
Objective Evaluation of Food
Objective Evaluation of Food

Categories of Objective Methods 1. Chemical Methods 2. Physicochemical Methods 3. Microscopic Examination 4. Physical Properties
Categories of Objective Methods 1. Chemical Methods 2. Physicochemical Methods 3. Microscopic Examination 4. Physical Properties

Texture 5792 0 2要款 ① ., 0,年年e FIGURE 3.9 Cutting box used to obtain slices of uniform thicknesses

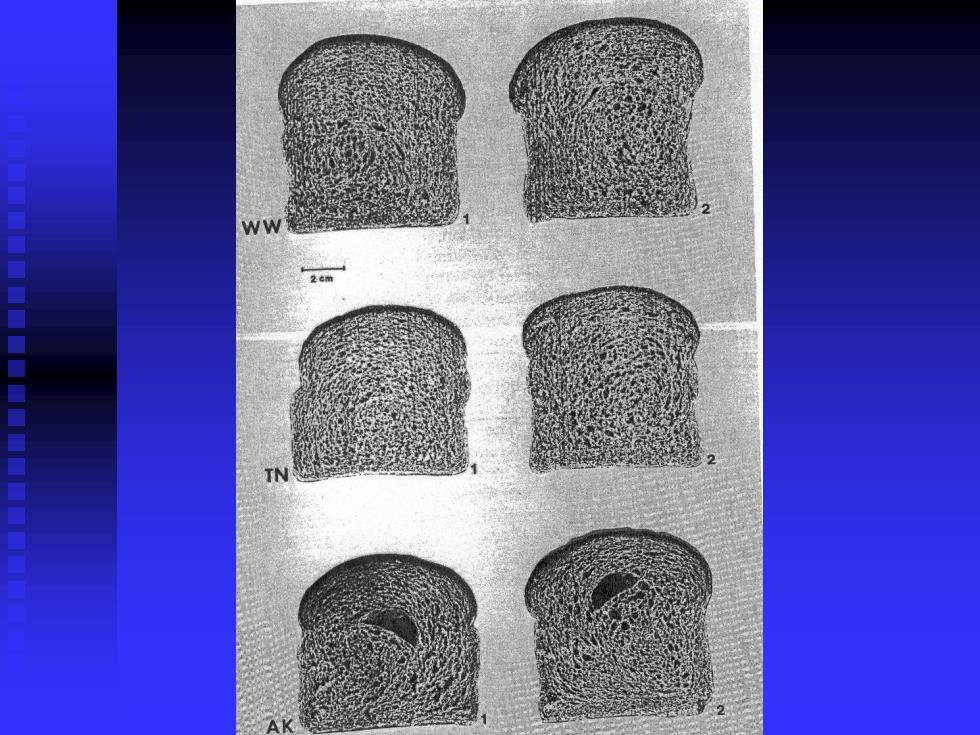
Appearance 1. Photo 2. Photocopying
Appearance 1. Photo 2. Photocopying

