
The Cardiovascular System Anne M.Gilroy UMass Medical School
The Cardiovascular System Anne M. Gilroy UMass Medical School
Cardiovascular System Heart Arterial system Capillary network Venous system Lymphatic system
Cardiovascular System Heart Arterial system Capillary network Venous system Lymphatic system
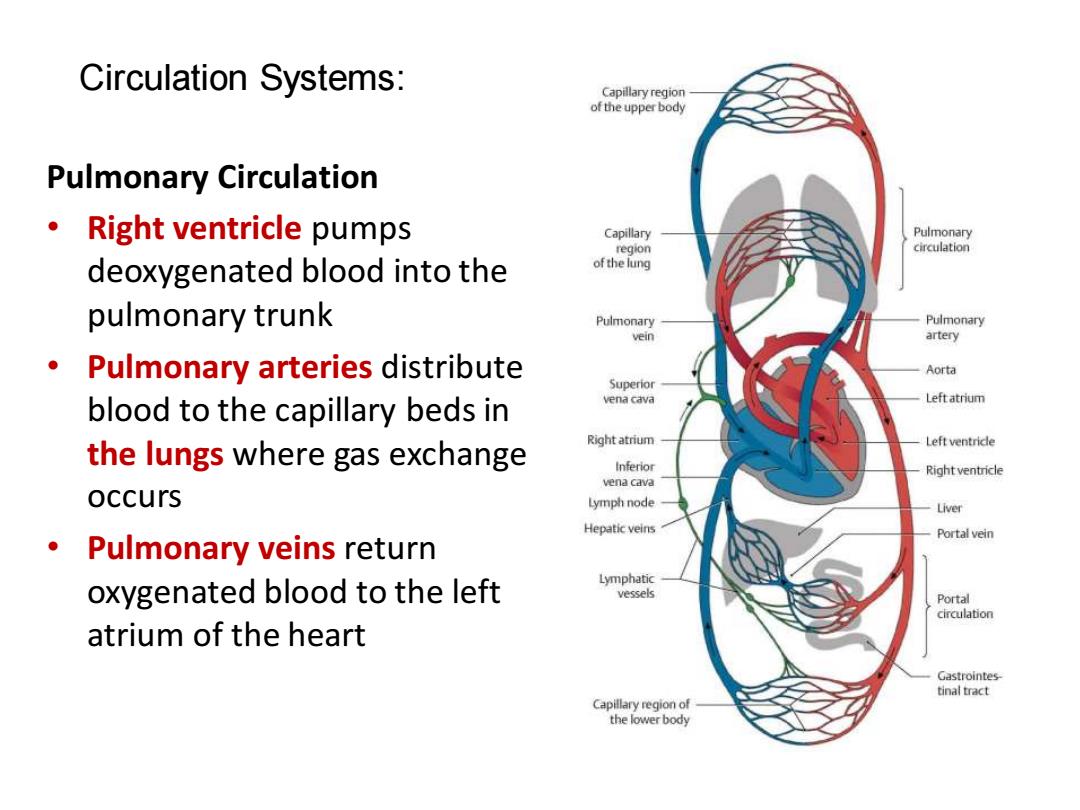
Circulation Systems: of the upper body Pulmonary Circulation Right ventricle pumps Capillary Pulmonary region circulation deoxygenated blood into the of the lung pulmonary trunk Pulmonary Pulmonary vein artery Pulmonary arteries distribute Aorta Superior blood to the capillary beds in vena cava Left atrium Right atrium the lungs where gas exchange Left ventrice Right