
The Value of Information Xiaohong Pang Automation Department Shanghai Jiaotong University
The Value of Information Xiaohong Pang Automation Department Shanghai Jiaotong University

Lecture Outline Introduction ■The Bullwhip Effect ■Effective Forecasts Information for the Coordination of Systems Locating Desired Products Lead time reduction Integrating the Supply Chain
Lecture Outline Introduction The Bullwhip Effect Effective Forecasts Information for the Coordination of Systems Locating Desired Products Lead time reduction Integrating the Supply Chain

Introduction What is the Bullwhip Effect? What are the main factors contributing to the Bullwhip Effect?
Introduction What is the Bullwhip Effect? What are the main factors contributing to the Bullwhip Effect?
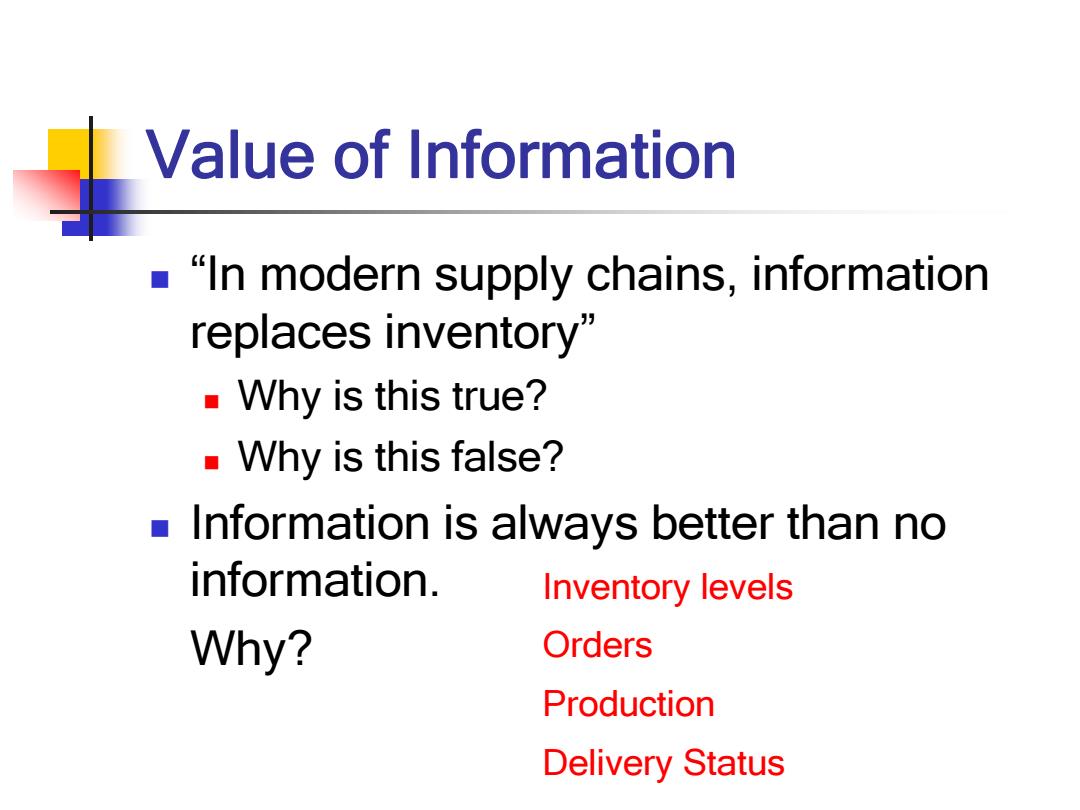
Value of Information "In modern supply chains,information replaces inventory Why is this true? ■Why is this false? Information is always better than no information. Inventory levels Why? Orders Production Delivery Status
Value of Information “In modern supply chains, information replaces inventory” Why is this true? Why is this false? Information is always better than no information. Why? Production Delivery Status Inventory levels Orders

