
空腔脏器常见疾病 北京协和医院放射科薛华丹
空腔脏器常见疾病 北京协和医院放射科 薛华丹

急腹症 ■检查方法及应用范围: -1、腹部平片:主要应于胃肠道穿孔性或梗阻性急腹症。 一2、钡灌肠造影:应用于肠套叠、扭转等梗阻性急腹症 的诊治。 -3、CT检查:可应用于所有急腹症检查,价值较高。 -4、超声检查:主要应用于实质性脏器外伤、腹腔积液、 局限性脓肿、结石与梗阻、肠套叠及急性炎症的检查
一 急腹症 检查方法及应用范围: – 1、腹部平片:主要应于胃肠道穿孔性或梗阻性急腹症。 – 2、钡灌肠造影:应用于肠套叠、扭转等梗阻性急腹症 的诊治。 – 3、CT检查:可应用于所有急腹症检查,价值较高。 – 4、超声检查:主要应用于实质性脏器外伤、腹腔积液、 局限性脓肿、结石与梗阻、肠套叠及急性炎症的检查

Possible causes of intestinal obstuction Congenital Inflammatory Lesion (extrinsic and intrinsic bowel) Trauma
Possible causes of intestinal obstuction Congenital Inflammatory Lesion (extrinsic and intrinsic bowel) Trauma
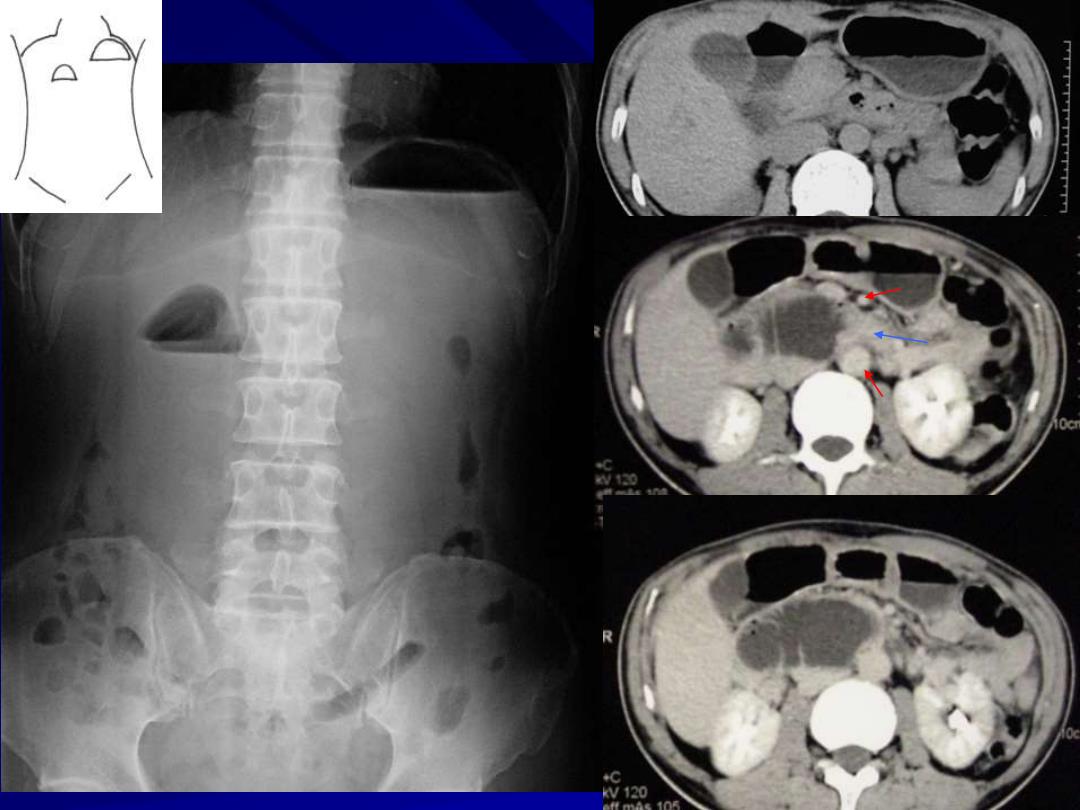

