
Bones and Joints PUMCH 2008
Bones and Joints PUMCH 2008
Imaging methods X-ray:multi-orientation;bilateral(knee) ■Computed tomography Magnetic resonance imaging ■Angiography ■Ultrasonography ■ Radionuclide imaging ■PET
Imaging methods ◼ X-ray: multi-orientation; bilateral(knee) ◼ Computed tomography ◼ Magnetic resonance imaging ◼ Angiography ◼ Ultrasonography ◼ Radionuclide imaging ◼ PET
Normal anatomy ■Classification: ■Structure ■Compact bone ■Spongy bone Shape ■Long tubular bone ■Short tubular bone ■Flat bone ■Irregular bone
Normal anatomy ◼ Classification : ◼ Structure ◼ Compact bone ◼ Spongy bone ◼ Shape ◼ Long tubular bone ◼ Short tubular bone ◼ Flat bone ◼ Irregular bone
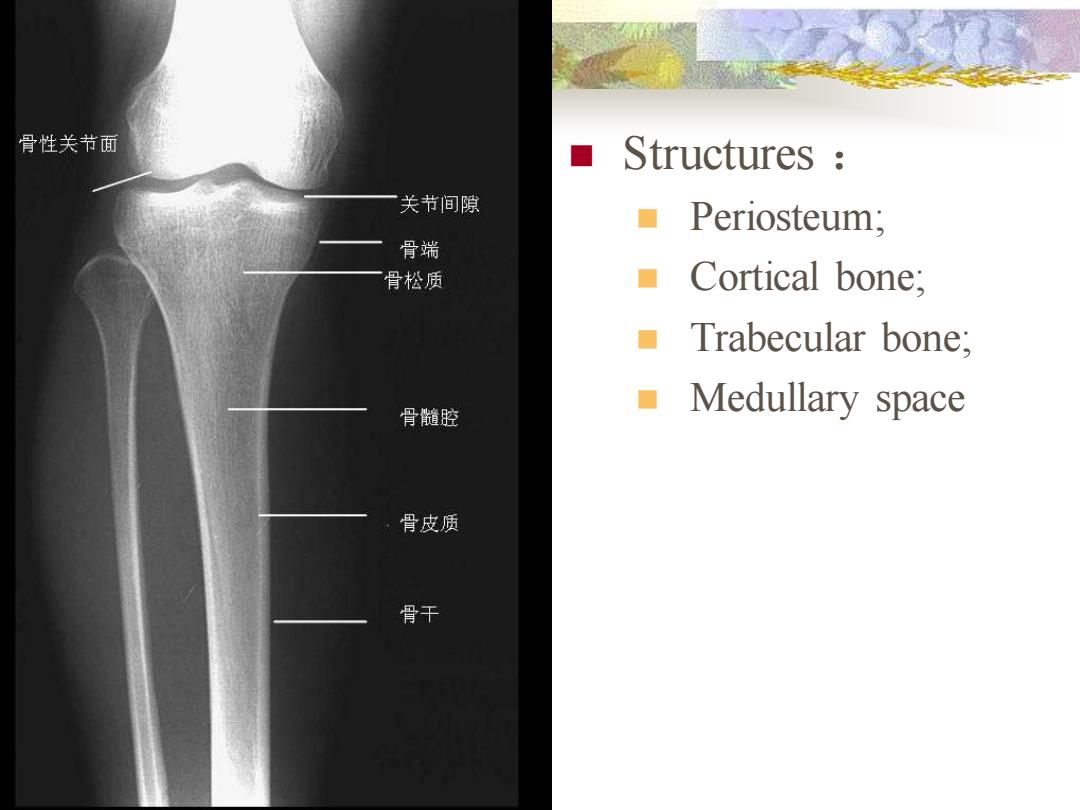
