
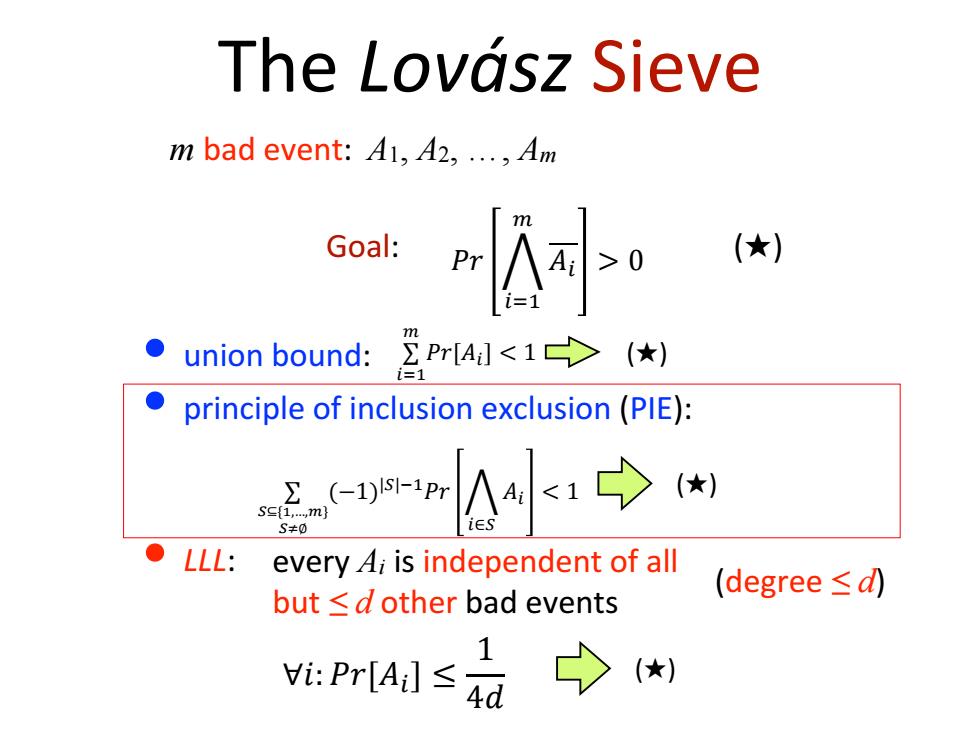
The Lovasz sieve m bad event:41,42,...,Am Goal: 小 (★) union bound:Pr[A (★) ● principle of inclusion exclusion(PIE): s=2-1051r 小:→ S≠0 ●LLL: every 4;is independent of all (degree≤ but≤d other bad events i:Pr[A]≤4d
The Lovász Sieve m bad event: A1, A2, …, Am Goal: • union bound: • principle of inclusion exclusion (PIE): (★) ∑ 𝑖=1 𝑚 𝑃𝑟[𝐴𝑖 ] 0
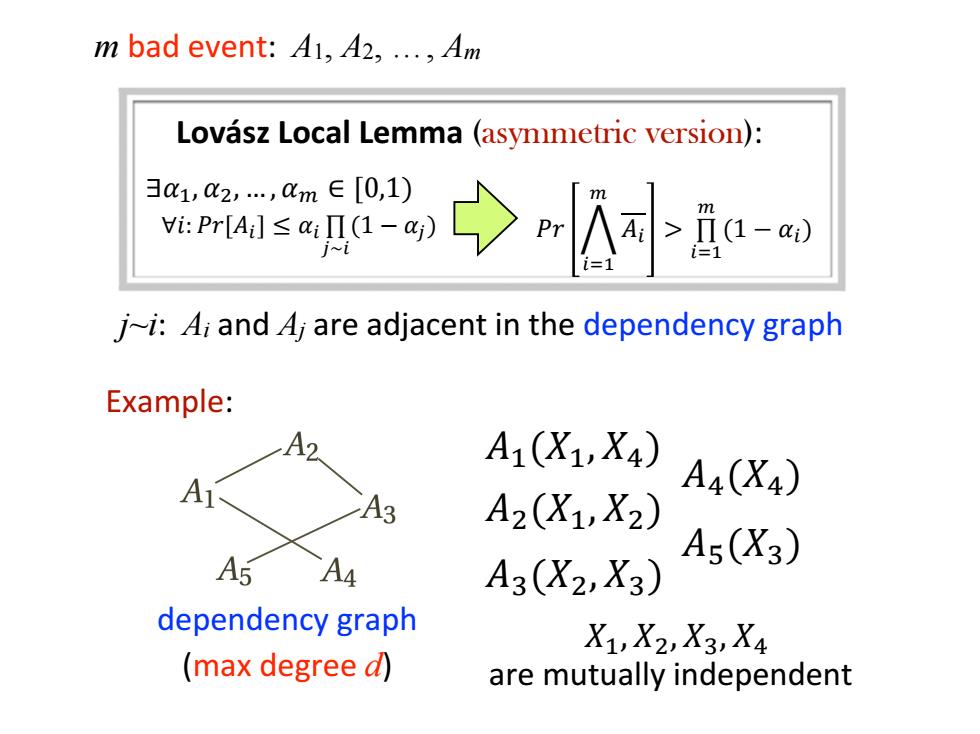
m bad event:A1,42,...4m Lovasz Local Lemma (asymmetric version): 3a1,Q2,…,Qm∈[0,1) Vi:Pr[A≤aiI-) 〉m m Ha-@) j~i:A;and 4j are adjacent in the dependency graph Example: A2 A1(X1,X4) A4(X4) A3 A2(X1,X2) A5(X3) A5 A4 A3(X2,X3) dependency graph X1,X2,X3,X4 (max degree d) are mutually independent
m bad event: A1, A2, …, Am 𝐴1(𝑋1, 𝑋4) 𝐴2(𝑋1, 𝑋2) 𝐴3(𝑋2, 𝑋3) 𝐴4(𝑋4) 𝐴5(𝑋3) 𝑋1, 𝑋2, 𝑋3, 𝑋4 are mutually independent dependency graph Example: (max degree d) Lovász Local Lemma (asymmetric version): 𝑃𝑟 ሥ 𝑖=1 𝑚 𝐴𝑖 > ∏ 𝑖=1 𝑚 (1 − 𝛼𝑖) ∃𝛼1, 𝛼2, … , 𝛼𝑚 ∈ [0,1) ∀𝑖: 𝑃𝑟[𝐴𝑖 ] ≤ 𝛼𝑖 ∏ 𝑗∼𝑖 (1 − 𝛼𝑗) j~i: Ai and Aj are adjacent in the dependency graph
