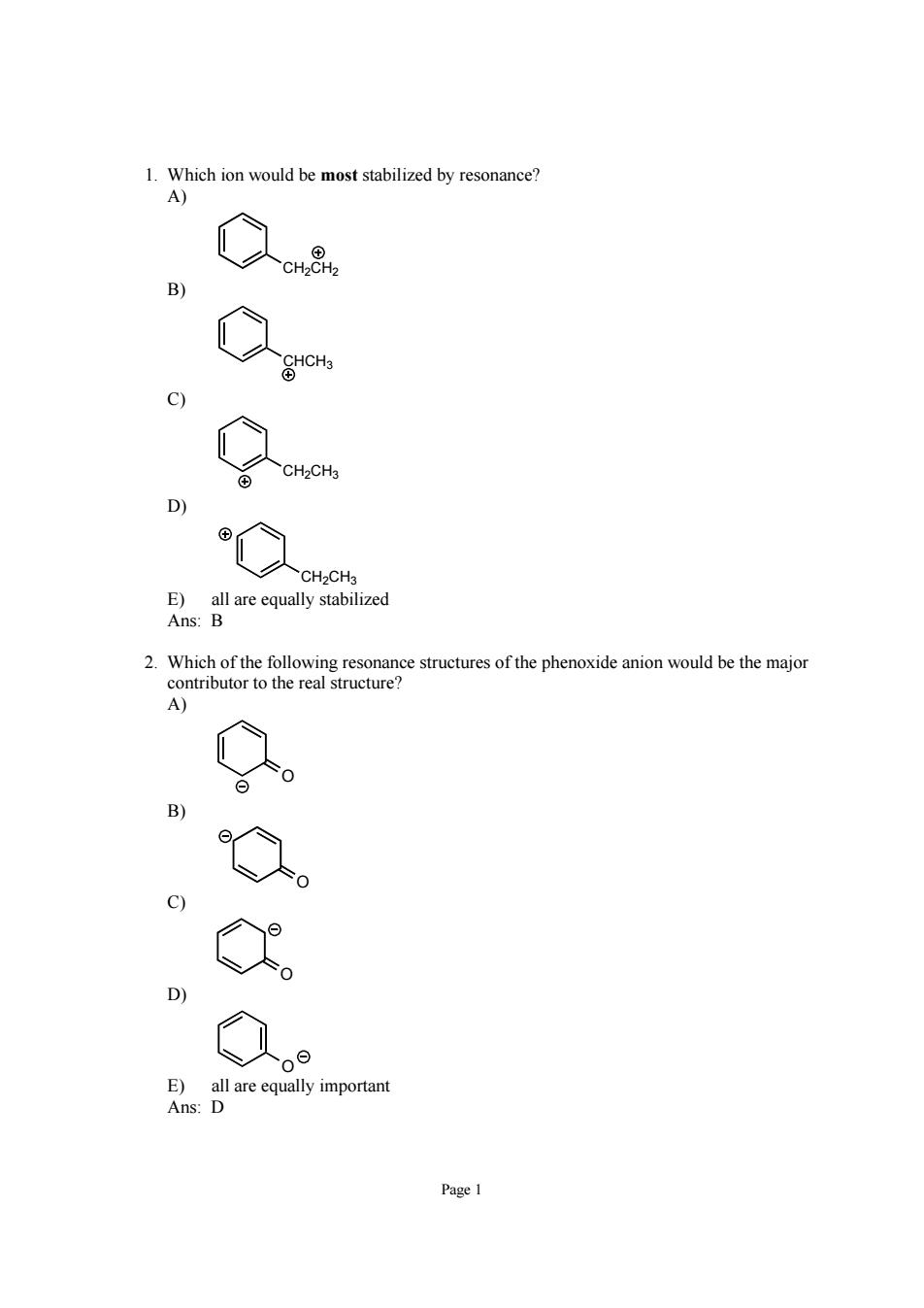
1.Which ion would be most stabilized by resonance? A)】 g 9 ④ D C CH-CHa E)all are equally stabilized Ans:B 之c6ee8 o0odck时r structure c) E)all are equally important Ans:D
Page 1 1. Which ion would be most stabilized by resonance? A) CH2CH2 B) CHCH3 C) CH2CH3 D) CH2CH3 E) all are equally stabilized Ans: B 2. Which of the following resonance structures of the phenoxide anion would be the major contributor to the real structure? A) O B) O C) O D) O E) all are equally important Ans: D
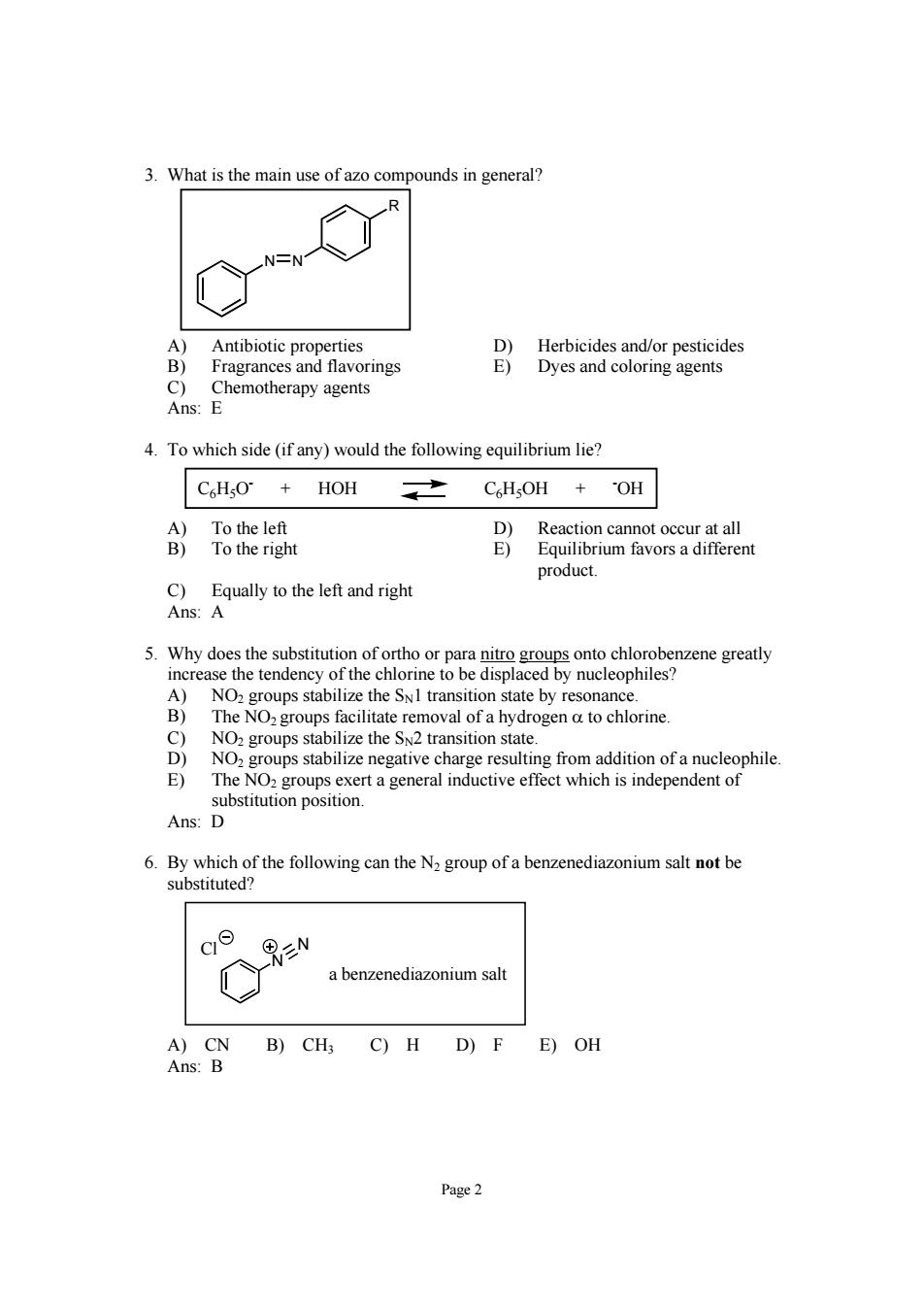
3.What is the main use of azo compounds in general? A) Antibiotic properties D)Herbicides and/or pesticides B) Fragrances and flavorings E)Dyes and coloring agents Chemotherapy agents Ans: 4.To which side(if any)would the