
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 COURSE SYLLABUS CIVIL ENGINEERING:FOUNDATION ENGINEERING INSTRUCTOR:SUNG-SIK PARK Division of Civil,Environmental and Urban Engineering Wonkwang University Office:1201 Engineering Building Tel:850-6716 E-mail:sspark@wku.ac.kr Web site:www.geocentrifuge.com Office hours:any time Lecture Room:Engineering Building409(class 1)/E刈生列Y((class2), Course Description:3 credits.Site investigation:foundation bearing capacity and settlement design of spread and combined footings,lateral earth pressures,retaining wall design;slope stability analysis,pile foundations. Textbook:Braja M.Das,Principles of Foundation Engineering,Sixth Edition,2007. (出巴))引号利6巴云卧)引金 References: Donald,P.Coduto,Foundation Design Principles and Practices,Second Edition Bowles.Foundation Analysis and Design Prerequisites by Topics: 1.Knowledge in soil mechanics especially shear strength of soil 2.Working knowledge in mechanics of materials is essential.This includes Statics and Strength of materials Course Objectives: Broad Objectives 1.Students will learn how to design shallow and deep foundations,retaining walls,and slopes. 2.Students will learn how to utilize their knowledge in soil mechanics to perform various types of engineering calculations.This includes consolidation analysis for foundations. and stability analysis of slopes and retaining walls. Learning Outcomes 1.Students will be able to design and analyze a variety of geotechnical engineering
