
NANJING UNIVERSITY Pushdown Automata Definition Moves of the PDA Languages of the PDA Deterministic PDA's .1
Definition Moves of the PDA Languages of the PDA Deterministic PDA’s Pushdown Automata 1
效绵鼎 Pushdown Automata The PDA is an automaton equivalent to the CFG in language-defining power. ■ Only the nondeterministic PDA defines all the CFL's. ■ But the deterministic version models parsers. Most programming languages have deterministic PDA's. 2
Pushdown Automata ◼ The PDA is an automaton equivalent to the CFG in language-defining power. ◼ Only the nondeterministic PDA defines all the CFL’s. ◼ But the deterministic version models parsers. Most programming languages have deterministic PDA’s. 2

效绵鼎 Intuition:PDa Think of an E-NFA with the additional power that it can manipulate a stack. Its moves are determined by: The current state(of its“NFA”), 2. The current input symbol (or E),and 3. The current symbol on top of its stack. 3
Intuition: PDA ◼ Think of an ε-NFA with the additional power that it can manipulate a stack. ◼ Its moves are determined by: 1. The current state (of its “NFA”), 2. The current input symbol (or ε), and 3. The current symbol on top of its stack. 3
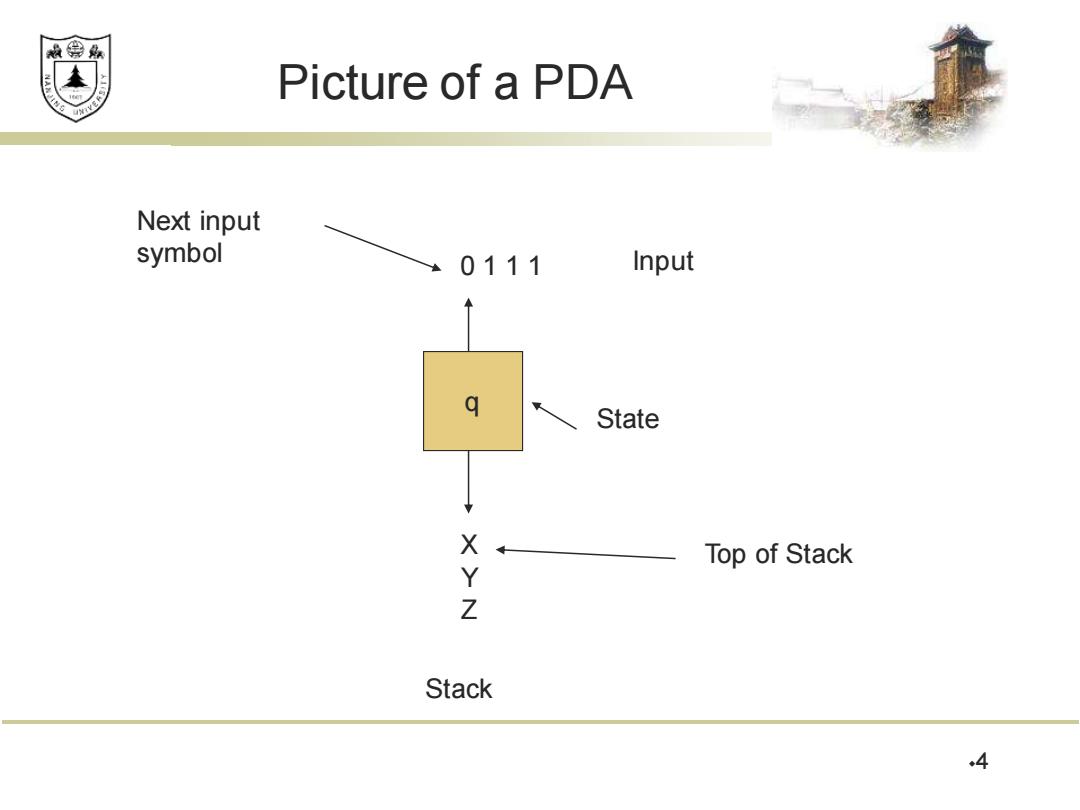
赖绵县 Picture of a PDa Next input symbol 0111 Input State X Top of Stack Y Z Stack 4
Picture of a PDA 4 q 0 1 1 1 X Y Z State Stack Top of Stack Input Next input symbol
效绵鼎 Intuition:PDA-(2) Being nondeterministic,the PDA can have a choice of next moves. In each choice,the PDA can: 1.Change state,and also 2.Replace the top symbol on the stack by a sequence of zero or more symbols. u Zero symbols=“pop.” Many symbols=sequence of“pushes.” .5
Intuition: PDA – (2) ◼ Being nondeterministic, the PDA can have a choice of next moves. ◼ In each choice, the PDA can: 1. Change state, and also 2. Replace the top symbol on the stack by a sequence of zero or more symbols. u Zero symbols = “ pop.” u Many symbols = sequence of “pushes.” 5
效绵鼎 PDA Formalism A PDA is described by: 1.A finite set of states (Q,typically). 2.An input alphabet(Σ,typically) 3. A stack alphabet(「,typically). 4. A transition function(δ,typically) 5. A start state (qo,in Q,typically) 6. A start symbol(Zo,in「,typically). 7.A set of final states (FQ,typically) 6
PDA Formalism ◼ A PDA is described by: 1. A finite set of states (Q, typically). 2. An input alphabet (Σ, typically). 3. A stack alphabet (Γ, typically). 4. A transition function (δ, typically). 5. A start state (q0 , in Q, typically). 6. A start symbol (Z0 , in Γ, typically). 7. A set of final states (F ⊆ Q, typically). 6