The Lovasz Sieve m bad event:41,42,...Am Goal: () ● union bound:Pr[A (★) ● principle of inclusion exclusion(PIE): ∑(-1)s-1Pr ssf1,...m} S≠0 LLL: every 4;is independent of all (degree≤d) but≤d other bad events i:Pr[Ail≤4d (女)
The Lovász Sieve m bad event: A1, A2, …, Am Goal: • union bound: • principle of inclusion exclusion (PIE): (★) ∑ 𝑖=1 𝑚 𝑃𝑟[𝐴𝑖 ] 0
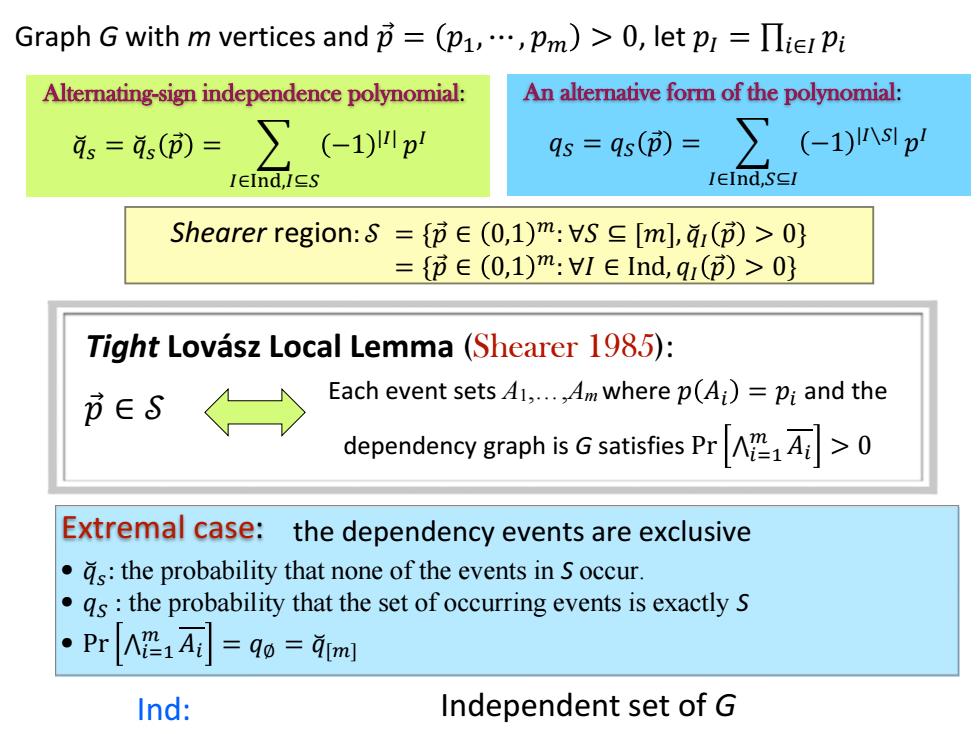
Graph G with m vertices and节=(p1,…,pm)>0,let pr=Πte Pi Alternating-sign independence polynomial: An alternative form of the polynomial: 。=,()=∑(-1)叫川p 9s=qs()= ∑(-1)nsp IEInd,IES IEInd,SEI Shearer region:s={i∈(0,1)m:S∈[m],ai()>0} ={i∈(0,1)m:H1∈Ind,qu()>0} Tight Lovasz Local Lemma(Shearer 1985): 币ES Each event sets 41,...,4m where p(Ai)=pi and the dependency graph isGsatisfies Pr Extremal case:the dependency events are exclusive ds:the probability that none of the events in s occur. .qs:the probability that the set of occurring events is exactly s ·Pr∧1A=qo=4m Ind: Independent set of G