ventricle vena cava occurs Lymph node Liver Hepatic veins Portal vein Pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood to the left Lymphatic vessels Portal circulation atrium of the heart Gastrointes tinal tract Capillary region of the lower body
Circulation Systems: Pulmonary Circulation • Right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary trunk • Pulmonary arteries distribute blood to the capillary beds in the lungs where gas exchange occurs • Pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood to the left atrium of the heart
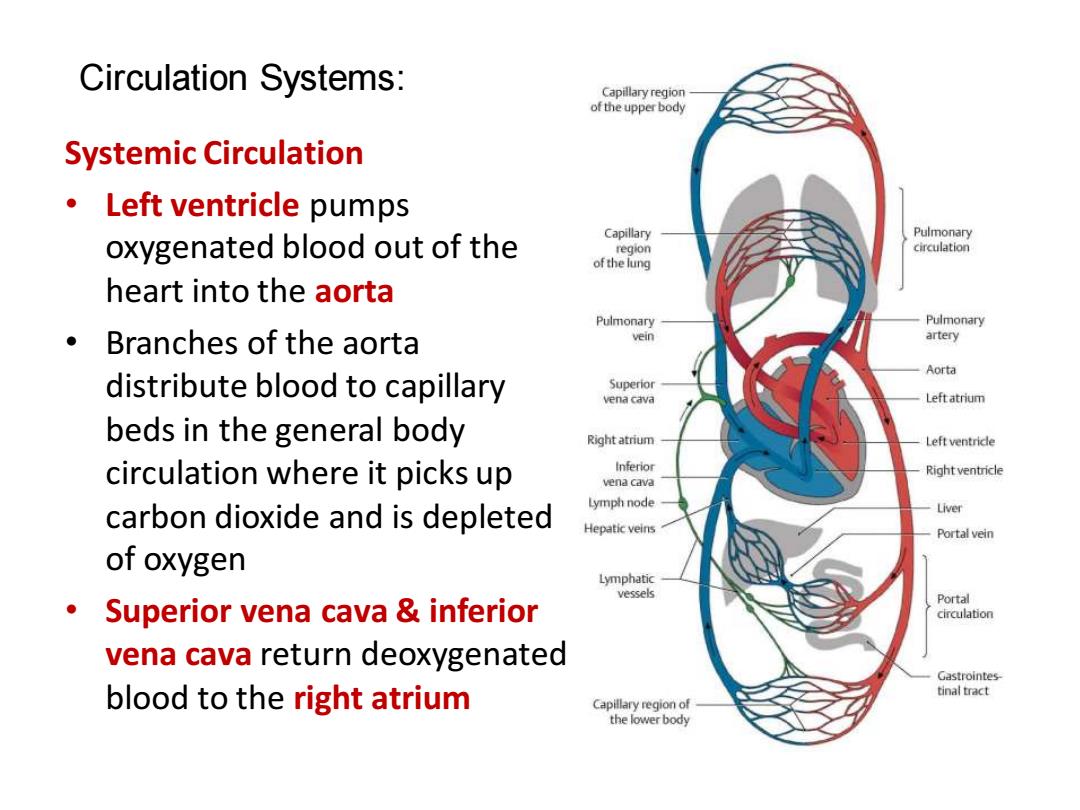
Circulation Systems: Capillary region of the upperbody Systemic Circulation ·Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood