
The abdomen I May Lee李颖 Department of anatomy&neurobiology Room 119
The abdomenⅡ May Lee 李颖 Department of anatomy& neurobiology Room 119

Landmarks of abdomen ·Pubic symphysis ·Pubic tubercle ·lliac crest ·Umbilicus ·Linea alba1--9-5-13 Transpyloric plane L1 909 1.Xphoid procoss.2.Costal margin.3.Tip of the ninth costa cartiage. First layer-liver,gallbladder,stomach 4.Tendnous intersections 5.Umbillous 6.liac crest.7.Anserior supenor itac spine 8.Lnea semlunanis.9.Linea aba.10.Inguinal ligament.11.Putic tcercule Second layer-duodenum,pancreas,spleen 12.Pubic crest 13.Pubic symphysis. Third layer-suprarenal gland,kidney,ureter,inferior vena cava,abdominal aorta,nerves and lymphatics
Landmarks of abdomen • Pubic symphysis • Pubic tubercle • Iliac crest • Umbilicus • Linea alba 1---9--5--13 • Transpyloric plane L1 First layer-liver, gallbladder, stomach Second layer-duodenum, pancreas, spleen Third layer-suprarenal gland, kidney, ureter, inferior vena cava, abdominal aorta, nerves and lymphatics
Objects ● the muscles of abdominal wall Review Inguinal ligament and canal The peritoneum Peritoneum Peritoneal reflections omentum;mesentery,ligaments ●Greater sac Peritoneal cavity Lesser sac(omental bursa)
Objects Review • the muscles of abdominal wall • Inguinal ligament and canal Peritoneum • The peritoneum • Peritoneal reflections :omentum; mesentery, ligaments Peritoneal cavity • Greater sac • Lesser sac (omental bursa)
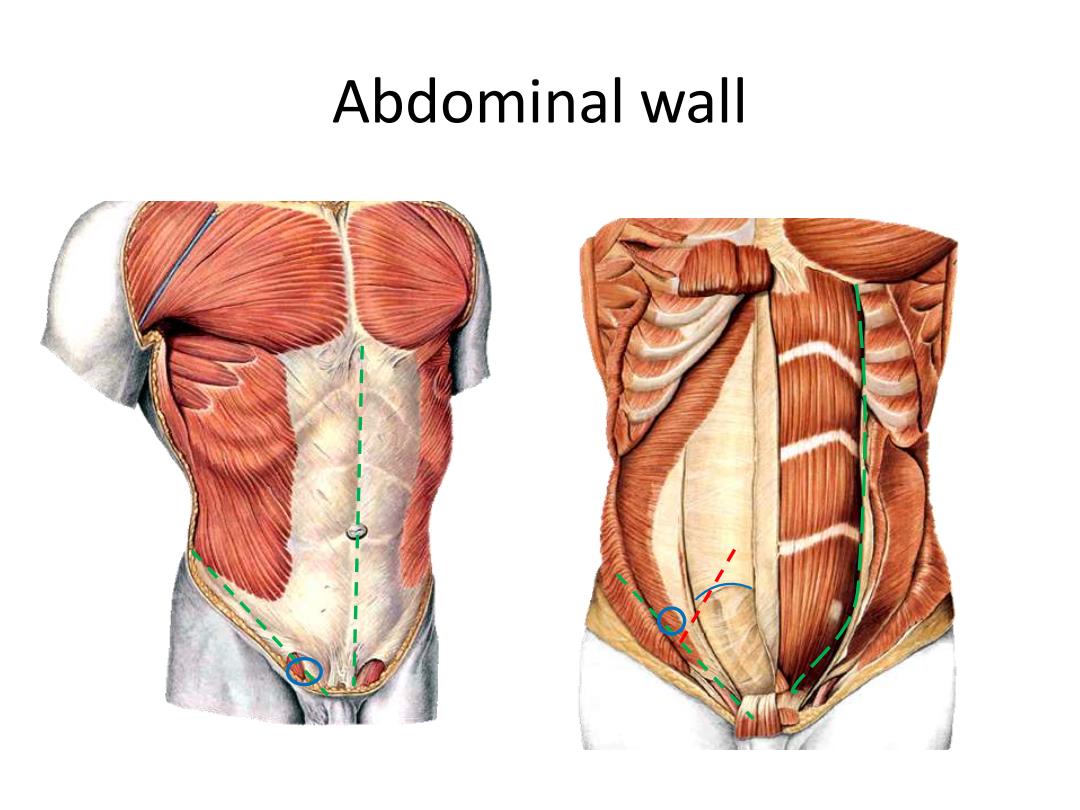
Abdominal wall
Abdominal wall
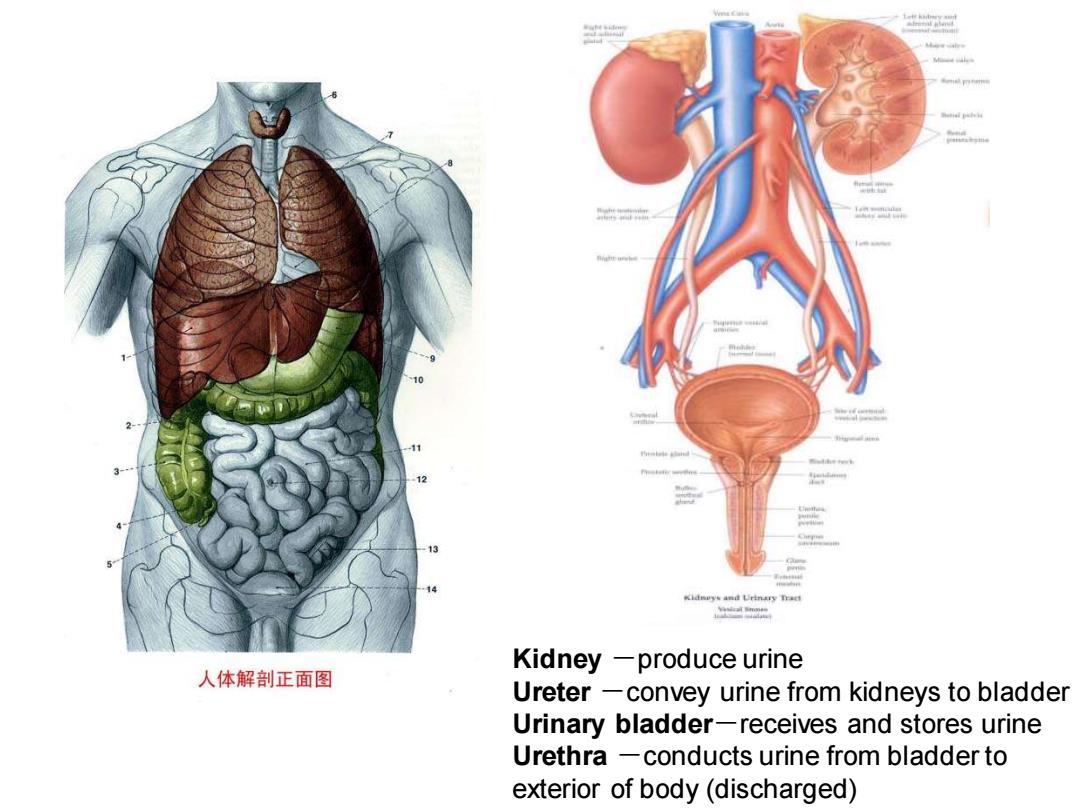
Kidneys and Urinary Tract 人体解剖正面图 Kidney -produce urine Ureter -convey urine from kidneys to bladder Urinary bladder-receives and stores urine Urethra -conducts urine from bladder to exterior of body(discharged)
