
1.Of the following.what is the most likely reason that cooking with Nutrasweet (Aspartame)destroys the sweetness? HO-C-CH2-CH-C CH-C-OCHa NH2 CHz-CeHs Aspartame It undergoes decarboxylatior t un ergoes an intramol rcyclization D ergoes amide E)It undergoes loss of N Ans:B 2.What is dicyclohexylearbodiimide(DCC)used for in peptide synthesis? DCC protects the oxyl group towar eophill es the n the id ng gro ntia E)DCC nthesis Ans:B 3.Which of the following amino acids is theoretically capable of existing in two diastereomeric forms A)Cysteine B)Threonine C)Leucine D)Serine E) 4.A heptapeptide containing 2 alanine residues and one each of glutamine,phenylalanine, proline,tyrosine and valine was analyzed as follows: 1.Treatment with 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene followed by complete hydrolysis yielded 2.4-dinitrophenylalanine. 2.Partial hydrolysis with aqueousacid yielded the following fragments ala-glu pro-tyr,ala-val,tyr-ala,and val-phe-pro What is the structure of the peptide? D)ala-val-phe-tyr-pro-ala-glu ala-val-phe-pro-tyr-glu-ala val-ala-phe-tyr-pro-ala-glu
Page 1 1. Of the following, what is the most likely reason that cooking with Nutrasweet (Aspartame) destroys the sweetness? HO C O CH2 CH NH2 C O N CH H CH2 C6H5 C O OCH3 Aspartame A) It undergoes decarboxylation B) It undergoes an intramolecular cyclization C) It undergoes amide hydrolysis D) It undergoes evaporation E) It undergoes loss of N2 Ans: B 2. What is dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) used for in peptide synthesis? A) DCC protects the amino group of the intended N-terminal amino acid. B) DCC activates the carboxyl group toward nucleophillic attack. C) DCC cleaves the blocking groups from the final peptide. D) DCC is the resin (solid support) used to anchor the growing polypeptide. E) DCC removes the peptide from the resin at the conclusion of the synthesis. Ans: B 3. Which of the following amino acids is theoretically capable of existing in two