
MINERALS Ashing A. Dry Ashing 1. 550oC until light-gray ash or to constant wt. 2. Cool in dessicator 3. Weigh soon after reaching room temperature
MINERALS Ashing A. Dry Ashing 1. 550oC until light-gray ash or to constant wt. 2. Cool in dessicator 3. Weigh soon after reaching room temperature

Advantages: 1. Safe 2. Multiple samples 3. Only oven and dishes needed Disadvantages: Contamination
Advantages: 1. Safe 2. Multiple samples 3. Only oven and dishes needed Disadvantages: Contamination

B. Wet Ashing Oxidation of organic compounds Time: Completely oxidized Advantages: Complete digestion Disadvantages: 1. Explosion or corrosion 2. Requires time
B. Wet Ashing Oxidation of organic compounds Time: Completely oxidized Advantages: Complete digestion Disadvantages: 1. Explosion or corrosion 2. Requires time

Step 1: Ashing Step 2: Solublize ash in Conc. HCl - boil and evaporate solution to dryness. Step 3: Re-dissolve residue in 0.5 N HCl. Step 4: Conc. or dilute as desired Step 5: Determination of individual components. Elemental Analysis
Step 1: Ashing Step 2: Solublize ash in Conc. HCl - boil and evaporate solution to dryness. Step 3: Re-dissolve residue in 0.5 N HCl. Step 4: Conc. or dilute as desired Step 5: Determination of individual components. Elemental Analysis

1. Spectrometric Methods 2. Emission Spectroscopy - Flame Photometry Method 3. Atomic Absorption Spectrometry METHODS FOR DETERMINING MINERAL CONSTITUENTS
1. Spectrometric Methods 2. Emission Spectroscopy - Flame Photometry Method 3. Atomic Absorption Spectrometry METHODS FOR DETERMINING MINERAL CONSTITUENTS

Formation of colored complex with some ligand. Example: Fe++ (Ferrous Ion) with phenanthroline (orthophenanthrolines). 1. Spectrophotometric Method N N Fe++ .
Formation of colored complex with some ligand. Example: Fe++ (Ferrous Ion) with phenanthroline (orthophenanthrolines). 1. Spectrophotometric Method N N Fe++ .

