
Cranial Nerves
Cranial Nerves

Contents Name of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves The site where they leave or enter the brain and the skull The functional compositions 口 The innervations and functions

夜思热经onu The name and the order 车神经ear6 是热0-将就c急 I olfactory nerve 热c经」 Ⅱoptic nerve Ⅲoculomotor nerve IV trochlear nerve V trigeminal nerve VI abducent nerve Ⅶfacial nerve VI vestibulocochlear nerve 煎底防格s IX glossopharyngeal nerve X vagus nerve XⅪ accessory nerve XⅫhypoglossal nerve 一彩排经 爱osu
Ⅰ olfactory nerve Ⅱ optic nerve Ⅲ oculomotor nerve Ⅳ trochlear nerve Ⅴ trigeminal nerve Ⅵ abducent nerve Ⅶ facial nerve Ⅷ vestibulocochlear nerve Ⅸ glossopharyngeal nerve Ⅹ vagus nerve Ⅺ accessory nerve Ⅻ hypoglossal nerve The name and the order
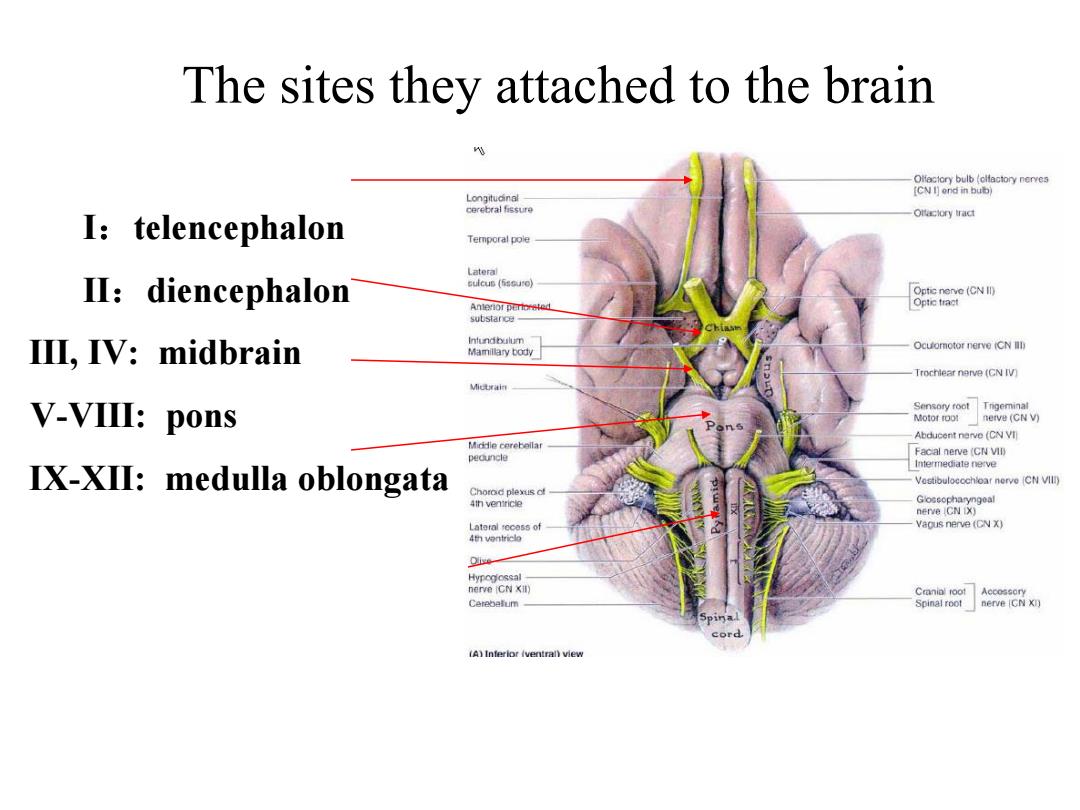
The sites they attached to the brain &sia2mtietboynenes e2ra I:telencephalon Temporal pole II:diencephalon d 8aeoNn Ⅱ,IV:midbrain Ocuomotor nerve CN V-VIII:pons V) Abducent nerve (CN VI) IX-XII:medulla oblongata Vestibulocochioar nerve CN VIll) 9eesd evC of Vaous nerve (CN X) Hypogiossal nerve iCN Xil) amce8刘 (A)Interior iventral)view
Ⅱ:diencephalon Ⅲ, Ⅳ: midbrain Ⅴ-Ⅷ: pons The sites they attached to the brain Ⅸ-Ⅻ: medulla oblongata Ⅰ:telencephalon
Seven functional components of the cranial nerves general somatic efferen eye(Ⅲ,V、I)and tongue(Ⅻ) 99888 >general visceral efferen fiber travel within III,VII,IX,X special visceral efferent 88 the branchial arches involved in swallowing (IX.X),producing v Fish Salamander Tortoise Chick Hog Calf Rabbit Human FIGURE 1.The appearance of ertebrate embryos at damental observation suggests that these different ani arious stages of development.The similarity of different mals share both a common ancestor and the same bas embryos during early development is striking;this fun-mechanisms of development.(From Romanes,1901.)
