
同©大学 Tongji University Lesson X Membrane technology Tang Yulin 25May2017
Tongji University Lesson X Membrane technology Tang Yulin 25 May 2017
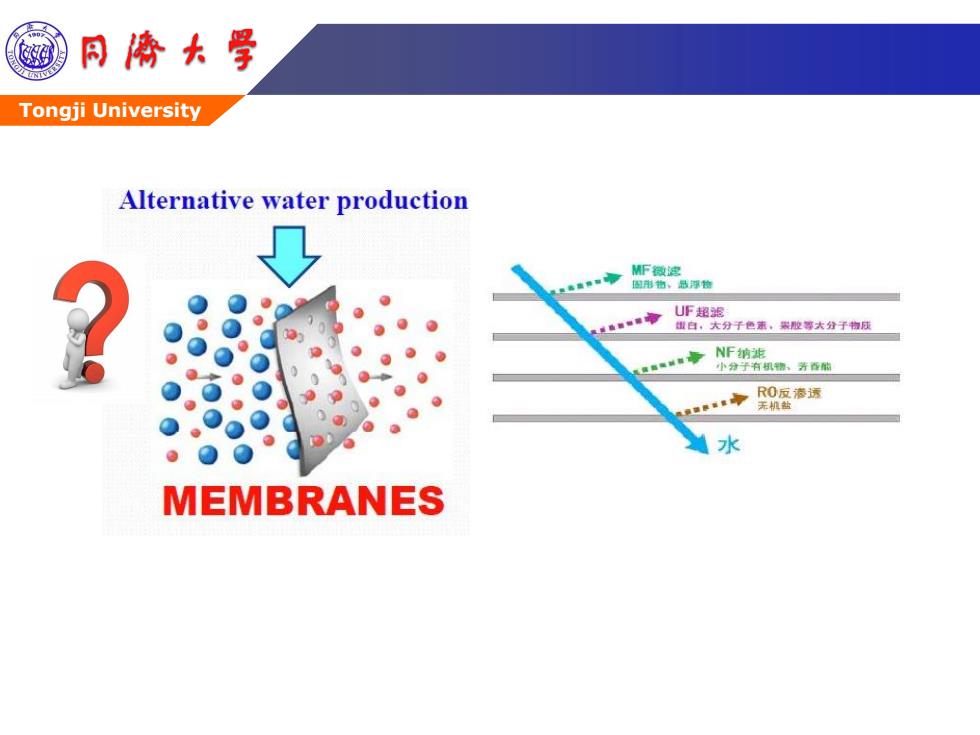
酒 同©大号 Tongji University Alternative water production MF微这 固形物、品浮物 UF超返 出白,大分千色蒸,黑胶等大分子物质 NF纳滤 小分子有机物、芳香能 RO反渗透 无机盐 水 MEMBRANES
Tongji University
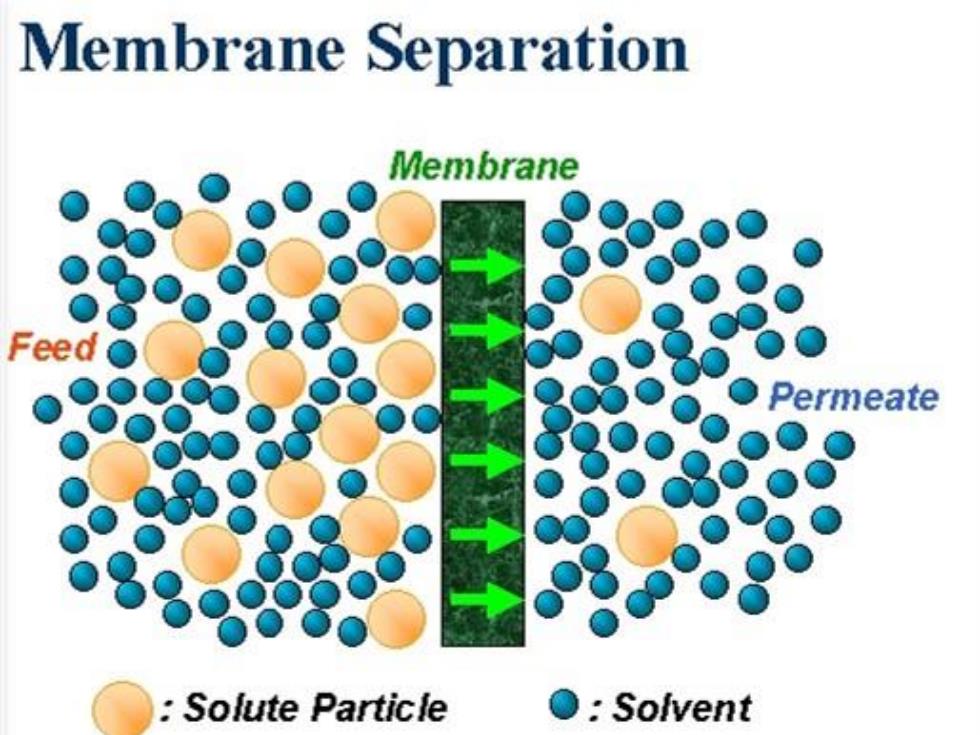
Membrane Separation Membrane Feed Permeate Solute Particle O:Solvent
Tongji University

g© 同©大学 Tongji University Introduction to membrane 。Classification of membrane processes Characteristics of membrane processes 用下
Tongji University Introduction to membrane Classification of membrane processes Characteristics of membrane processes

同燎大学 rocesses Tongji University A membrane is a selective barrier that permits the separation of certain species i in a a fluid by combination of sieving and diffusion mechanisms. Membranes can separate particles and molecules and over a wide particle size range and molecular weights Membrane processes are becoming popular because they are considered "Green"technology -no chemicals are used in the process