Value of Information Information Helps reduce variability Helps improve forecasts Enables coordination of systems and strategies Improves customer service Enables firms to react more quickly to changing market conditions. Facilitates lead time reductions
Value of Information Information Helps reduce variability Helps improve forecasts Enables coordination of systems and strategies Improves customer service Enables firms to react more quickly to changing market conditions. Facilitates lead time reductions
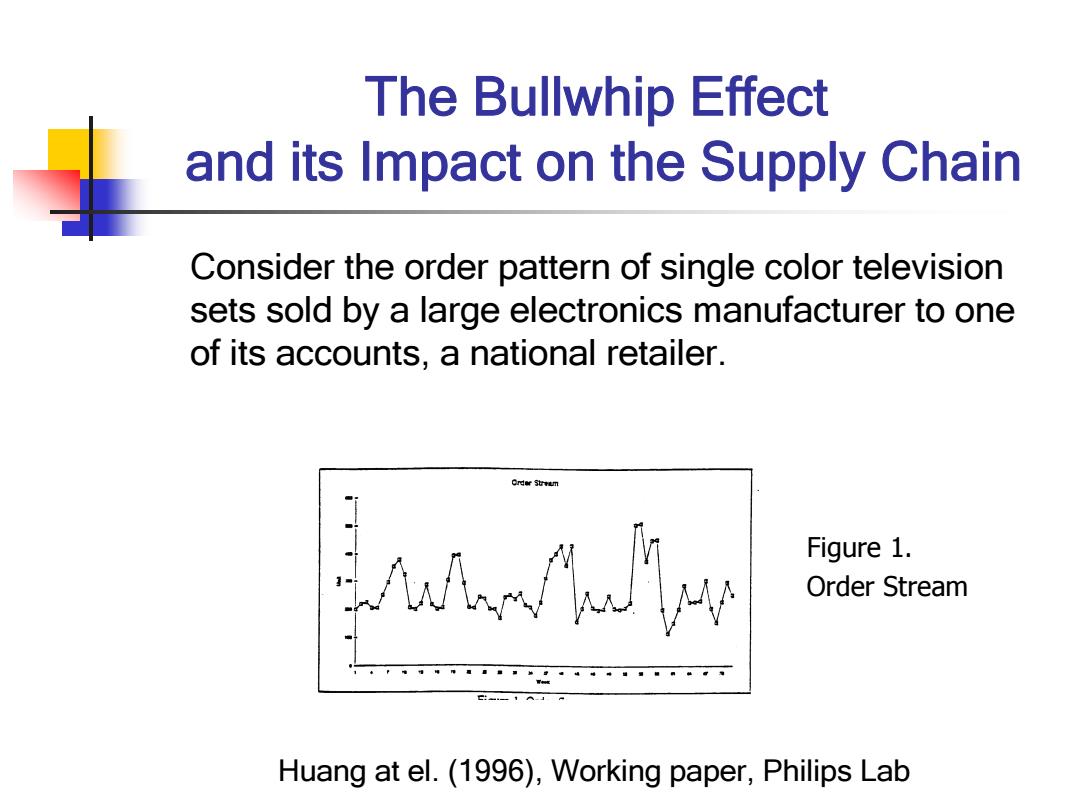
The Bullwhip Effect and its Impact on the Supply Chain Consider the order pattern of single color television sets sold by a large electronics manufacturer to one of its accounts,a national retailer. Cr时rstn Figure 1. Order Stream Huang at el.(1996),Working paper,Philips Lab
The Bullwhip Effect and its Impact on the Supply Chain Consider the order pattern of single color television sets sold by a large electronics manufacturer to one of its accounts, a national retailer. Figure 1. Order Stream Huang at el. (1996), Working paper, Philips Lab

The Bullwhip Effect and its Impact on the Supply Chain Pount-af-esles Orta af Three DCa-Origiral Figure 2.Point-of-sales Data-Original Point-of-sales Data of Three DCa.Removing Promotions Figure 3.POS Data After x%2f1 Removing Promotions
Figure 2. Point-of-sales Data-Original Figure 3. POS Data After Removing Promotions The Bullwhip Effect and its Impact on the Supply Chain