效绵鼎 Conventions ■ a,b,..are input symbols. 0 But sometimes we allow e as a possible value. ■.,X,Y,Z are stack symbols. ...w,X,y,z are strings of input symbols. a,B,...are strings of stack symbols. 7
Conventions ◼ a, b, … are input symbols. But sometimes we allow ε as a possible value. ◼ …, X, Y, Z are stack symbols. ◼ …, w, x, y, z are strings of input symbols. ◼ , ,… are strings of stack symbols. 7
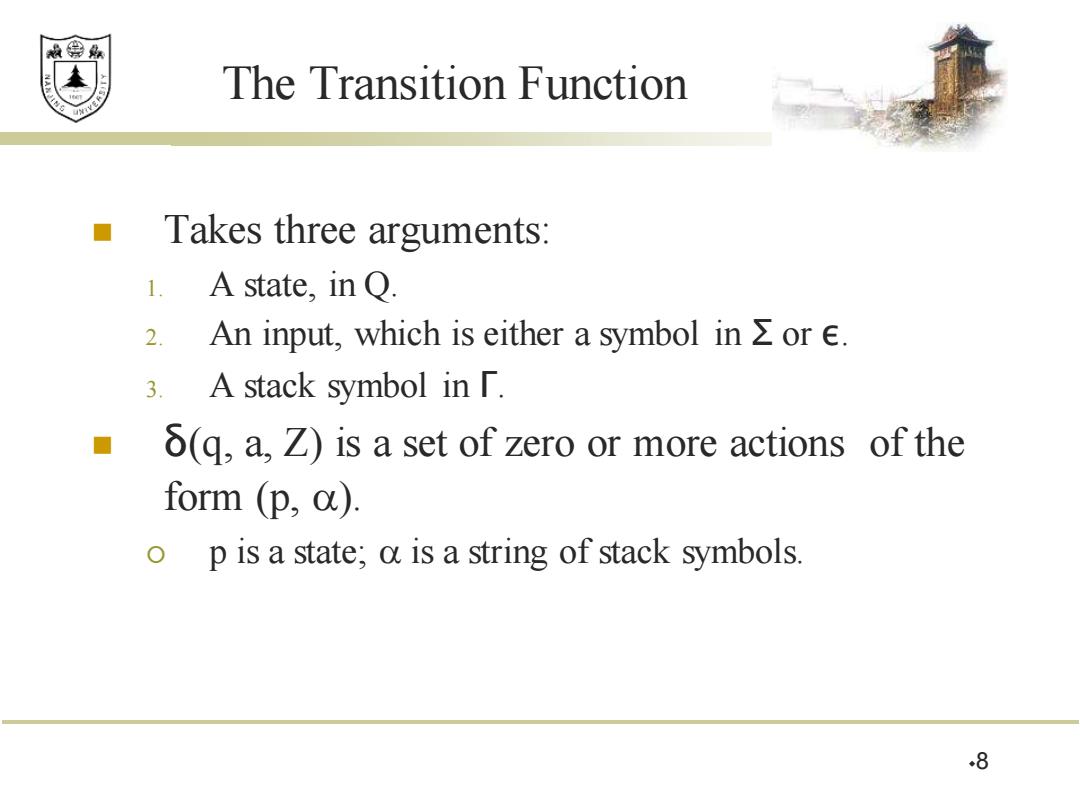
效绵鼎 The Transition Function Takes three arguments: 1.A state,in Q. 2.An input,which is either a symbol in or E. 3. A stack symbol in「. 6(q,a,Z)is a set of zero or more actions of the form (p,a). o p is a state;a is a string of stack symbols. ◆8
The Transition Function ◼ Takes three arguments: 1. A state, in Q. 2. An input, which is either a symbol in Σ or ε. 3. A stack symbol in Γ. ◼ δ(q, a, Z) is a set of zero or more actions of the form (p, ). p is a state; is a string of stack symbols. 8

效绵鼎 Actions of the pda If 8(q,a,Z)contains (p,a)among its actions,then one thing the PDA can do in state q,with a at the front of the input,and Z on top of the stack is: 1. Change the state to p. 2. Remove a from the front of the input(but a may be e) 3. Replace Z on the top of the stack by a. 9
Actions of the PDA ◼ If δ(q, a, Z) contains (p, ) among its actions, then one thing the PDA can do in state q, with a at the front of the input, and Z on top of the stack is: 1. Change the state to p. 2. Remove a from the front of the input (but a may be ε). 3. Replace Z on the top of the stack by . 9

效绵鼎 Example:PDA Design a PDA to accept {on1n |n1). The states: q=start state.We are in state q if we have seen only 0's so far. o p=we've seen at least one 1 and may now proceed only if the inputs are 1's. o f=final state;accept. .10
Example: PDA ◼ Design a PDA to accept {0n1 n | n > 1}. ◼ The states: q = start state. We are in state q if we have seen only 0’s so far. p = we’ve seen at least one 1 and may now proceed only if the inputs are 1’s. f = final state; accept. 10