Tongji University A membrane is a selective barrier that permits the separation of certain species in a fluid by combination of sieving and diffusion mechanisms. Membranes can separate particles and molecules and over a wide particle size range and molecular weights . Membrane processes are becoming popular because they are considered “Green” technology - no chemicals are used in the process. Membrane Processes
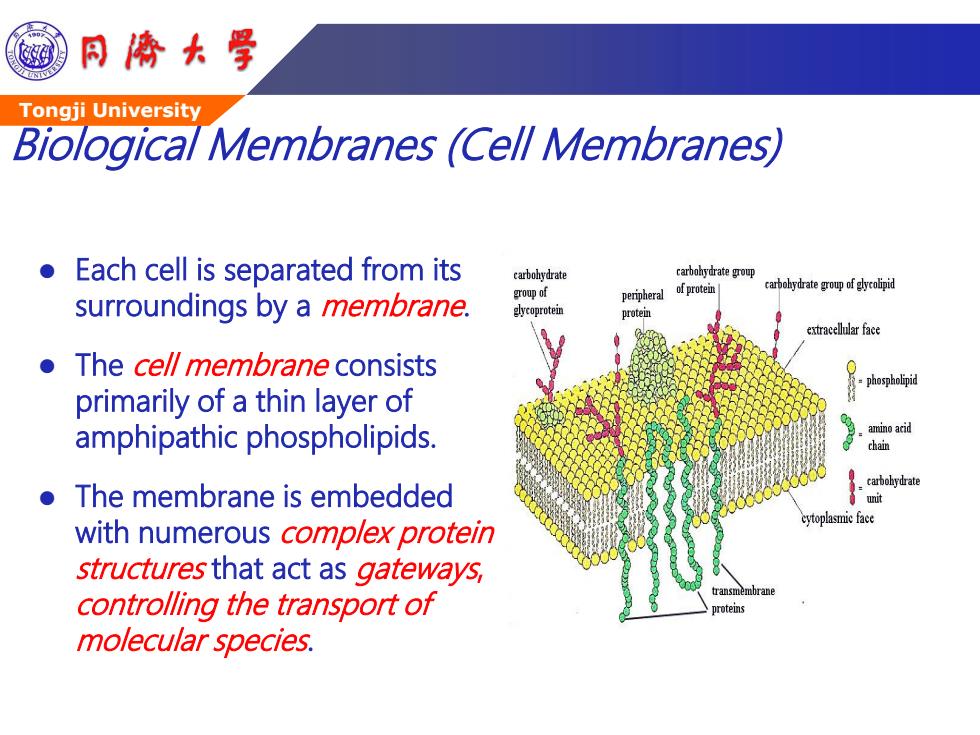
同©大学 Tongji University Biological Membranes (Cell Membranes) Each cell is separated from its carbobydrate carbohydrate group of protein oyrateoufid surroundings by a membrane. group of peripheral glycoprotein protein extracellular face The cell membrane consists -phospholipid primarily of a thin layer of amphipathic phospholipids. amino acid chain carbohydrate The membrane is embedded unit cytoplasmie face with numerous complex protein structures that act as gateways, controlling the transport of t女ansmembrane proteins molecular species
Tongji University Biological Membranes (Cell Membranes) Each cell is separated from its surroundings by a membrane. The cell membrane consists primarily of a thin layer of amphipathic phospholipids. The membrane is embedded with numerous complex protein structures that act as gateways, controlling the transport of molecular species