diastereomeric forms? A) Cysteine B) Threonine C) Leucine D) Serine E) Tryptophan Ans: B 4. A heptapeptide containing 2 alanine residues and one each of glutamine, phenylalanine, proline, tyrosine and valine was analyzed as follows: 1. Treatment with 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene followed by complete hydrolysis yielded 2,4-dinitrophenylalanine. 2. Partial hydrolysis with aqueous acid yielded the following fragments: ala-glu, pro-tyr, ala-val, tyr-ala, and val-phe-pro. What is the structure of the peptide? A) ala-phe-pro-tyr-ala-glu-val D) ala-val-phe-tyr-pro-ala-glu B) ala-val-phe-pro-tyr-glu-ala E) val-ala-phe-tyr-pro-ala-glu C) ala-val-phe-pro-tyr-ala-glu Ans: C

5.Why is the following not a good two step route for the preparation of pure L-alanine? catalytic excess CH:CH2CO2H Br2 PBr2 NH The bromin a secondary brom Only the CHa group is brominated The product will he racemie E)Propanamide would be the major product. Ans:D 6.Disulfide bonds in proteins B刷 (RSH) h f proteins mk e in e can be broken n E) All of these are true. Ans:E 7.Which amino acid does not form ac B) Lysine E)Tryptophan 8.What material can be used repetitively (on a given sample)to sequence a polypeptide from the N-terminal end? A)Chymotrypsin D)Edman reagent B)Sanger reagent E)Carboxypeptidase Ans:Drypsin 9.How many tripeptides containing one residue each ofLalanine,L-valine,and glycine ssibl B)3C)4D)6E)9 Ans:D Page2
Page 2 5. Why is the following not a good two step route for the preparation of pure L-alanine? CH3CH2CO2H + Br2 catalytic PBr3 excess NH3 A) The bromination is not selective (the CH3 and CH2 groups are both brominated). B) Ammonia is not sufficiently nucleophillic to react with a secondary bromide. C) Only the CH3 group is brominated. D) The product will be racemic. E) Propanamide would be the major product. Ans: D 6. Disulfide bonds in proteins A) result from oxidation of thiols (RSH). B) function to help maintain the shape of proteins. C) can be broken by