general somatic efferent fiber (GSE): striated muscles involved in eye (Ⅲ , Ⅳ、Ⅵ ) and tongue (Ⅻ) general visceral efferent fiber (GVE): preganglionic parasympathetic fiber travel within Ⅲ , Ⅶ, Ⅸ , Ⅹ special visceral efferent fiber (SVE): striated muscles derived from the branchial arches involved in chewing (Ⅴ), making facial expressions (Ⅶ ), swallowing (Ⅸ、Ⅹ), producing vocal sounds (Ⅹ) and turning the head (Ⅺ) Seven functional components of the cranial nerves

Seven functional components of the cranial nerves >general somatic efferent fiber (GSE):striated muscles involved in eye (Ⅲ,V、M)and tongue(XⅫ >general visceral efferent fiber (GVE):preganglionic parasympathetic fiber travel withinⅢ,VL,x,X >special visceral efferent fiber (SVE):striated muscles derived from the branchial arches involved in chewing (V),making facial expressions(VII), swallowing (IX.X),producing vocal sounds(X)and turning the head (X1) general somatic afferent fiber (GSA):sensation from skin,mucous membrane travel within V,VIl,IX,X general visceral afferent fiber (GVA):sensation from all viscera Ix,x special visceral afferent fiber (SVA):smell (I)and taste (VI,IX,X) ▣special somatic afferent fiber (SSA:visual(Ⅱ),hearing and equilibrium(Ⅷ)
general somatic efferent fiber (GSE): striated muscles involved in eye (Ⅲ , Ⅳ、Ⅵ ) and tongue (Ⅻ) general visceral efferent fiber (GVE): preganglionic parasympathetic fiber travel within Ⅲ , Ⅶ, Ⅸ , Ⅹ special visceral efferent fiber (SVE): striated muscles derived from the branchial arches involved in chewing (Ⅴ), making facial expressions (Ⅶ ), swallowing (Ⅸ、Ⅹ), producing vocal sounds (Ⅹ) and turning the head (Ⅺ) general somatic afferent fiber (GSA): sensation from skin, mucous membrane travel within Ⅴ, Ⅶ, Ⅸ, Ⅹ general visceral afferent fiber (GVA): sensation from all viscera Ⅸ, Ⅹ special visceral afferent fiber (SVA): smell (Ⅰ) and taste (Ⅶ, Ⅸ, X) special somatic afferent fiber (SSA): visual(Ⅱ), hearing and equilibrium (Ⅷ) Seven functional components of the cranial nerves
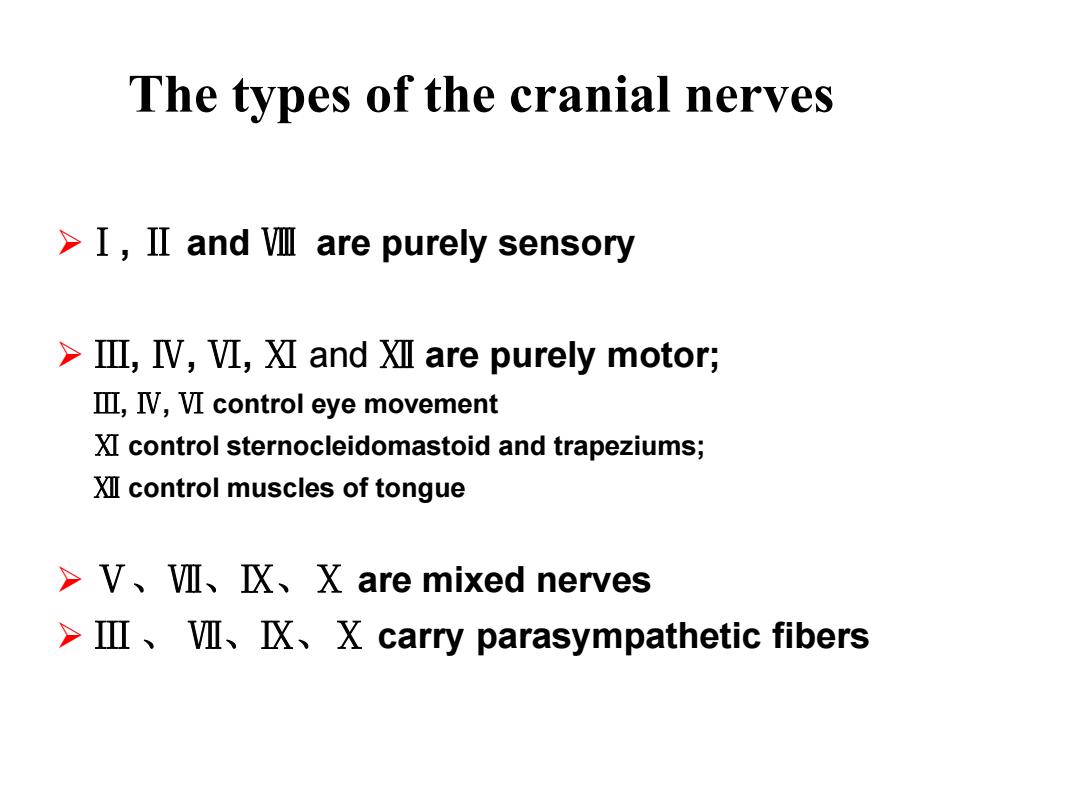
