
上海交通大学教授李大伟电邮daweili(@sjtu.edu.cn 电话:34204744 助教周冰洁 电话:34205436 上海交通大学通识核心课 Genes and Human 基因是生命延续的必然选择 Gene Is The Choice of Lives 5.Genes and Human Evolution 第五章:人类进化基因选择 >人类的历史是人类基因扩张的历史
2017/12/5 1 1 Genes and Human 上海交通大学通识核心课 上海交通大学教授 李大伟 电邮 daweili@sjtu.edu.cn 电话:34204744 助教 周冰洁 电话:34205436 基因是生命延续的必然选择 Gene Is The Choice of Lives 人类的历史是人类基因扩张的历史 5. Genes and Human Evolution 第五章 :人类进化-基因选择

5.Genes and Human Evolution 第五章:人类进化基因选择 1. Life forms Have Common Ancestry 不同生命形式具有同源性。 2. Human Genes:Mutation Drive Human History 人类基因:基因突变推动人类历史 3.Modern Human( (Homo Sapiens) v.s.The Last Neanderthal 现代人和最后一个尼安德特人 4. Genes and Collaboration: Power and Knowledge Beyond Death 基因与合作:超越死亡的力量扩展与知识积累 2017/12/5
2017/12/5 1 2 5. Genes and Human Evolution 第五章 :人类进化-基因选择 1. Life forms Have Common Ancestry 不同生命形式具有同源性。 