
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 1 Physical Chemistry Peter Atkins Peter Atkins (Sixth edition) (Sixth edition) Bilingual Program
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 1 Physical Chemistry Peter Atkins Peter Atkins (Sixth edition) (Sixth edition) Bilingual Program

版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 2 Part 1: Equilibrium Bilingual Program 5. The Second Law:the machinery
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 2 Part 1: Equilibrium Bilingual Program 5. The Second Law:the machinery
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 3 In this chapter: First: to find relations between properties that might not be thought to be related; to derive expressions for the variation of the G with T and p. Second: to introduce the chemical potential, a property that will be at the center of discussions in the remaining chapters of this part of the text; to derive expression of fugacity. The 'chemical potential', the quantity on which almost all the most important applications of thermodynamics to chemistry are based. 5. The Second Law: the machinery
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 3 In this chapter: First: to find relations between properties that might not be thought to be related; to derive expressions for the variation of the G with T and p. Second: to introduce the chemical potential, a property that will be at the center of discussions in the remaining chapters of this part of the text; to derive expression of fugacity. The 'chemical potential', the quantity on which almost all the most important applications of thermodynamics to chemistry are based. 5. The Second Law: the machinery

版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 4 Combing the First and Second Laws 5.1 Properties of the internal energy 5.2 Properties of the Gibbs energy 5.3 The chemical potential of a pure substance Real gases:the fugacity 5.4 The definition of fugacity 5.5 Standard states of real gases 5.6 The relation between fugacity and pressure 5. The Second Law: the machinery
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 4 Combing the First and Second Laws 5.1 Properties of the internal energy 5.2 Properties of the Gibbs energy 5.3 The chemical potential of a pure substance Real gases:the fugacity 5.4 The definition of fugacity 5.5 Standard states of real gases 5.6 The relation between fugacity and pressure 5. The Second Law: the machinery
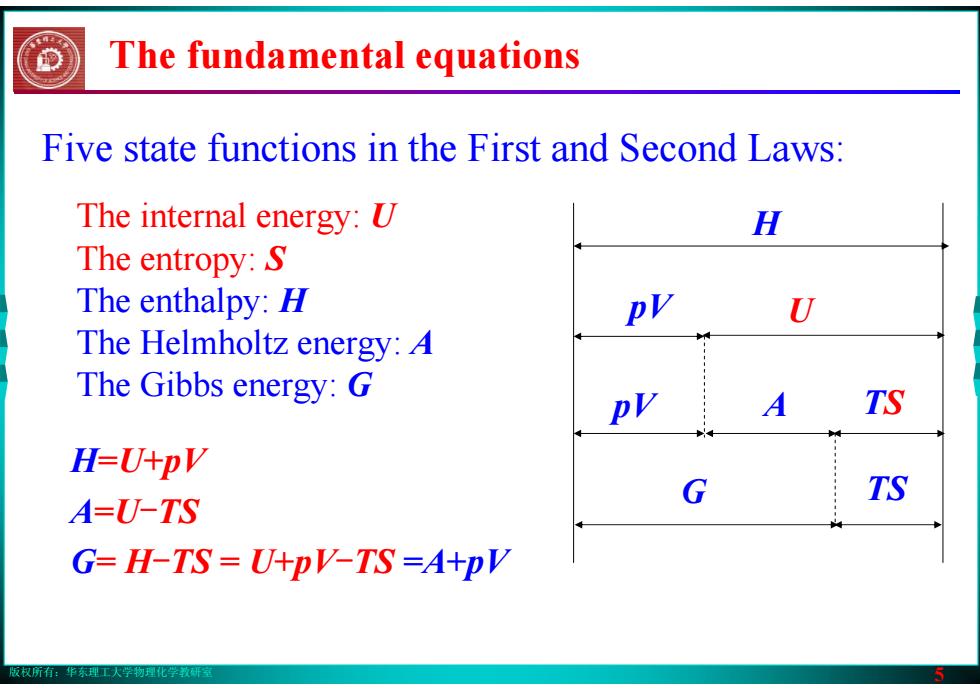
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 5 The fundamental equations Five state functions in the First and Second Laws: The internal energy: U The entropy: S The enthalpy: H The Helmholtz energy: A The Gibbs energy: G H pV U pV A TS G TS H=U+pV A=U-TS G= H-TS = U+pV-TS =A+pV
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 5 The fundamental equations Five state functions in the First and Second Laws: The internal energy: U The entropy: S The enthalpy: H The Helmholtz energy: A The Gibbs energy: G H pV U pV A TS G TS H=U+pV A=U-TS G= H-TS = U+pV-TS =A+pV
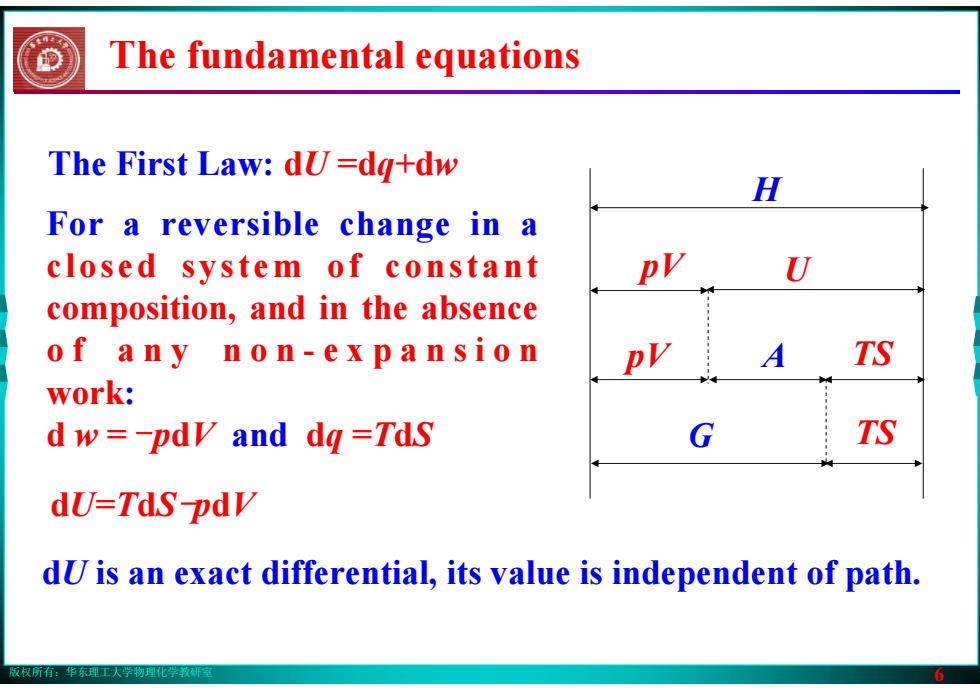
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 6 The First Law: dU =dq+dw H pV U pV A TS G TS For a reversible change in a closed system of constant composition, and in the absence o f a n y n o n - e x p a n s i o n work: d w = -pdV and dq =TdS dU=TdS-pdV dU is an exact differential, its value is independent of path. The fundamental equations