Graph G with m vertices and 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝑝1, ⋯ , 𝑝𝑚 > 0, let 𝑝𝐼 = ∏𝑖∈𝐼 𝑝𝑖 Alternating-sign independence polynomial: 𝑞෬𝑠 = 𝑞෬𝑠 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝐼∈Ind,𝐼⊆𝑆 −1 |𝐼| 𝑝 𝐼 An alternative form of the polynomial: 𝑞𝑆 = 𝑞𝑆 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝐼∈Ind,𝑆⊆𝐼 −1 |𝐼∖𝑆| 𝑝 𝐼 Shearer region: 𝒮 = {𝑝 Ԧ ∈ 0,1 𝑚: ∀𝑆 ⊆ [𝑚], 𝑞෬𝐼 𝑝 Ԧ > 0} = {𝑝 Ԧ ∈ 0,1 𝑚: ∀𝐼 ∈ Ind, 𝑞𝐼 𝑝 Ԧ > 0} Tight Lovász Local Lemma (Shearer 1985): Each event sets A1,…,Am where 𝑝 𝐴𝑖 = 𝑝𝑖 and the dependency graph is G satisfies Pr ٿ=��1 𝑚 𝐴𝑖 > 0 𝑝 Ԧ ∈ 𝒮 Ind: Independent set of G Extremal case: • 𝑞෬𝑠 : the probability that none of the events in S occur. • 𝑞𝑆 : the probability that the set of occurring events is exactly S • Pr ٿ=��1 𝑚 𝐴𝑖 = 𝑞∅ = 𝑞෬[𝑚] the dependency events are exclusive

Symmetric Asymmetric Cluster Shearer's LLL LLL Expansion Lemma
Shearer ’s Lemma Cluster Expansion Asymmetric LLL Symmetric LLL

Example:the r-partite Turan problem Consider an r-partite graph,at least plVilVil edges between every pair (Vi,Vi). Va V V2 Question:at what density p must G contain K,?