reduction reactions. D) link two cysteine amino acid residues. E) All of these are true. Ans: E 7. Which amino acid does not form a characteristic blue color with ninhydrin? A) Cysteine B) Lysine C) Proline D) Valine E) Tryptophan Ans: C 8. What material can be used repetitively (on a given sample) to sequence a polypeptide from the N-terminal end? A) Chymotrypsin D) Edman reagent B) Sanger reagent E) Carboxypeptidase C) Trypsin Ans: D 9. How many tripeptides containing one residue each of L-alanine, L-valine, and glycine are possible? A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 6 E) 9 Ans: D
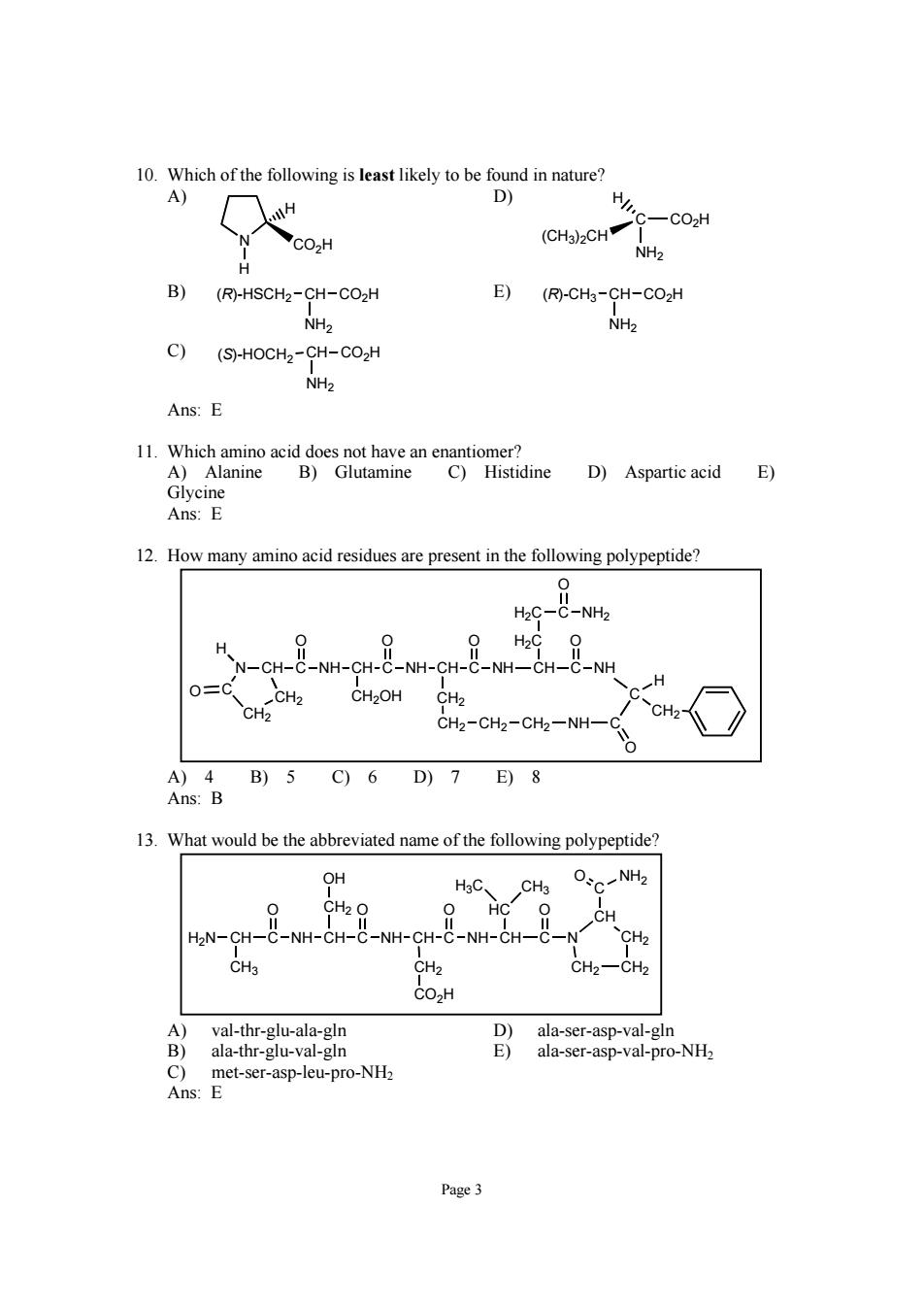
10.Which of the following is least likely to be found in nature? A) D) H H C-CO2H CO2H (CHa)2CH NH> B) (R)-HSCH2-CH-CO2H E)(风-CH-CH-C02H NH2 NH2 C)(S)-HOCH2-CH-CO2H NH2 Ans:E 1. D)Aspartic acid E) Ans:E 12.How many amino acid residues are present in the following polypeptide? H2C-C-NH2 H O=C H CH-CH CH2OH CH2 CH2-CH2-CH2-NH- c、 A)4 B)5C)6D)7E)8 Ans:B 13.What would be the abbreviated name of the following polypeptide? OH CHs 0 HC 0、 H2N-CH-C NH. NH. CH-C-NH-CH-C CH2 CH2一CH2 CO2H A)val-thr-glu-ala-gln ala-ser-asp-val-gln ap-leu-pro-NH. ala-thr-glu-val-gln 91 ala-ser-asp-val-pro-NHz Page3
Page 3 10. Which of the following is least likely to be found in nature? A) N CO2H H H D) (CH3)2CH C H CO2H NH2 B) (R)-HSCH2 CH CO2H NH2 E) (R)-CH3 CH CO2H NH2 C) (S)-HOCH2 CH CO2H NH2 Ans: E 11. Which amino acid does not have an enantiomer? A) Alanine B) Glutamine C) Histidine D) Aspartic acid E) Glycine Ans: E 12. How many amino acid residues are present in the following polypeptide? N CH C NH CH C NH CH C NH CH OOO O C NH C CH2OH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 NH C O C H CH2 H2C H2C C O NH2 CH2 CH2 H O A) 4 B) 5 C) 6 D) 7 E) 8 Ans: B 13. What would be the abbreviated name of the following polypeptide? H2N CH C NH CH C NH CH C NH CH O OO O C N CH2 CO2H CH2 OH CH CH2 CH3 CH2 CH2 C O NH2 HC H3C CH3 A) val-thr-glu-ala-gln D) ala-ser-asp-val-gln B) ala-thr-glu-val-gln E) ala-ser-asp-val-pro-NH2 C) met-ser-asp-leu-pro-NH2 Ans: E
