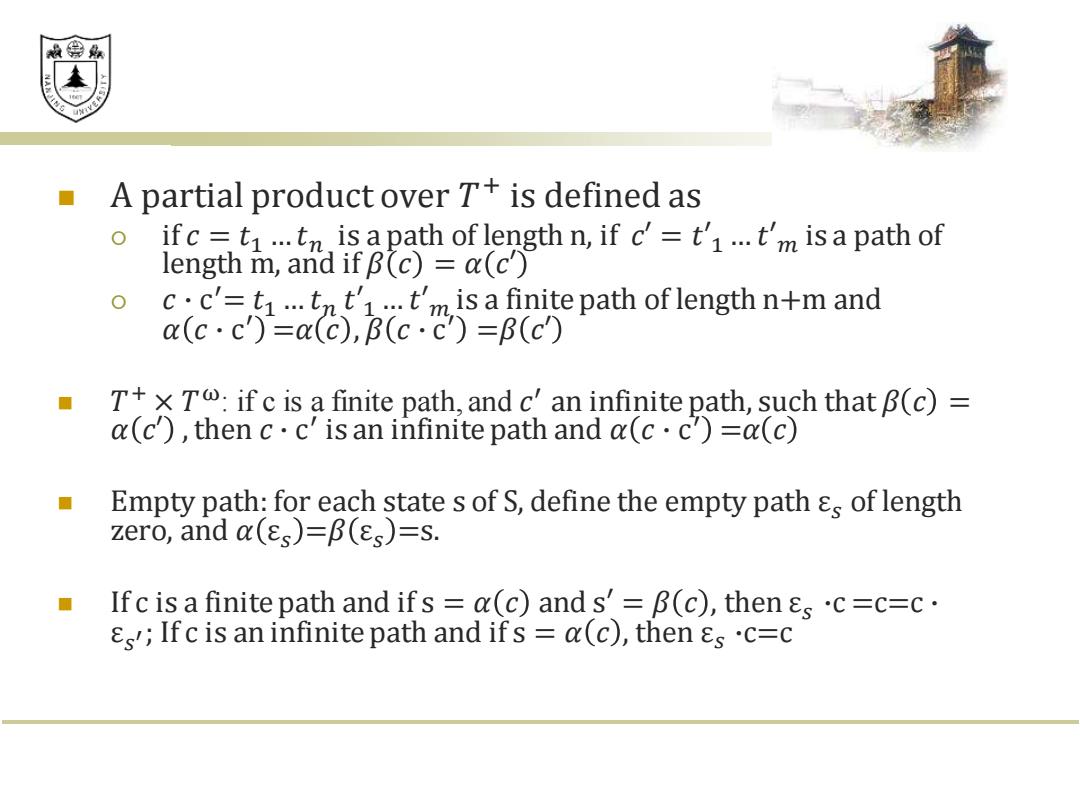
效绵鼎 ■ A partial product over T+is defined as 0 ifc=ti...tn is apath of length n,if c'=t'1...t'm is a path of length m,and if B(c)=a(c) cc'=ti...tnt't'm is a finite path of length n+m and a(c·c)=a(C),B(c·c)=B(c) T+x T:if c is a finite path,and c'an infinite path,such that B(c)= a(c),then c.c'is an infinite path and a(c.c=a(c) Empty path:for each state s of S,define the empty path &s of length zero,and a(s)=B(s)=s. Ifc is a finite path and ifs a(c)and s'=B(c),then sc=c=c. Ifc is an infinite path and ifs =a(c),then s.c=c
◼ A partial product over 𝑇 + is defined as if 𝑐 = 𝑡1 …𝑡𝑛 is a path of length n, if 𝑐′ = 𝑡′1 … 𝑡′𝑚 is a path of length m, and if 𝛽 𝑐 = 𝛼 𝑐′ 𝑐 ∙ c ′ = 𝑡1 … 𝑡𝑛 𝑡′1 … 𝑡′𝑚 is a finite path of length n+m and 𝛼 𝑐 ∙ c ′ =𝛼 𝑐 , 𝛽 𝑐 ∙ c ′ =𝛽 𝑐′ ◼ 𝑇 + × 𝑇 ω: if c is a finite path, and 𝑐 ′ an infinite path, such that 𝛽 𝑐 = 𝛼 𝑐′ ,then 𝑐 ∙ c ′ is an infinite path and 𝛼 𝑐 ∙ c ′ =𝛼 𝑐 ◼ Empty path: for each state s of S, define the empty path ε𝑠 of length zero, and 𝛼 ε𝑠 =𝛽 ε𝑠 =s. ◼ If c is a finite path and if s = 𝛼 𝑐 and s′ = 𝛽 𝑐 , then ε𝑠 ∙c =c=c ∙ ε𝑠 ′ ; If c is an infinite path and if s = 𝛼 𝑐 , then ε𝑠 ∙c=c