2. Human Genes: Mutation Drive Human History 人类基因:基因突变推动人类历史 3. Modern Human (Homo Sapiens) v.s. The Last Neanderthal 现代人和最后一个尼安德特人 4. Genes and Collaboration: Power and Knowledge Beyond Death 基因与合作:超越死亡的力量扩展与知识积累
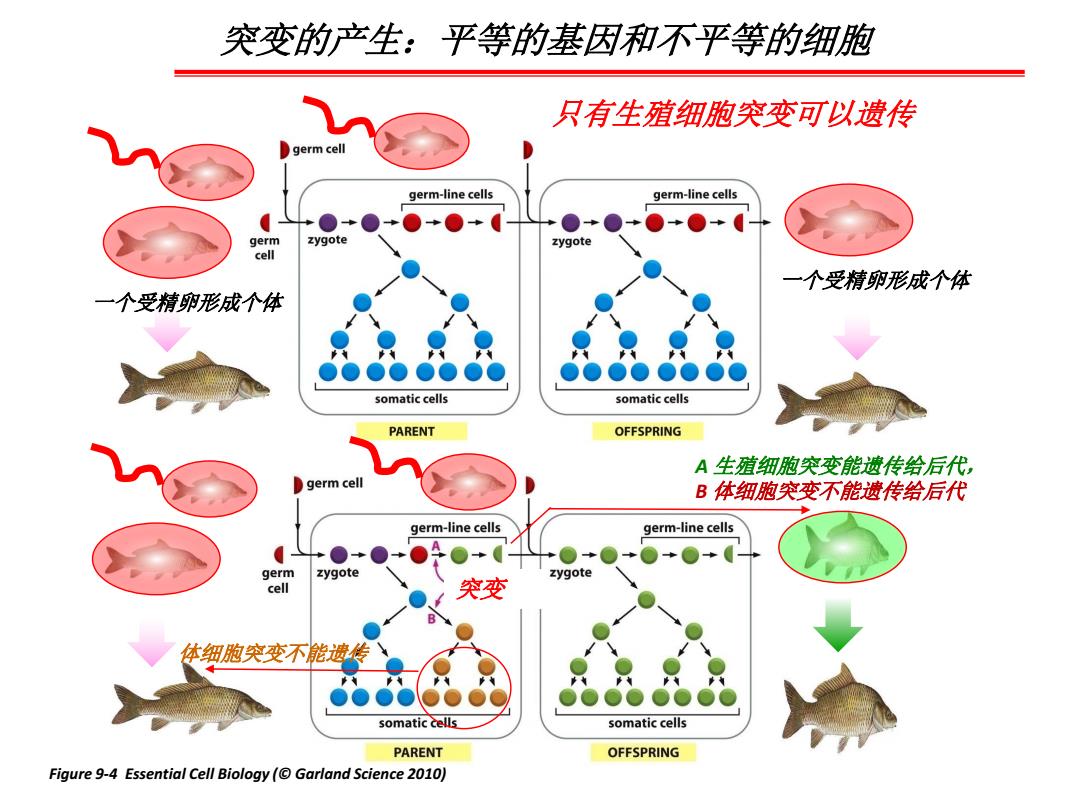
突变的产生:平等的基因和不平等的细胞 只有生殖细胞突变可以遗传 germ cell germ-line cells germ-line cells ●+ +●+ ●→ germ zygote zygote cell 一个受精卵形成个体 一个受精卵形成个体 somatic cells somatic cells PARENT OFFSPRING A生殖细胞突变能遗传给后代, germ cell B体细胞突变不能遗传给后代 germ-line cells germ-line cells ●+●+●0+ +●+0 germ zygot zygote cell ●. 突变 B 体细胞突变不能遗传 somatic cells somatic cells PARENT OFFSPRING Figure 9-4 Essential Cell Biology(Garland Science 2010)
突变的产生:平等的基因和不平等的细胞 Figure 9-4 Essential Cell Biology (© Garland Science 2010) 体细胞突变不能遗传 突变 A 生殖细胞突变能遗传给后代, B 体细胞突变不能遗传给后代 一个受精卵形成个体 一个受精卵形成个体 只有生殖细胞突变可以遗传
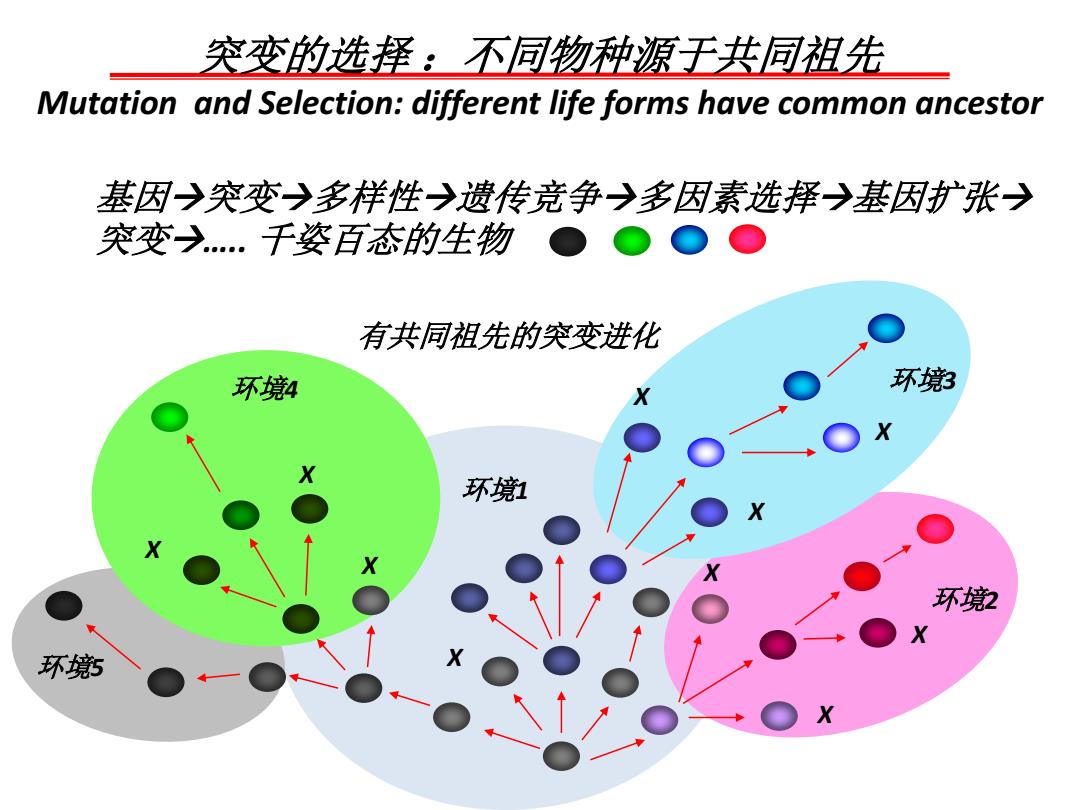
突变的选择:不同物种源于共同祖先 Mutation and Selection:different life forms have common ancestor 基因→突变→多样性→遗传竞争→多因素选择→基因书扩张→ 突变→..千姿百态的生物●○○● 有共同祖先的突变进化 环境4 环境 环 环境 环鄉
