
Supply Contracts Xiaohong Pang Automation Department Shanghai Jiaotong University
Supply Contracts Xiaohong Pang Automation Department Shanghai Jiaotong University

SnowTime Costs Production cost per unit(C):$80 o Selling price per unit(S):$125 o Salvage value per unit (V):$20 Fixed production cost(F):$100,000 Q is production quantity,D is demand Profit Revenue-Variable Cost-Fixed Cost Salvage
SnowTime : Costs Production cost per unit (C): $80 Selling price per unit (S): $125 Salvage value per unit (V): $20 Fixed production cost (F): $100,000 Q is production quantity, D is demand Profit = Revenue - Variable Cost - Fixed Cost + Salvage

Key Insights from this Model The optimal order quantity is not necessarily equal to average forecast demand. The optimal quantity depends on the relationship between marginal profit and marginal cost As order quantity increases,average profit first increases,and then decreases. As production quantity increases,risk increases.In other words,the probability of large gains and of large losses increases
Key Insights from this Model The optimal order quantity is not necessarily equal to average forecast demand. The optimal quantity depends on the relationship between marginal profit and marginal cost. As order quantity increases, average profit first increases, and then decreases. As production quantity increases, risk increases. In other words, the probability of large gains and of large losses increases

Supply Contracts Distributor optimal order quantity is 12.000 units Distributor expected profit is $470,000 Manufacturer profit is $440,000 Supply Chain Profit is $910,000 How can the distributor and manufacturer increase the profit of both?
Supply Contracts Distributor optimal order quantity is 12,000 units Distributor expected profit is $470,000 Manufacturer profit is $440,000 Supply Chain Profit is $910,000 How can the distributor and manufacturer increase the profit of both?