Question: at what density 𝜌 must G contain 𝐾𝑟? Example: the r-partite Turán problem Consider an r-partite graph, at least 𝜌 𝑉𝑖 |𝑉𝑗 | edges between every pair (𝑉𝑖 , 𝑉𝑗)

Graph G with m vertices andp=(p1,,Pm)>0,let pr=Ilie Pi Alternating-sign independence polynomial: An alternative form of the polynomial: 。=。(例=∑(-1)四p 9s=qs()= ∑(10np IEInd,IES IEInd,SEI Shearer region:S =pE(0,1)m:VS [m],qi(p)>0 ={i∈(0,1)m:I∈Ind,q(p)>0} Tight Lovasz Local Lemma (Shearer 1985): 币eS Each event sets 41,...,4m where p(Ai)=pi and the dependency graph is Gsatisfies Pr Extremal case:the dependency events are exclusive ds:the probability that none of the events in S occur. .qs:the probability that the set of occurring events is exactly s ·PrA1A=qo=am Ind: Independent set of G
Alternating-sign independence polynomial: 𝑞෬𝑠 = 𝑞෬𝑠 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝐼∈Ind,𝐼⊆𝑆 −1 |𝐼| 𝑝 𝐼 An alternative form of the polynomial: 𝑞𝑆 = 𝑞𝑆 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝐼∈Ind,𝑆⊆𝐼 −1 |𝐼∖𝑆| 𝑝 𝐼 Shearer region: 𝒮 = {𝑝 Ԧ ∈ 0,1 𝑚: ∀𝑆 ⊆ [𝑚], 𝑞෬𝐼 𝑝 > 0} = {𝑝 Ԧ ∈ 0,1 𝑚: ∀𝐼 ∈ Ind, 𝑞𝐼 𝑝 > 0} Tight Lovász Local Lemma (Shearer 1985): Each