突变的选择 :不同物种源于共同祖先 Mutation and Selection: different life forms have common ancestor 基因突变多样性遗传竞争多因素选择基因扩张 突变….. 千姿百态的生物 X X X X X X X X X 有共同祖先的突变进化 X 环境1 环境2 环境 环境3 4 环境5
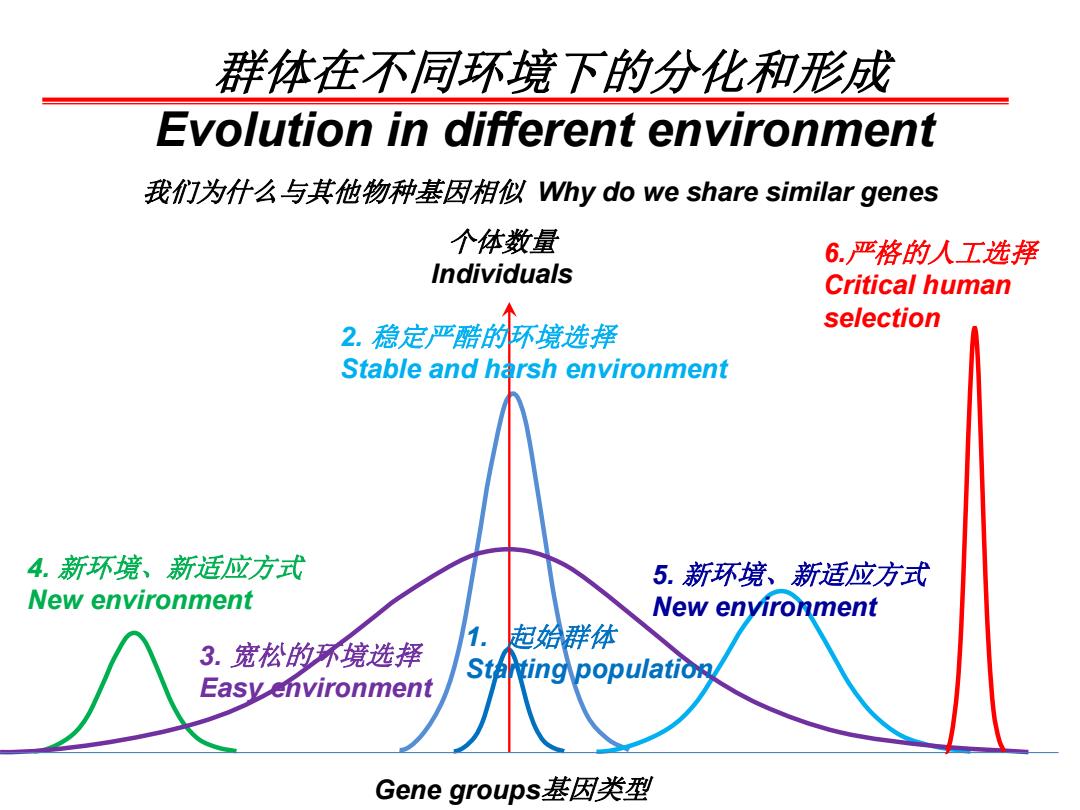
群体在不同环境下的分化和形成 Evolution in different environment 我们为什么与其他物种基因相似Why do we share similar genes 个体数量 6.严格的人工选择 Individuals Critical human 2.稳定严酷的杯境选择 selection Stable and harsh environment 4.新环境、新适应方式 5.新环境、新适应方式 New environment New enyironment 3.宽松的环镜选择 1.起始群体 StaNting population Easyenvironment Gene groups基因类型
1. 起始群体 Starting population 2. 稳定严酷的环境选择 Stable and harsh environment 3. 宽松的环境选择 Easy environment 群体在不同环境下的分化和形成 Evolution in different environment 4. 新环境、新适应方式 New environment 5. 新环境、新适应方式 New environment 个体数量 Individuals Gene groups基因类型 6.严格的人工选择 Critical human selection 我们为什么与其他物种基因相似 Why do we share similar genes