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 6 The First Law: dU =dq+dw H pV U pV A TS G TS For a reversible change in a closed system of constant composition, and in the absence o f a n y n o n - e x p a n s i o n work: d w = -pdV and dq =TdS dU=TdS-pdV dU is an exact differential, its value is independent of path. The fundamental equations
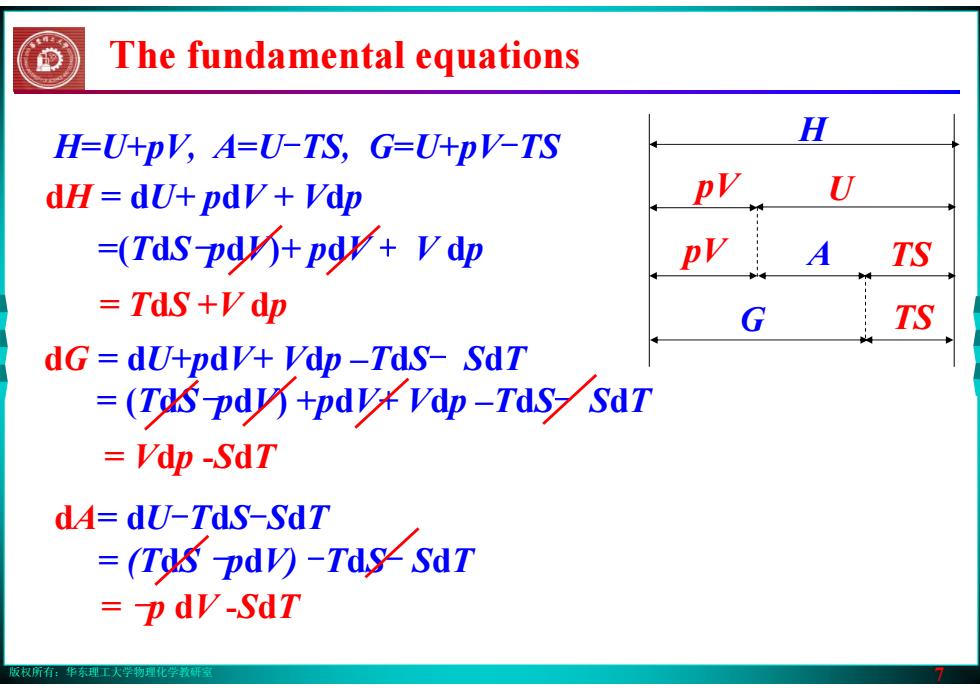
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 7 H pV U pV A TS G TS dH = dU+ pdV + Vdp =(TdS-pdV)+ pdV + V dp H=U+pV, A=U-TS, G=U+pV-TS dA= dU-TdS-SdT = (TdS -pdV) -TdS- SdT dG = dU+pdV+ Vdp –TdS- SdT = (TdS-pdV) +pdV+ Vdp –TdS- SdT = TdS +V dp = Vdp -SdT = -p dV -SdT The fundamental equations
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 7 H pV U pV A TS G TS dH = dU+ pdV + Vdp =(TdS-pdV)+ pdV + V dp H=U+pV, A=U-TS, G=U+pV-TS dA= dU-TdS-SdT = (TdS -pdV) -TdS- SdT dG = dU+pdV+ Vdp –TdS- SdT = (TdS-pdV) +pdV+ Vdp –TdS- SdT = TdS +V dp = Vdp -SdT = -p dV -SdT The fundamental equations
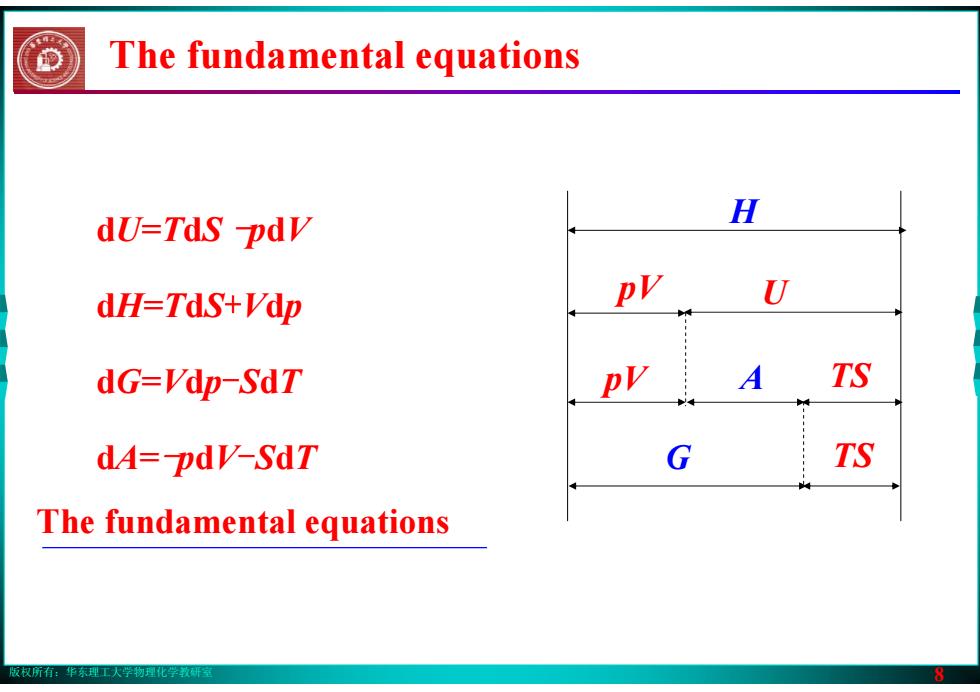
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 8 dU=TdS -pdV dH=TdS+Vdp dG=Vdp-SdT dA=-pdV-SdT H pV U pV A TS G TS The fundamental equations The fundamental equations
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 8 dU=TdS -pdV dH=TdS+Vdp dG=Vdp-SdT dA=-pdV-SdT H pV U pV A TS G TS The fundamental equations The fundamental equations

