
m/AIMA tutorial:11-1 today and Monday.27 Soda Reminders INTELLIGENT AGENT 80 A vacuum-cleaner agent Vacuum-cleaner world agent program runs on the physical ar he agent function maps from percept histork 鞋
Intelligent Agents Chapter 2 Chapter 2 1 Reminders Assignment 0 (lisp refresher) due 1/28 Lisp/emacs/AIMA tutorial: 11-1 today and Monday, 271 So Chapter da 2 2 Outline ♦ Agents and environments ♦ Rationality ♦ PEAS (Performance measure, Environment, Actuators, Sensors) ♦ Environment types ♦ Agent types Chapter 2 3 Agents and environments agent ? percepts sensors actions environment actuators Agents include humans, robots, softbots, thermostats, etc. The agent function maps from percept histories to actions: f : P ∗ → A The agent program runs on the physical architecture to produce f Chapter 2 4 Vacuum-cleaner world A B Percepts: location and contents, e.g., [A, Dirty] Actions: Left, Right, Suck, NoOp Chapter 2 5 A vacuum-cleaner agent Percept sequence Action [A, Clean] Right [A, Dirty] Suck [B, Clean] Left [B, Dirty] Suck [A, Clean], [A, Clean] Right [A, Clean], [A, Dirty] Suck . . . . . . function Reflex-Vacuum-Agent([location,status]) returns an action if status = Dirty then return Suck else if location = A then return Right else if location = B then return Left What is the right function? Can it be implemented in a small agent program? Chapter 2 6

a rational agent R must square per an autom PEAS PEAS one point per square cleaned up in time 7? Rationality sen horn,speak specify the task en time step,minus one per move? ... Solitaire Backgammon Intermnet shopping Taxi Environment types 7HTML pages (text,graphics,scripts) current and future WWWsites,vendors,shipper price,quality.appropriateness,efficiency Internet shopping agent Internet shopping agent
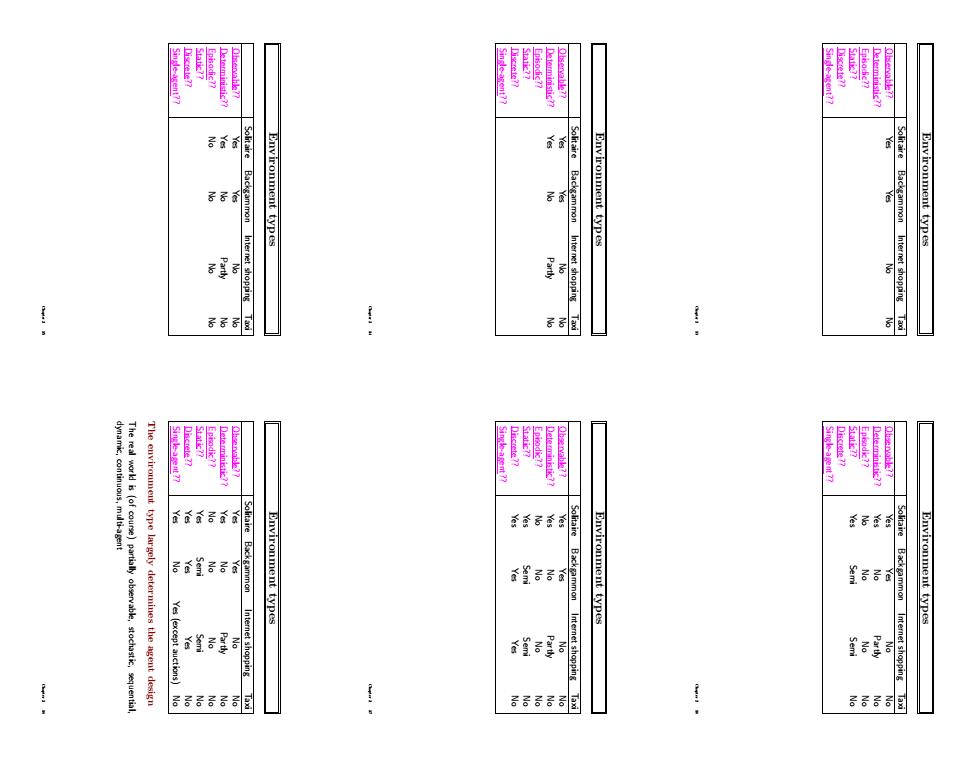