Kidney -produce urine Ureter -convey urine from kidneys to bladder Urinary bladder-receives and stores urine Urethra -conducts urine from bladder to exterior of body (discharged)
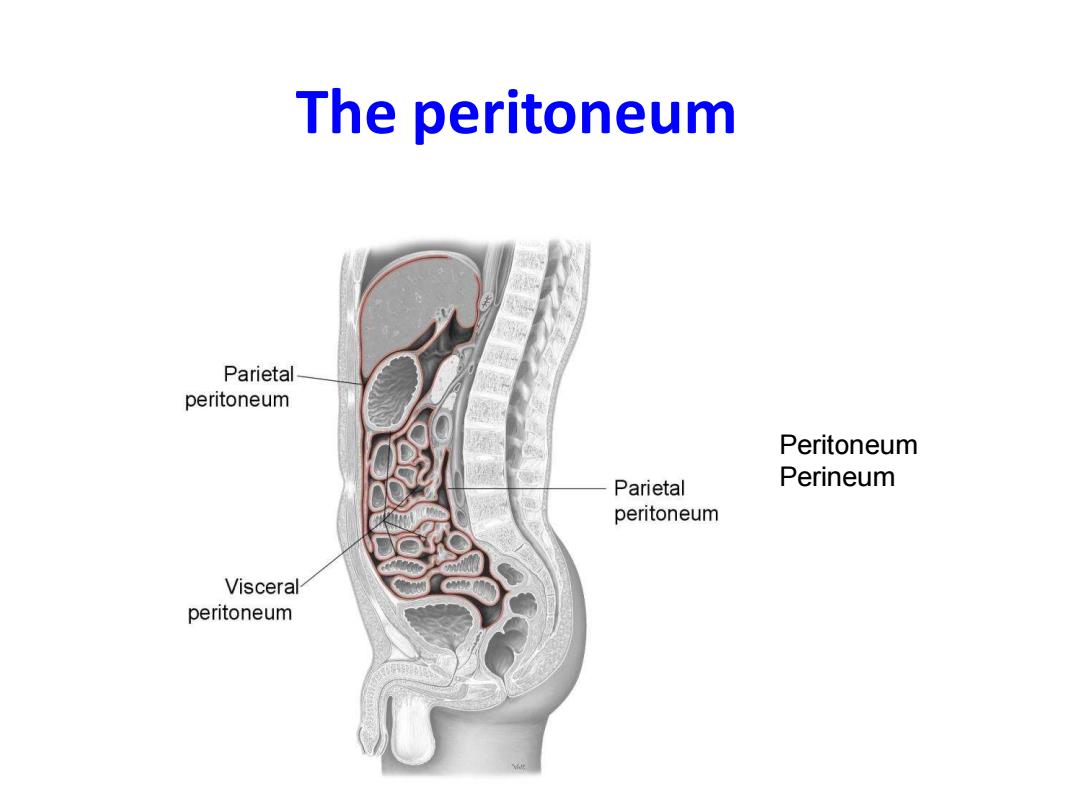
The peritoneum Parietal peritoneum Peritoneum Parietal Perineum peritoneum Visceral peritoneum
The peritoneum Peritoneum Perineum
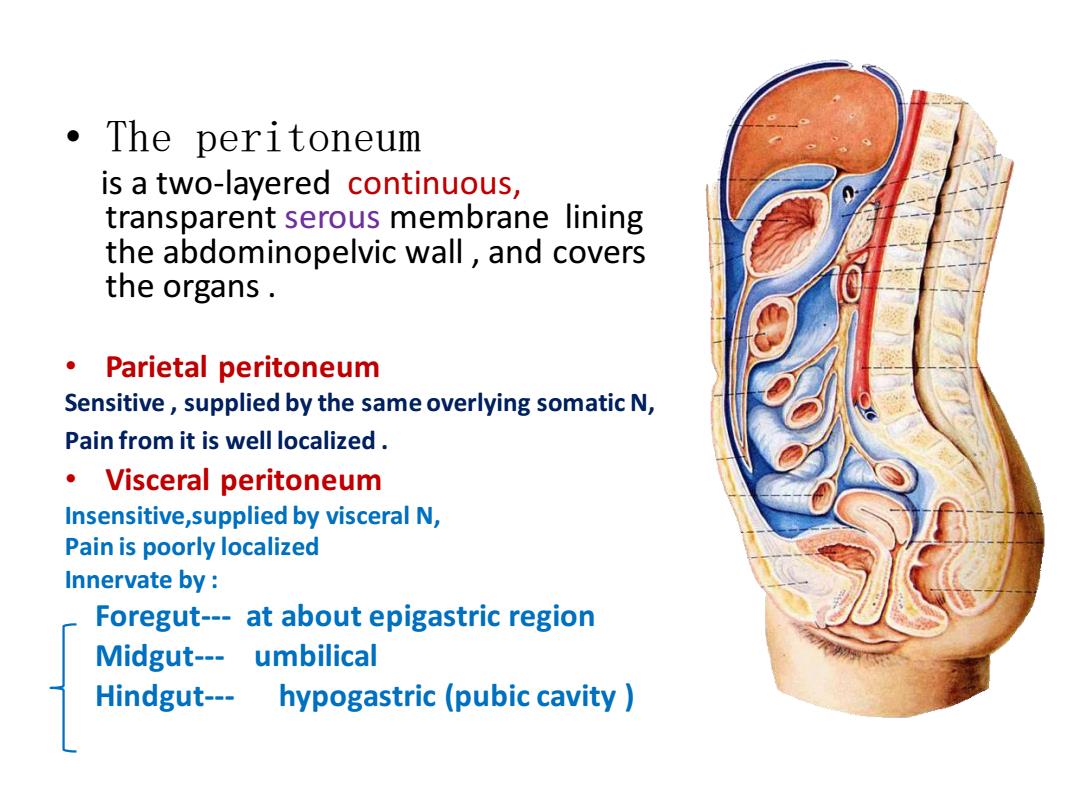
·The peritoneum is a two-layered continuous, transparent serous membrane lining the abdominopelvic wall,and covers the organs. 。Parietal peritoneum Sensitive,supplied by the same overlying somatic N, Pain from it is well localized ·Visceral peritoneum Insensitive,supplied by visceral N, Pain is poorly localized Innervate by: Foregut---at about epigastric region Midgut---umbilical Hindgut--- hypogastric(pubic cavity
• The peritoneum is a two-layered continuous, transparent serous membrane lining the abdominopelvic wall , and covers the organs . • Parietal peritoneum Sensitive , supplied by the same overlying somatic N, Pain from it is well localized . • Visceral peritoneum Insensitive,supplied by visceral N, Pain is poorly localized Innervate by : Foregut--- at about epigastric region Midgut--- umbilical Hindgut--- hypogastric (pubic cavity )
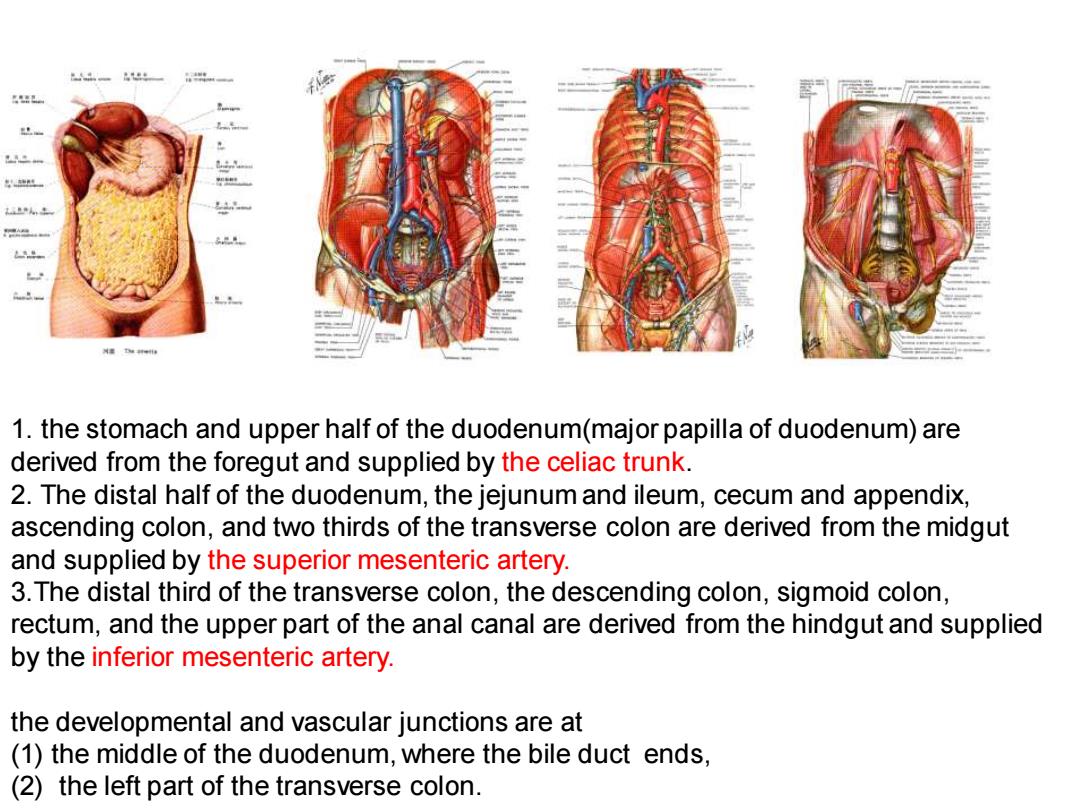
1.the stomach and upper half of the duodenum(major papilla of duodenum)are derived from the foregut and supplied by the celiac trunk. 2.The distal half of the duodenum,the jejunum and ileum,cecum and appendix, ascending colon,and two thirds of the transverse colon are derived from the midgut and supplied by the superior mesenteric artery. 3.The distal third of the transverse colon,the descending colon,sigmoid colon, rectum,and the upper part of the anal canal are derived from the hindgut and supplied by the inferior mesenteric artery. the developmental and vascular junctions are at (1)the middle of the duodenum,where the bile duct ends, (2)the left part of the transverse colon