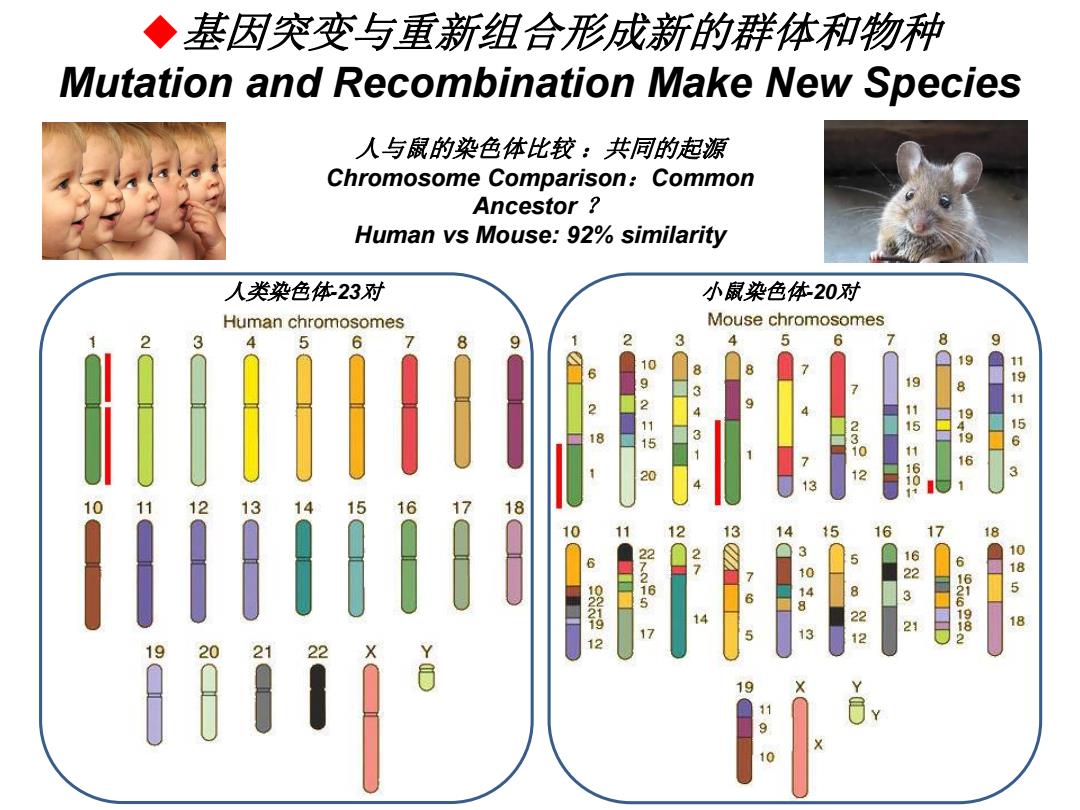
◆基因突变与重新组合形成新的群体和物种 Mutation and Recombination Make New Species 人与鼠的染色体比较:共同的起源 Chromosome Comparison:Common Ancestor Human vs Mouse:92%similarity 人类染色体23对 小鼠染色体20对 Human chromosomes Mouse chromosomes 6 8 9 2 3 5 7 8 9 19 RMMRl 10 921 3 8 18 15 43. 230 9151601 194196 19115 1 20 12 3 1 0 71 12 13 14 1516 18 llil 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 3 6 72165 1048 8 1623 6626982 10185 02892 3 21 18 17 5 12 19 19 11 9 10
2017/12/5 1 6 人类染色体-23对 小鼠染色体-20对 人与鼠的染色体比较 :共同的起源 Chromosome Comparison:Common Ancestor ? Human vs Mouse: 92% similarity 基因突变与重新组合形成新的群体和物种 Mutation and Recombination Make New Species

◆生命共源:人与其它生物之间的基因相似度 How Similar Are We:Shared Genes Fruit Fly 44% Mouse 23andMe 92% Yeast 26% Chimp 98% Plant 18% What percent of your genes do you share? www.23andme.com
2017/12/5 1 7 生命共源:人与其它生物之间的基因相似度 How Similar Are We: Shared Genes