following equilibrium lie? C6HO+HOH CHsOH +OH C)Equally to the left and right Ans:A 5.Why does the substitution of ortho or para nito groups onto chlorobenzene greatly the e to be displ d by nucleophiles n state by resc nanc sin a hy rogen a to chlorine NO. negative charge resulting from addition of a nucleophile E) The NOz groups exert a general inductive effect which is independent of substitution position. Ans:D 6.By which of the following can the N group of a benzenediazonium salt not be substituted? c N a benzenediazonium salt A)CN B)CH3 C)H D)F E)OH Ans:B Page2
Page 2 3. What is the main use of azo compounds in general? N N R A) Antibiotic properties D) Herbicides and/or pesticides B) Fragrances and flavorings E) Dyes and coloring agents C) Chemotherapy agents Ans: E 4. To which side (if any) would the following equilibrium lie? C6H5O- + HOH C6H5OH + - OH A) To the left D) Reaction cannot occur at all B) To the right E) Equilibrium favors a different product. C) Equally to the left and right Ans: A 5. Why does the substitution of ortho or para nitro groups onto chlorobenzene greatly increase the tendency of the chlorine to be displaced by nucleophiles? A) NO2 groups stabilize the SN1 transition state by resonance. B) The NO2 groups facilitate removal of a hydrogen α to chlorine. C) NO2 groups stabilize the SN2 transition state. D) NO2 groups stabilize negative charge resulting from addition of a nucleophile. E) The NO2 groups exert a general inductive effect which is independent of substitution position. Ans: D 6. By which of the following can the