骨性关节面 ■Structures: 一关节间隙 ■Periosteum; 骨端 骨松质 ■Cortical bone; ■Trabecular bone, 骨髓腔 ■Medullary space 骨皮质 骨干
◼ Structures : ◼ Periosteum; ◼ Cortical bone; ◼ Trabecular bone; ◼ Medullary space
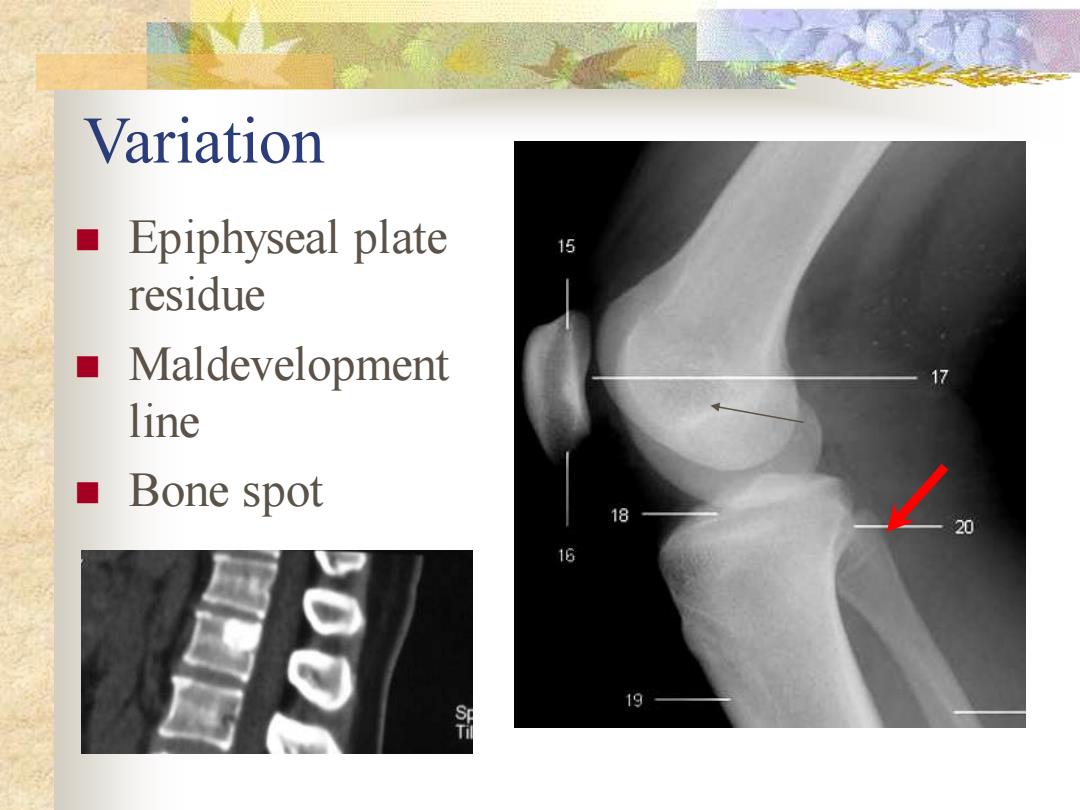
Variation ■Epiphyseal plate 15 residue ■Maldevelopment line ■ Bone spot 16 19