1. the stomach and upper half of the duodenum(major papilla of duodenum) are derived from the foregut and supplied by the celiac trunk. 2. The distal half of the duodenum, the jejunum and ileum, cecum and appendix, ascending colon, and two thirds of the transverse colon are derived from the midgut and supplied by the superior mesenteric artery. 3.The distal third of the transverse colon, the descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, and the upper part of the anal canal are derived from the hindgut and supplied by the inferior mesenteric artery. the developmental and vascular junctions are at (1) the middle of the duodenum, where the bile duct ends, (2) the left part of the transverse colon
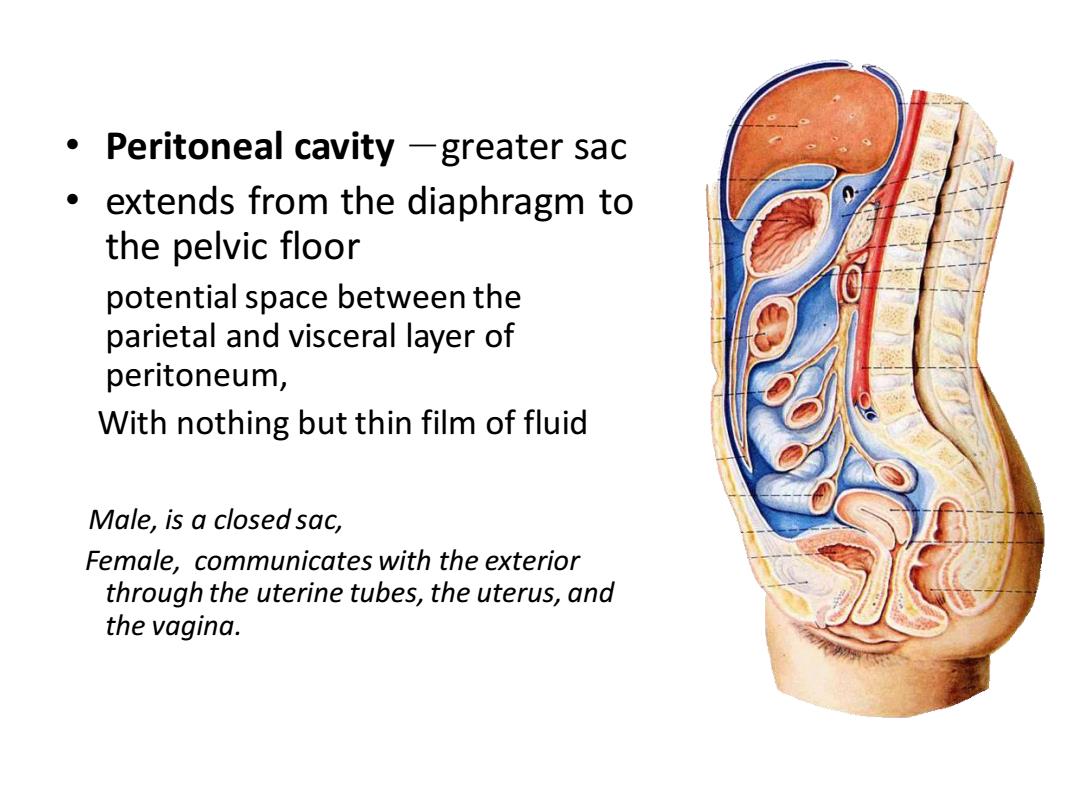