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 1 COURSE SYLLABUS CIVIL ENGINEERING: FOUNDATION ENGINEERING fINSTRUCTOR: SUNG-SIK PARK Division of Civil, Environmental and Urban Engineering Wonkwang University fOffice: 1201 Engineering Building fTel: 850-6716 fE-mail: sspark@wku.ac.kr fWeb site: www.geocentrifuge.com fOffice hours: any time fLecture Room: Engineering Building 409(class 1) / 도시설계실(class 2), fCourse Description: 3 credits. Site investigation; foundation bearing capacity and settlement; design of spread and combined footings; lateral earth pressures; retaining wall design; slope stability analysis; pile foundations. fTextbook: Braja M. Das, Principles of Foundation Engineering, Sixth Edition, 2007. (번역판) 기초공학 제 6판 동화기술 fReferences: Donald, P. Coduto, Foundation Design Principles and Practices, Second Edition. Bowles, Foundation Analysis and Design fPrerequisites by Topics: 1. Knowledge in soil mechanics especially shear strength of soil 2. Working knowledge in mechanics of materials is essential. This includes Statics and Strength of materials. fCourse Objectives: Broad Objectives 1. Students will learn how to design shallow and deep foundations, retaining walls, and slopes. 2. Students will learn how to utilize their knowledge in soil mechanics to perform various types of engineering calculations. This includes consolidation analysis for foundations, and stability analysis of slopes and retaining walls. Learning Outcomes 1. Students will be able to design and analyze a variety of geotechnical engineering

Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 structures including foundations.piles.retaining walls.geosynthetic-reinforced soil structures,and slopes. 2.Students lear how to interact professionally among themselves during their assigned design projects where they will be divided into teams. 3.Students are responsible for submitting professionally-written reports for their design projects. 4.Students will present their projects to the class(10-15 minutes presentations) Topics Covered ·Review 1.Soil Properties and soil classification 2.Compaction 3.Stress analysis 4.Consolidation 5.Shear strength ·Topics 1.Shallow foundations 2.Mat foundation 3.Lateral earth pressure and retaining wall 4.Sheet piles 5.Piles in sand 6.Piles in clay 7.Slope stability .Projects 1.Project 1:Design of a spread footing 2.Project 2:Design of a retaining wall 3.Project 3:Design of piles Contribution of Course to Meeting the Professional Component: Students will learn how to utilize the soil mechanies knowledge they acquired in the Soil Mechanics course to perform various types of engineering calculations.This includes consolidation analysis for foundations and stability analysis of slopes and retaining walls. They will learn the basics of foundation engineering in this course.This includes the design of shallow and deep foundations.retaining walls,and slopes Relationship to Program Objectives: 1.Students use simple mathematics to derive relationships among soil properties.They use elementary partial differential equations to solve simple boundary-value flow and consolidation problems.Soil Mechanics.Statics.and Strength of Materials are heavily 2
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 2 structures including foundations, piles, retaining walls, geosynthetic-reinforced soil structures, and slopes. 2. Students learn how to interact professionally among themselves during their assigned design projects where they will be divided into teams. 3. Students are responsible for submitting professionally-written reports for their design projects. 4. Students will present their projects to the class (10–15 minutes presentations). fTopics Covered: • Review 1. Soil Properties and soil classification 2. Compaction 3. Stress analysis 4. Consolidation 5. Shear strength • Topics 1. Shallow foundations 2. Mat foundation 3. Lateral earth pressure and retaining wall 4. Sheet piles 5. Piles in sand 6. Piles in clay 7. Slope stability • Projects 1. Project 1: Design of a spread footing 2. Project 2: Design of a retaining wall 3. Project 3: Design of piles fContribution of Course to Meeting the Professional Component: Students will learn how to utilize the soil mechanics knowledge they acquired in the Soil Mechanics course to perform various types of engineering calculations. This includes consolidation analysis for foundations and stability analysis of slopes and retaining walls. They will