Think-Pair-Share Take 2 min.to read example 4-1(p105),consider the following questions,then discuss with your neighbors. 1.Who takes the risk? 2.What would the manufacturer like the retailer to do?
1. Who takes the risk? 2. What would the manufacturer like the retailer to do? Think – Pair – Share Take 2 min. to read example 4-1(p105), consider the following questions, then discuss with your neighbors
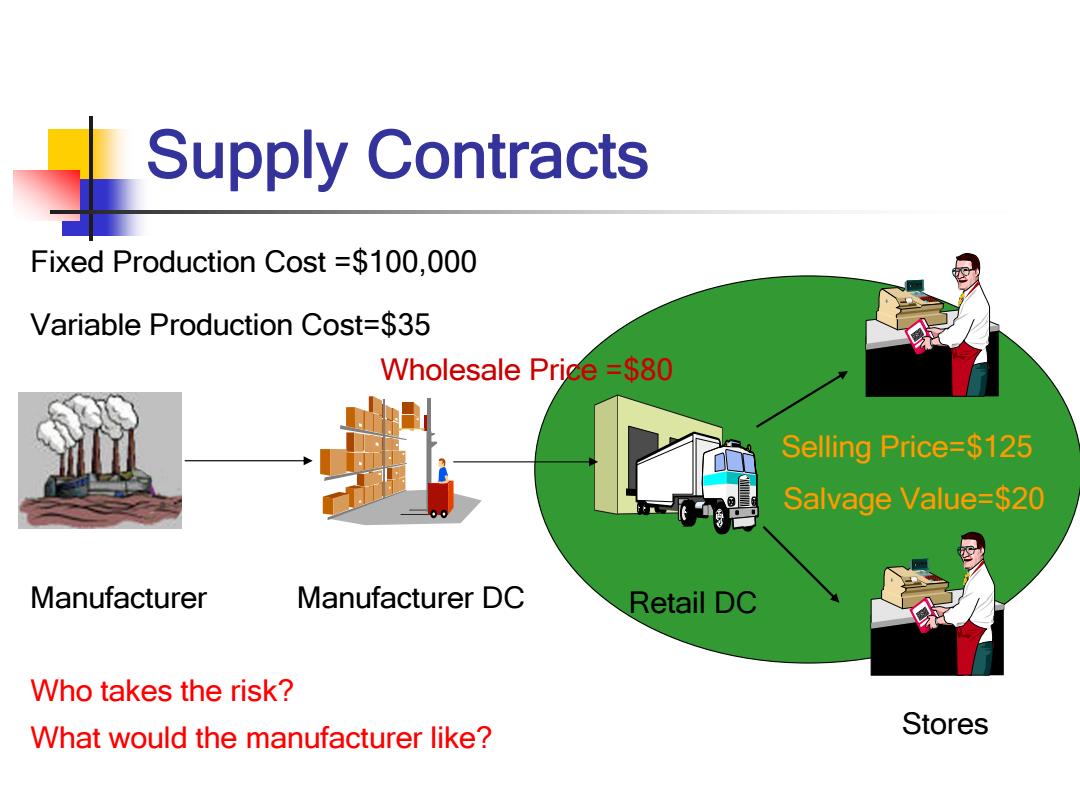
_Supply Contracts Fixed Production Cost =$100,000 Variable Production Cost=$35 Wholesale Price =$80 Selling Price=$125 Salvage Value=$20 Manufacturer Manufacturer DC Retail DC Who takes the risk? What would the manufacturer like? Stores
Manufacturer Manufacturer DC Retail DC Stores Fixed Production Cost =$100,000 Variable Production Cost=$35 Selling Price=$125 Salvage Value=$20 Wholesale Price =$80 Who takes the risk? What would the manufacturer like? Supply Contracts
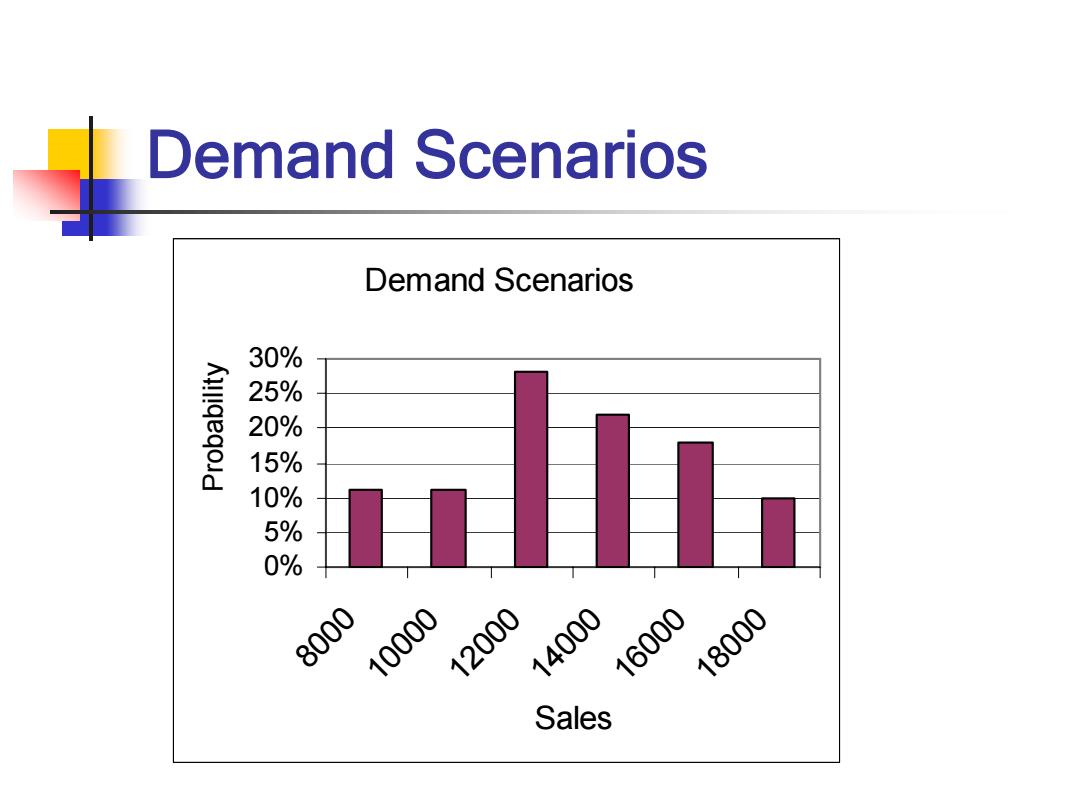
Demand Scenarios Demand Scenarios 30% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 0% 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 18000 Sales
Demand Scenarios Demand Scenarios 0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 18000 Sales Probability
