
RFID and Ticketing By5080309314尹贤骏5080309286尹成模5080309341张镇宽 5100309763肖幸瑜5100309657郑浩天5100209189薛冰菡 1.Introduction 1.1 Background of RFID RFID is considered one of today's "hottest"technologies due to its specialized capacity to track and trace objects across the extended supply chain in real time.However,the RFID concept is not new but has been around for decades;in fact,it was introduced to the world for the first time during World War ll by the British Air Force to distinguish Allied aircraft from enemy aircraft using radar.Since then,this technology has been used for various niche applications such as ticketing,antitheft systems,luggage tracking systems in airports,electronic toll collection systems,etc. 1.2 RFID techniques RFID technology is a wireless Automatic ldentification and Data Capture (AIDC)technology.AIDC technologies include bar coding,optical recognition,biometrics,card technology,touch or contact memory technology,and RFID technology (see the following figure).RFID allows the accurate and automatic identification,tracking and tracing of every product from the factory,through shipping and warehousing,to the retail location without human intervention. An RFID system is composed of three main components:tags,a reader and its antennas,and a middleware application that is integrated into a host system
RFID and Ticketing By 5080309314 尹贤骏 5080309286 尹成模 5080309341 张镇宽 5100309763 肖幸瑜 5100309657 郑浩天 5100209189 薛冰菡 1. Introduction 1.1 Background of RFID RFID is considered one of today’s “hottest” technologies due to its specialized capacity to track and trace objects across the extended supply chain in real time. However, the RFID concept is not new but has been around for decades; in fact, it was introduced to the world for the first time during World War II by the British Air Force to distinguish Allied aircraft from enemy aircraft using radar. Since then, this technology has been used for various niche applications such as ticketing, antitheft systems, luggage tracking systems in airports, electronic toll collection systems, etc. 1.2 RFID techniques RFID technology is a wireless Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC) technology. AIDC technologies include bar coding, optical recognition, biometrics, card technology, touch or contact memory technology, and RFID technology (see the following figure). RFID allows the accurate and automatic identification, tracking and tracing of every product from the factory, through shipping and warehousing, to the retail location without human intervention. An RFID system is composed of three main components: tags, a reader and its antennas, and a middleware application that is integrated into a host system
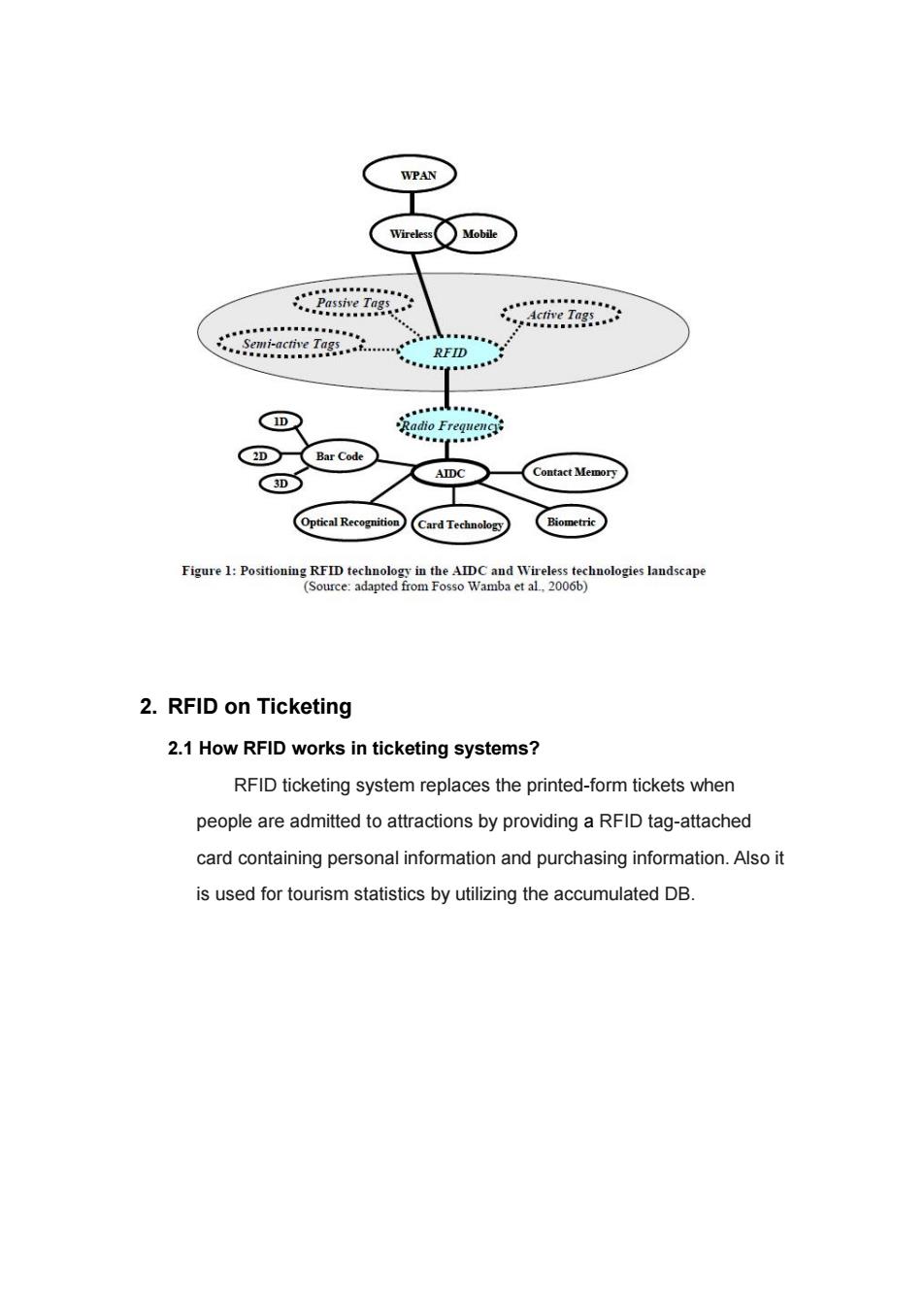
WPAN Wireles○Mobile hcmk0 RFID e 2D Bar Code AIDC Contact Memory 3D Optical Recognition Card Technology Biometric Figure 1:Positioning RFID technology in the AIDC and Wireless technologies landscape (Source:adapted from Fosso Wamba et al,2006b) 2.RFID on Ticketing 2.1 How RFID works in ticketing systems? RFID ticketing system replaces the printed-form tickets when people are admitted to attractions by providing a RFID tag-attached card containing personal information and purchasing information.Also it is used for tourism statistics by utilizing the accumulated DB