N2 group of a benzenediazonium salt not be substituted? N N a benzenediazonium salt Cl A) CN B) CH3 C) H D) F E) OH Ans: B
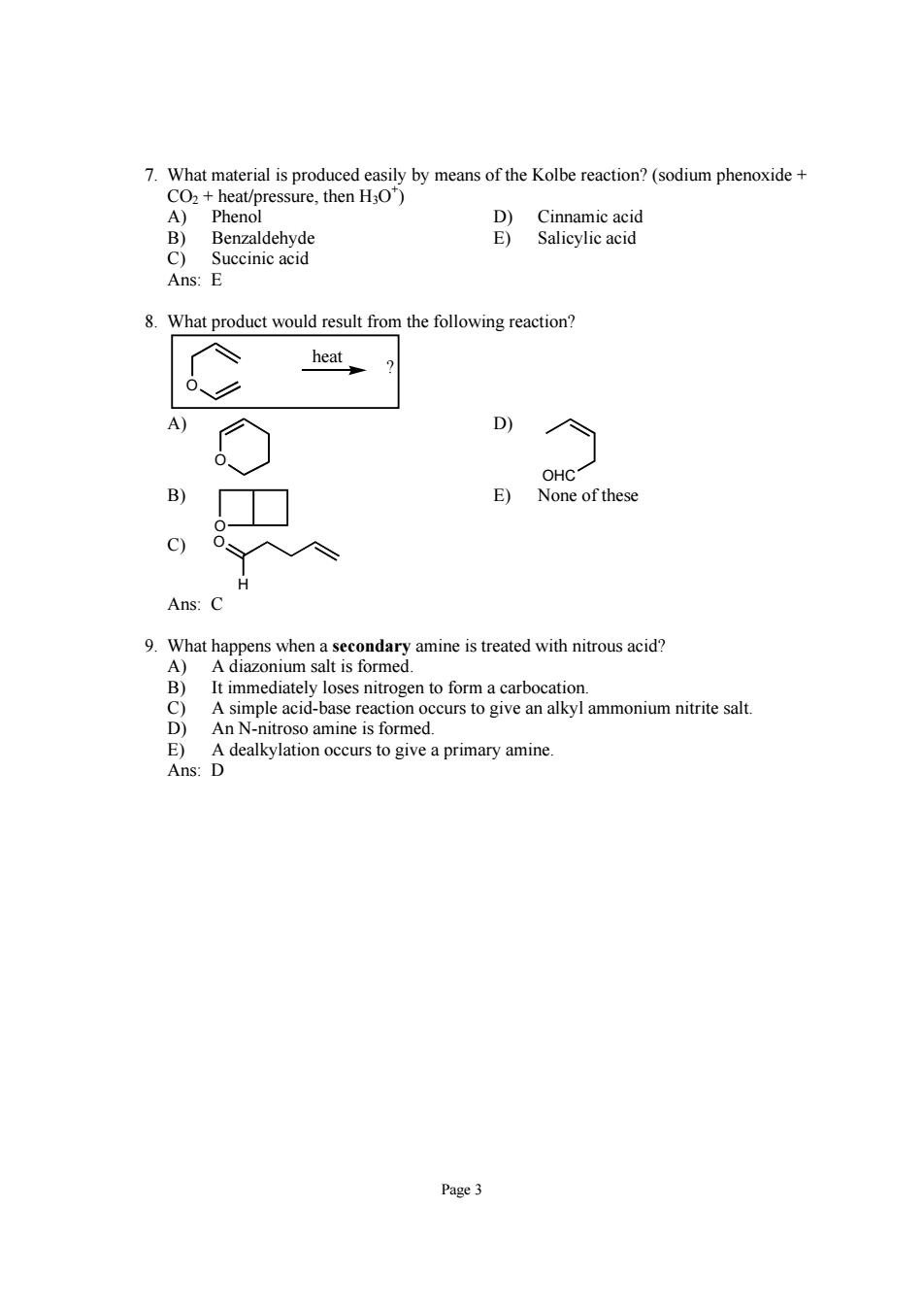
7.What material is produced easily by means of the Kolbe reaction?(sodium phenoxide heat/pressure,then HO) Succinic acid Ans:E 8.What product would result from the following reaction? heat D OHC E) None ofthese Ans: 9.What happens when a secondary amine is treated with nitrous acid? A)A diazonium salt is formed. It immediately loses nitrogen to form a carbocation. A simple acid-base reaction occurs to give an alkyl ammonium nitrite salt. troso amine is formed D dealkylation occurs to give a primary amine Page 3