Rationality Fixed performance measure evaluates the environment sequence – one point per square cleaned up in time T? – one point per clean square per time step, minus one per move? – penalize for > k dirty squares? A rational agent chooses whichever action maximizes the expected value of the performance measure given the percept sequence to date Rational 6= omniscient – percepts may not supply all relevant information Rational 6= clairvoyant – action outcomes may not be as expected Hence, rational 6= successful Rational ⇒ exploration, learning, autonomy Chapter 2 7 PEAS To design a rational agent, we must specify the task environment Consider, e.g., the task of designing an automated taxi: Performance measure?? Environment?? Actuators?? Sensors?? Chapter 2 8 PEAS To design a rational agent, we must specify the task environment Consider, e.g., the task of designing an automated taxi: Performance measure?? safety, destination, profits, legality, comfort, . . . Environment?? US streets/freeways, traffic, pedestrians, weather, . . . Actuators?? steering, accelerator, brake, horn, speaker/display, . . . Sensors?? video, accelerometers, gauges, engine sensors, keyboard, GPS, . . . Chapter 2 9 Internet shopping agent Performance measure?? Environment?? Actuators?? Sensors?? Chapter 2 10 Internet shopping agent Performance measure?? price, quality, appropriateness, efficiency Environment?? current and future WWW sites, vendors, shippers Actuators?? display to user, follow URL, fill in form Sensors?? HTML pages (text, graphics, scripts) Chapter 2 11 Environment types Solitaire Backgammon Internet shopping Taxi Observable?? Deterministic?? Episodic?? Static?? Discrete?? Single-agent?? Chapter 2 12
Sinde-arent?7 olitaire Backgammon Internet shopping Environment types Environment types Environment types Yes (except auctions) gammon Internet shopping Environment types Environment types Environment types Internet shopping .. 后后后后
Environment types Solitaire Backgammon Internet shopping Taxi Observable?? Yes Yes No No Deterministic?? Episodic?? Static?? Discrete?? Single-agent?? Chapter 2 13 Environment types Solitaire Backgammon Internet shopping Taxi Observable?? Yes Yes No No Deterministic?? Yes No Partly No Episodic?? Static?? Discrete?? Single-agent?? Chapter 2 14 Environment types Solitaire Backgammon Internet shopping Taxi Observable?? Yes Yes No No Deterministic?? Yes