同海大学 Tongji University Synthetic Membranes 1956 -early 1980s:RO desalination,no commercial MF/UF for drinking water mid-1980 -early 1990s:Development of Memcor(MF), Aquasource (UF),clean waters small capacities mid-1990-2002:Start of market growth,new competitors (Zenon,Xflow,Hydranautics,Pall,lonics)with second generation membranes/modules Use on not so clean waters,start of immersed MBR products Now:Large plants 200000m3/d;Strong growth of RO desalination market
Tongji University Synthetic Membranes 1956 -early 1980s: RO desalination, no commercial MF/UF for drinking water mid-1980 -early 1990s: Development of Memcor (MF), Aquasource (UF), clean waters & small capacities mid-1990 -2002: Start of market growth, new competitors (Zenon, Xflow, Hydranautics, Pall, Ionics) with second generation membranes/modules ; Use on not so clean waters, start of immersed MBR products Now: Large plants > 200000m3 /d; Strong growth of RO desalination market

同海大学 Tongji U Source The McILVAINE COMPANY (2004) Chemical 5.6% 40%for water Desalination 20.4% Food&Bev.12.9% Metals 4.9% Mining 1.4% Oil&Gas 1.5% Water 15.4% Other industries 9.6% Wastewater 4.3% Pharmaceutical 10.4% Semiconductor 5.1% Power 3.8% Refineries1.4% Pulp&paper 3.1% GVEOUA Global Market Share
Tongji University Global Market Share
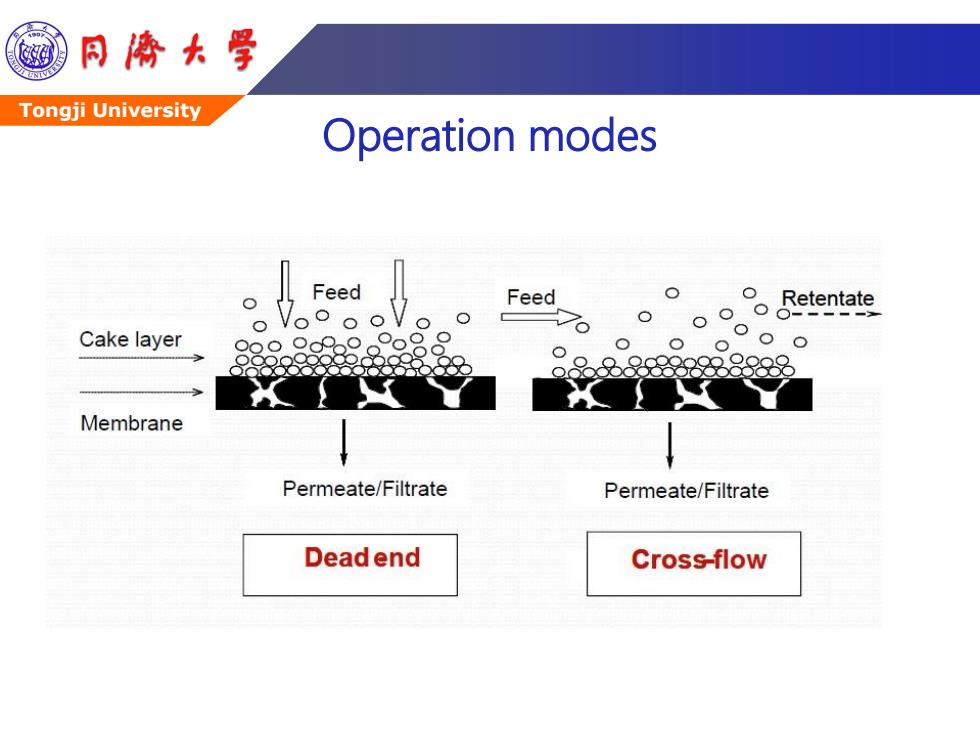
G 同©大号 Tongji University Operation modes Feed Feed O Retentate Cake layer Membrane Permeate/Filtrate Permeate/Filtrate Dead end Cross-flow
Tongji University Operation modes
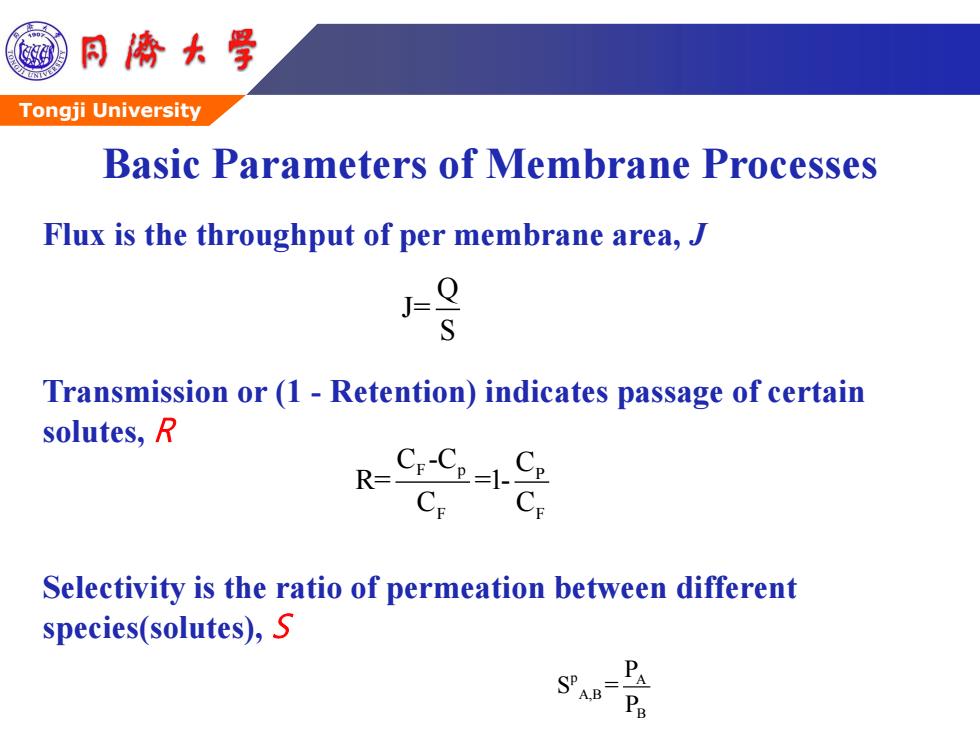
同©大学 Tongji University Basic Parameters of Membrane Processes Flux is the throughput of per membrane area,J J= S Transmission or (1 Retention)indicates passage of certain solutes,R R-Cr Selectivity is the ratio of permeation between different species(solutes),S =PA
Tongji University Flux is the throughput of per membrane area, J Transmission or (1 - Retention) indicates passage of certain solutes, R Selectivity is the ratio of permeation between different species(solutes), S F p P F F C -C C R= =1- C C Q J= S p A A,B B P S = P Basic Parameters of Membrane Processes