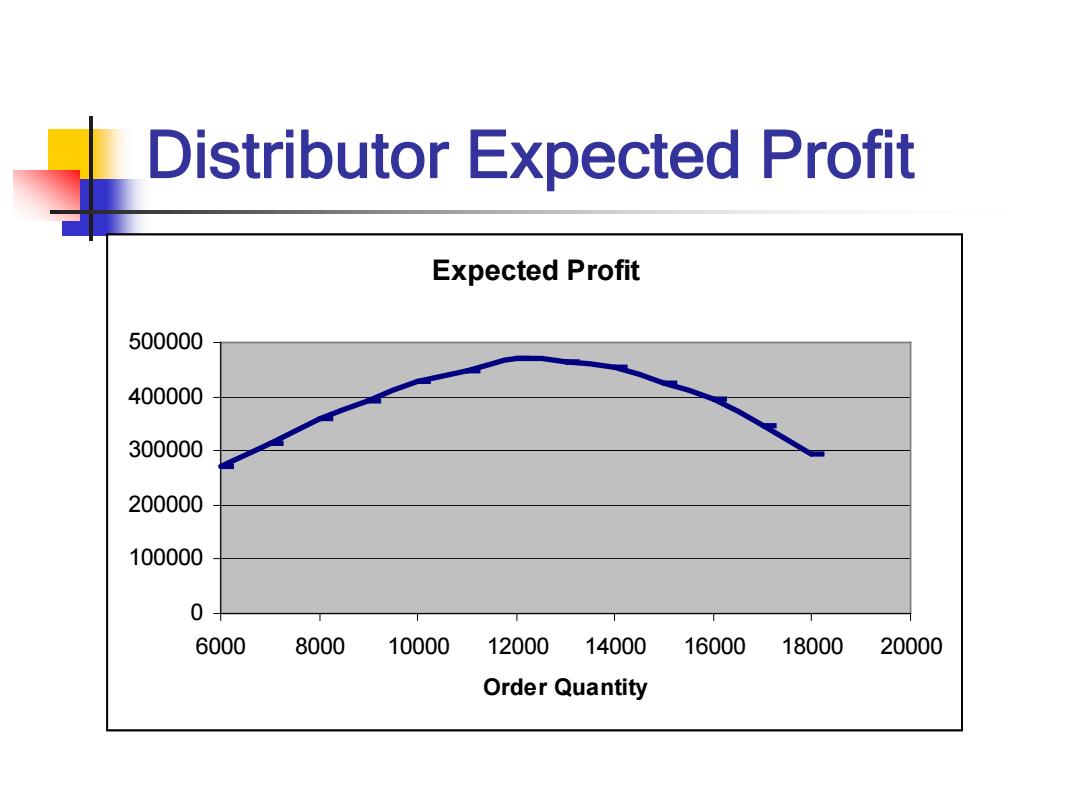
Distributor Expected Profit Expected Profit 500000 400000 300000 200000 100000 0 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 18000 20000 Order Quantity
Distributor Expected Profit Expected Profit 0 100000 200000 300000 400000 500000 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 18000 20000 Order Quantity
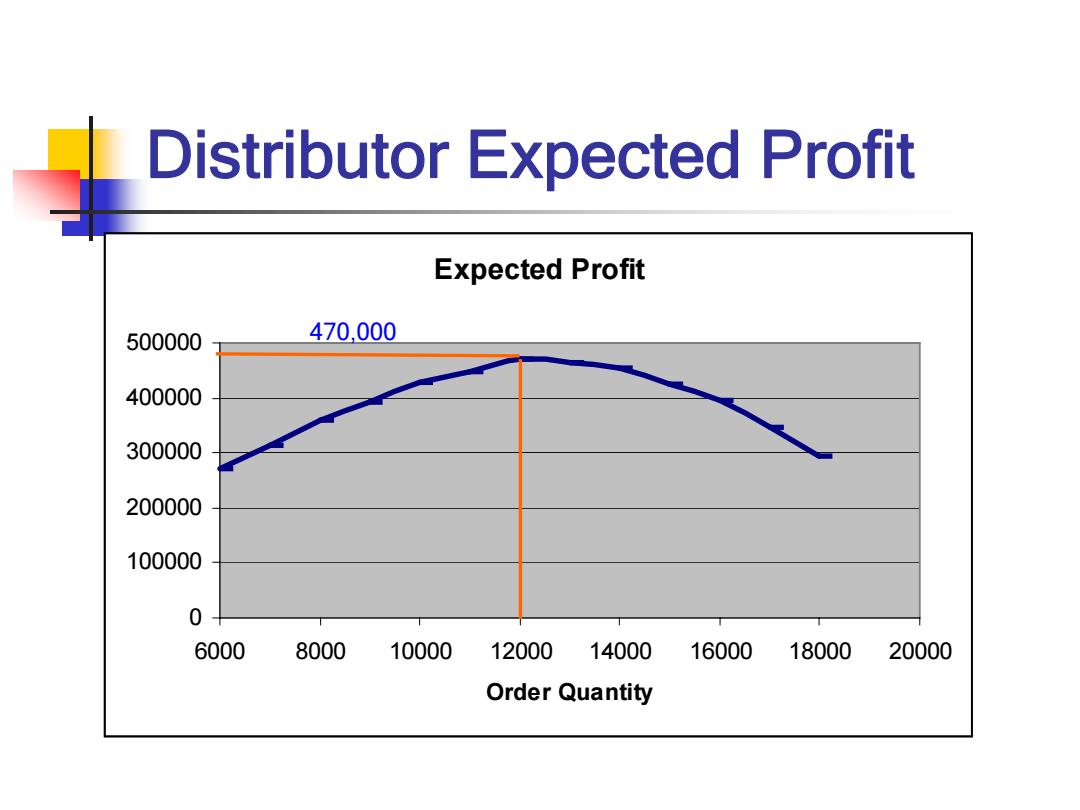
Distributor Expected Profit Expected Profit 500000 470,000 400000 300000 200000 100000 0 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 18000 20000 Order Quantity
Distributor Expected Profit Expected Profit 0 100000 200000 300000 400000 500000 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 18000 20000 Order Quantity 470,000

Supply Contracts Distributor optimal order quantity is 12.000 units Distributor expected profit is $470,000 Manufacturer profit is $440,000 Supply Chain Profit is $910,000 How can the distributor and manufacturer increase the profit of both?
Supply Contracts Distributor optimal order quantity is 12,000 units Distributor expected profit is $470,000 Manufacturer profit is $440,000 Supply Chain Profit is $910,000 How can the distributor and manufacturer increase the profit of both?