learn the basics of foundation engineering in this course. This includes the design of shallow and deep foundations, retaining walls, and slopes. fRelationship to Program Objectives: 1. Students use simple mathematics to derive relationships among soil properties. They use elementary partial differential equations to solve simple boundary-value flow and consolidation problems. Soil Mechanics, Statics, and Strength of Materials are heavily

Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 utilized in this course 2.Students solve problems related to the theoretical part of this course. 3.Design of shallow and deep foundations,retaining walls,geosynthetic-reinforced soil structures,and design of slopes will be dealt with throughout this course 4.Projects include written reports and oral presentations. 5.Students who have a special interest in geotechnical engineering can pursue a higher degree in CE with emphasis on geotechnical engineering.They also can pursue a career in geotechnical engineering. 6.Occasionally,students will be assigned projects that will require teamwork Methods of Assessment: ·Graded Projects .Graded Examinations ·Instructor Judgment Mid term,Final Examinations Desirable Student Competencies Ability to work in team settings .Ability to prepare professional reports for design projects .Ability to use computers and some computer graphics
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 3 utilized in this course. 2. Students solve problems related to the theoretical part of this course. 3. Design of shallow and deep foundations, retaining walls, geosynthetic-reinforced soil structures, and design of slopes will be dealt with throughout this course. 4. Projects include written reports and oral presentations. 5. Students who have a special interest in geotechnical engineering can pursue a higher degree in CE with emphasis on geotechnical engineering. They also can pursue a career in geotechnical engineering. 6. Occasionally, students will be assigned projects that will require teamwork. fMethods of Assessment: • Graded Projects • Graded Examinations • Instructor Judgment • Mid term, Final Examinations fDesirable Student Competencies: • Ability to work in team settings • Ability to prepare professional reports for design projects • Ability to use computers and some computer graphics

Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 The following materials are copied from eBook Foundation Engineering by Prof.Bengt B.Broms at www.geoforum.com. Table of Contents 1.Aspects of foundation engineering 2.Soil mechanics 3.Geotechnical field investigations 4.Bearing capacity of foundations 5.Foundation settlements 6.Factors to consider in foundation design 7.Spread footing design 8.Special footings and beams on elastic foundations 9.Mat foundations 10.Lateral earth pressure 11.Soil retaining structures 12.Pile foundations-Single piles 13.Single piles-Dynamic analysis 14.Pile foundations-Pile Groups