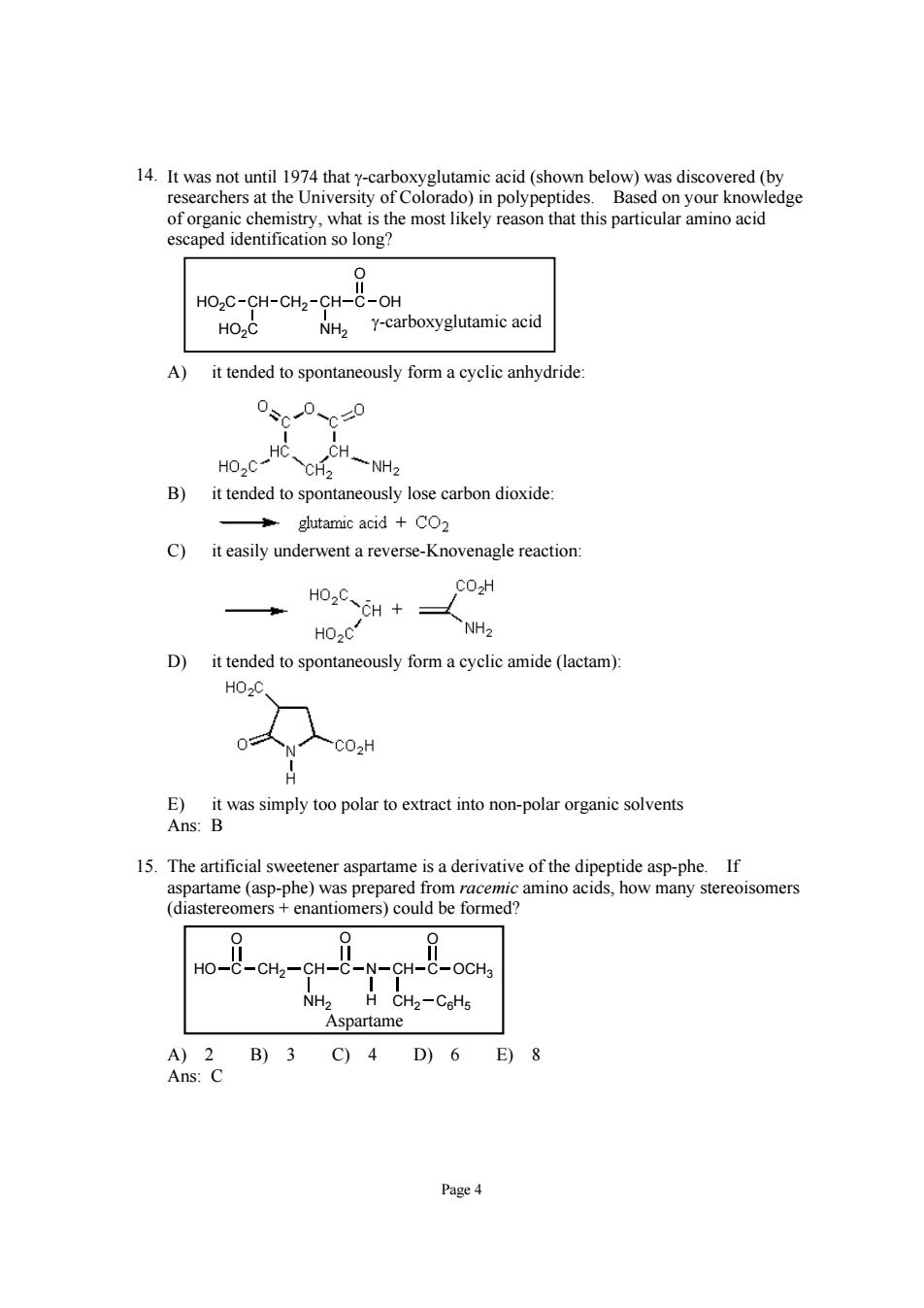
researchers ledge cation so long HO2C-CH-CH2-CH-C-OH HO2C NH2 Y-carboxyglutamic acid A) it tended to spontaneously form a cyclic anhydride 0、0、0 B)it tended to spontaneously lose carbon dioxide glutamic acid +CO2 C)it easily underwent a reverse-Knovenagle reaction HO.CCH+ CO2H HO2C D)it tended to spontaneously form a cyclic amide(lactam) HO.O 0 CO2H E)it was simply too polar to extract into non-polar organic solvents Ans:B 15.The artificial sweetener aspartame is a derivative of the dipeptide asp-phe.If aspartame(asp-phe)was prepared from racemic amino acids,how many stereoisomers (diastereomers enantiomers)could be formed? Ho--CH-CH- -C-OCHa Aspartame A)2B)3C)4D)6E)8 Ans:C Page4
Page 4 14. It was not until 1974 that γ-carboxyglutamic acid (shown below) was discovered (by researchers at the University of Colorado) in polypeptides. Based on your knowledge of organic chemistry, what is the most likely reason that this particular amino acid escaped identification so long? CH CH2 CH C OH O HO2C HO2C NH2 γ-carboxyglutamic acid A) it tended to spontaneously form a cyclic anhydride: B) it tended to spontaneously lose carbon dioxide: C) it easily underwent a reverse-Knovenagle reaction: D) it tended to spontaneously form a cyclic amide (lactam): E) it was simply too polar to extract into non-polar organic solvents Ans: B 15. The artificial sweetener aspartame is a derivative of the dipeptide asp-phe. If aspartame (asp-phe) was prepared from racemic amino acids, how many stereoisomers (diastereomers + enantiomers) could be formed? HO C O CH2 CH NH2 C O N CH H CH2 C6H5 C O OCH3 Aspartame A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 6 E) 8 Ans: C