Classification Gastric outlet obstruction: only one/two air-fluid levels Homogeneous mass displacing transverse colon Duodenal obstruction: double-bubble sign; Frequently normal due to absence of gas from vomiting
Classification Gastric outlet obstruction: – only one/two air-fluid levels – Homogeneous mass displacing transverse colon Duodenal obstruction: – double-bubble sign; – Frequently normal due to absence of gas from vomiting
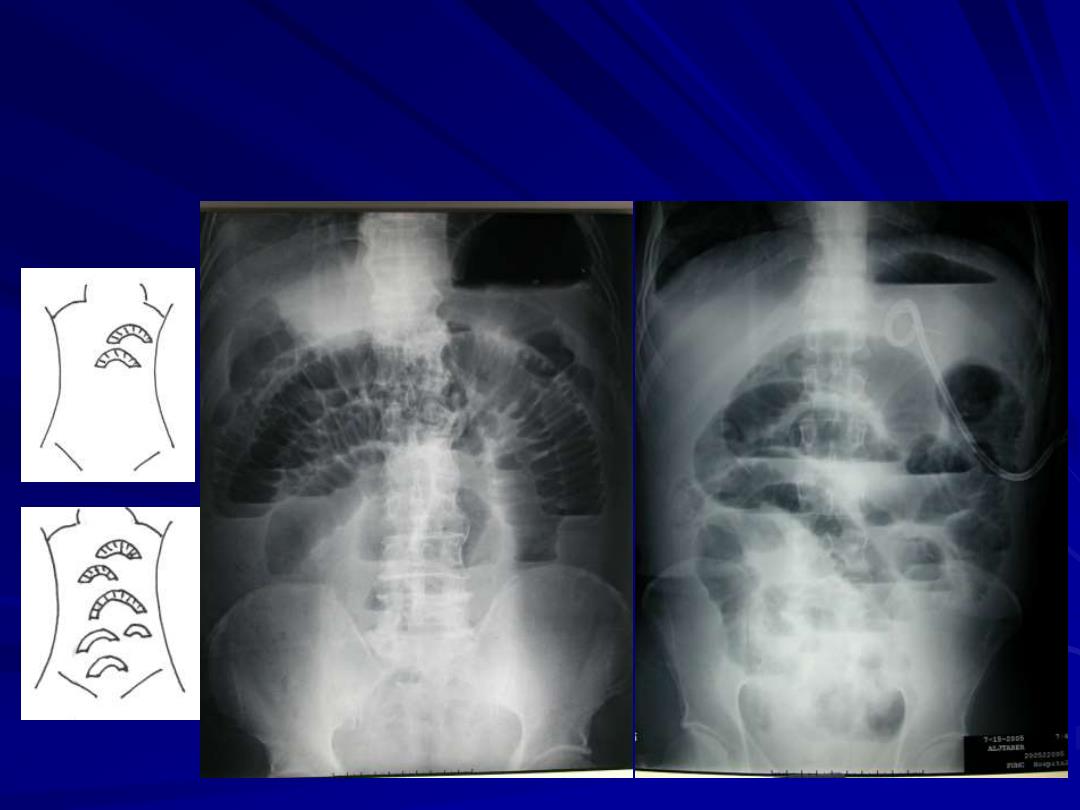

Classification Jejunal and ileal obstruction: Candy cane:>3 loops+>3cm gas-fluid levels+>3~5 hours onset Disparity in size between obstructed and normal loops Little/no gas stool in colon with complete mechanical obstruction after 12-24 hours Stepladder appearance;string-of-bead; Cave:fluid-distended loops may lead one to overlook obstruction!!!
Classification Jejunal and ileal obstruction: – Candy cane: >3 loops+>3cm gas-fluid levels+>3~5 hours onset – Disparity in size between obstructed and normal loops – Little/no gas + stool in colon with complete mechanical obstruction after 12-24 hours – Stepladder appearance; string-of-bead; Cave: fluid-distended loops may lead one to overlook obstruction!!!
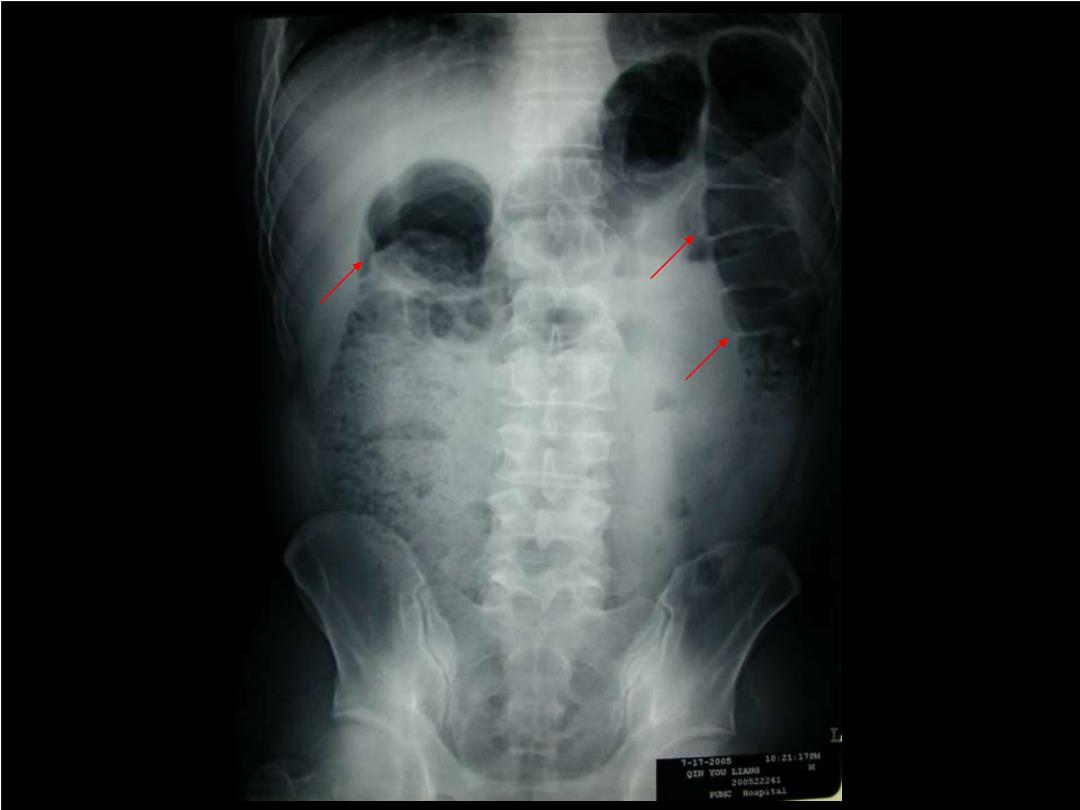