A pair of unshared electrons can coordinate certain metallic ions to give complexes. In the case of ferrous ion, the orthophenanthroline complex is quite stable and is intensely red in color. The complex is sometimes called Ferroin
A pair of unshared electrons can coordinate certain metallic ions to give complexes. In the case of ferrous ion, the orthophenanthroline complex is quite stable and is intensely red in color. The complex is sometimes called Ferroin
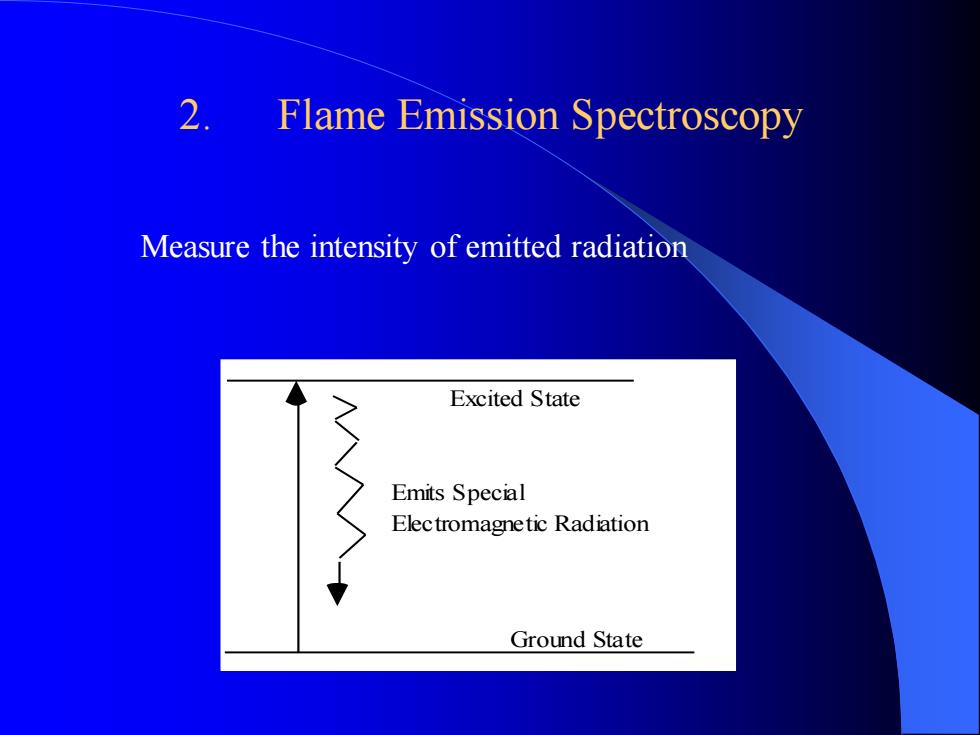
Measure the intensity of emitted radiation 2. Flame Emission Spectroscopy Ground State Excited State Emits Special Electromagnetic Radiation
Measure the intensity of emitted radiation 2. Flame Emission Spectroscopy Ground State Excited State Emits Special Electromagnetic Radiation
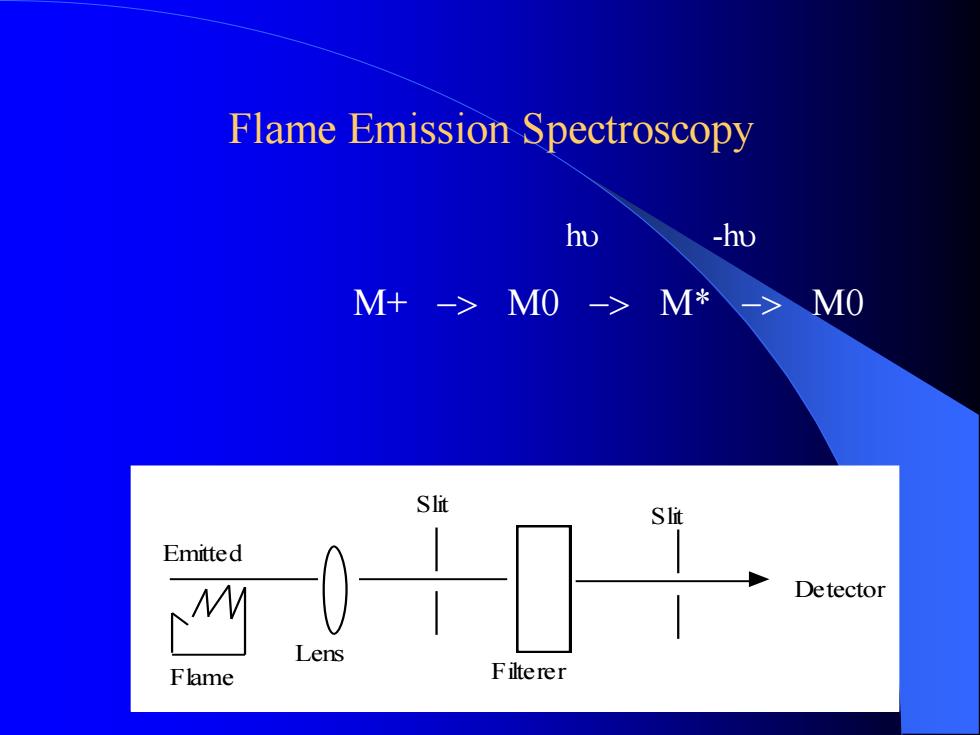
Flame Emission Spectroscopy Flame Lens Slit Filterer Slit Detector Emitted hu -hu M+ -> M0 -> M* -> M0
Flame Emission Spectroscopy Flame Lens Slit Filterer Slit Detector Emitted hu -hu M+ -> M0 -> M* -> M0
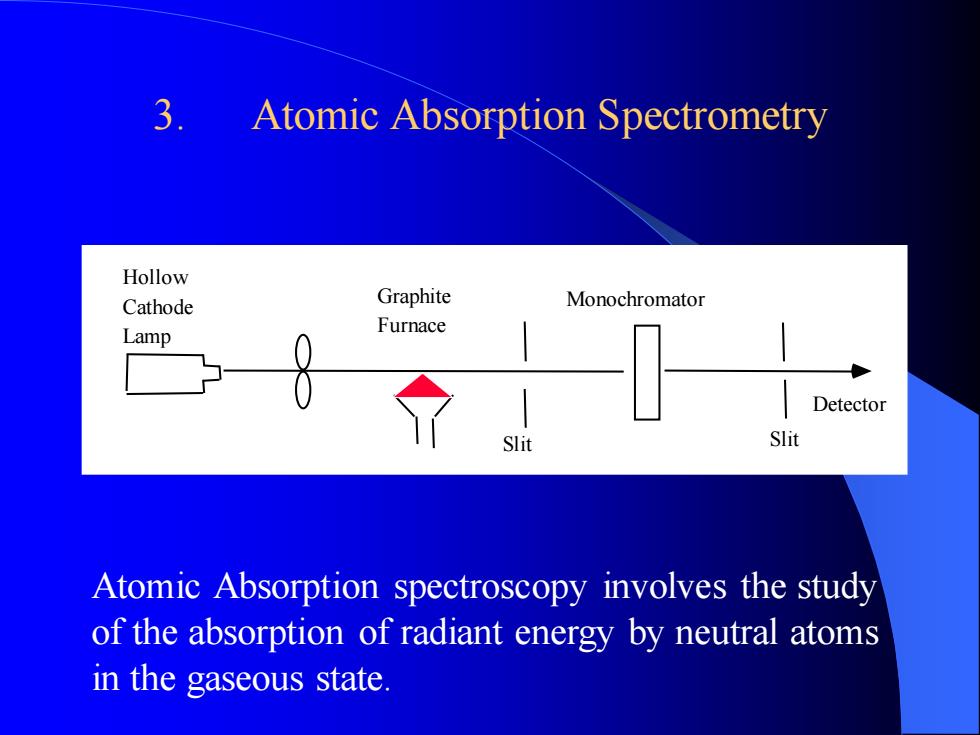
3. Atomic Absorption Spectrometry Hollow Cathode Lamp Graphite Furnace Slit Monochromator Slit Detector Atomic Absorption spectroscopy involves the study of the absorption of radiant energy by neutral atoms in the gaseous state
3. Atomic Absorption Spectrometry Hollow Cathode Lamp Graphite Furnace Slit Monochromator Slit Detector Atomic Absorption spectroscopy involves the study of the absorption of radiant energy by neutral atoms in the gaseous state