16.Chymotrypsin catalyzes hydrolysis of peptide bonds where? residue in question 0 0 NU-CL NH-etc "carboxy end" "amino end" A)At the carboxy end of residues with basic side chains At the of re dues w ith aromatic es with aromat Ans:C 17.The primary structure of a protein refers to the A) sequence of amino acids. one degree of 18.Which of the following amino acids would have the highest isoelectric point? A)Lysine B)Glutamine C)Aspartic acid D)Alanine E) Tryptophan Ans:A 19.Nearly all a A Lysine B)Histidine C)Tyrosine D)Cysteine E)Proline Ans:E Page5
Page 5 16. Chymotrypsin catalyzes hydrolysis of peptide bonds where? etc. C NH CH C NH etc. O O R residue in question "amino end" "carboxy end" A) At the carboxy end of residues with basic side chains B) At the amino end of residues containing aliphatic residues C) At the carboxy end of residues with aromatic side chains D) At the amino end of residues with aromatic side chains E) At the carboxy end of methionine residues Ans: C 17. The primary structure of a protein refers to the A) sequence of amino acids. B) overall 3-dimensional shape. C) localized shape of the backbone. D) degree of aggregation with other proteins. E) structure of the active site. Ans: A 18. Which of the following amino acids would have the highest isoelectric point? A) Lysine B) Glutamine C) Aspartic acid D) Alanine E) Tryptophan Ans: A 19. Nearly all amino acids immediately release N2 gas upon diazotization (treatment with aqueous HCl and sodium nitrite). Which amino acid would not? A) Lysine B) Histidine C) Tyrosine D) Cysteine E) Proline Ans: E
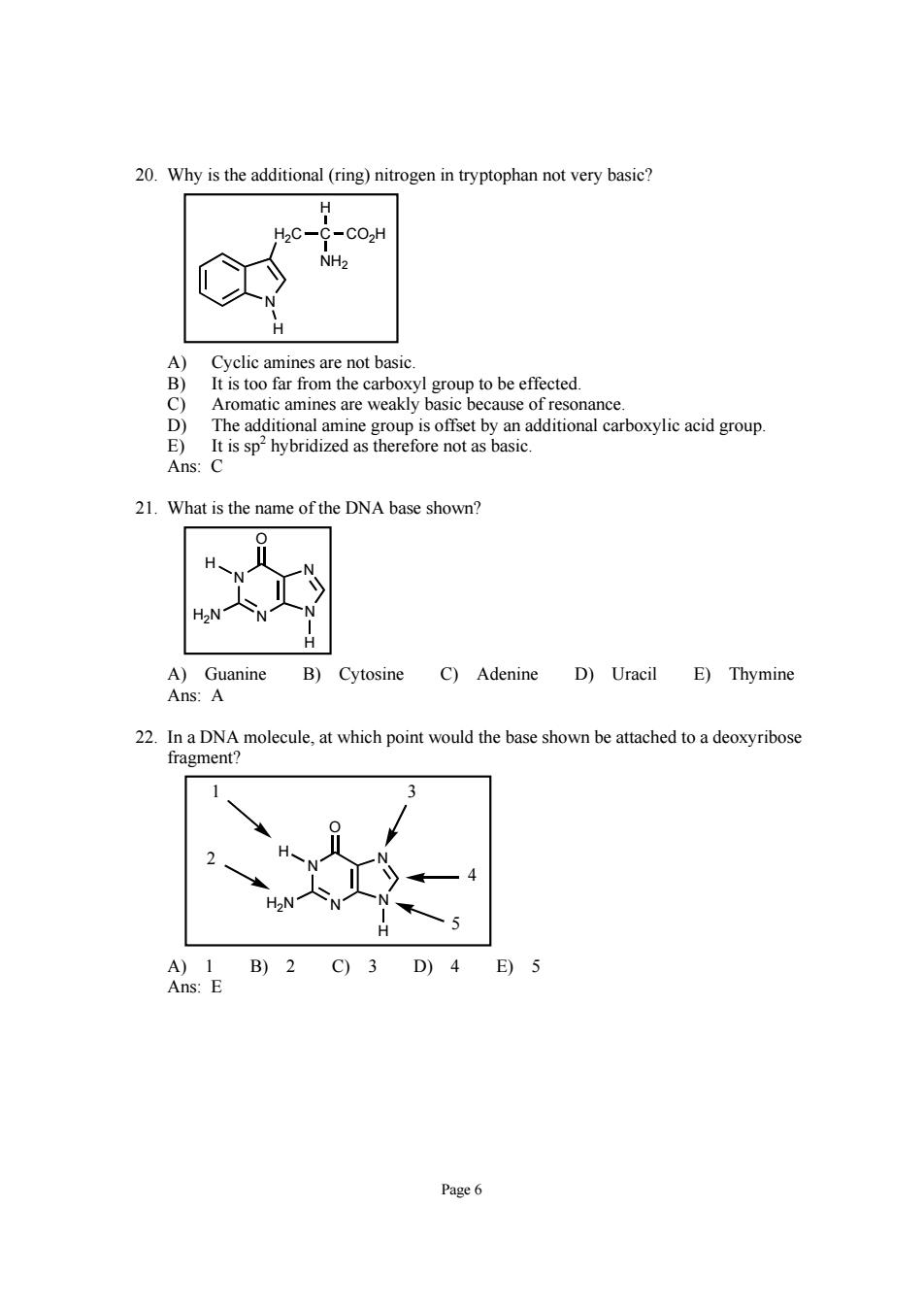
20.Why is the additional (ring)nitrogen in tryptophan not very basic? -C02h NH2 Cyclic amines are not bas car in The additional amine s oup is offset by an additional carboxylic acid group. E)It is sp2hybridized as therefore not as basic. Ans:C 21.What is the name of the DNA base shown? A)Guanine B)Cytosine C)Adenine D)Uracil E)Thymine Ans:A 22.In a DNA molecule,at which point would the base shown be attached to a deoxyribose fragment? A)1B)2C)3D)4E)5 Ans:E Page6