Page 3 7. What material is produced easily by means of the Kolbe reaction? (sodium phenoxide + CO2 + heat/pressure, then H3O+ ) A) Phenol D) Cinnamic acid B) Benzaldehyde E) Salicylic acid C) Succinic acid Ans: E 8. What product would result from the following reaction? O ? heat A) O D) OHC B) O E) None of these C) O H Ans: C 9. What happens when a secondary amine is treated with nitrous acid? A) A diazonium salt is formed. B) It immediately loses nitrogen to form a carbocation. C) A simple acid-base reaction occurs to give an alkyl ammonium nitrite salt. D) An N-nitroso amine is formed. E) A dealkylation occurs to give a primary amine. Ans: D
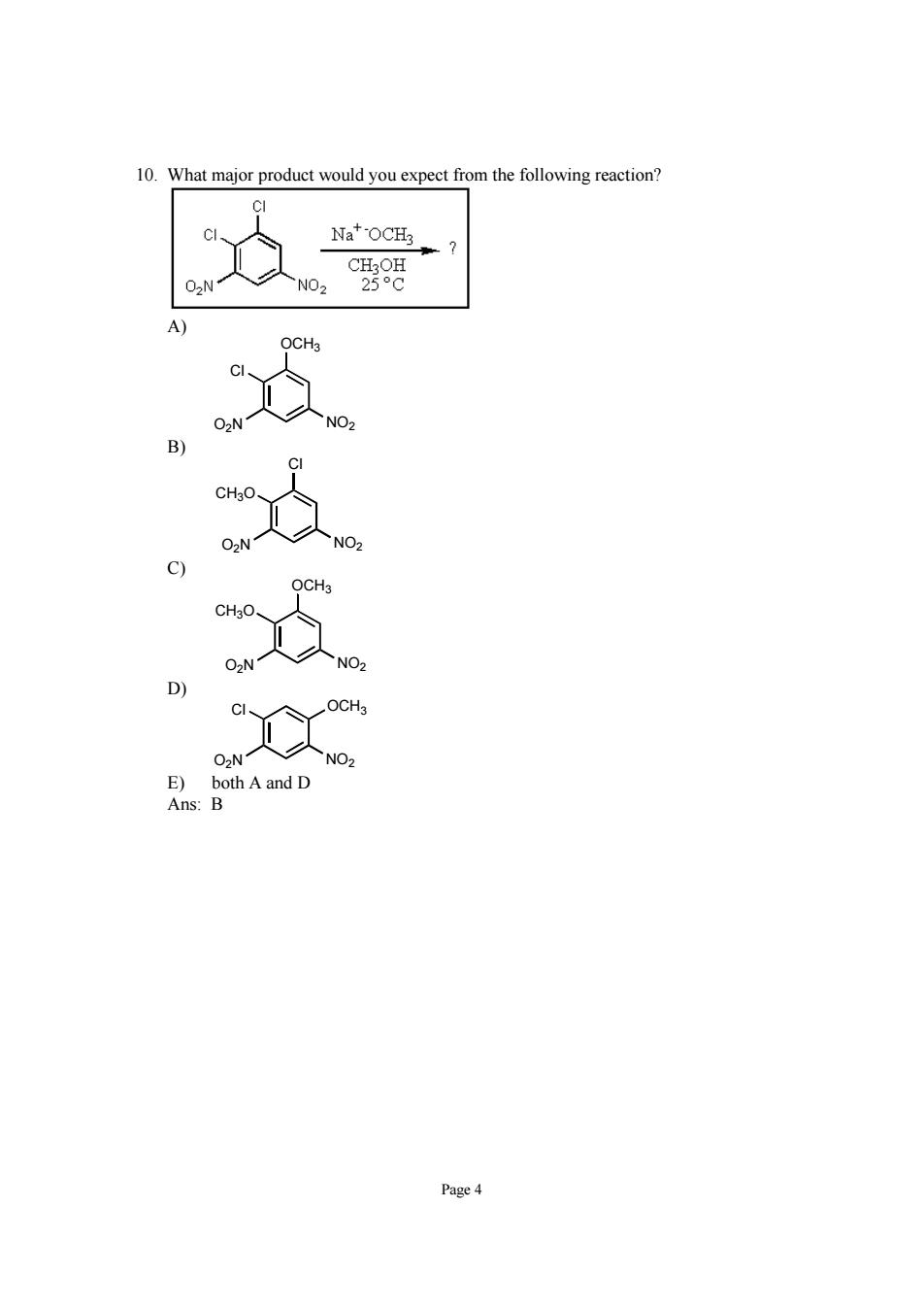
0 What major product would you expect from the following reaction? Na*OCH 、c8 Page 4
Page 4 10. What major product would you expect from the following reaction? A) Cl OCH3 O2N NO2 B) CH3O Cl O2N NO2 C) CH3O OCH3 O2N NO2 D) Cl OCH3 O2N NO2 E) both A and D Ans: B
