
大纲 Functional Language and MapReduce ■MapReduce Basic MapReduce Algorithm Design Hadoop and Java Practice 2
2 大纲 ◼ Functional Language and MapReduce ◼ MapReduce Basic ◼ MapReduce Algorithm Design ◼ Hadoop and Java Practice

NC&IS Functional Language and MapReduce
Functional Language and MapReduce

What is Functional Programming? In computer science,functional programming is a programming paradigm that treats computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions and avoids state and mutable data.It emphasizes the application of functions,in contrast with the imperative programming style that emphasizes changes in state.[1] 4
4 What is Functional Programming? ◼ In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm that treats computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions and avoids state and mutable data. It emphasizes the application of functions, in contrast with the imperative programming style that emphasizes changes in state.[1]
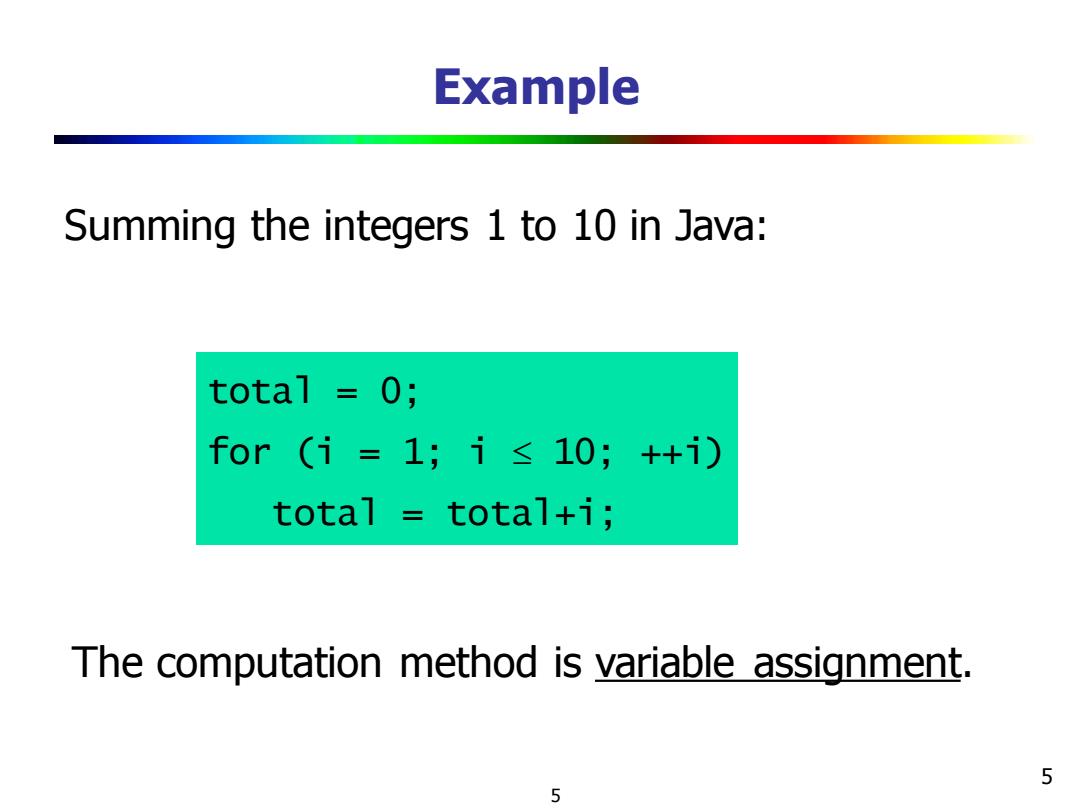
Example Summing the integers 1 to 10 in Java: total =0; for(i=1;i≤10;++1) total total+i; The computation method is variable assignment. 5 5
5 Example Summing the integers 1 to 10 in Java: total = 0; for (i = 1; i 10; ++i) total = total+i; The computation method is variable assignment. 5
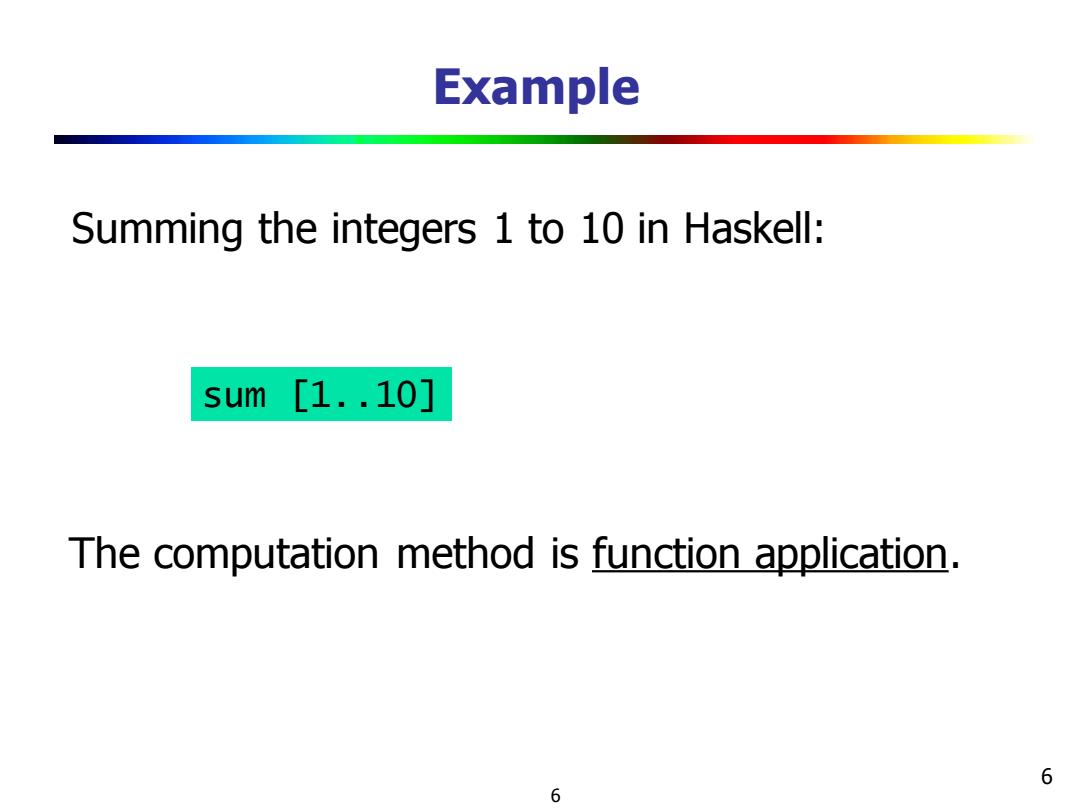
Example Summing the integers 1 to 10 in Haskell: sum[1..10] The computation method is function application. 6 6
6 Example Summing the integers 1 to 10 in Haskell: sum [1..10] The computation method is function application. 6