Variation ◼ Epiphyseal plate residue ◼ Maldevelopment line ◼ Bone spot
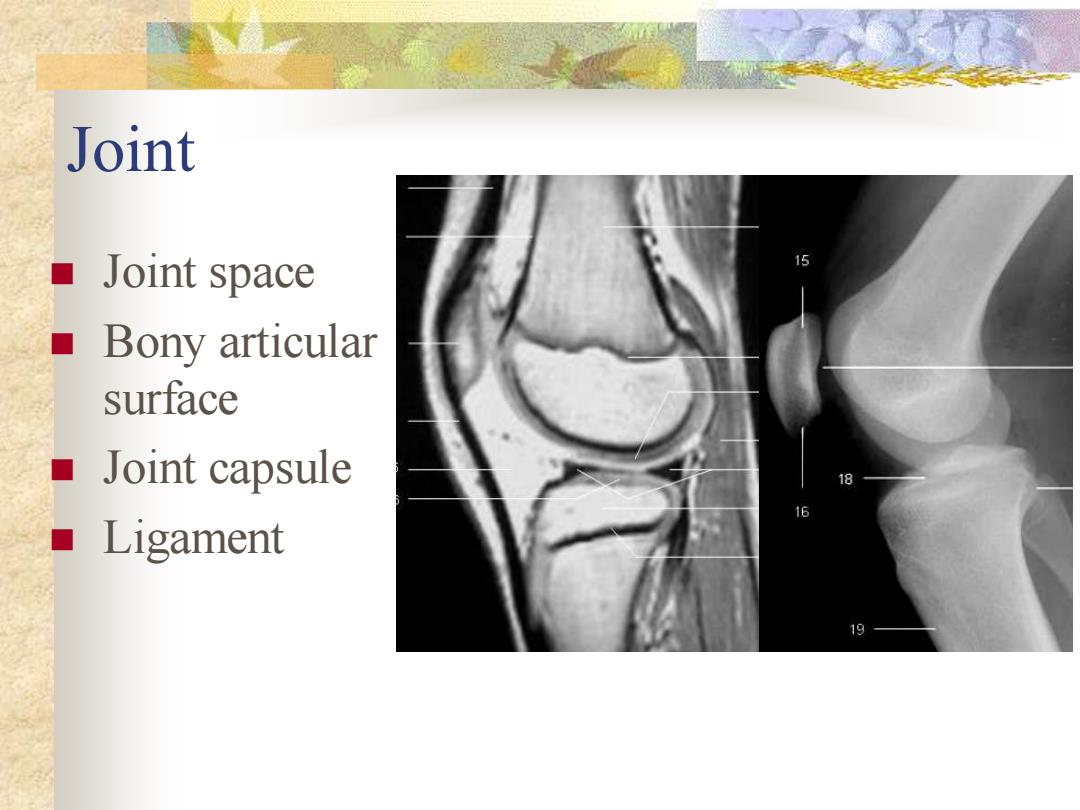
Joint ■Joint space ■Bony articular surface ■Joint capsule ■Ligament
Joint ◼ Joint space ◼ Bony articular surface ◼ Joint capsule ◼ Ligament
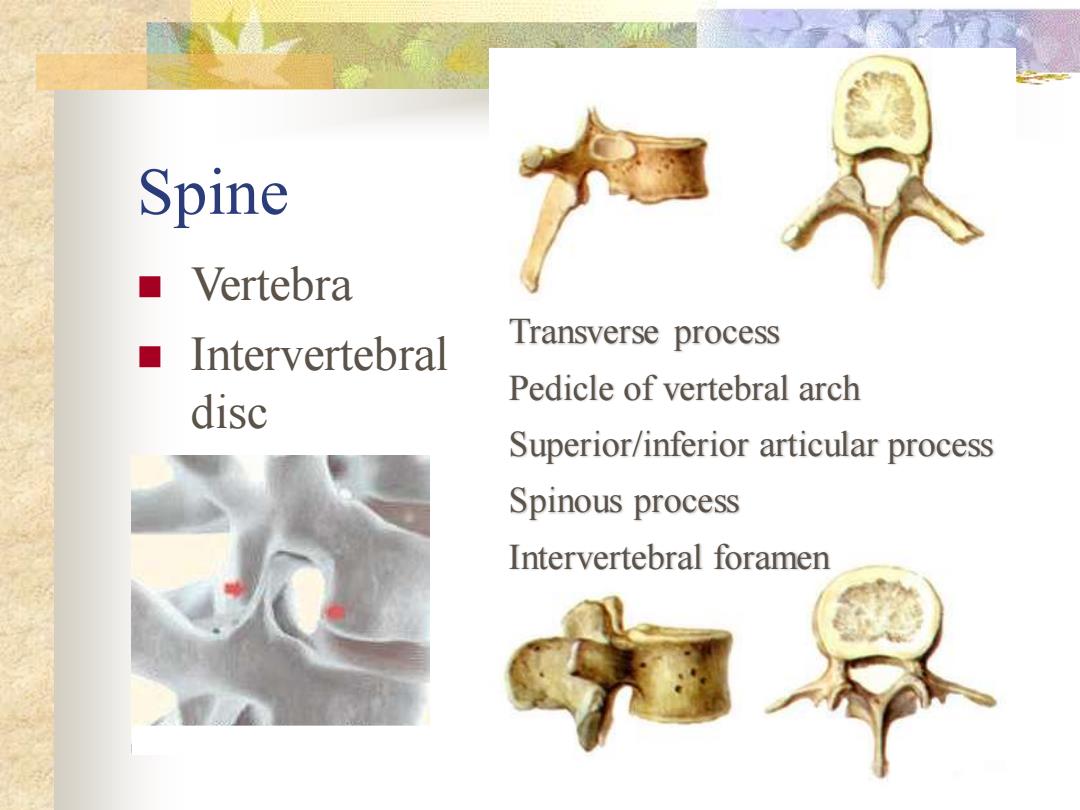
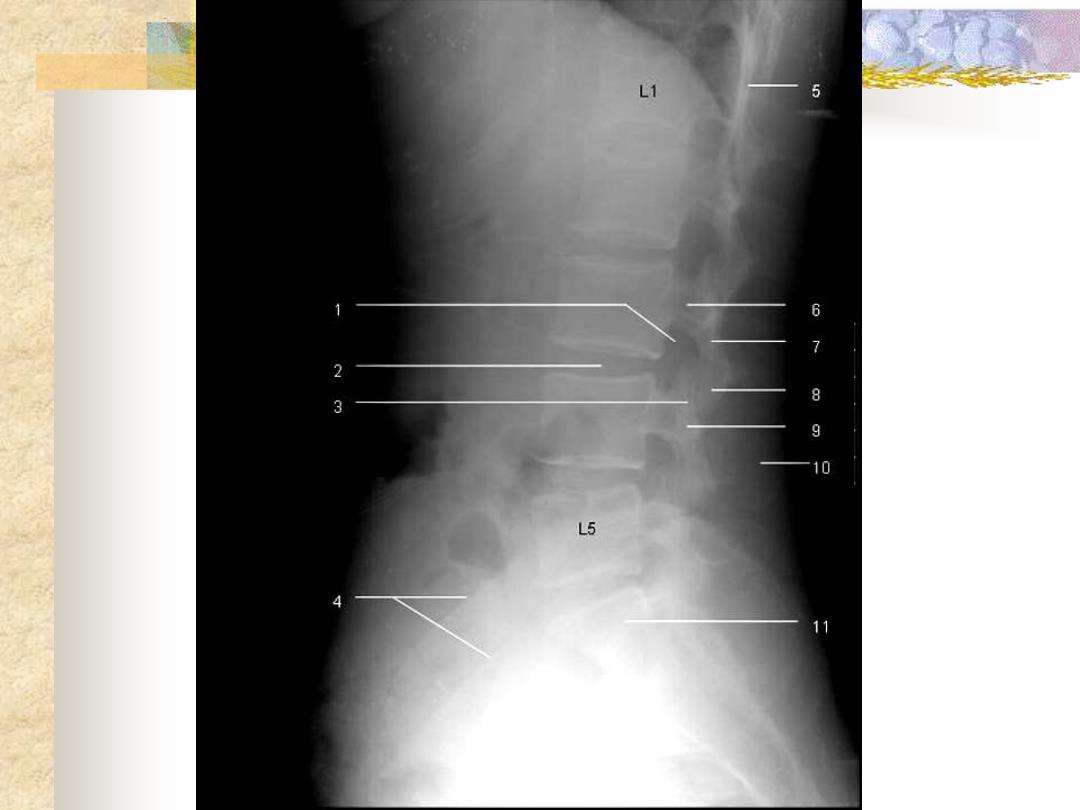