Color Hue: Predominant Wavelength Value: Lightness Chroma: Purity( Saturation)
Color Hue: Predominant Wavelength Value: Lightness Chroma: Purity( Saturation)
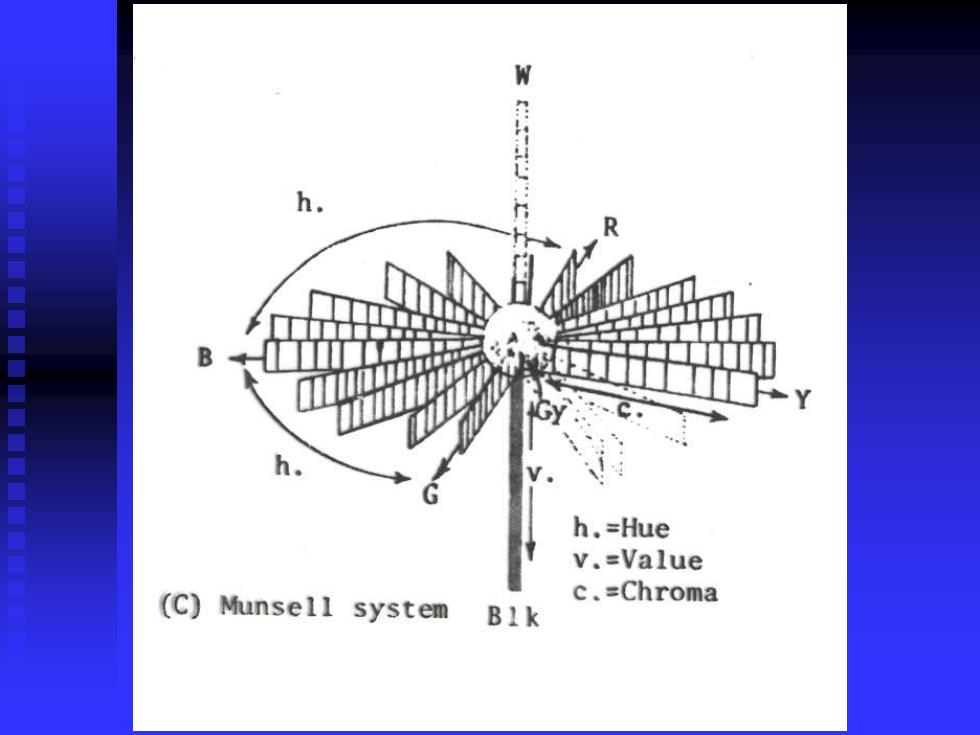
W h. R h.=Hue v.=Value (C)Munsell system c.=Chroma B1k
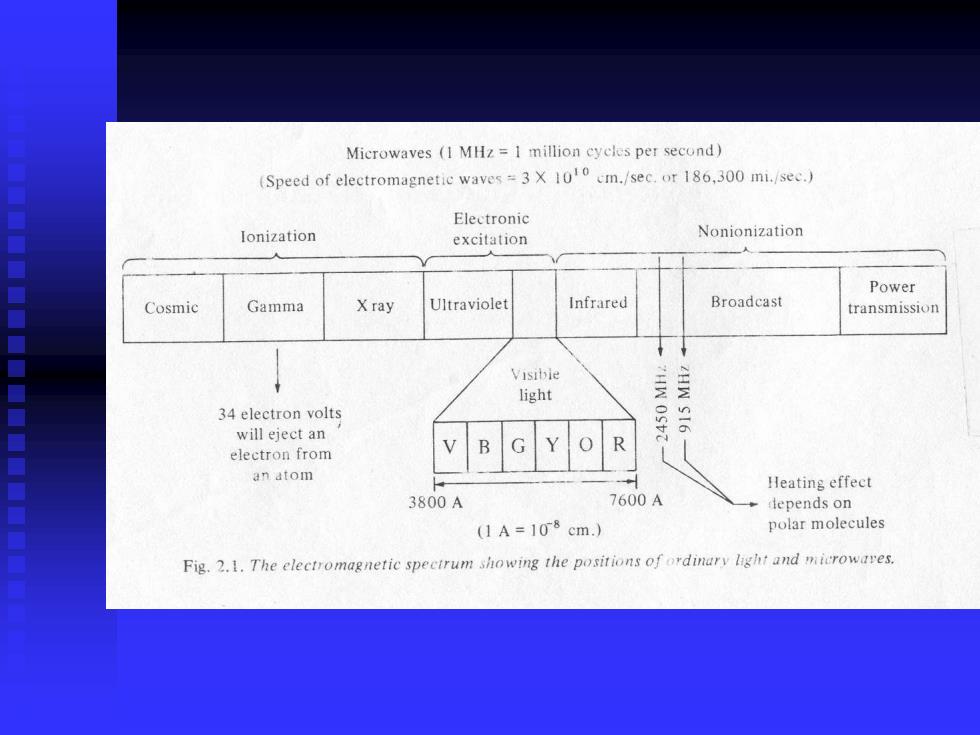
Microwaves (I MHz=I million cycles per second) (Speed of electromagnetic waves=3X 100 cm./sec.or 186,300 mi./see.) Electronic lonization excitation Nonionization Power Cosmic Gamma X ray Ultraviolet Infrared Broadcast transmission Visibie light 34 electron volts will eject an 0530 electron from B an atom Heating effect 3800A 7600A lepends on (1A=108cm.) polar molecules Fig.2.1.The electromagnetic specirum showing the positions of ordinary light and microwares
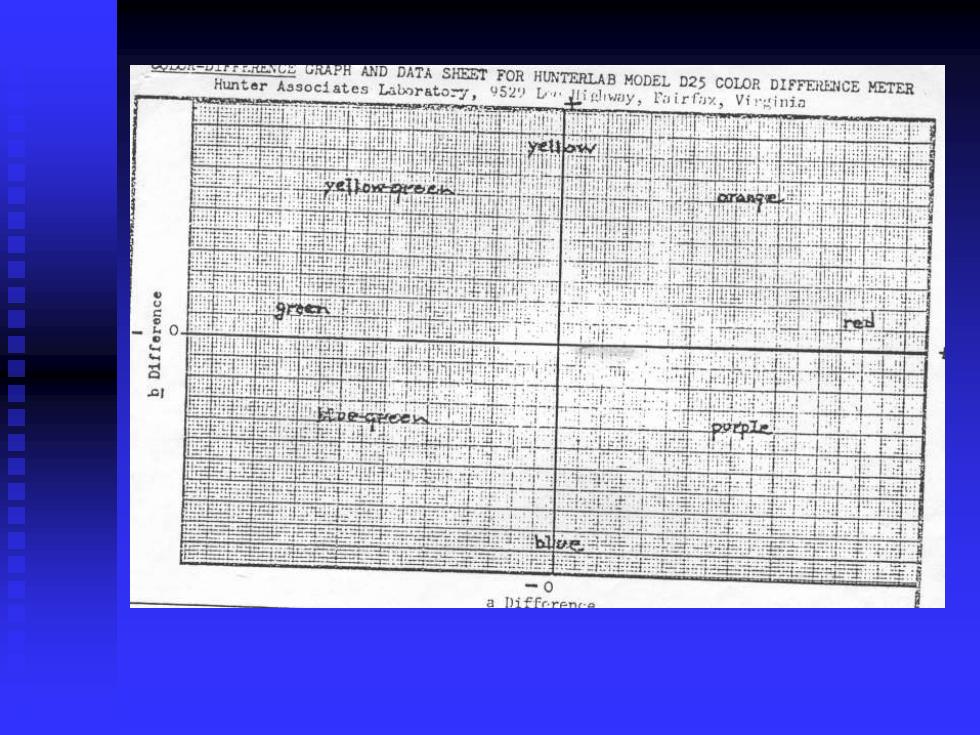
RCGRAPH AND DATA SHEET FOR HUNTERLAB MODEL D25 COLOR DIFFERENCE METER Hunter Associates Laboratory, 9529 L liglway,Fairfax,Virginia a Diffcren