The Bullwhip Effect and its Impact on the Supply Chain Point-of-sales Data of Three DC3-Removing Promotlon Trend 00c1c391 Figure 4.POS Data After Removing Promotion Trend
The Bullwhip Effect and its Impact on the Supply Chain Figure 4. POS Data After Removing Promotion & Trend
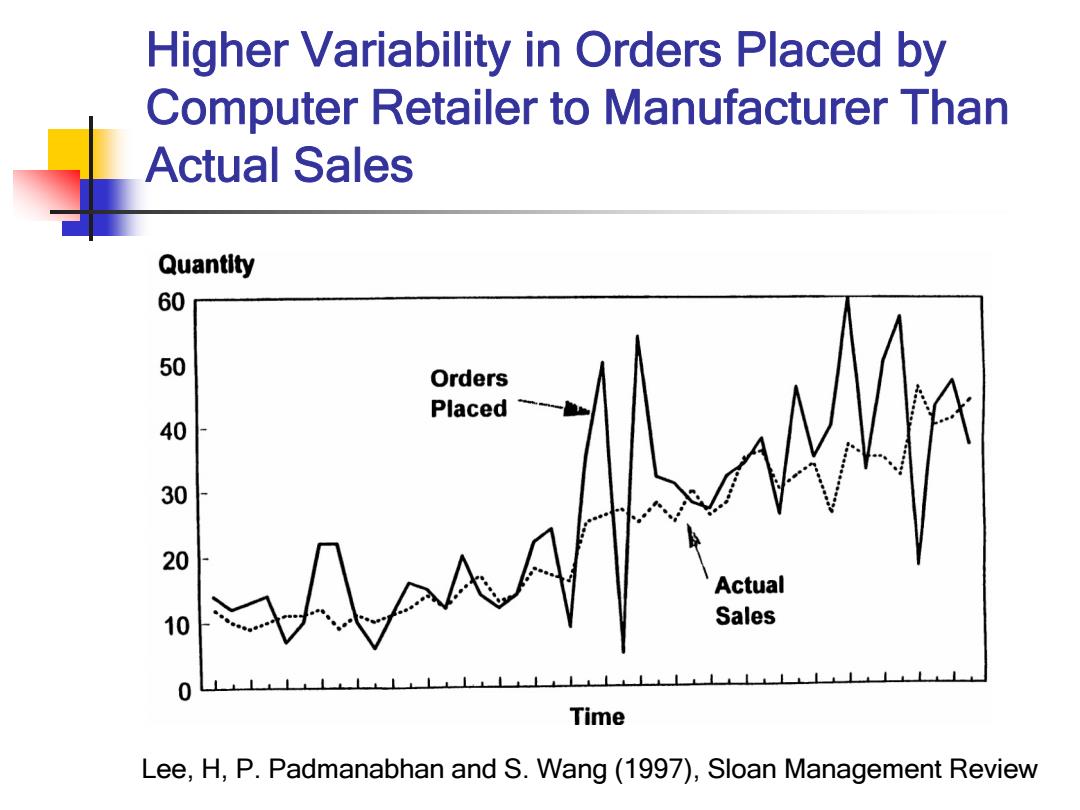
Higher Variability in Orders Placed by Computer Retailer to Manufacturer Than Actual Sales Quantity 60 50 Orders Placed 40 30 20 Actual 10 Sales 0 Time Lee,H,P.Padmanabhan and S.Wang(1997),Sloan Management Review
Higher Variability in Orders Placed by Computer Retailer to Manufacturer Than Actual Sales Lee, H, P. Padmanabhan and S. Wang (1997), Sloan Management Review

A Four-Stage Supply Chain External Demand A single retailer ■A single wholesaler Retailer Order lead time Delivery lead time A single distributor Wholesaler A single factory Order lead time Delivery lead time Distributor Order lead time Delivery lead time Factory Production lead time
A Four-Stage Supply Chain A single retailer A single wholesaler A single distributor A single factory