event sets A1,…,Am where 𝑝 𝐴𝑖 = 𝑝𝑖 and the dependency graph is G satisfies Pr ٿ=��1 𝑚 𝐴𝑖 > 0 𝑝 Ԧ ∈ 𝒮 Ind: Independent set of G Extremal case: • 𝑞෬𝑠 : the probability that none of the events in S occur. • 𝑞𝑆 : the probability that the set of occurring events is exactly S • Pr ٿ=��1 𝑚 𝐴𝑖 = 𝑞∅ = 𝑞෬[𝑚] the dependency events are exclusive Graph G with m vertices and 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝑝1, ⋯ , 𝑝𝑚 > 0, let 𝑝𝐼 = ∏𝑖∈𝐼 𝑝𝑖
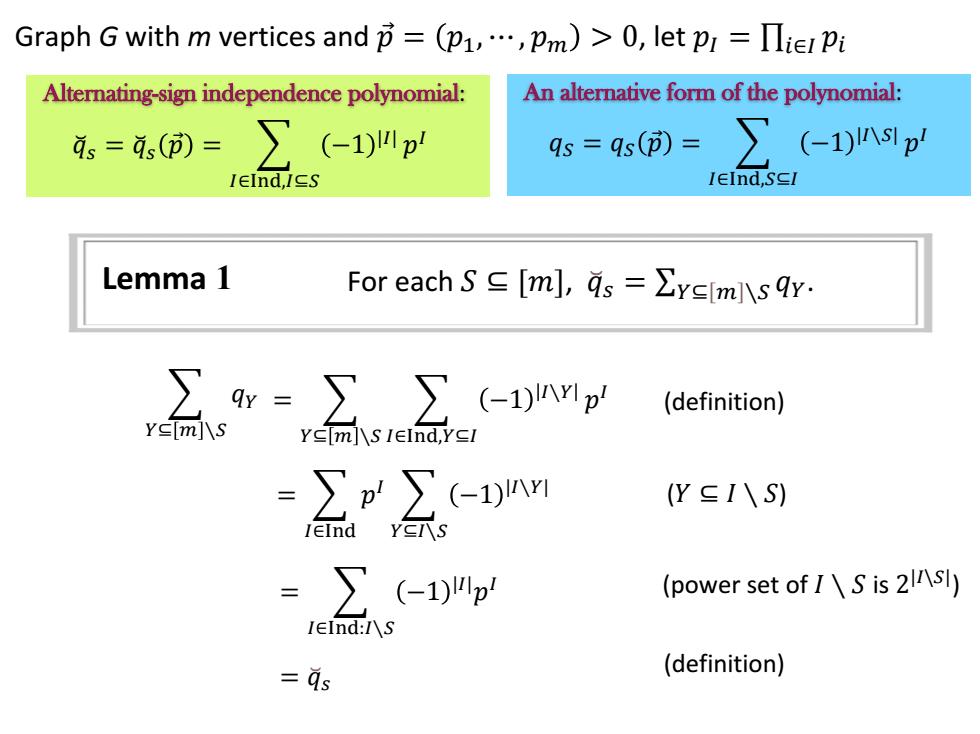
Graph G with m vertices and节=(p1,…,pm)>0,let pr=Πte Pi Alternating-sign independence polynomial: An alternative form of the polynomial: 。=,()=∑(-1)叫川p qs=qs(D=∑(←1)s1p IEInd,IES IEInd,SCI Lemma 1 For each S∈[ml,as=∑YEIml\sqr ∑9w=∑∑(-1)nwp (definition) YE[ml\S Y≤m]\s IEInd,Ycl =∑p'∑(-Dnm (Y∈I\S) =∑(-1)p (power set of IS is 2\5l) IEInd:I\S as (definition)
Lemma 1 For each 𝑆 ⊆ [𝑚], 𝑞 ෬ 𝑠 = ∑𝑌⊆ 𝑚 ∖𝑆 𝑞𝑌. (definition) 𝑌⊆ 𝑚 ∖𝑆 𝑞𝑌 = 𝑌⊆ 𝑚 ∖𝑆 𝐼∈Ind,𝑌⊆𝐼 −1 𝐼∖𝑌 𝑝 𝐼 = 𝐼∈Ind 𝑝 𝐼 𝑌⊆𝐼∖𝑆 −1 |𝐼∖𝑌| (𝑌 ⊆ 𝐼 ∖ 𝑆) = 𝐼∈Ind:𝐼∖𝑆 −1 |𝐼|𝑝 𝐼 (power set of 𝐼 ∖ 𝑆 is 2 |𝐼\𝑆| ) = 𝑞෬𝑠 (definition) Alternating-sign independence polynomial: 𝑞෬𝑠 = 𝑞෬𝑠 