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 4 The following materials are copied from eBook Foundation Engineering by Prof. Bengt B. Broms at www.geoforum.com. Table of Contents 1. Aspects of foundation engineering 2. Soil mechanics 3. Geotechnical field investigations 4. Bearing capacity of foundations 5. Foundation settlements 6. Factors to consider in foundation design 7. Spread footing design 8. Special footings and beams on elastic foundations 9. Mat foundations 10. Lateral earth pressure 11. Soil retaining structures 12. Pile foundations - Single piles 13. Single piles - Dynamic analysis 14. Pile foundations - Pile Groups
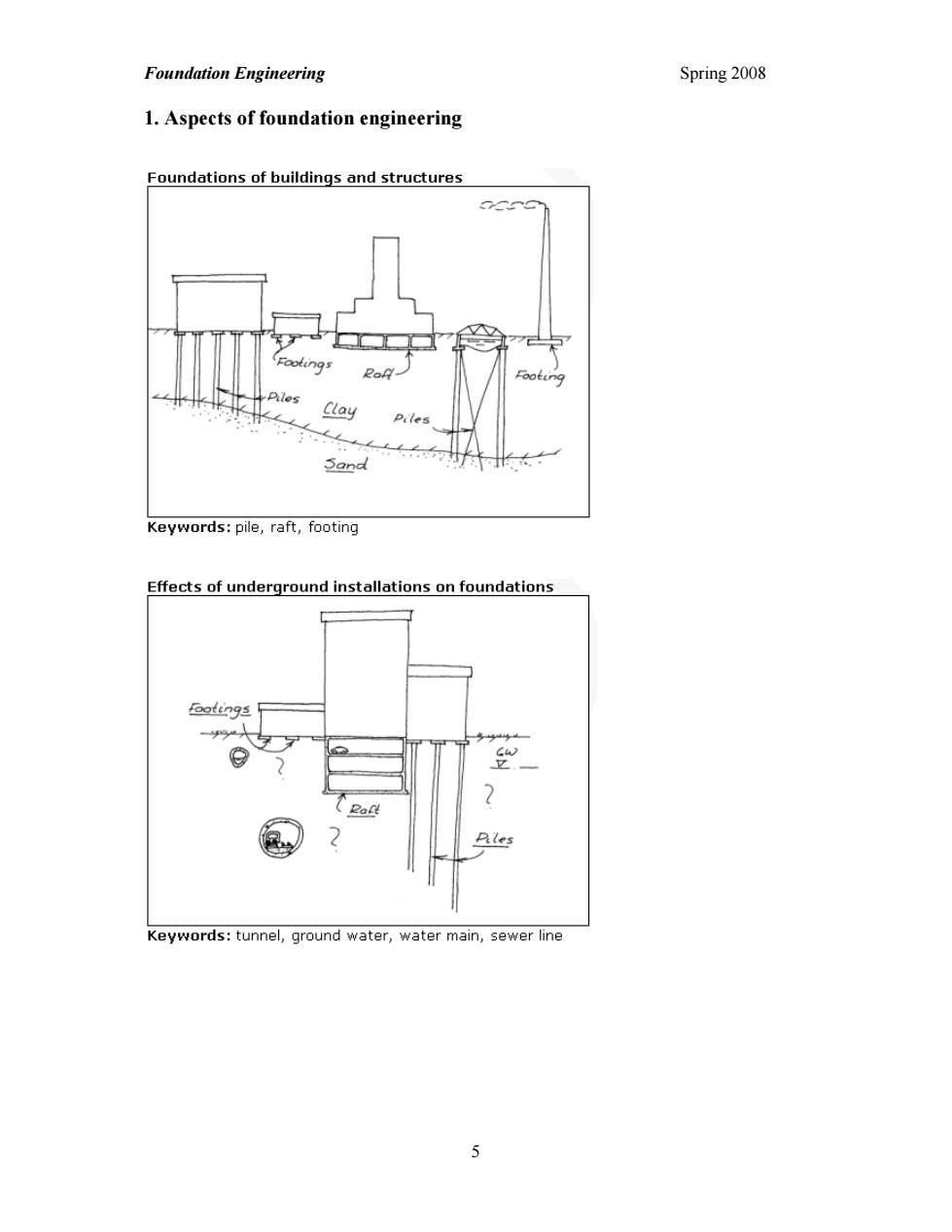
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 1.Aspects of foundation engineering Foundations of buildings and structures Keywords:pile,raft,footing Effects of underground installations on foundations Keywords:tunnel,ground water,water main,sewer line
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 5 1. Aspects of foundation engineering
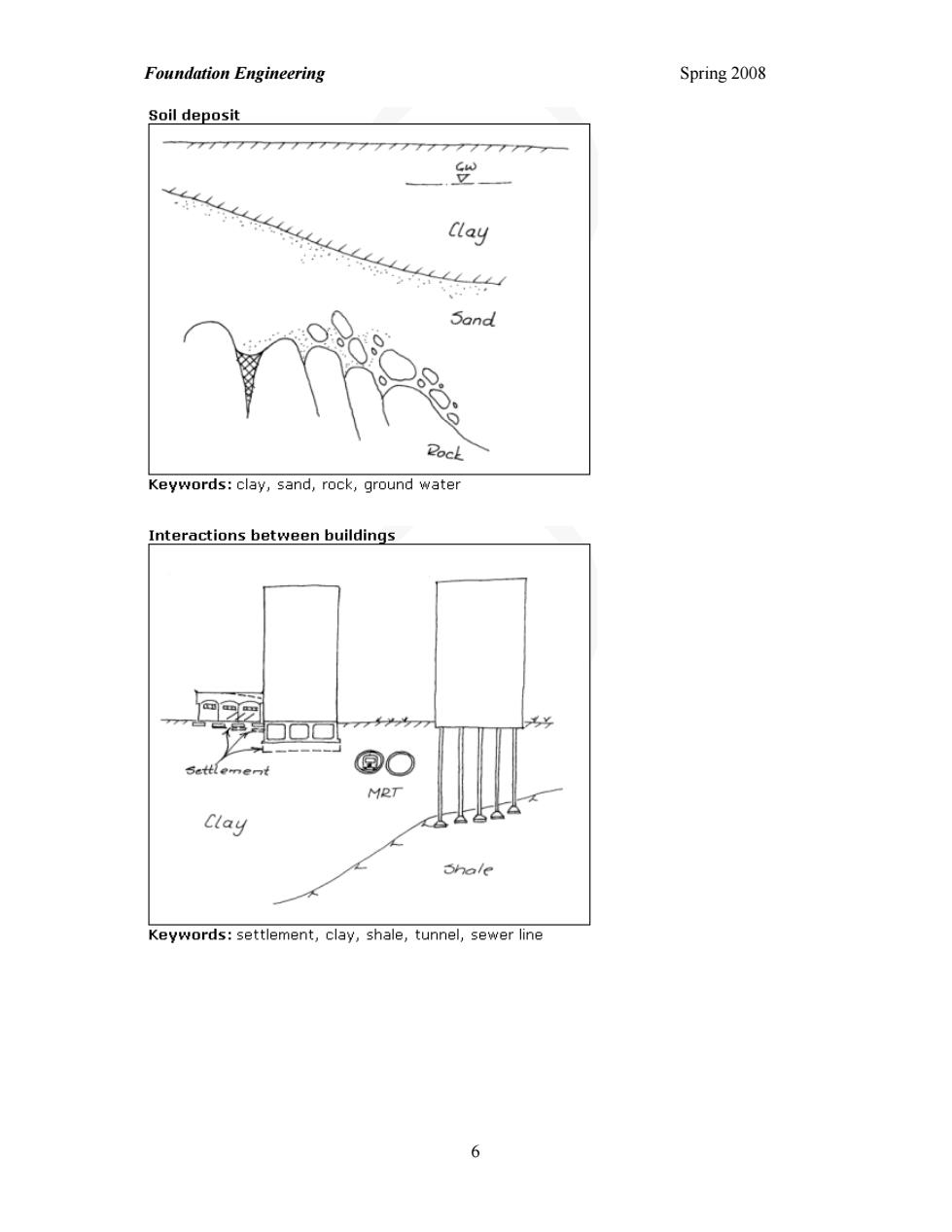
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 Soil deposit Clay Keywords:clay,sand,rock,ground water Interactions between buildings @○ MRT Clay Keywords:settlement,clay,shale,tunnel,sewer line 6
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 6
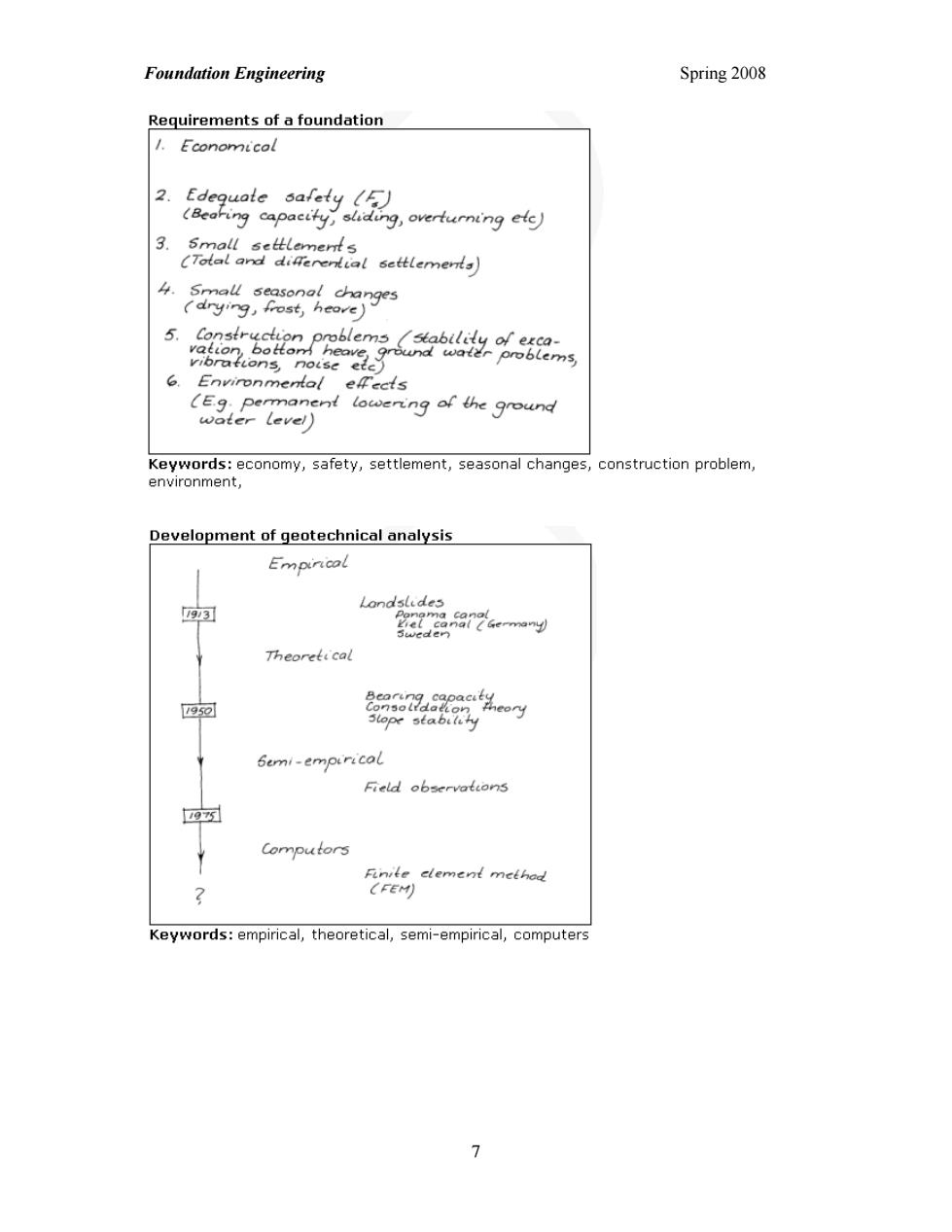