2. RFID on Ticketing 2.1 How RFID works in ticketing systems? RFID ticketing system replaces the printed-form tickets when people are admitted to attractions by providing a RFID tag-attached card containing personal information and purchasing information. Also it is used for tourism statistics by utilizing the accumulated DB

1Online ticket purcha 2 check online purchase 3 Purchase history by customers card Wri Center Manogement System Operator Mansgement 益7门4tmn9m门t Ticket salls Tourist comgany management Ticketing Management system Customers entry 4 save by RFID stomers DB Manager Administration (Adults.admission fee) Ticketing Management Manage customers INTERNET Sat65轴n时答他t地m已nt ds车初七Ts的: 3 Customer entry transmission by RFID (Adults.admission fee) 2 entered sightseeing spots Tag RFID card After Ticketing RFID ticketing system consists of online ticket selling system, center management systems,broker management system,ticketing management system,and online ticket reselling system utilizing existing systems.(See figure above.) 2.2 Applications In the field of ticketing,RFID is mainly applied in the following fields. Bus Tickets 2008 Olympics Amusement Park Certain ballgame tickets Tourist attractions tickets 2.3 Operational Practices One of the operational practices of RFID on ticketing is the application
RFID ticketing system consists of online ticket selling system, center management systems, broker management system, ticketing management system, and online ticket reselling system utilizing existing systems. (See figure above.) 2.2 Applications In the field of ticketing, RFID is mainly applied in the following fields. Bus Tickets 2008 Olympics Amusement Park Certain ballgame tickets Tourist attractions tickets 2.3 Operational Practices One of the operational practices of RFID on ticketing is the application

on the 2008 Olympics. When the 2008 Summer Olympic Games was held in August,the event put many athletes in the spotlight.The bright lights will also shine on high-tech ticketing and food-tracking systems built on RFID technology. In fact,success of the 2008 Beijing Olympics and the 2008 Beijing Paralympics Summer Games in September meant that RFID companies will receive orders for 70 million tickets to support the World Expo in Shanghai in 2010. 3.Comparison with other techniques When thinking about other techniques functioning similarly to RFID,we think of barcode.Barcode is one of the most common used techniques for recognizing.Then what's the difference between barcode and RFID?What are the advantages and disadvantages of RFID over barcode? 3.1What is Barcode? A barcode is a visual representation of data that is scanned and interpreted for information.Each barcode contains a certain code which works as a tracking technology for products;and is represented in a sequence of lines or other shapes. 3.2 Different Capacities of RFID barcode RFID Barcode Line of Site Not required (in most cases) Required Passive UHF RFID: Up to 40 feet(fixed readers) Up to 20 feet (handheld readers) Several inches up to several Read Range Active RFID: feet Up to 100's of feet or more Read Rate 10's,100's0r1000's Only one at a time