Page 6 20. Why is the additional (ring) nitrogen in tryptophan not very basic? N H2C C NH2 CO2H H H A) Cyclic amines are not basic. B) It is too far from the carboxyl group to be effected. C) Aromatic amines are weakly basic because of resonance. D) The additional amine group is offset by an additional carboxylic acid group. E) It is sp2 hybridized as therefore not as basic. Ans: C 21. What is the name of the DNA base shown? N N N N O H H H2N A) Guanine B) Cytosine C) Adenine D) Uracil E) Thymine Ans: A 22. In a DNA molecule, at which point would the base shown be attached to a deoxyribose fragment? N N N N O H H H2N 1 3 2 5 4 A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 Ans: E

23.Theifern(btwn DNAand RNA is (re) deoxyribose sugars rather than ribose DNA RNA D) Two of the above are t uses uraci All of the above are true Ans:E 2AAahnian2anmmeasonehEaceseadnm6tvs natura s on Ear R Amino acids are of the(R)configuration Amino acids are of the(S)configuration. 9 Amino acids are not chiral. Amino acids are meso compounds. Amino acids easily change configuration. Ans:B 25.Which attractive force is responsible for maintaining the tertiary structure of proteins? lvgen Disulfide linkages D) hobic interactions C) Salt bridges Ans:E .Which then nown as(PKU) ryptophan B) D)Proline E) valin Ans:C 27.Which of the following statements is not true of amino acids? A) They are less acidic than carboxylic acids. 2) ney are so w would show an IR absorption near 3300 cm Ans:D Page7
Page 7 23. The difference(s) between DNA and RNA is (are): A) DNA incorporates 2-deoxyribose sugars rather than ribose. B) RNA is smaller than DNA. C) DNA uses thymine, RNA uses uracil. D) Two of the above are true. E) All of the above are true. Ans: E 24. Although traces of racemic amino acids have been found in meteorites, nearly all naturally occurring amino acids on Earth have the stereochemistry shown. What is true of this stereochemistry? (Assume R = alkyl) R C H CO2H NH2 A) Amino acids are of the (R) configuration. B) Amino acids are of the (S) configuration. C) Amino acids