Why is it Useful? The abstract nature of functional programming leads to considerably simpler programs; It also supports a number of powerful new ways to structure and reason about programs. 7
7 Why is it Useful? ◼ The abstract nature of functional programming leads to considerably simpler programs; ◼ It also supports a number of powerful new ways to structure and reason about programs

Functional Programming Review Functional operations do not modify data structures: they always create new ones Original data still exists in unmodified form Data flows are implicit in program design Order of operations does not matter 8
8 Functional Programming Review ◼ Functional operations do not modify data structures: ◼ they always create new ones ◼ Original data still exists in unmodified form ◼ Data flows are implicit in program design ◼ Order of operations does not matter

Functional Programming Review fun foo(l:int list)= sum(I)mul(I)length(I) Order of sum()and mul(),etc does not matter They do not modify I 9
9 Functional Programming Review fun foo(l: int list) = sum(l) + mul(l) + length(l) ◼ Order of sum() and mul(), etc does not matter ◼ They do not modify l
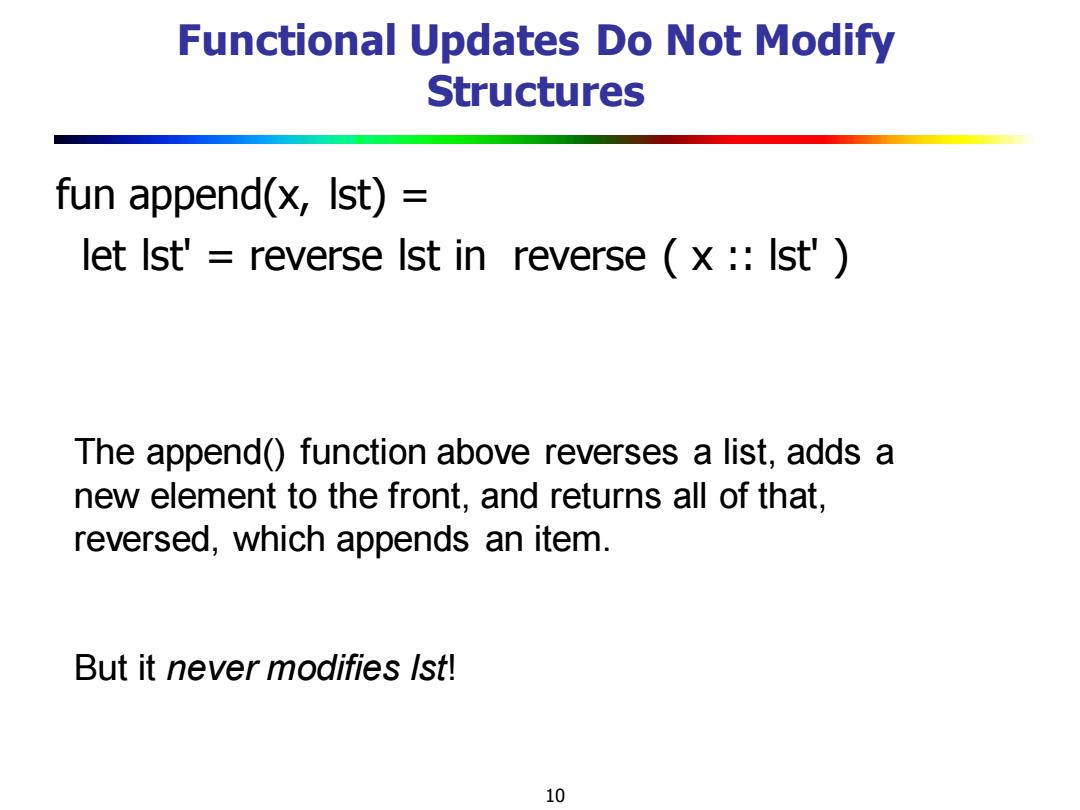
Functional Updates Do Not Modify Structures fun append(x,Ist) = let Ist'reverse Ist in reverse (x Ist') The append()function above reverses a list,adds a new element to the front,and returns all of that, reversed,which appends an item. But it never modifies Ist! 10
10 Functional Updates Do Not Modify Structures fun append(x, lst) = let lst' = reverse lst in reverse ( x :: lst' ) The append() function above reverses a list, adds a new element to the front, and returns all of that, reversed, which appends an item. But it never modifies lst!
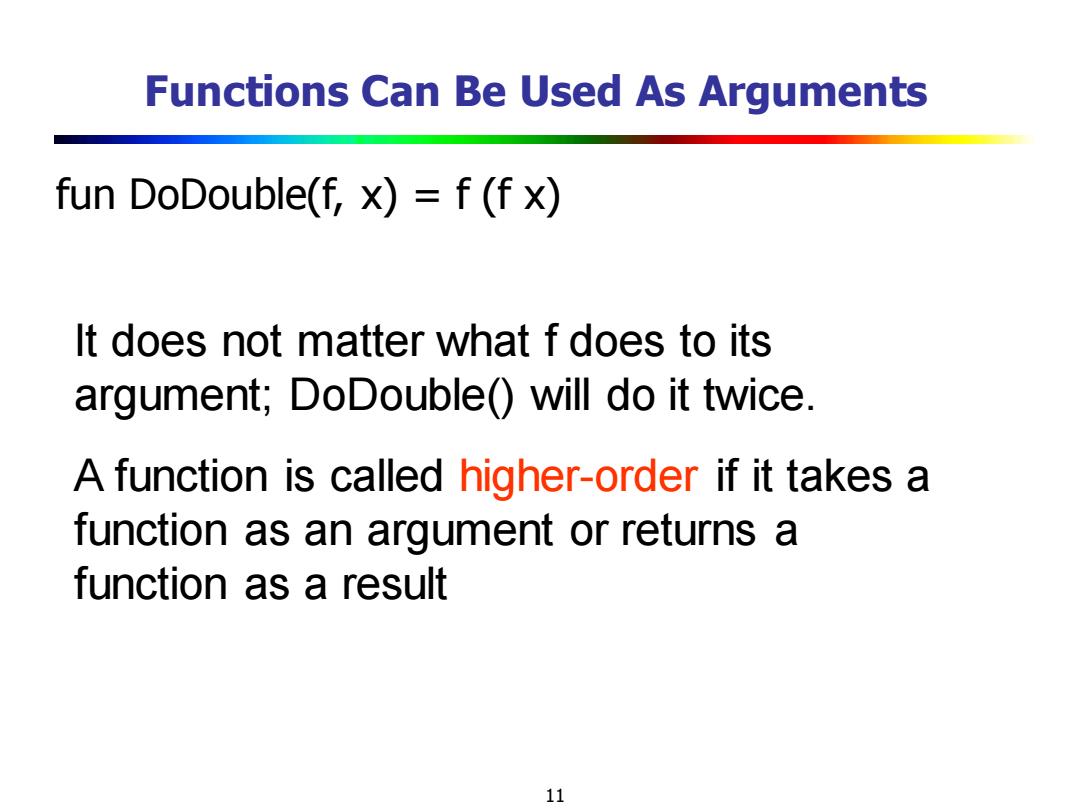
Functions Can Be Used As Arguments fun DoDouble(f,x)=f(f x) It does not matter what f does to its argument;DoDouble()will do it twice. A function is called higher-order if it takes a function as an argument or returns a function as a result 11
11 Functions Can Be Used As Arguments fun DoDouble(f, x) = f (f x) It does not matter what f does to its argument; DoDouble() will do it twice. A function is called higher-order if it takes a function as an argument or returns a function as a result