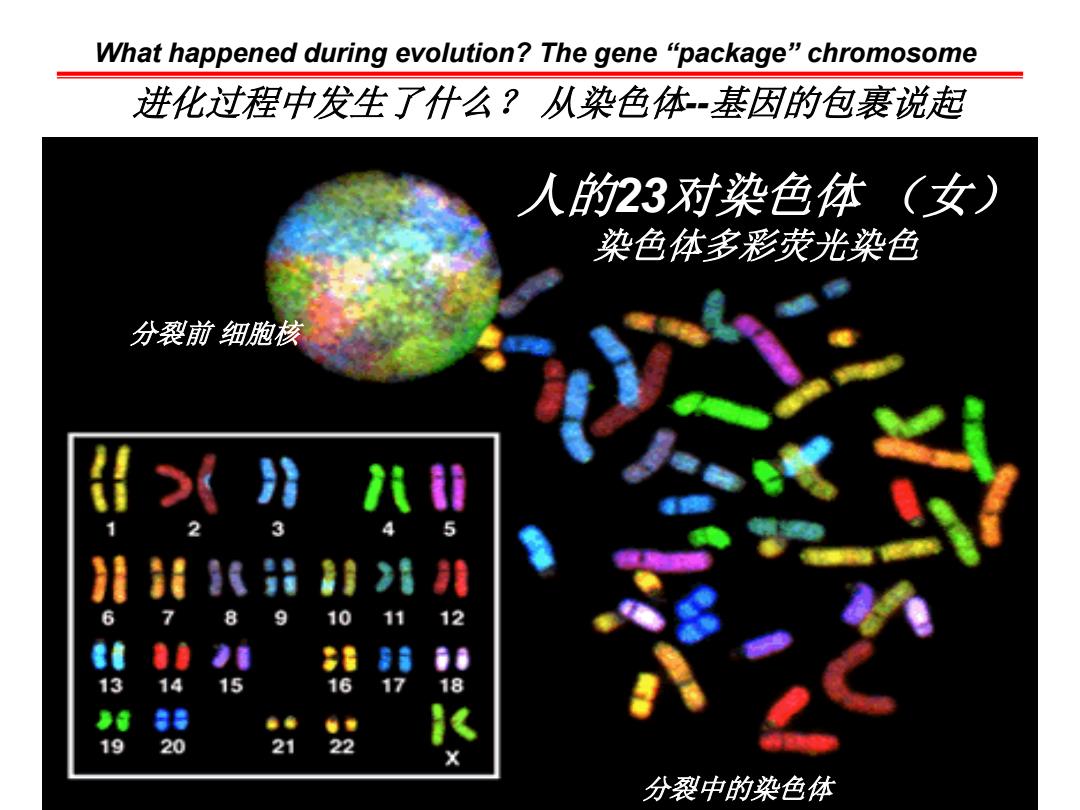
What happened during evolution?The gene“package”chromosome 进化过程中发生了什么?从染色体-基因的包裹说起 人的23对染色体(女) 染色体多彩荧光染色 分裂前细胞核 >射八t 1 2 3 5 引i8出9朝沿非 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 8 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 X 分裂中的染色体
人的23对染色体 (女) 染色体多彩荧光染色 分裂前 细胞核 分裂中的染色体 What happened during evolution? The gene “package” chromosome 进化过程中发生了什么? 从染色体--基因的包裹说起
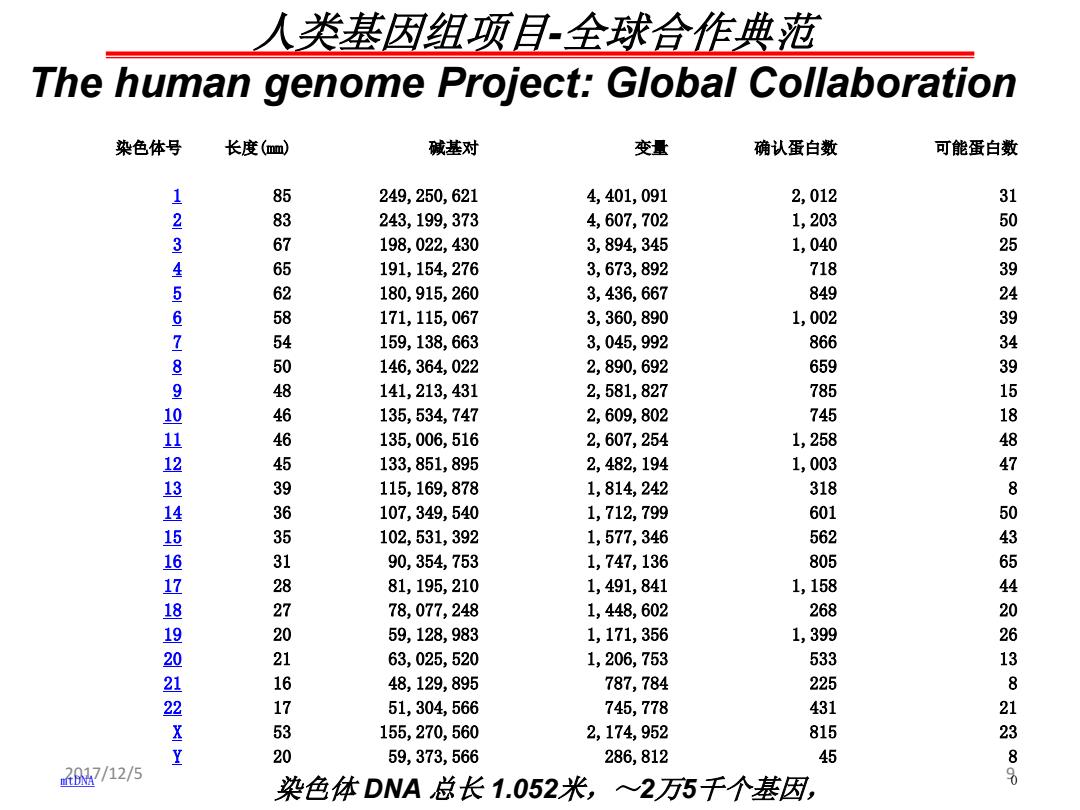
人类基因组顶目全球合作典范 The human genome Project:Global Collaboration 染色体号 长度(mm) 碱基对 变量 确认蛋白数 可能蛋白数 1 85 249,250,621 4,401,091 2,012 3 23 243,199,373 4,607,702 1,203 50 67 198,022,430 3,894,345 1,040 4 65 191,154,276 3,673,892 718 39 5 62 180,915,260 3,436,667 849 24 6 58 171,115,067 3,360,890 1,002 3 7 54 159,138,663 3,045,992 866 34 50 146,364,022 2,890,692 659 48 141,213,431 2,581,827 785 15 46 135,534,747 2,609,802 