Peritoneal cavity -greater sac extends from the diaphragm to the pelvic floor potential space between the parietal and visceral layer of peritoneum, With nothing but thin film of fluid Male,is a closed sac, Female,communicates with the exterior through the uterine tubes,the uterus,and the vagina
• Peritoneal cavity -greater sac • extends from the diaphragm to the pelvic floor potential space between the parietal and visceral layer of peritoneum, With nothing but thin film of fluid Male, is a closed sac, Female, communicates with the exterior through the uterine tubes, the uterus, and the vagina
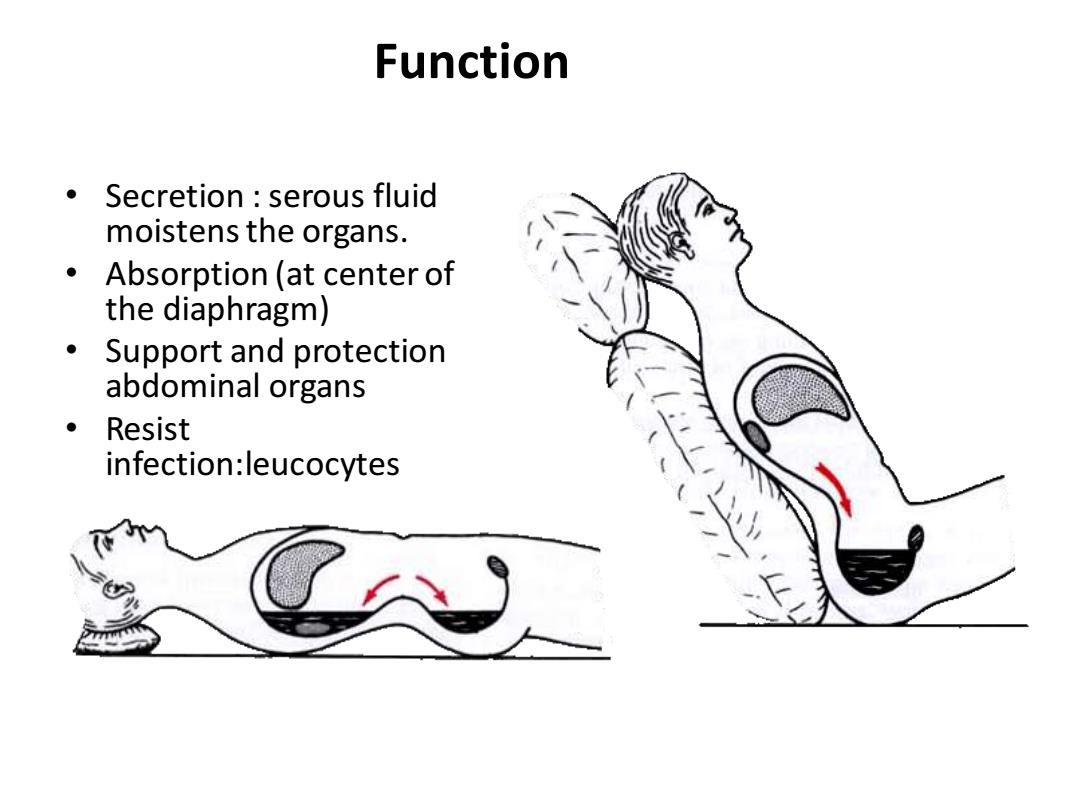
Function Secretion serous fluid moistens the organs. Absorption(at center of the diaphragm) ● Support and protection abdominal organs Resist infection:leucocytes
Function • Secretion : serous fluid moistens the organs. • Absorption (at center of the diaphragm) • Support and protection abdominal organs • Resist infection:leucocytes