out of the Capillary region of the lung heart into the aorta Pulmonary Pulmonary ·Branches of the aorta vein artery Aorta distribute blood to capillary Superior vena cava Leftatrium beds in the general body Right atrium Left ventrice circulation where it picks up Inferior Right ventricle vena cava Lymph node carbon dioxide and is depleted Liver Hepatic veins Portal vein of oxygen Lymphatic vessels Superior vena cava inferior Portal circulation vena cava return deoxygenated Gastrointes blood to the right atrium tinal tract
Circulation Systems: Systemic Circulation • Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood out of the heart into the aorta • Branches of the aorta distribute blood to capillary beds in the general body circulation where it picks up carbon dioxide and is depleted of oxygen • Superior vena cava & inferior vena cava return deoxygenated blood to the right atrium
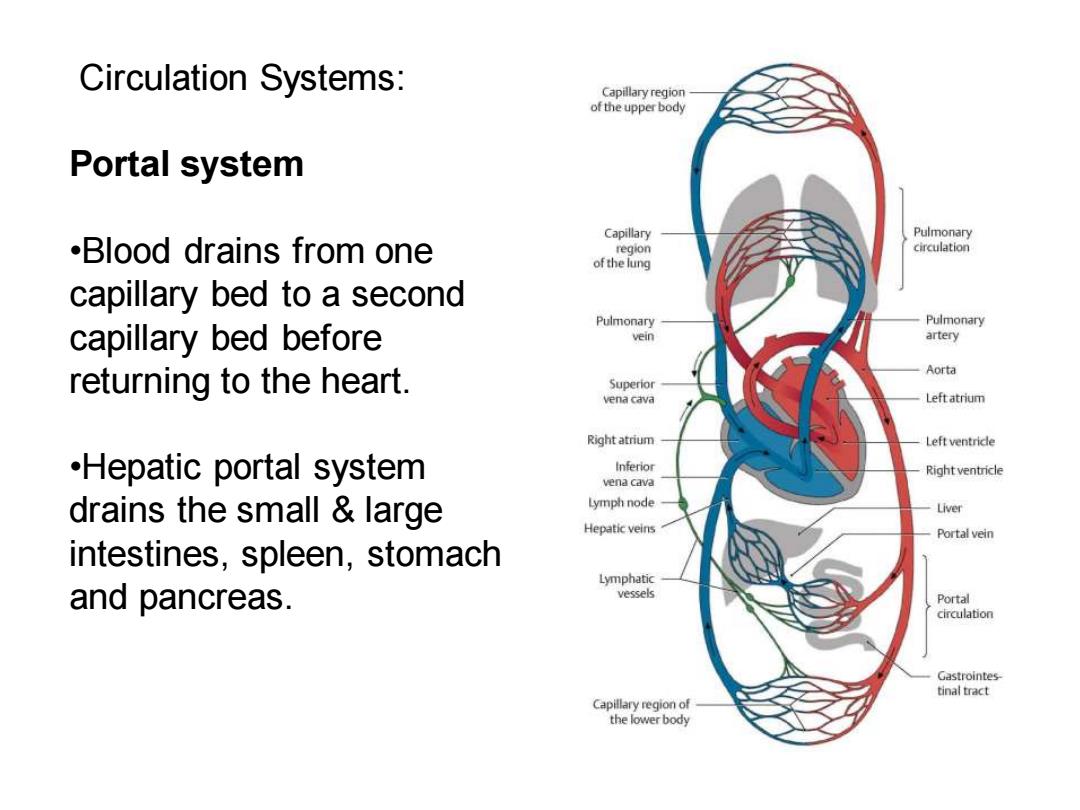
Circulation Systems: of the upper body Portal system Capillary Pulmonary .Blood drains from one region circulation of the lung capillary bed to a second capillary bed before Pulmonary Pulmonary vein artery returning to the heart. Aorta Superior vena cava Leftatrium Rightatrium Left ventrice .Hepatic portal system Right ventricle vena cava drains the small large Lymph node Liver Hepatic veins Portal vein intestines,spleen,stomach Lymphatic and pancreas. vessels Portal circulation inal tract Capillary region of the lower body