on the 2008 Olympics. When the 2008 Summer Olympic Games was held in August, the event put many athletes in the spotlight. The bright lights will also shine on high-tech ticketing and food-tracking systems built on RFID technology. In fact, success of the 2008 Beijing Olympics and the 2008 Beijing Paralympics Summer Games in September meant that RFID companies will receive orders for 70 million tickets to support the World Expo in Shanghai in 2010. 3. Comparison with other techniques When thinking about other techniques functioning similarly to RFID, we think of barcode. Barcode is one of the most common used techniques for recognizing. Then what’s the difference between barcode and RFID? What are the advantages and disadvantages of RFID over barcode? 3.1What is Barcode? A barcode is a visual representation of data that is scanned and interpreted for information. Each barcode contains a certain code which works as a tracking technology for products; and is represented in a sequence of lines or other shapes. 3.2 Different Capacities of RFID & barcode RFID Barcode Line of Site Not required (in most cases) Required Read Range Passive UHF RFID: - Up to 40 feet (fixed readers) - Up to 20 feet (handheld readers) Active RFID: - Up to 100's of feet or more Several inches up to several feet Read Rate 10's, 100's or 1000's Only one at a time
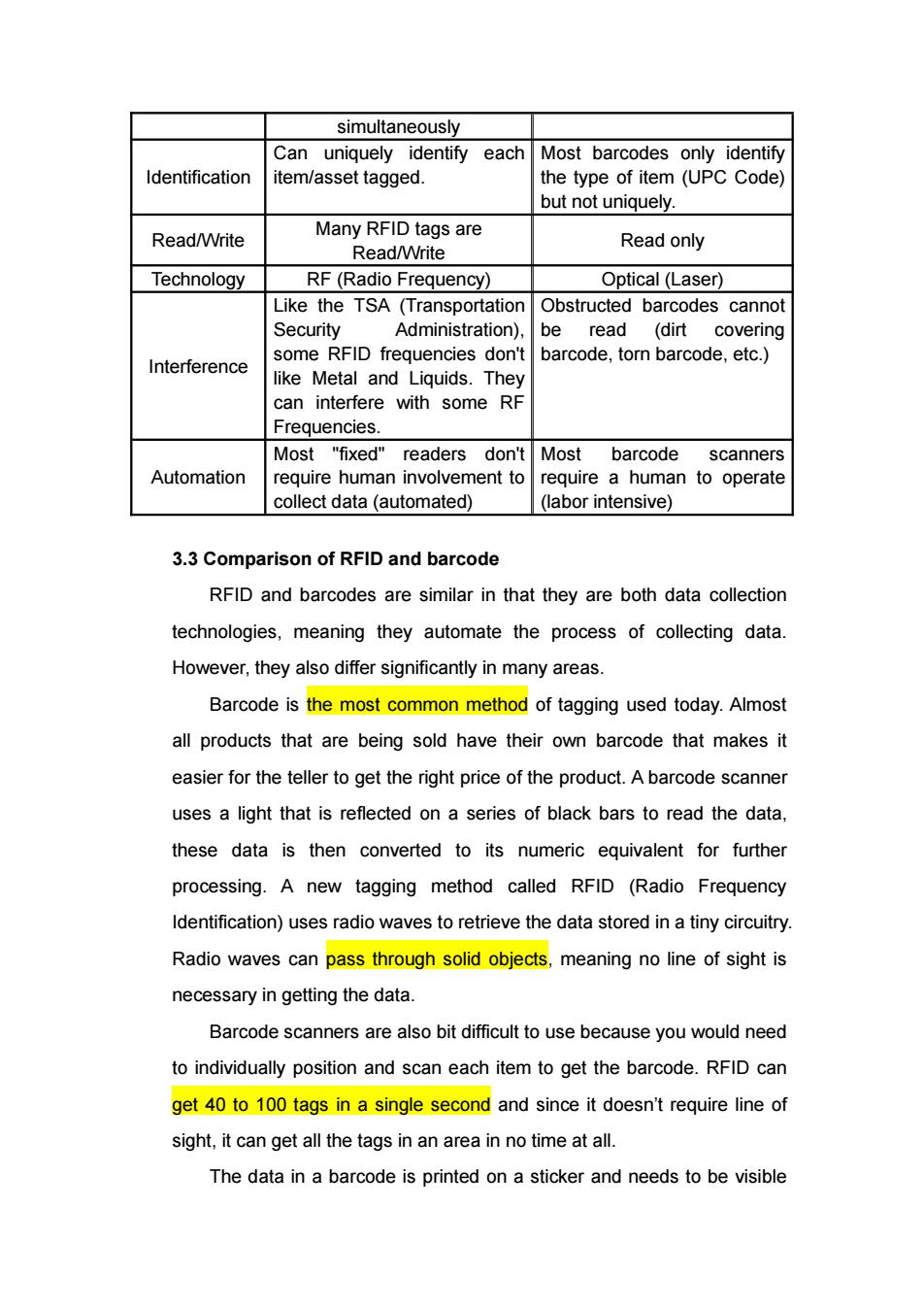
simultaneously Can uniquely identify each Most barcodes only identify Identification item/asset tagged. the type of item(UPC Code) but not uniquely. Read/Write Many RFID tags are Read/Write Read only Technology RF(Radio Frequency) Optical (Laser) Like the TSA (Transportation Obstructed barcodes cannot Security Administration), be read (dirt covering some RFID frequencies don't barcode,torn barcode,etc.) Interference like Metal and Liquids.They can interfere with some RF Frequencies. Most "fixed"readers don't Most barcode scanners Automation require human involvement to require a human to operate collect data(automated) (labor intensive) 3.3 Comparison of RFID and barcode RFID and barcodes are similar in that they are both data collection technologies,meaning they automate the process of collecting data. However,they also differ significantly in many areas. Barcode is the most common method of tagging used today.Almost all products that are being sold have their own barcode that makes it easier for the teller to get the right price of the product.A barcode scanner uses a light that is reflected on a series of black bars to read the data. these data is then converted to its numeric equivalent for further processing.A new tagging method called RFID (Radio Frequency Identification)uses radio waves to retrieve the data stored in a tiny circuitry Radio waves can pass through solid objects,meaning no line of sight is necessary in getting the data. Barcode scanners are also bit difficult to use because you would need to individually position and scan each item to get the barcode.RFID can get 40 to 100 tags in a single second and since it doesn't require line of sight,it can get all the tags in an area in no time at all. The data in a barcode is printed on a sticker and needs to be visible