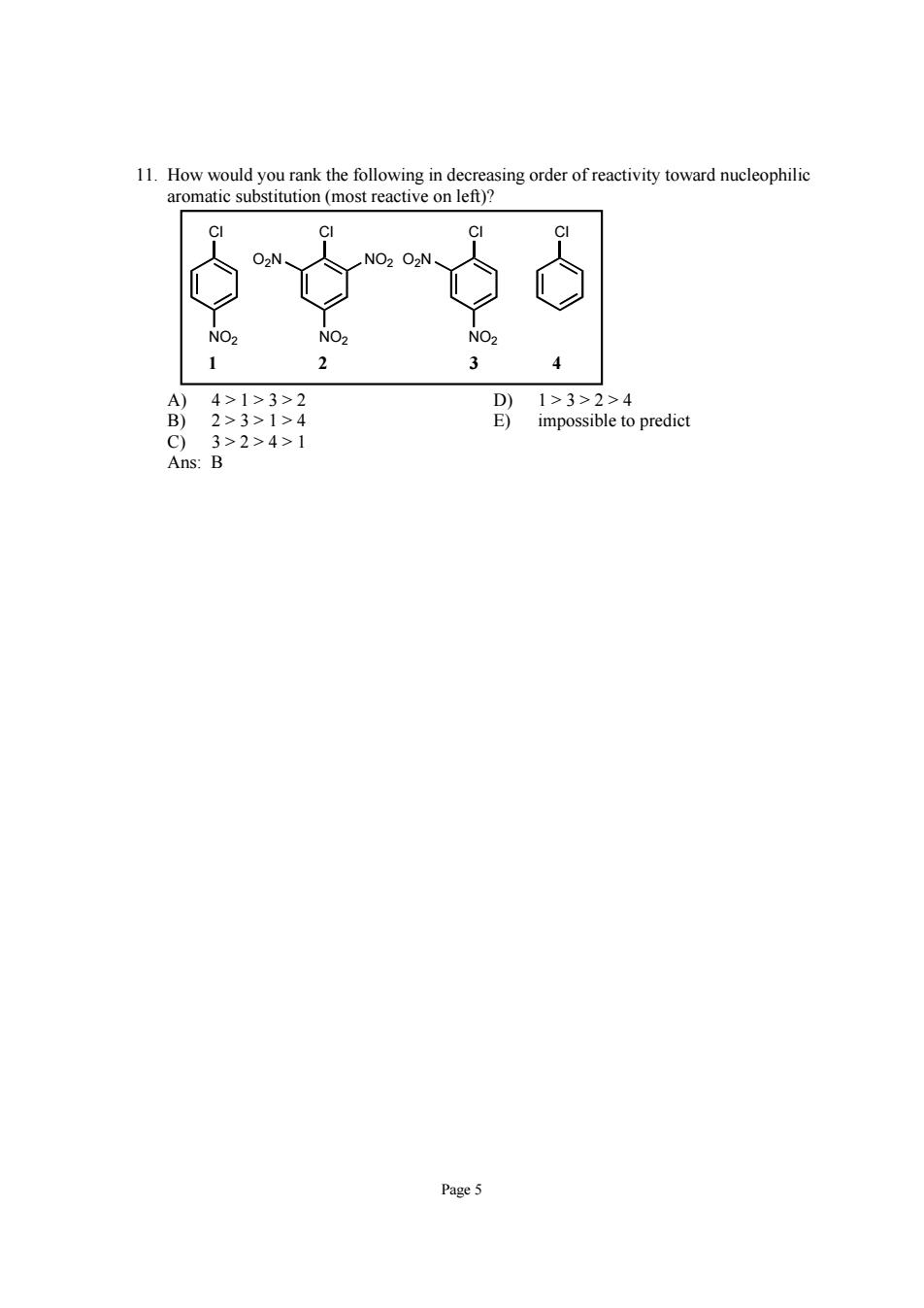
11.How would you rank the following in decreasing order of reactivity toward nucleophilic aromatic substitution (most reactive on left)? 4>1>3>2 2>3>1>4 impossible to predict 3>2>4>1 B Page 5
Page 5 11. How would you rank the following in decreasing order of reactivity toward nucleophilic aromatic substitution (most reactive on left)? Cl Cl Cl NO2 O2N NO2 Cl NO2 O2N NO2 1 2 34 A) 4 > 1 > 3 > 2 D) 1 > 3 > 2 > 4 B) 2 > 3 > 1 > 4 E) impossible to predict C) 3 > 2 > 4 > 1 Ans: B
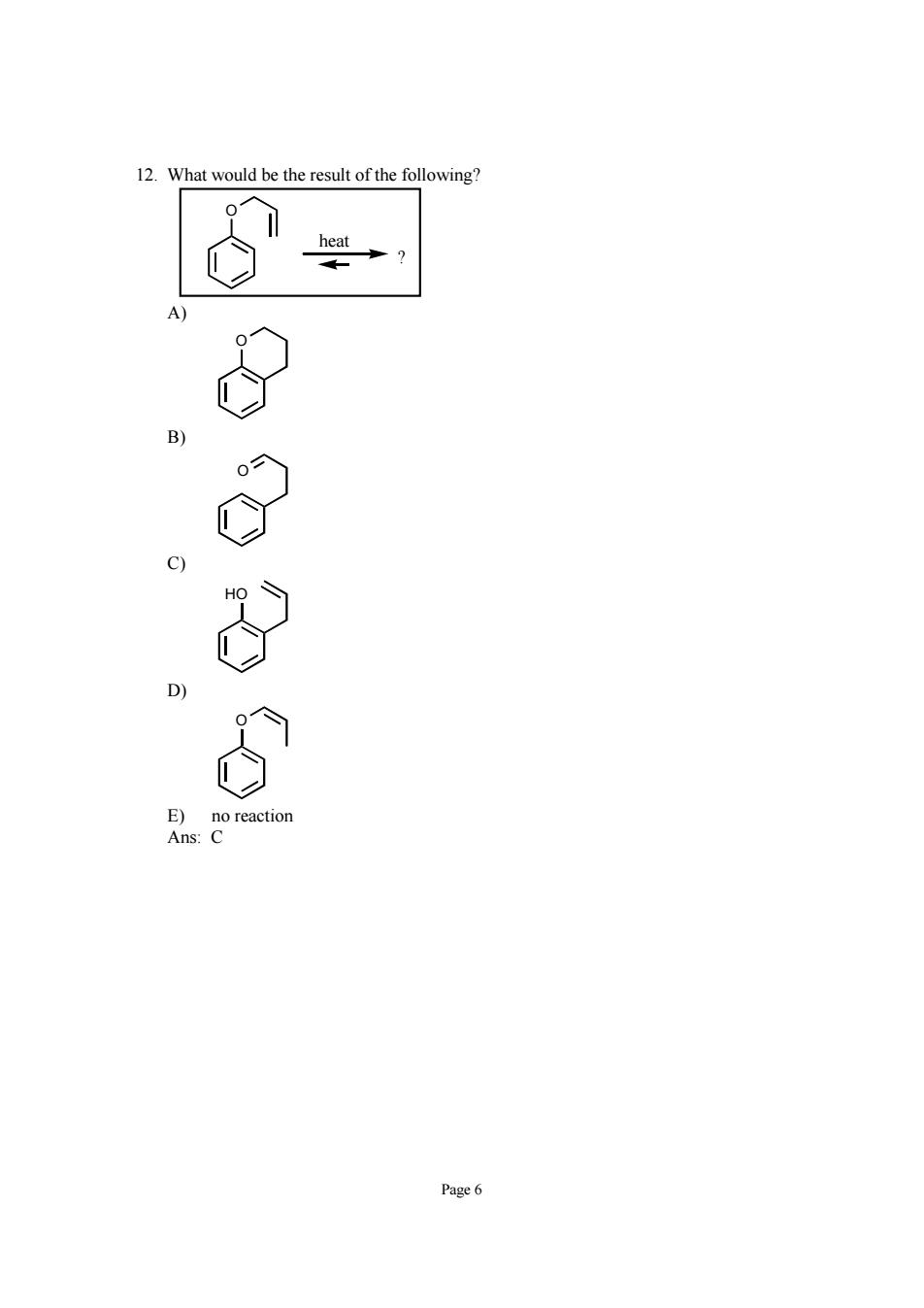
What would be the result of the following Page6
Page 6 12. What would be the result of the following? O ? heat A) O B) O C) HO D) O E) no reaction Ans: C