The types of the cranial nerves >I,ⅡandⅧare purely sensory >Ⅲ,V,I,ⅪandXⅫare purely motor; Ⅲ,V,VI control eye movement XI control sternocleidomastoid and trapeziums; XII control muscles of tongue >V、Ⅶ、X、X are mixed nerves >Ⅲ、Ⅶ、X、X carry parasympathetic fibers
Ⅰ, Ⅱ and Ⅷ are purely sensory Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅵ, Ⅺ and Ⅻ are purely motor; Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅵ control eye movement Ⅺ control sternocleidomastoid and trapeziums; Ⅻ control muscles of tongue Ⅴ、Ⅶ、Ⅸ、Ⅹ are mixed nerves Ⅲ 、 Ⅶ、Ⅸ、Ⅹ carry parasympathetic fibers The types of the cranial nerves
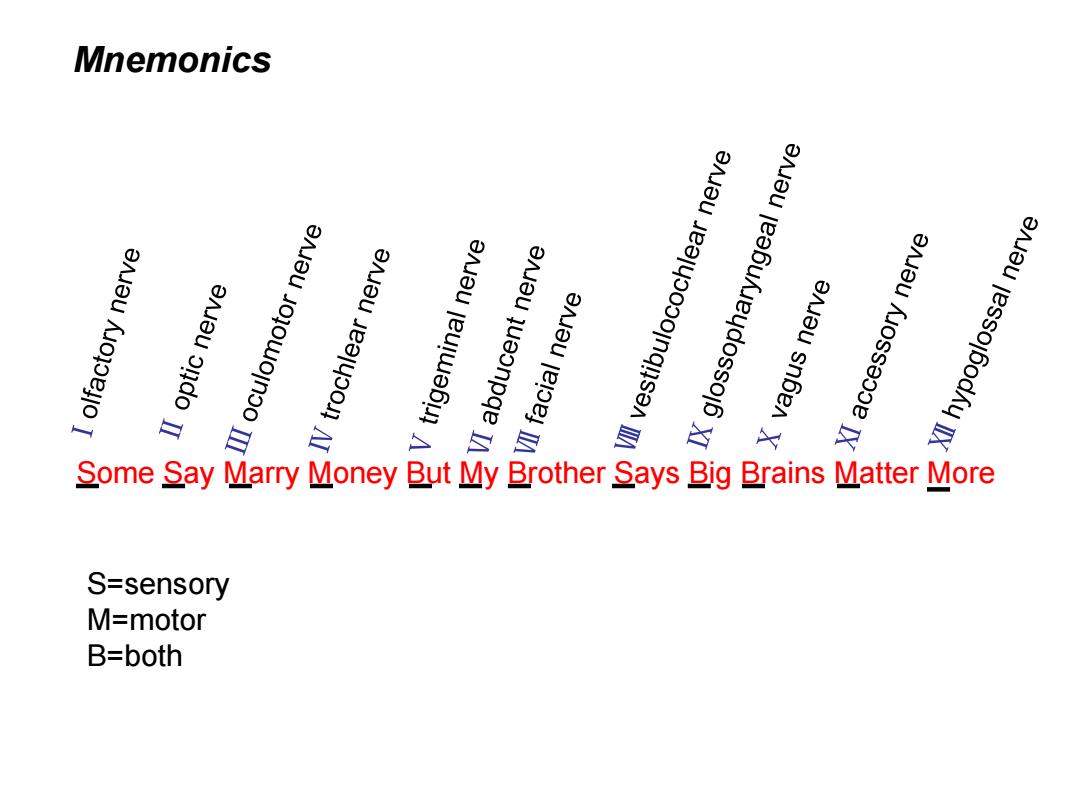
Mnemonics IⅡoptic nerve eneu queonpqe IA enJeu snbe XⅫhypoglossal nerve 2 9 Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Big Brains Matter More S=sensory M=motor B=both
Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Big Brains Matter More S=sensory M=motor B=both Mnemonics
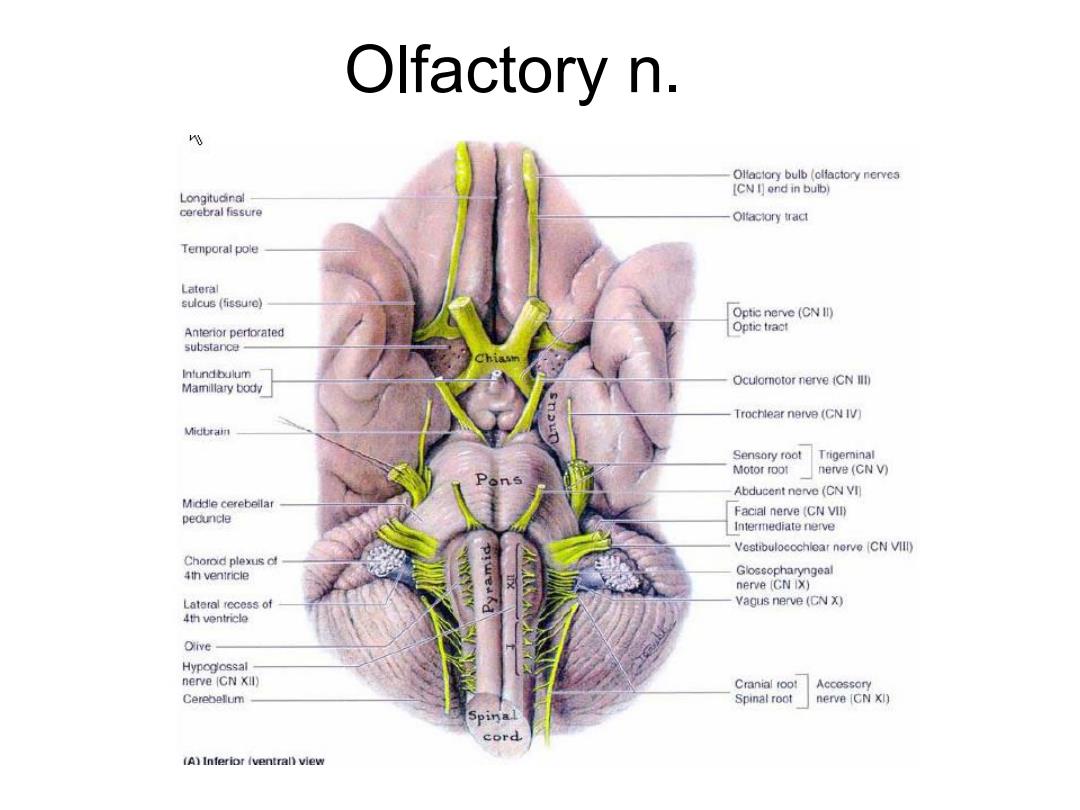