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝐼∈Ind,𝐼⊆𝑆 −1 |𝐼| 𝑝 𝐼 An alternative form of the polynomial: 𝑞𝑆 = 𝑞𝑆 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝐼∈Ind,𝑆⊆𝐼 −1 |𝐼∖𝑆| 𝑝 𝐼 Graph G with m vertices and 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝑝1, ⋯ , 𝑝𝑚 > 0, let 𝑝𝐼 = ∏𝑖∈𝐼 𝑝𝑖
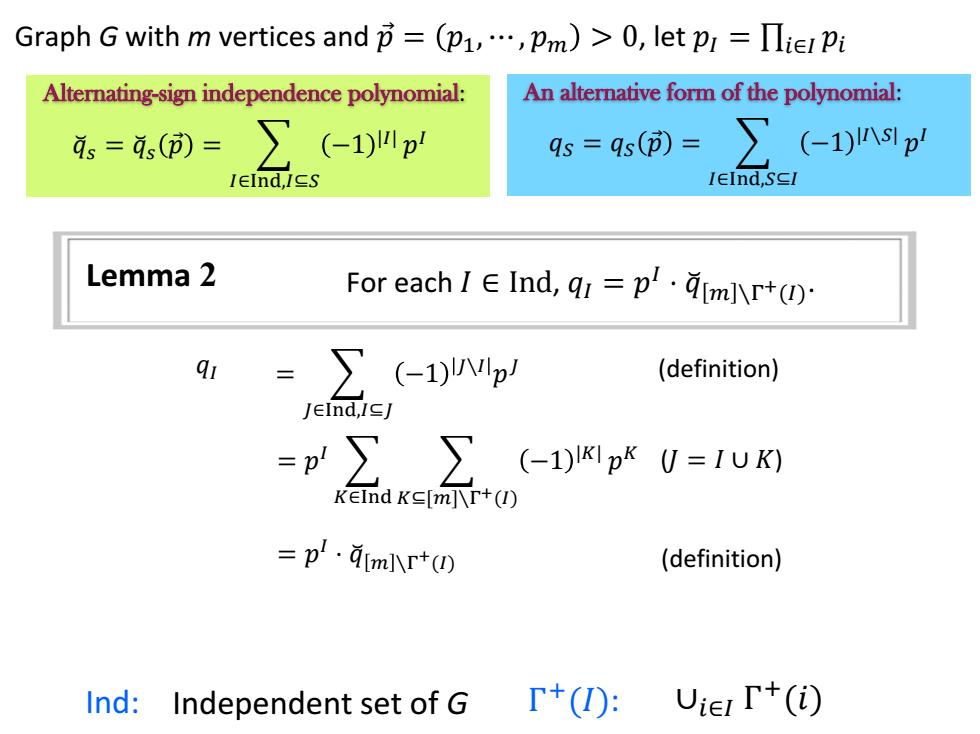
Graph G with m vertices andp=(p1,,Pm)>0,let pr=Ilie Pi Alternating-sign independence polynomial: An alternative form of the polynomial: 4s=4()= ∑(-104p qs=9s()= ∑(-1)nsp IEInd,ICS IEInd,SCI Lemma 2 For eachI∈Ind,q1=p'·9mIr+(0 =∑(-1)p (definition) JEInd,ICJ =p∑∑(-1)K1pkU=1UK) KEInd KE[m]\r+(I) =p.qmj小r+(四 (definition) Ind:Independent set of G T+(): Uier T+(i)
Lemma 2 𝑞𝐼 = (definition) 𝐽∈Ind,𝐼⊆𝐽 −1 𝐽∖𝐼 𝑝 𝐽 = 𝑝 𝐼 𝐾∈Ind 𝐾⊆[𝑚]∖Γ+(𝐼) −1 |𝐾| 𝑝 𝐾 (𝐽 = 𝐼 ∪ 𝐾) = 𝑝 𝐼 ⋅ 𝑞෬ 𝑚 ∖Γ +(𝐼) (definition) Alternating-sign independence polynomial: 𝑞෬𝑠 = 𝑞෬𝑠 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝐼∈Ind,𝐼⊆𝑆 −1 |𝐼| 𝑝 𝐼 An alternative form of the polynomial: 𝑞𝑆 = 𝑞𝑆 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝐼∈Ind,𝑆⊆𝐼 −1 |𝐼∖𝑆| 𝑝 𝐼 For each 𝐼 ∈ Ind, 𝑞𝐼 = 𝑝 𝐼 ⋅ 𝑞 ෬ 𝑚 ∖Γ +(𝐼) . Ind: Independent set of G ∪𝑖∈𝐼 Γ + Γ (𝑖) +(𝐼): Graph G with m vertices and 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝑝1, ⋯ , 𝑝𝑚 > 0, let 𝑝𝐼 = ∏𝑖∈𝐼 𝑝𝑖