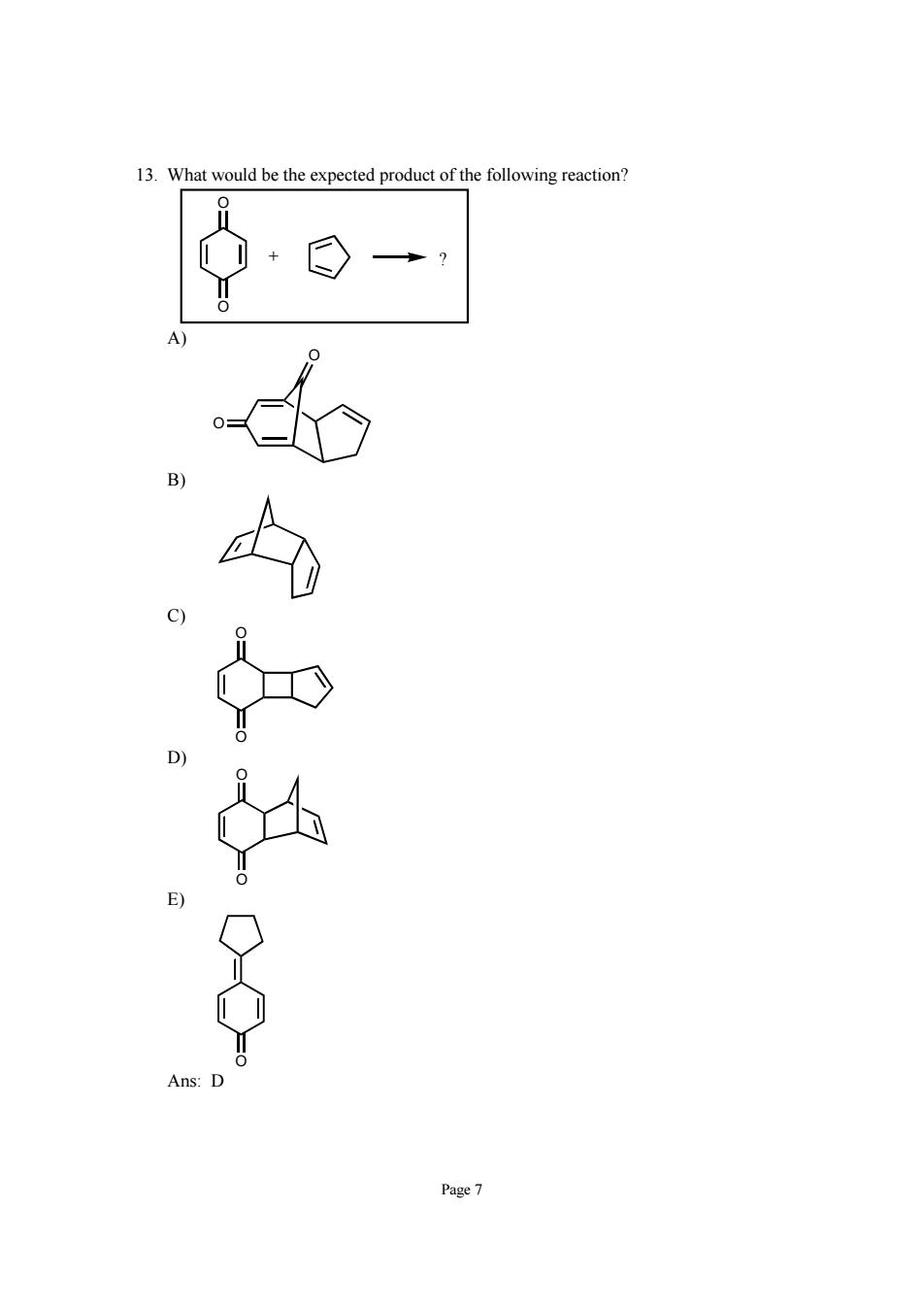
3 What would be the expected product of the following reaction o.c Page 7
Page 7 13. What would be the expected product of the following reaction? O O + ? A) O O B) C) O O D) O O E) O Ans: D
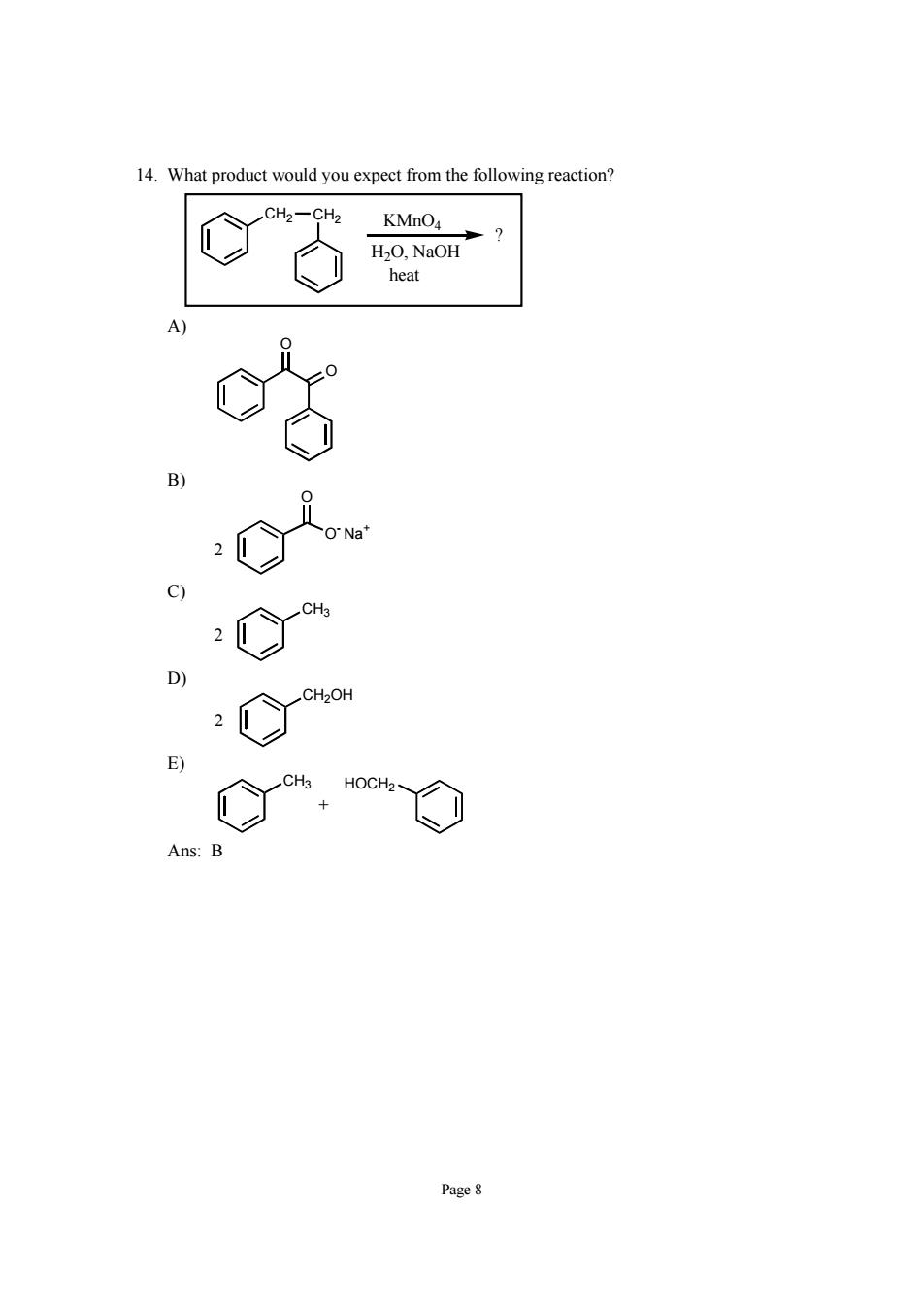
14.What product would you expect from the following reaction? KMnO4 Page8
Page 8 14. What product would you expect from the following reaction? CH2 CH2 KMnO4 H2O, NaOH heat ? A) O O B) O O- Na+ 2 C) CH3 2 D) CH2OH 2 E) CH3 HOCH2 + Ans: B
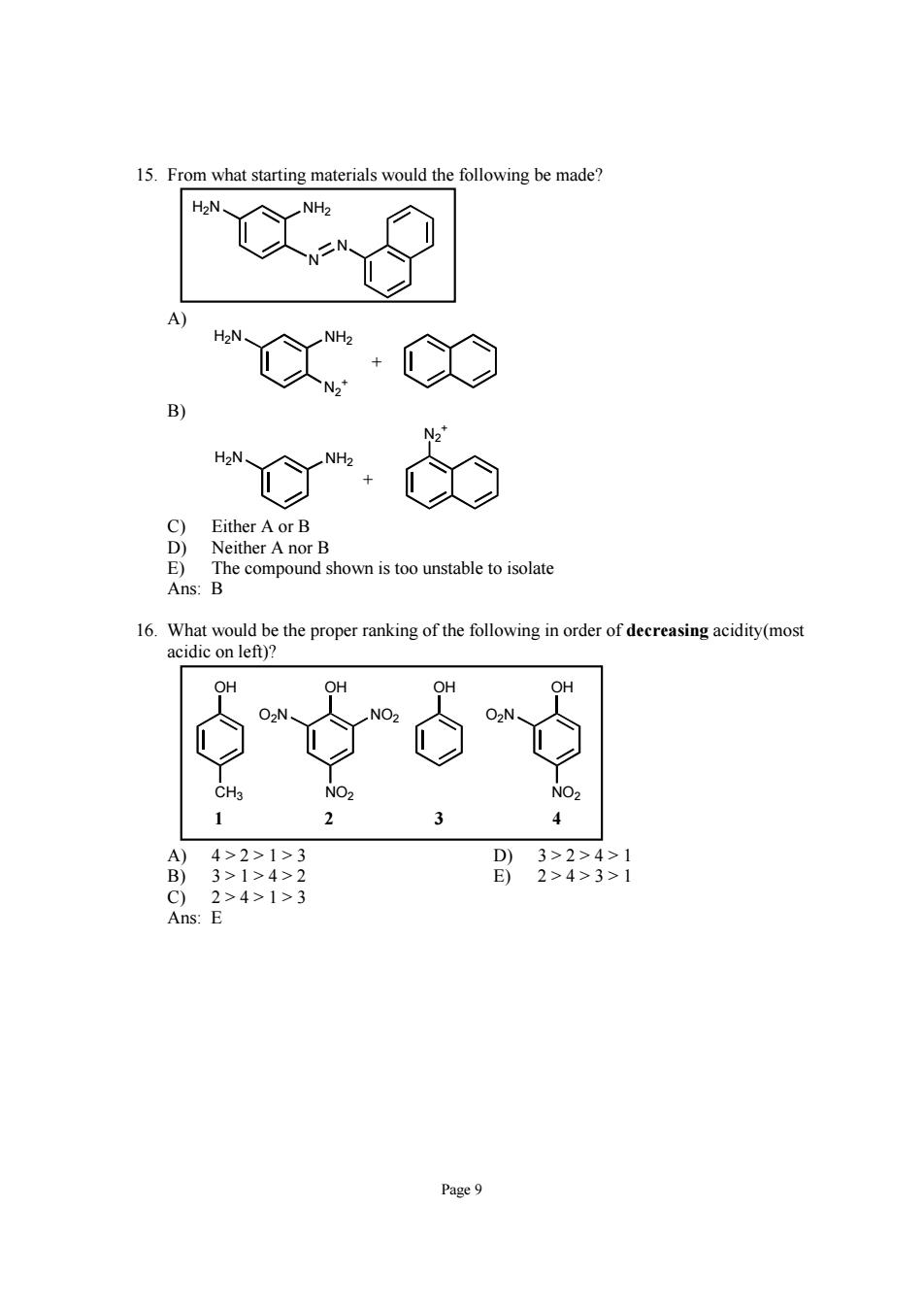
15.From what starting materials would the following be made? X·Ce E The compound shown is too unstable to isolate Ans:B 16.What would be the proper ranking of the following in order of decreasing acidity(most acidic on left)? A)4>2>1>3 B)3>1>4>2 Page9