Circulation Systems: Portal system •Blood drains from one capillary bed to a second capillary bed before returning to the heart. •Hepatic portal system drains the small & large intestines, spleen, stomach and pancreas
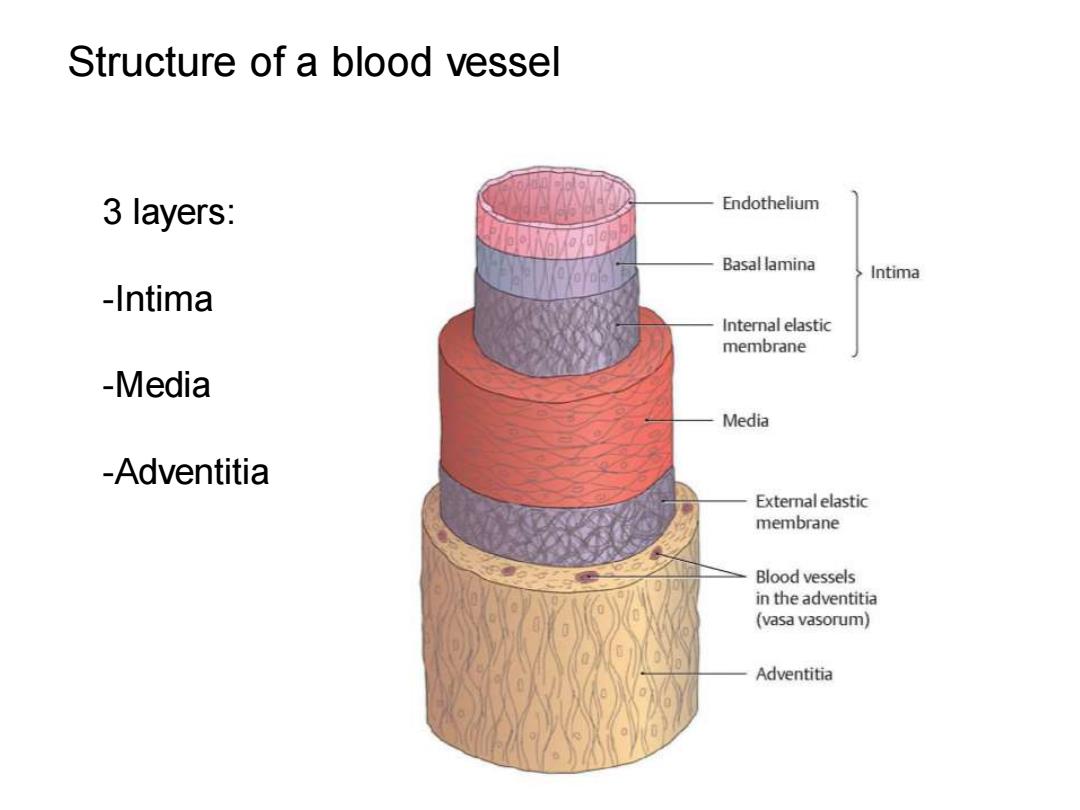
Structure of a blood vessel 3 layers: Endothelium Basal lamina Intima -Intima Internal elastic membrane -Media Media -Adventitia Extemnal elastic membrane Blood vessels in the adventitia (vasa vasorum) Adventitia
Structure of a blood vessel 3 layers: -Intima -Media -Adventitia
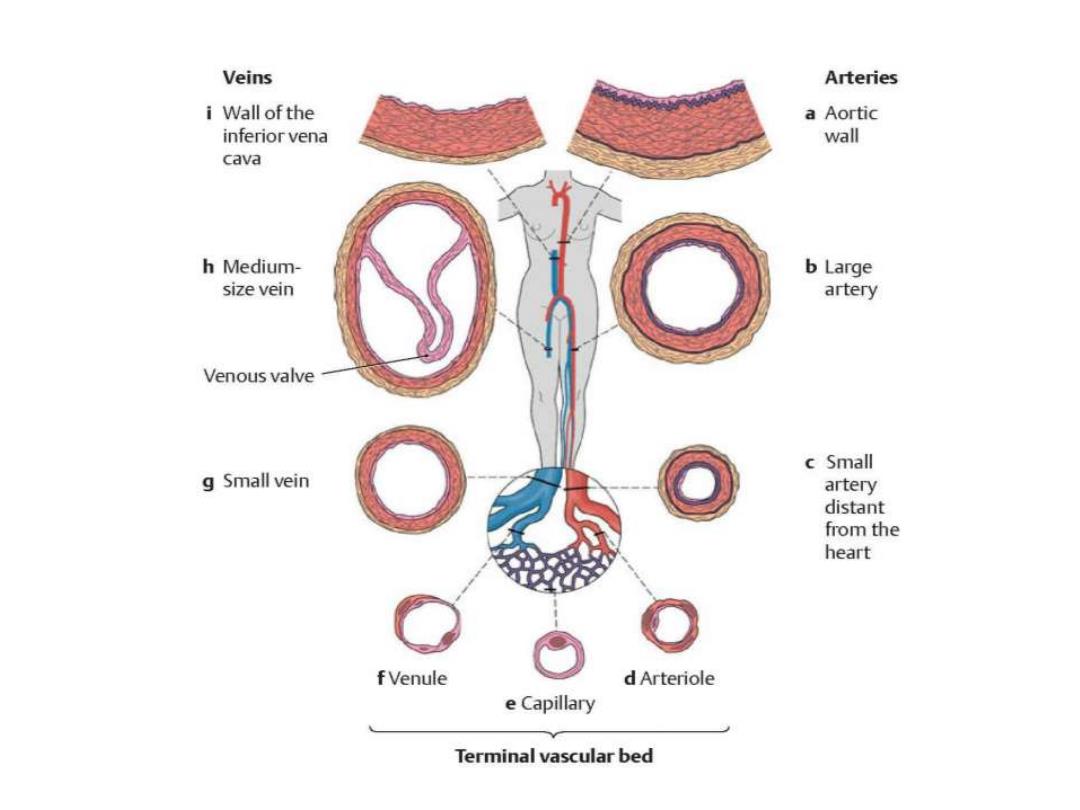
Veins Arteries i Wall of the a Aortic inferior vena wall cava h Medium- b Large size vein artery Venous valve c Small g Small vein artery distant from the heart fVenule d Arteriole e Capillary Terminal vascular bed