are not chiral. D) Amino acids are meso compounds. E) Amino acids easily change configuration. Ans: B 25. Which attractive force is responsible for maintaining the tertiary structure of proteins? A) Disulfide linkages D) Hydrophobic interactions B) Hydrogen bonds E) All of these C) Salt bridges Ans: E 26. Which amino acid is responsible for the condition known as phenylketonuria (PKU) which occurs in a small fraction of the population? A) Tryptophan B) Histidine C) Phenylalanine D) Proline E) Valine Ans: C 27. Which of the following statements is not true of amino acids? A) They are less acidic than carboxylic acids. B) In acid solution (pH ~ 2) they would show an IR absorption near 1720 cm-1 . C) They are soluble in water but not in non-polar organic solvents. D) They are more basic than amines. E) In basic solution (pH ~ 12) they would show an IR absorption near 3300 cm-1 . Ans: D

28.The organic portion of which of the following biological materials D)Membranes E) Insulin zyme Ans:D 29.What would result from the following reactions? HO* HgC-C-HHCN heat 7 H2N- -OCH 3 H2N- H2N-CH2- H一C三N Ans:e Page 8
Page 8 28. The organic portion of which of the following biological materials does not consist mainly of polypeptides and/or proteins? A) Enzymes B) Hair C) Hemoglobin D) Membranes E) Insulin Ans: D 29. What would result from the following reactions? H3C C O H HCN heat ? H3O NH + 3 A) H2N C H H C O OCH3 B) H2N C H CH3 C O OH C) CH2 C H H C O H2N OH D) H2N C H H CH2 C N E) H3C C H2N CH3 C O OH Ans: B
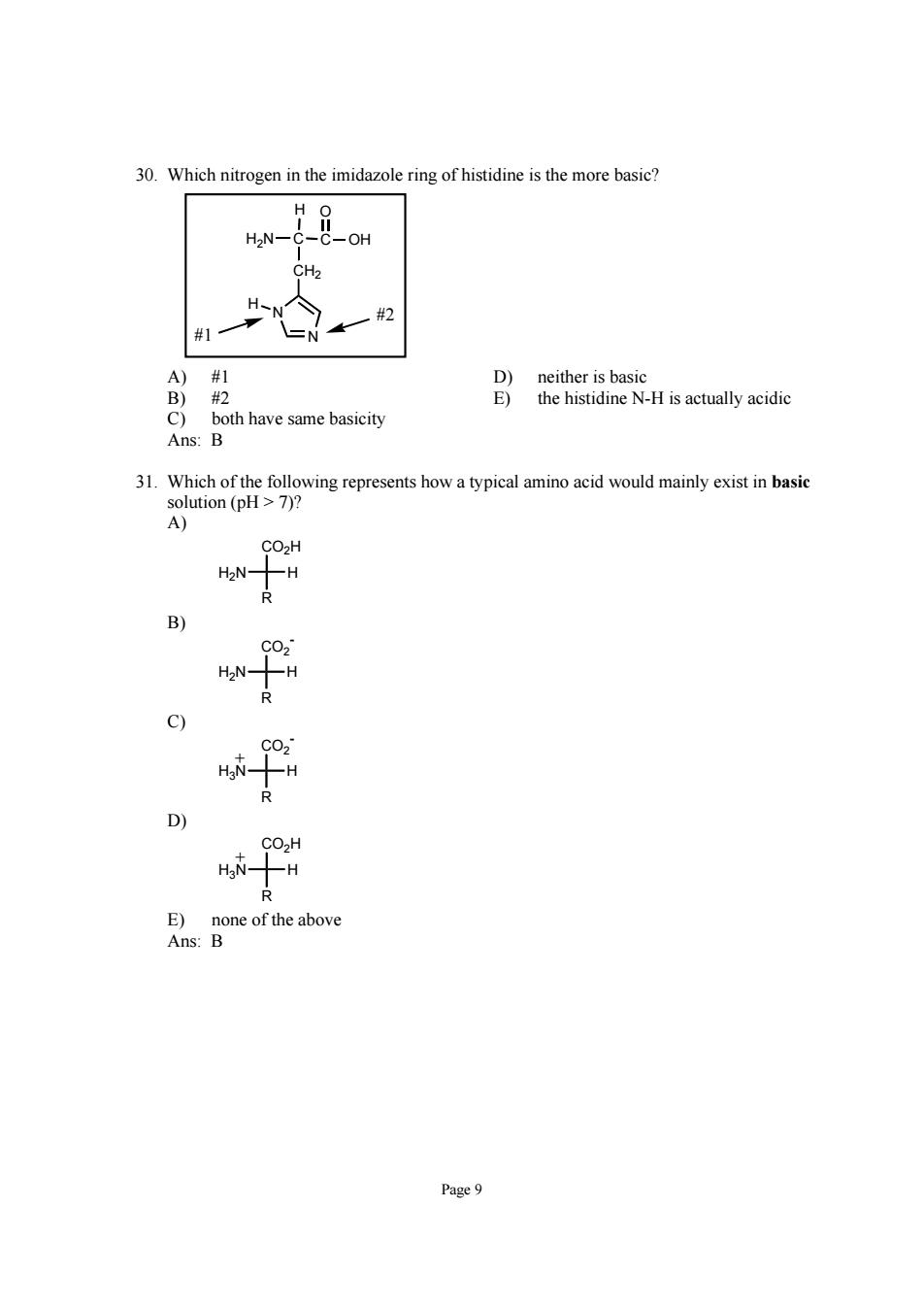
30.Which nitrogen in the imidazole ring of histidine is the more basic? H2N- -O 一2 #1 A)#1 D)neither is basic E)the histidine N-H is actually acidic both have same basicity Ans: B 31.Which of the following represents how a typical amino acid would mainly exist in basie solution (pH>7)? R C) Page9