版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 9 5.1 Properties of the internal energy 1). The Maxwell relations = gdx + hdy z = f ( x , y) y y z x x z z y x d d d ⎟⎟⎠⎞ ⎜⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ ⎟ + ⎠⎞ ⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ = y x y z h x z g ⎟⎟⎠⎞ ⎜⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ ⎟ = ⎠⎞ ⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ where =
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 9 5.1 Properties of the internal energy 1). The Maxwell relations = gdx + hdy z = f ( x , y) y y z x x z z y x d d d ⎟⎟⎠⎞ ⎜⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ ⎟ + ⎠⎞ ⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ = y x y z h x z g ⎟⎟⎠⎞ ⎜⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ ⎟ = ⎠⎞ ⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ where =
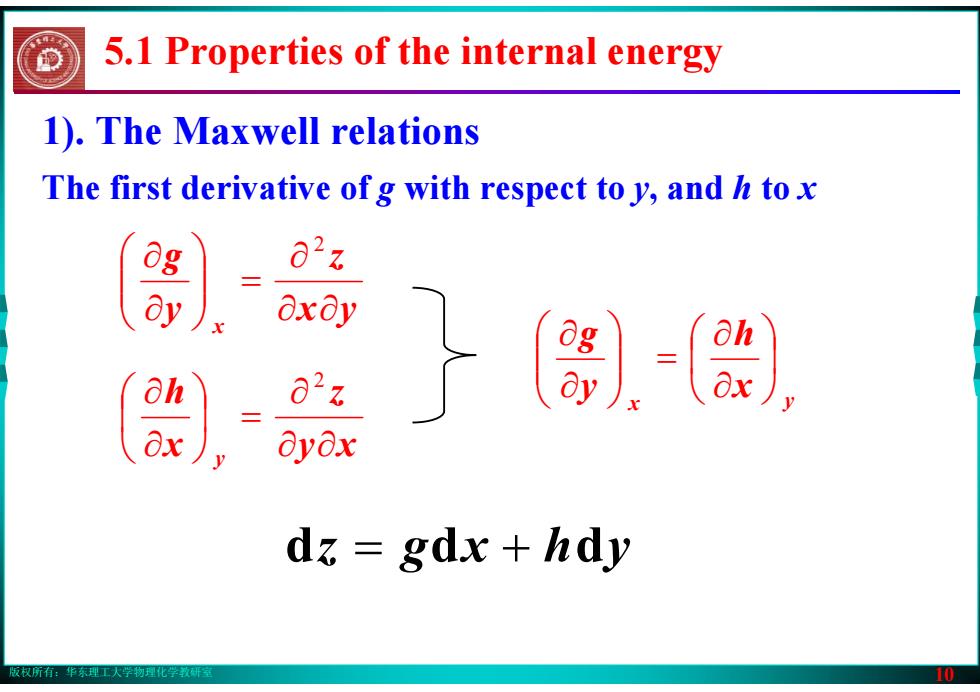
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 10 1). The Maxwell relations x y z y g x ∂ ∂ ∂ = ⎟⎟⎠⎞ ⎜⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ 2 y x z x h y ∂ ∂ ∂ ⎟ = ⎠⎞ ⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ 2 x y x h y g ⎟⎠⎞ ⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ = ⎟⎟⎠⎞ ⎜⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ dz = gdx + hdy The first derivative of g with respect to y, and h to x 5.1 Properties of the internal energy
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 10 1). The Maxwell relations x y z y g x ∂ ∂ ∂ = ⎟⎟⎠⎞ ⎜⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ 2 y x z x h y ∂ ∂ ∂ ⎟ = ⎠⎞ ⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ 2 x y x h y g ⎟⎠⎞ ⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ = ⎟⎟⎠⎞ ⎜⎜⎝⎛ ∂∂ dz = gdx + hdy The first derivative of g with respect to y, and h to x 5.1 Properties of the internal energy