simultaneously Identification Can uniquely identify each item/asset tagged. Most barcodes only identify the type of item (UPC Code) but not uniquely. Read/Write Many RFID tags are Read/Write Read only Technology RF (Radio Frequency) Optical (Laser) Interference Like the TSA (Transportation Security Administration), some RFID frequencies don't like Metal and Liquids. They can interfere with some RF Frequencies. Obstructed barcodes cannot be read (dirt covering barcode, torn barcode, etc.) Automation Most "fixed" readers don't require human involvement to collect data (automated) Most barcode scanners require a human to operate (labor intensive) 3.3 Comparison of RFID and barcode RFID and barcodes are similar in that they are both data collection technologies, meaning they automate the process of collecting data. However, they also differ significantly in many areas. Barcode is the most common method of tagging used today. Almost all products that are being sold have their own barcode that makes it easier for the teller to get the right price of the product. A barcode scanner uses a light that is reflected on a series of black bars to read the data, these data is then converted to its numeric equivalent for further processing. A new tagging method called RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) uses radio waves to retrieve the data stored in a tiny circuitry. Radio waves can pass through solid objects, meaning no line of sight is necessary in getting the data. Barcode scanners are also bit difficult to use because you would need to individually position and scan each item to get the barcode. RFID can get 40 to 100 tags in a single second and since it doesn’t require line of sight, it can get all the tags in an area in no time at all. The data in a barcode is printed on a sticker and needs to be visible

so that the scanner can easily spot it and get the data.This creates two problems that make barcodes unsuitable for some applications.Exposure means that the tag can easily get damaged or worn out due to the weather or other reasons.It is also very easy to counterfeit,making it unsuitable for applications that require some level of security.RFID doesn't suffer from any of this.Since it doesn't require line of sight,it can be tucked inside where it is safe from damage.Its electronic nature also means that the data can be encrypted in order to prevent malicious people from copying it. The only drawback of RFID is its price.Because barcodes only use paper,it is substantially cheaper compared to RFID tags which are small integrated circuits.But the cost of RFID tags is still very low considering the capabilities that it provides. 3.4.Summary In summary,we can summarize the five main differences between the two techniques by comparing their capacities. a.Barcodes uses a sensor and light to read the data on the tag while RFID uses radio waves,which doesn't need line of sight,to get the data b.Barcode scanners can only process tags one at a time while RFID scanners can process dozens in a single second c.Barcodes are really simple and can be easily replicated or counterfeited while RFID is more complex and secure d.RFID tags can be hidden to protect against the environment while barcodes need to be exposed e..Barcodes are very cheap while RFID tags are substantial pricier. 4.Future Prospects After doing this research,members of our group have got general