745 18 890123456789012X7 46 135,006,516 2,607,254 1,258 48 45 133,851,895 2,482,194 1,003 47 39 115,169,878 1,814,242 318 8 3635 107,349,540 1,712,799 601 50 102,531,392 1,577,346 562 1 90,354,753 1,747,136 805 65 81,195,210 1,491,841 1,158 44 2 78,077,248 1,448,602 268 20 59,128,983 1,171,356 1,399 2 21 63,025,520 1,206,753 533 13 48,129,895 787,784 225 8 1 51,304,566 745,778 431 21 155,270,560 2,174,952 815 23 20 59,373,566 286,812 45 7/12/5 88 染色体DNA总长1.052米,~2万5千个基因
2017/12/5 1 9 染色体号 长度(mm) 碱基对 变量 确认蛋白数 可能蛋白数 1 85 249,250,621 4,401,091 2,012 31 2 83 243,199,373 4,607,702 1,203 50 3 67 198,022,430 3,894,345 1,040 25 4 65 191,154,276 3,673,892 718 39 5 62 180,915,260 3,436,667 849 24 6 58 171,115,067 3,360,890 1,002 39 7 54 159,138,663 3,045,992 866 34 8 50 146,364,022 2,890,692 659 39 9 48 141,213,431 2,581,827 785 15 10 46 135,534,747 2,609,802 745 18 11 46 135,006,516 