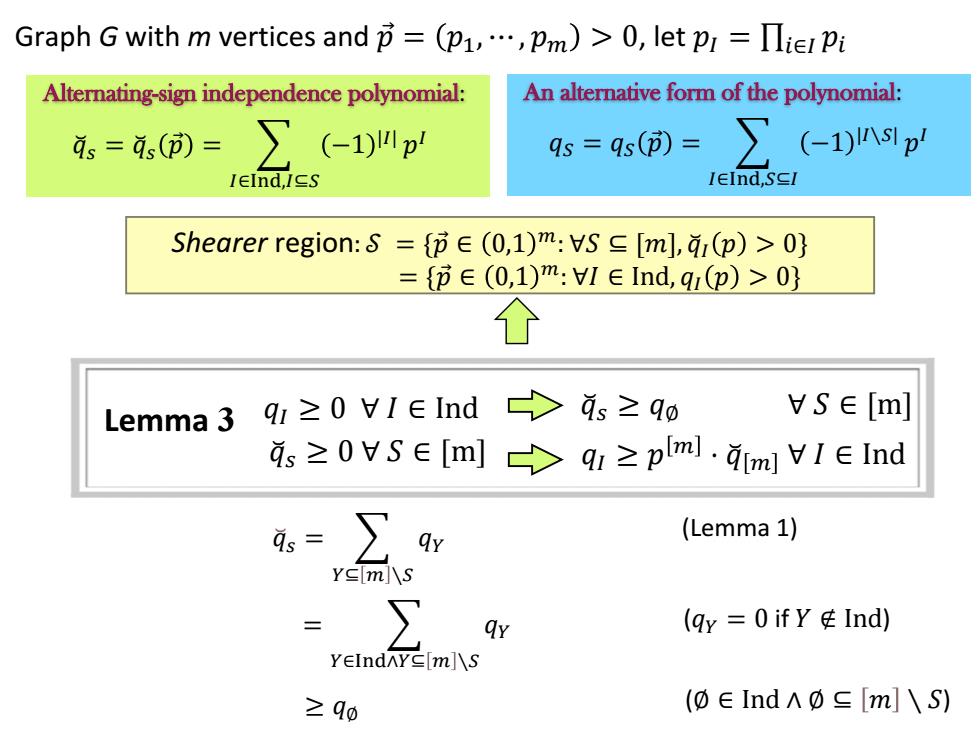
Graph G with m vertices and节=(p1,…,pm)>0,let pr=Πte Pi Alternating-sign independence polynomial: An alternative form of the polynomial: 。=,()=∑(-1)叫p 9s=9s()= ∑(-10np IEInd,IES IEInd,SEI Shearer region:S =pE(0,1)m:VS [m],qi(p)>0} ={∈(0,1)m:∀l∈Ind,qu(p)>0} 个 Lemma 3 q≥0H1∈Ind VSE [m] as≥0HS∈[m>q1≥pm.mV1eInd =∑ qy (Lemma 1) YEIml\S ∑ qy (qy=0ifY度Ind) YEIndAYE[m]\s ≥q0 (0∈IndA0∈[m]\S)
Lemma 3 (Lemma 1) = 𝑌∈Ind∧𝑌⊆ 𝑚 ∖𝑆 𝑞𝑌 (𝑞𝑌 = 0 if 𝑌 ∉ Ind) ≥ 𝑞∅ (∅ ∈ Ind ∧ ∅ ⊆ 𝑚 ∖ 𝑆) Alternating-sign independence polynomial: 𝑞෬𝑠 = 𝑞෬𝑠 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝐼∈Ind,𝐼⊆𝑆 −1 |𝐼| 𝑝 𝐼 An alternative form of the polynomial: 𝑞𝑆 = 𝑞𝑆 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝐼∈Ind,𝑆⊆𝐼 −1 |𝐼∖𝑆| 𝑝 𝐼 𝑞𝐼 ≥ 0 ∀ 𝐼 ∈ Ind Shearer region: 𝒮 = {𝑝 Ԧ ∈ 0,1 𝑚: ∀𝑆 ⊆ [𝑚], 𝑞෬𝐼 𝑝 > 0} = {𝑝 Ԧ ∈ 0,1 𝑚: ∀𝐼 ∈ Ind, 𝑞𝐼 𝑝 > 0} 𝑞 ෬ 𝑠 ≥ 𝑞∅ ∀ 𝑆 ∈ [m] 𝑞 ෬ 𝑠 ≥ 0 ∀ 𝑆 ∈ [m] 𝑞𝐼 ≥ 𝑝 𝑚 ⋅ 𝑞 ෬ 𝑚 ∀ 𝐼 ∈ Ind 𝑞෬𝑠 = 𝑌⊆ 𝑚 ∖𝑆 𝑞𝑌 Graph G with m vertices and 𝑝 Ԧ = 𝑝1, ⋯ , 𝑝𝑚 > 0, let 𝑝𝐼 = ∏𝑖∈𝐼 𝑝𝑖