No Partly No Episodic?? No No No No Static?? Discrete?? Single-agent?? Chapter 2 15 Environment types Solitaire Backgammon Internet shopping Taxi Observable?? Yes Yes No No Deterministic?? Yes No Partly No Episodic?? No No No No Static?? Yes Semi Semi No Discrete?? Single-agent?? Chapter 2 16 Environment types Solitaire Backgammon Internet shopping Taxi Observable?? Yes Yes No No Deterministic?? Yes No Partly No Episodic?? No No No No Static?? Yes Semi Semi No Discrete?? Yes Yes Yes No Single-agent?? Chapter 2 17 Environment types Solitaire Backgammon Internet shopping Taxi Observable?? Yes Yes No No Deterministic?? Yes No Partly No Episodic?? No No No No Static?? Yes Semi Semi No Discrete?? Yes Yes Yes No Single-agent?? Yes No Yes (except auctions) No The environment type largely determines the agent design The real world is (of course) partially observable, stochastic, sequential, dynamic, continuous, multi-agent Chapter 2 18
(setq joe (make-agent Agent location'A)'Right Condison-acsion rules Example Simple reflex agents 0 46 Agent types quewuoJAug percept))) ... Agent Agent Condtion-action iles What my actions do Goal-based agents Example Reflex agents with state quowuoJIAu3 quowuolaug
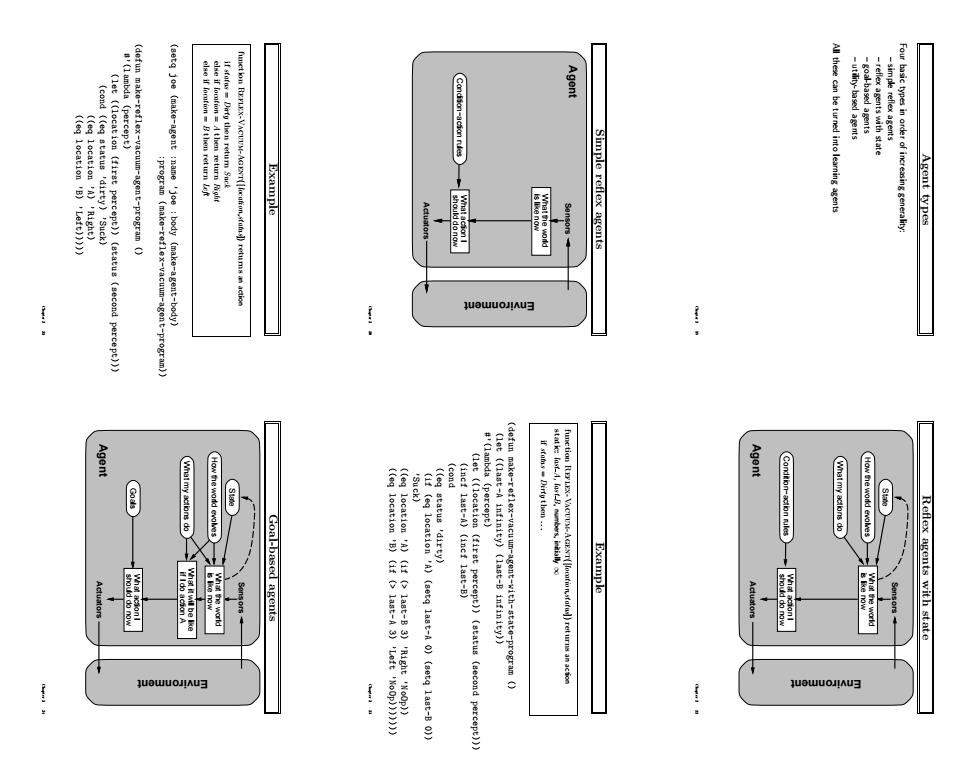
Agent types Four basic types in order of increasing generality: – simple reflex agents – reflex agents with state – goal-based agents – utility-based agents All these can be turned into learning agents Chapter 2 19 Simple reflex agents Agent Environment Sensors should do now What action I is like now What the world Condition−action rules Actuators Chapter 2 20 Example function Reflex-Vacuum-Agent([location,status]) returns an action if status = Dirty then return Suck else if location = A then return Right else if location = B then return Left (setq joe (make-agent :name ’joe :body (make-agent-body) :program (make-reflex-vacuum-agent-program))) (defun make-reflex-vacuum-agent-program () #’(lambda (percept) (let ((location (first percept)) (status (second percept))) (cond ((eq status ’dirty) ’Suck) ((eq location ’A) ’Right) ((eq location ’B) ’Left))))) Chapter 