Classification ■Colonic obstruction Dilated colon only Dilated small bowel (incompetent ileo-cecal valve) Gas-fluid levels distal to hepatic flexure (fluid is normal in cecum and ascending colon) Cecum most dilated portion (>10cm will be critical)
Classification Colonic obstruction – Dilated colon only – Dilated small bowel (incompetent ileo-cecal valve) – Gas-fluid levels distal to hepatic flexure (fluid is normal in cecum and ascending colon) – Cecum most dilated portion (>10cm will be critical)
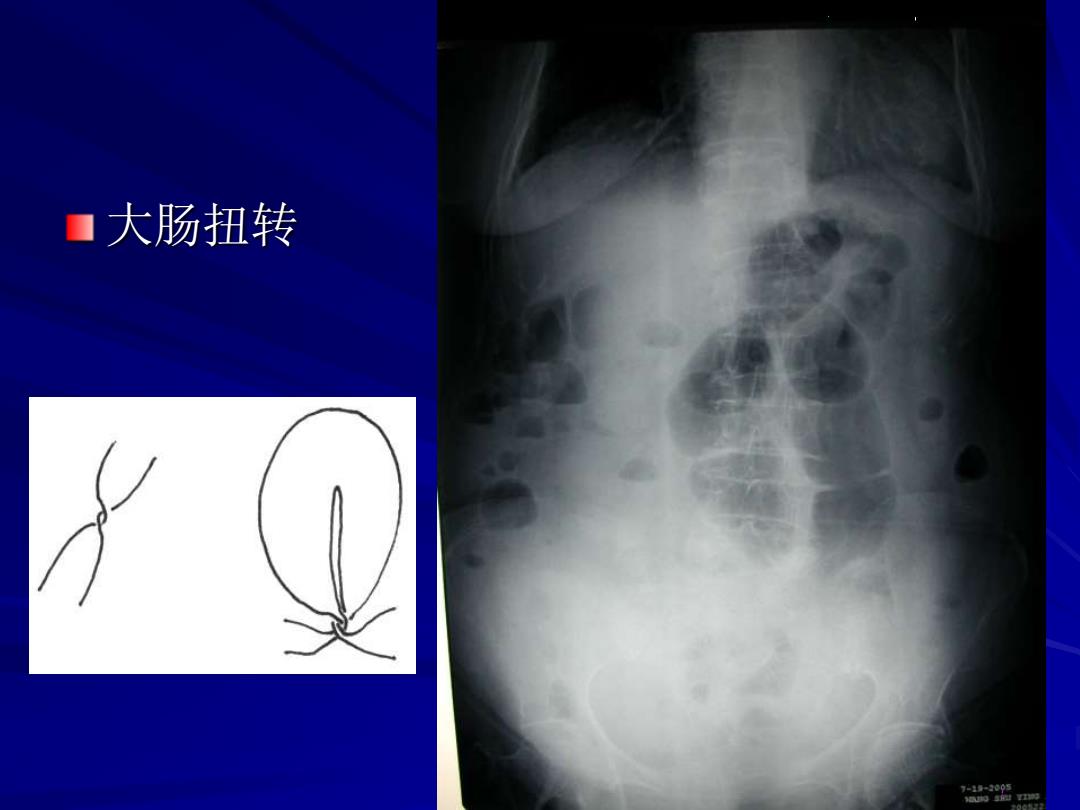
■大肠扭转
肠扭转 大肠扭转