Spine ■Vertebra ■Intervertebral Transverse process Pedicle of vertebral arch disc Superior/inferior articular process Spinous process Intervertebral foramen
Spine ◼ Vertebra ◼ Intervertebral disc Transverse process Pedicle of vertebral arch Superior/inferior articular process Spinous process Intervertebral foramen
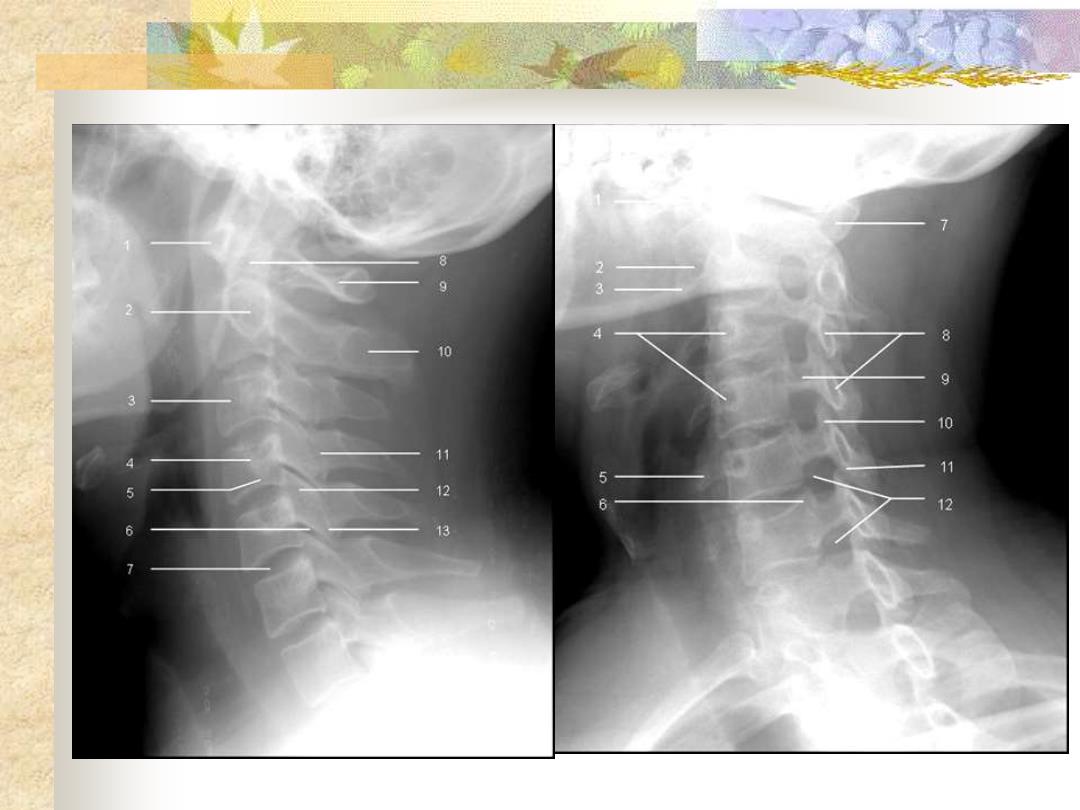
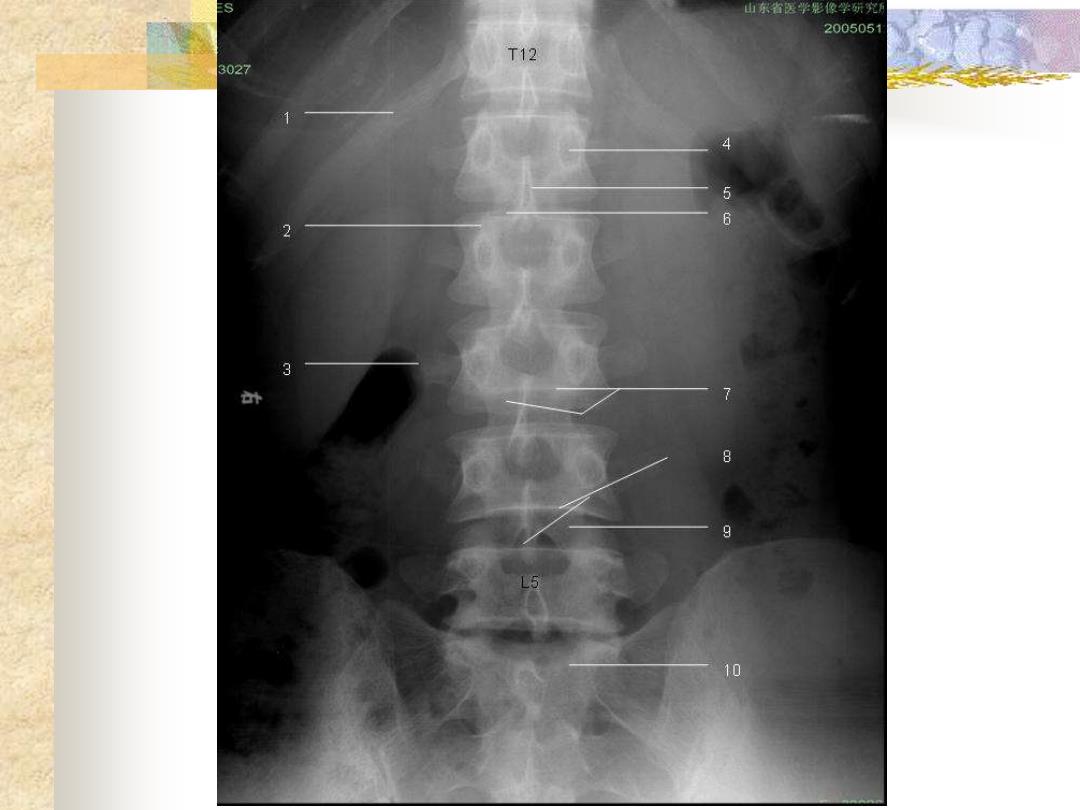
8