Olfactory n. Longitudinal cerebral fissure Oltactory tract Temporal pole Lateral sulcus (fissure) Antenor pertorated infundbulum Mamillary body Oculomotor nerve (CN Ill Trochlear nerve (CN IV) Sensory root Trigeminal Motor root nerve (CN V) Abducent nerve (CN VI] Middie cerebeilar pecuncle Facial nerve (CN VIl) Intermediate nerve Vestibuloecchiear nerve (CN VIll) Chorod plexus ct 4th ventricle Lateral recess of Vagus nerve (CN X) 4th ventricle Cranial toot Accessory Cerebelum Spinal root nerve (CN XI) (A)Inferior (ventral)view
Olfactory n
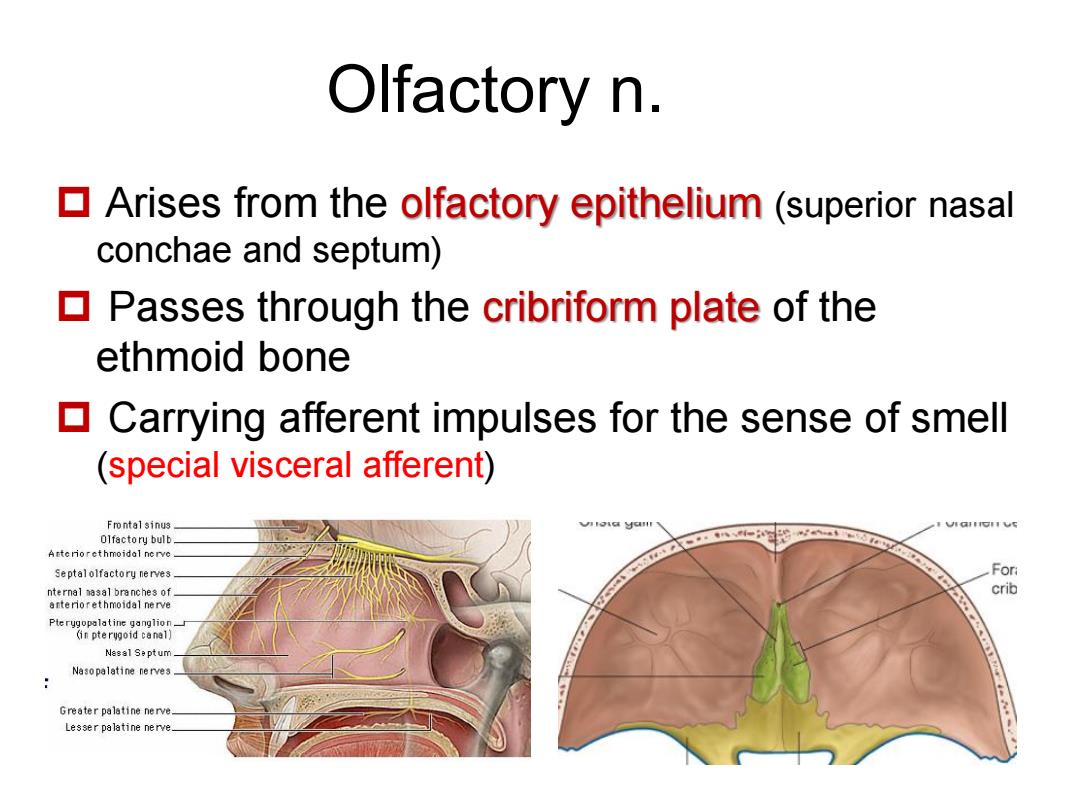
Olfactory n. Arises from the olfactory epithelium(superior nasal conchae and septum) Passes through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone ▣ Carrying afferent impulses for the sense of smell (special visceral afferent) Septalolfactory nerves For nternal nasal branches of crib arterorethmoidal nerve Nasal Se ptum Nasopalatine nerves. Greater palatine nerve. Lesser palatine nerve
Arises from the olfactory epithelium (superior nasal conchae and septum) Passes through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone Carrying afferent impulses for the sense of smell (special visceral afferent) Olfactory n