2 21 Reflex agents with state Agent Environment Sensors should do now What action I State How the world evolves What my actions do Condition−action rules Actuators is like now What the world Chapter 2 22 Example function Reflex-Vacuum-Agent([location,status]) returns an action static: last A, last B, numbers, initially ∞ if status = Dirty then . . . (defun make-reflex-vacuum-agent-with-state-program () (let ((last-A infinity) (last-B infinity)) #’(lambda (percept) (let ((location (first percept)) (status (second percept))) (incf last-A) (incf last-B) (cond ((eq status ’dirty) (if (eq location ’A) (setq last-A 0) (setq last-B 0)) ’Suck) ((eq location ’A) (if (> last-B 3) ’Right ’NoOp)) ((eq location ’B) (if (> last-A 3) ’Left ’NoOp))))))) Chapter 2 23 Goal-based agents Agent Environment Sensors if I do action A What it will be like should do now What action I State How the world evolves What my actions do Goals Actuators is like now What the world Chapter 2 24
Agent Agent Summary Learning agents Utility-based agents rete?single
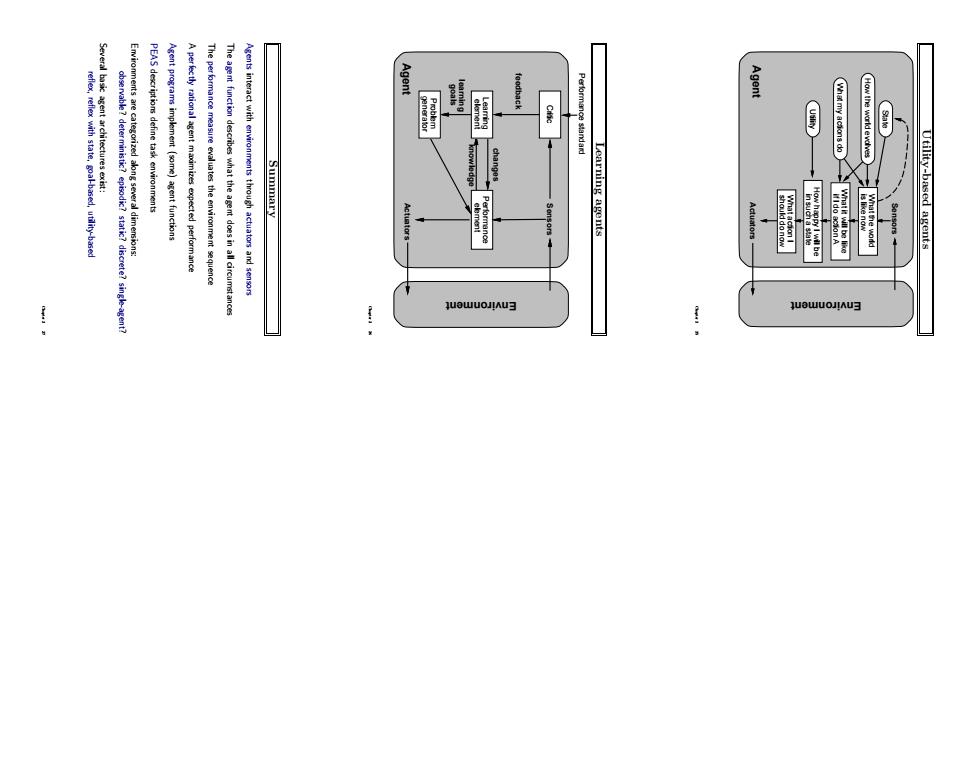
Utility-based agents Agent Environment Sensors How happy I will be if I do action A What it will be like in such a state should do now What action I State How the world evolves What my actions do Utility Actuators is like now What the world Chapter 2 25 Learning agents Performance standard Agent Environment Sensors element Performance changes knowledge goals learning generator Problem feedback element Learning Critic Actuators Chapter 2 26 Summary Agents interact with environments through actuators and sensors The agent function describes what the agent does in all circumstances The performance measure evaluates the environment sequence A perfectly rational agent maximizes expected performance Agent programs implement (some) agent functions PEAS descriptions define task environments Environments are categorized along several dimensions: observable? deterministic? episodic? static? discrete? single-agent? Several basic agent architectures exist: reflex, reflex with state, goal-based, utility-based Chapter 2 27