2,607,254 1,258 48 12 45 133,851,895 2,482,194 1,003 47 13 39 115,169,878 1,814,242 318 8 14 36 107,349,540 1,712,799 601 50 15 35 102,531,392 1,577,346 562 43 16 31 90,354,753 1,747,136 805 65 17 28 81,195,210 1,491,841 1,158 44 18 27 78,077,248 1,448,602 268 20 19 20 59,128,983 1,171,356 1,399 26 20 21 63,025,520 1,206,753 533 13 21 16 48,129,895 787,784 225 8 22 17 51,304,566 745,778 431 21 X 53 155,270,560 2,174,952 815 23 Y 20 59,373,566 286,812 45 8 mtDNA 0.0054染色体 16,569 929 13 0 DNA 总长 1.052米,~2万5千个基因, 人类基因组项目-全球合作典范 The human genome Project: Global Collaboration
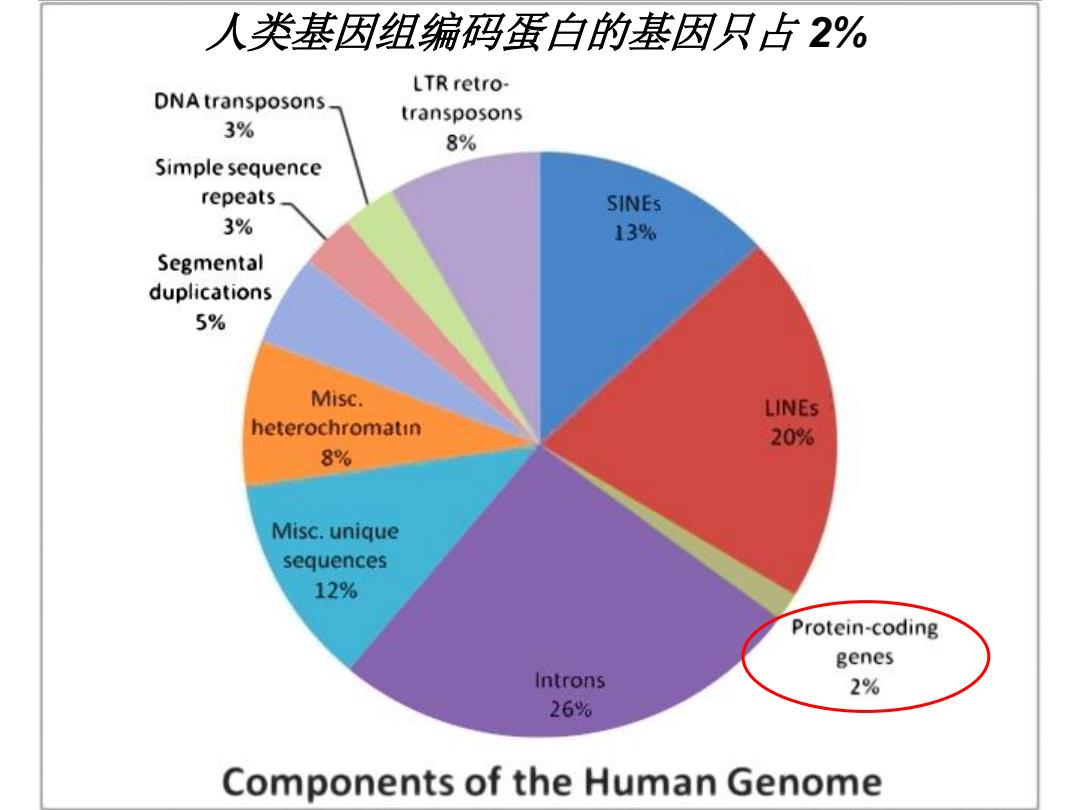
人类基因组编码蛋白的基因只占2% LTR retro- DNA transposons transposons 3% 8% Simple sequence repeats SINEs 3% 13% Segmental duplications 5% Misc. LINEs heterochromatin 20% 8% Misc.unique sequences 12% Protein-coding genes Introns 2% 26% Components of the Human Genome
人类基因组编码蛋白的基因只占 2%