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 Requirements of a foundation 1.Economicol 2. iing,overturning ele 3a:2g点iame 4. 5. 2 6 ns al lowering of the ground Keywords:economy,safety,settlement,seasonal changes,construction problem environment, Development of geotechnical analysis 2287tm 四包 Bemi-empirical Field observalions Computors Keywords:empirical.theoretical.semi-empirical.computers >
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 7
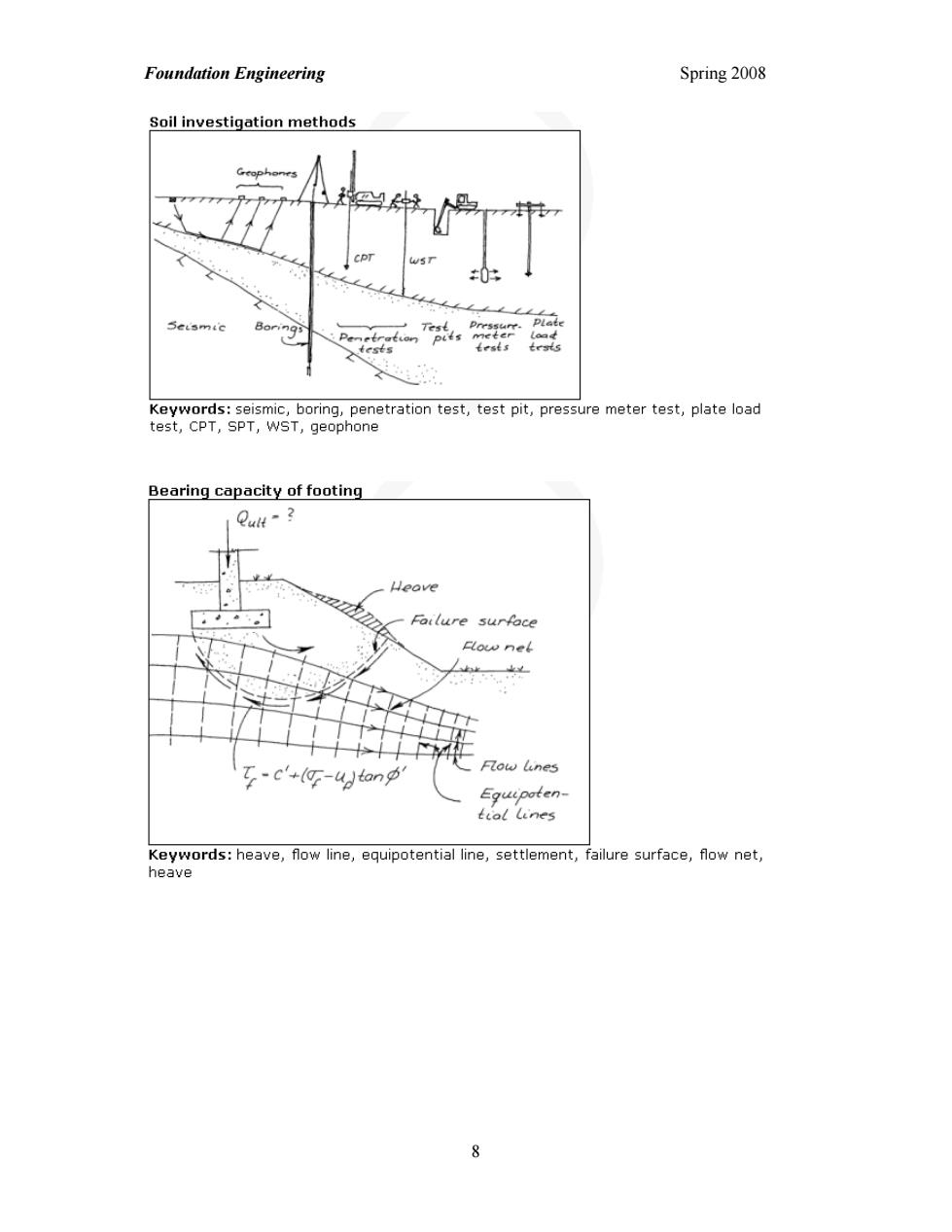
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 Soil investigation methods words:seismic,boring,penetration test,test pit,pressure meter test,plate load test,CPT,SPT,WST,geophone Bearing capacity of footing Failure surfoce Flow net c何-onp tial lines Kggords:heave,iowne,equpotentalne,setement,aiuresurface,fawnet
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 8
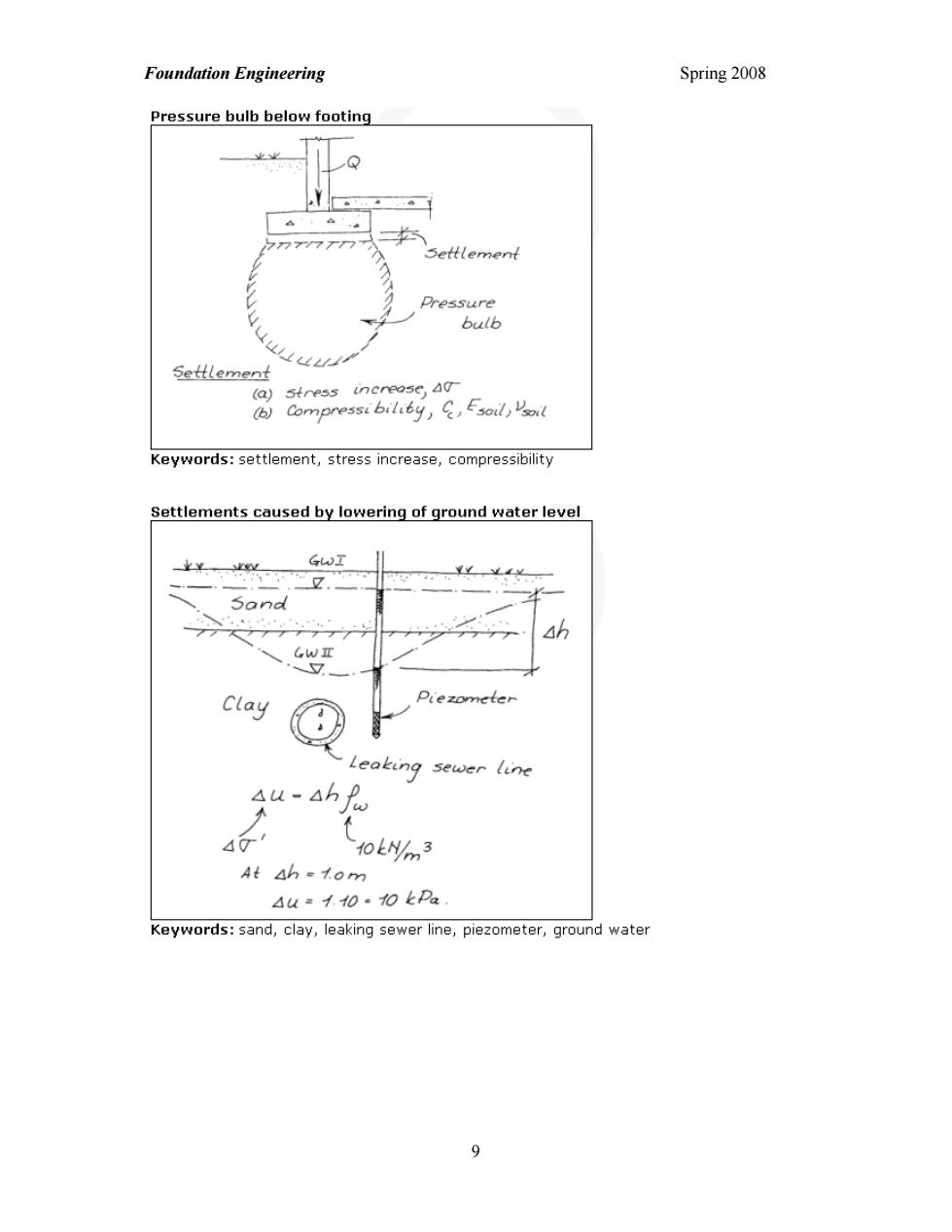
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 Pressure bulb below footing 业业 Q N✉ Pressure bulb Keywords:settlement,stress increase,compressibility Settlements caused by lowering of ground water level 46 clay Pie zometer Leaking sewer line A以-4hB 10LNI3 At ah-tom 4u=才0:0kDa Keywords:sand,clay,leaking sewer line,piezometer,ground water 9
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 9
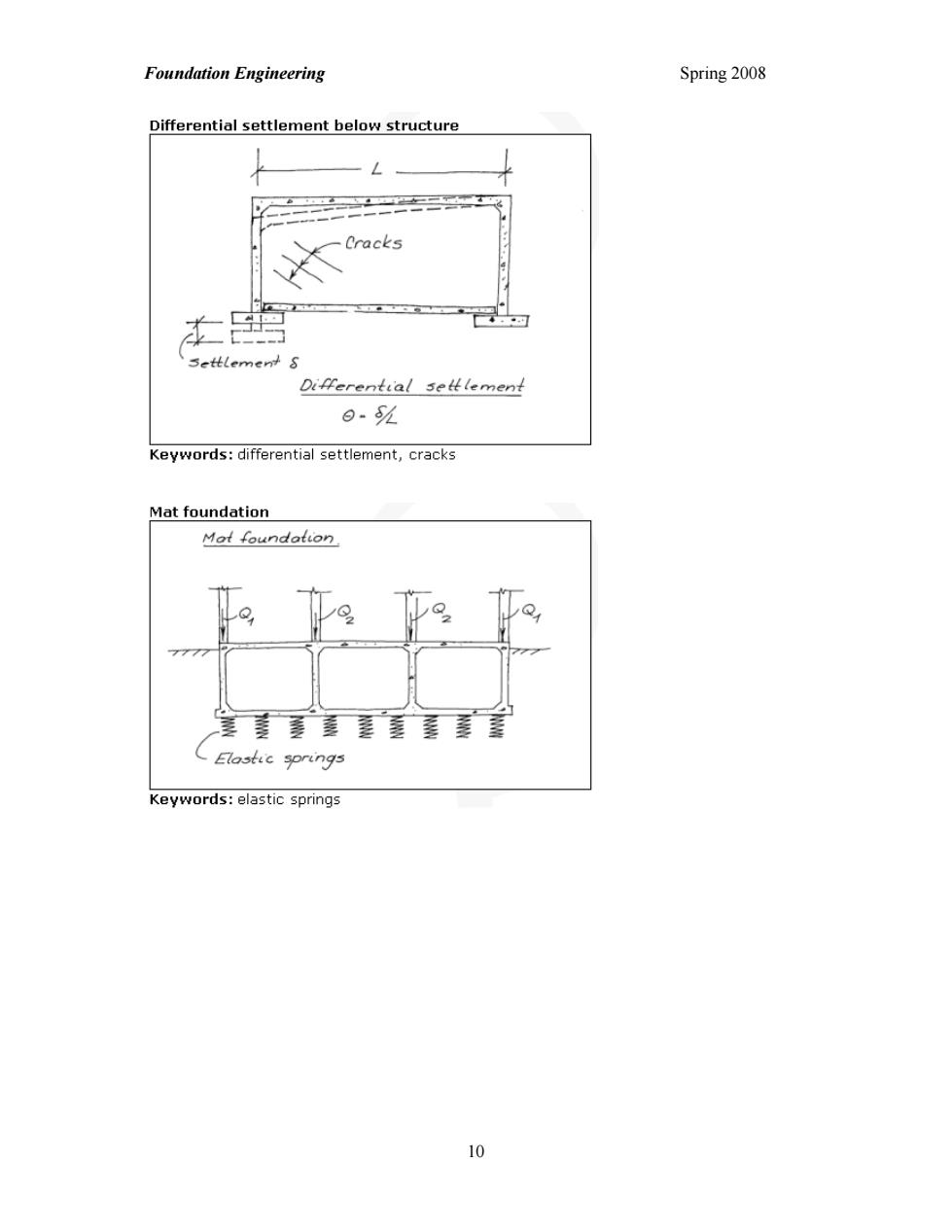
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 Differential settlement below structure ↓ L Differential seltlement 日.% Keywords:differential settlement,cracks Mat foundation Keywords:elastic springs o
Foundation Engineering Spring 2008 10