Page 9 30. Which nitrogen in the imidazole ring of histidine is the more basic? H2N C H CH2 C O OH N N H #2 #1 A) #1 D) neither is basic B) #2 E) the histidine N-H is actually acidic C) both have same basicity Ans: B 31. Which of the following represents how a typical amino acid would mainly exist in basic solution (pH > 7)? A) CO2H R H2N H B) CO2 - R H2N H C) CO2 - R H3N H + D) CO2H R H3N H + E) none of the above Ans: B
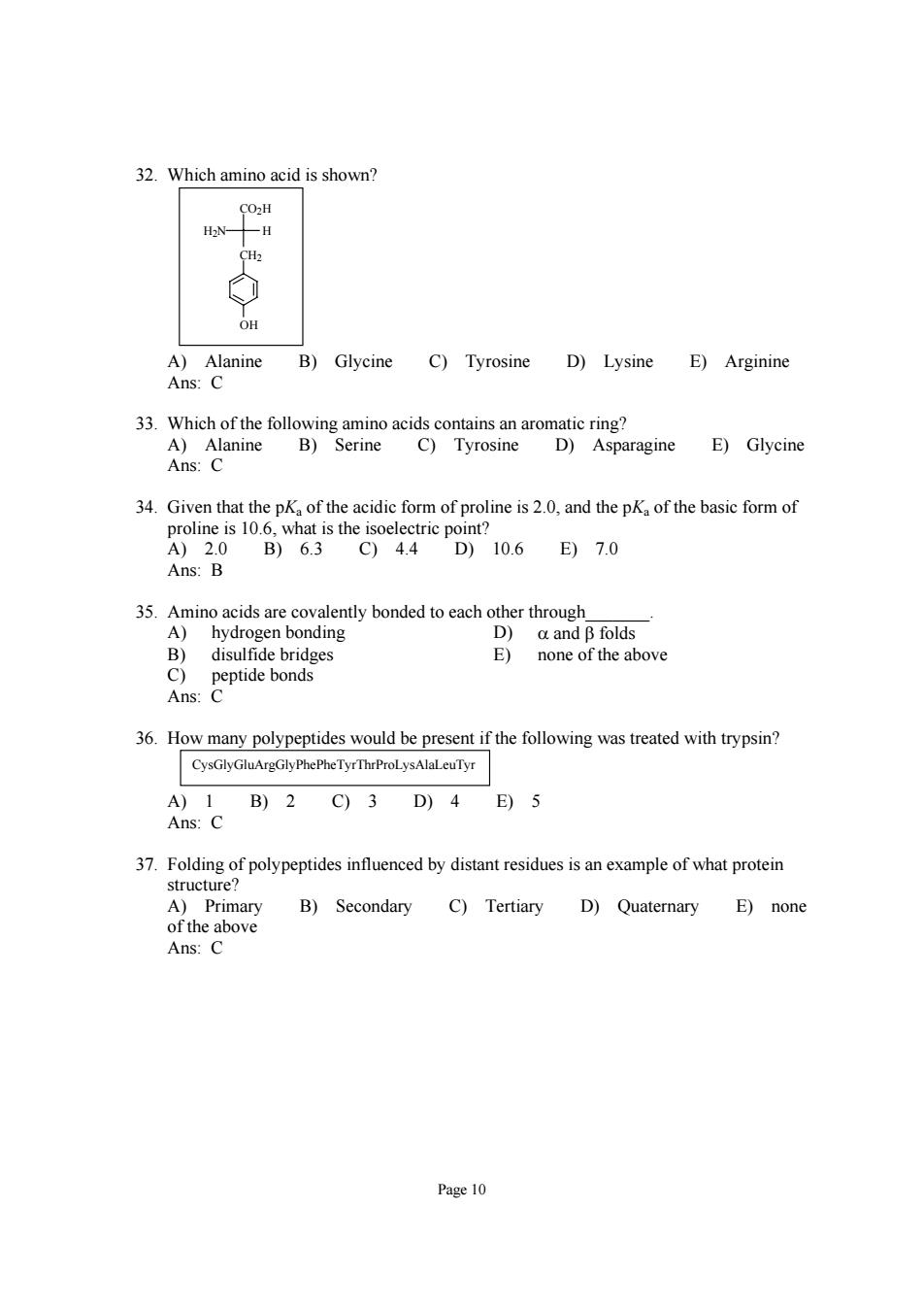
32.Which amino acid is shown? O: 2 ⊙ OH B)Glycine C)Tyrosine D)Lysine E)Arginine 33.Which of the following amino acids contains an aromatic ring? A)Alanine B)Serine C)Tyrosine D)Asparagine E)Glycine Ans:C B)og is the 44cp106目70 Ans:B 35.Amino acids are covalently bonded to each other through A)hydrogen bonding D)a and B folds B)disulfide bridges E)none of the above C) peptide bonds Ans:C 36.How many polypeptides would be present if the following was treated with trypsin? CysGlyGluArgGlyPhePheTyrThrProLysAlaLeuTyr A)1B)2C)3D)4E)5 Ans:C 37.Folding of polypeptides influenced by distant residues is an example of what protein structure B)Secondary C)Tertiary D)Quaternary E)none Ans:C Page 10
Page 10 32. Which amino acid is shown? CO2H H2N H CH2 OH A) Alanine B) Glycine C) Tyrosine D) Lysine E) Arginine Ans: C 33. Which of the following amino acids contains an aromatic ring? A) Alanine B) Serine C) Tyrosine D) Asparagine E) Glycine Ans: C 34. Given that the pKa of the acidic form of proline is 2.0, and the pKa of the basic form of proline is 10.6, what is the isoelectric point? A) 2.0 B) 6.3 C) 4.4 D) 10.6 E) 7.0 Ans: B 35. Amino acids are covalently bonded to each other through_______. A) hydrogen bonding D) α and β folds B) disulfide bridges E) none of the above C) peptide bonds Ans: C 36. How many polypeptides would be present if the following was treated with trypsin? CysGlyGluArgGlyPhePheTyrThrProLysAlaLeuTyr A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 Ans: C 37. Folding of polypeptides influenced by distant residues is an example of what protein structure? A) Primary B) Secondary C) Tertiary D) Quaternary E) none of the above Ans: C