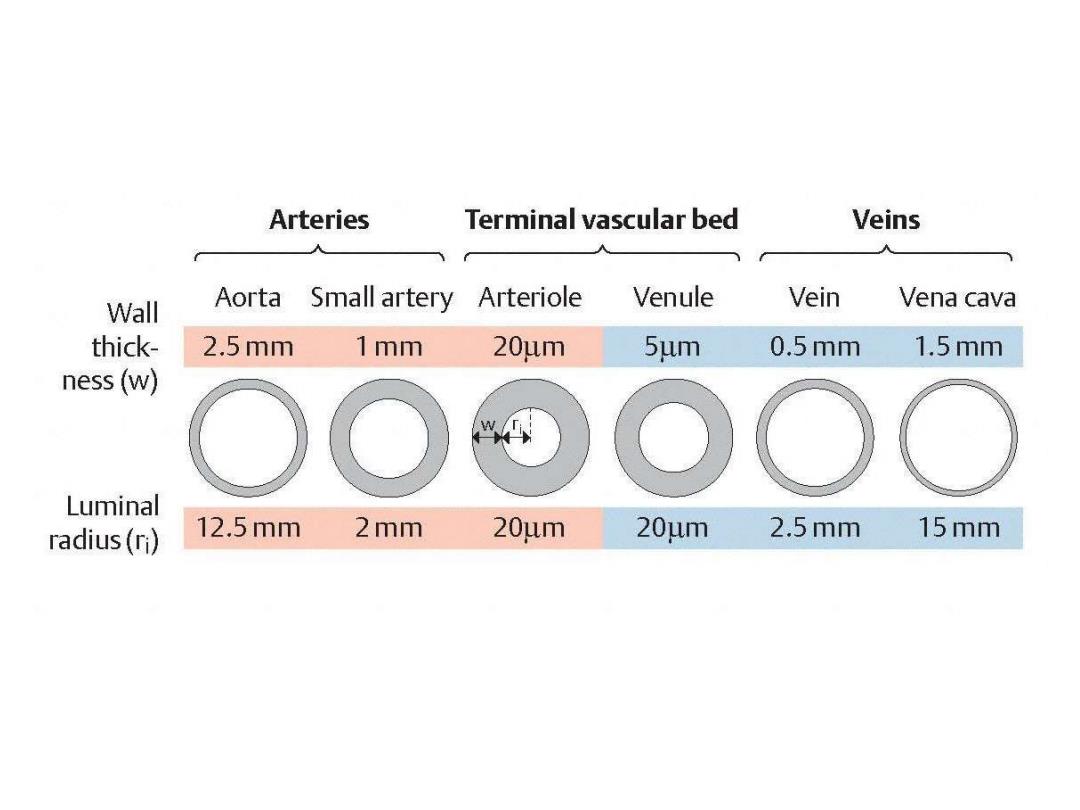
Arteries Terminal vascular bed Veins 人 Wall Aorta Small artery Arteriole Venule Vein Vena cava thick- 2.5mm 1mm 20um 5um 0.5mm 1.5mm ness(w) Luminal radius(ri) 12.5mm 2mm 20um 20um 2.5mm 15mm
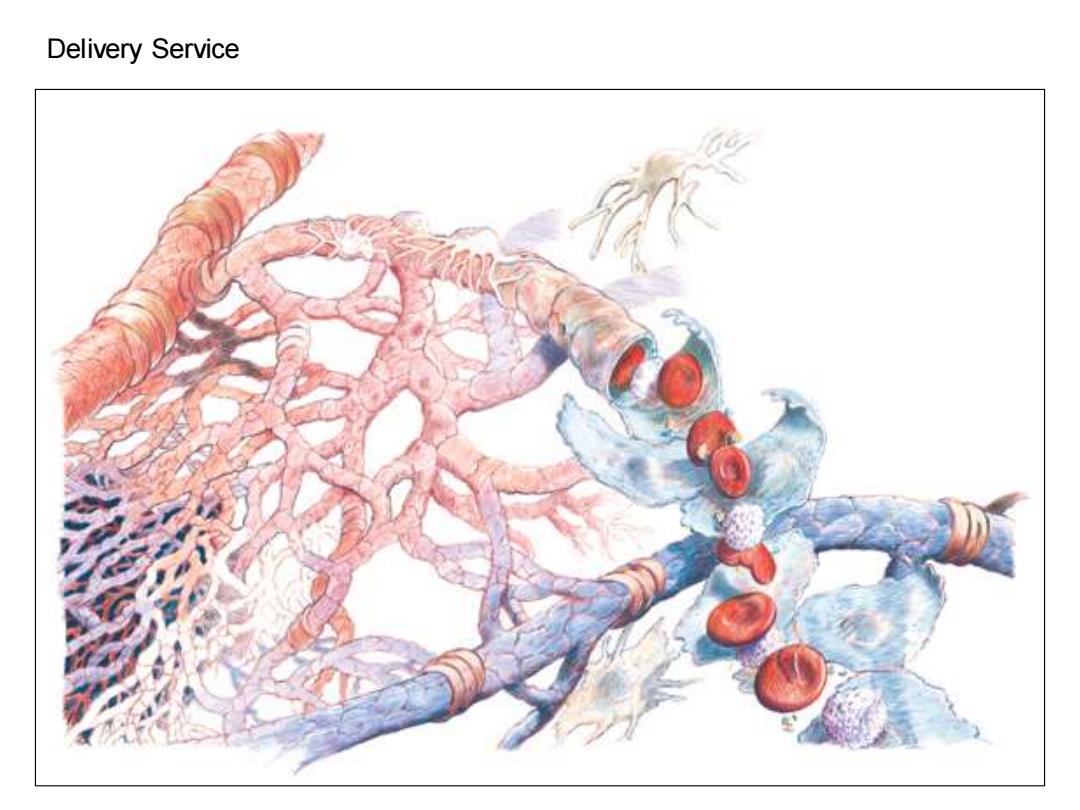
Delivery Service
Delivery Service

Aorta Large arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Venous branches Large veins Venae cavae Increasing 0.16x109 5x109 0.5x109 Decreasing Number of vessels 3.0 33 0.3 0.151.6 0.8 0.7 0.060.002 0.00090.0025 Diameter of the individual vessel (cm) 3500 2700 500 5.3 20 20 10030 18 Total cross-sectional area(cm)