Page 9 15. From what starting materials would the following be made? N N H2N NH2 A) N2 + H2N NH2 + B) H2N NH2 N2 + + C) Either A or B D) Neither A nor B E) The compound shown is too unstable to isolate Ans: B 16. What would be the proper ranking of the following in order of decreasing acidity(most acidic on left)? OH OH OH CH3 O2N NO2 OH NO2 O2N NO2 1 2 3 4 A) 4 > 2 > 1 > 3 D) 3 > 2 > 4 > 1 B) 3 > 1 > 4 > 2 E) 2 > 4 > 3 > 1 C) 2 > 4 > 1 > 3 Ans: E
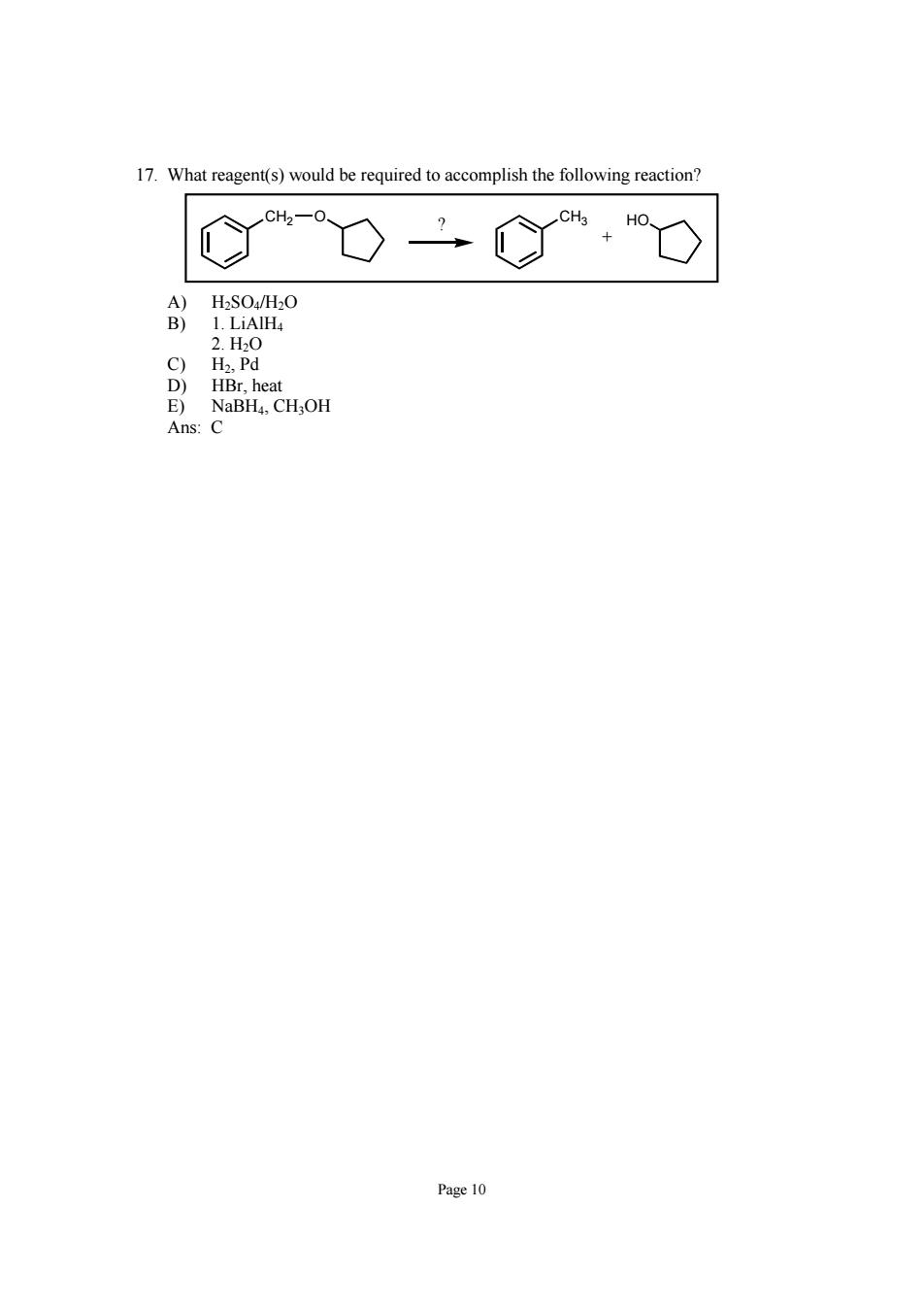
17.What reagent(s)would be required to accomplish the following reaction? C%O二C%,O A)H2SO4/H2O B)1.LiAlH 2.H0 Page 10
Page 10 17. What reagent(s) would be required to accomplish the following reaction? CH2 O CH3 HO + ? A) H2SO4/H2O B) 1. LiAlH4 2. H2O C) H2, Pd D) HBr, heat E) NaBH4, CH3OH Ans: C