so that the scanner can easily spot it and get the data. This creates two problems that make barcodes unsuitable for some applications. Exposure means that the tag can easily get damaged or worn out due to the weather or other reasons. It is also very easy to counterfeit, making it unsuitable for applications that require some level of security. RFID doesn’t suffer from any of this. Since it doesn’t require line of sight, it can be tucked inside where it is safe from damage. Its electronic nature also means that the data can be encrypted in order to prevent malicious people from copying it. The only drawback of RFID is its price. Because barcodes only use paper, it is substantially cheaper compared to RFID tags which are small integrated circuits. But the cost of RFID tags is still very low considering the capabilities that it provides. 3.4. Summary In summary, we can summarize the five main differences between the two techniques by comparing their capacities. a. Barcodes uses a sensor and light to read the data on the tag while RFID uses radio waves, which doesn’t need line of sight, to get the data b. Barcode scanners can only process tags one at a time while RFID scanners can process dozens in a single second c. Barcodes are really simple and can be easily replicated or counterfeited while RFID is more complex and secure d. RFID tags can be hidden to protect against the environment while barcodes need to be exposed e..Barcodes are very cheap while RFID tags are substantial pricier. 4. Future Prospects After doing this research, members of our group have got general

knowledge about RFID technology.And we consider RFID has broad development prospects.Here are some thoughts on future RFID from our point of view. RFID technique's application is limited mainly because of its high price today,while we think the cost of RFID will be much more lowered in the near future as our technology is developing very fast.And thus it will be widely used and become an important part of our life. In addition,one problem of RFID today is that information privacy is not secured as the information in the tags is read without touch.But in the future, we believe it will never be a problem.RFID technique will be used in safety and confidence one day. In one word,RFID is already the most widely used automatic identification technique,and it will be even more widely used in the future.RFID technique is certain to change our work and life deeply
knowledge about RFID technology. And we consider RFID has broad development prospects. Here are some thoughts on future RFID from our point of view. RFID technique’s application is limited mainly because of its high price today, while we think the cost of RFID will be much more lowered in the near future as our technology is developing very fast. And thus it will be widely used and become an important part of our life. In addition, one problem of RFID today is that information privacy is not secured as the information in the tags is read without touch. But in the future, we believe it will never be a problem. RFID technique will be used in safety and confidence one day. In one word, RFID is already the most widely used automatic identification technique, and it will be even more widely used in the future. RFID technique is certain to change our work and life deeply