
Leachate and Landfill Gas
Leachate and Landfill Gas

Outline of the presentation 1.What are landfill gas and leachate? 2.How to anticipate their production? 3.Treatment and disposal technologies for leachate 4. How do we collect and recycle the landfill gas? 5.What can we do with GHG emissions from landfills?
1. What are landfill gas and leachate? 2. How to anticipate their production? 3. Treatment and disposal technologies for leachate 4. How do we collect and recycle the landfill gas? 5. What can we do with GHG emissions from landfills? Outline of the presentation

What are leachate and landfill gas?
What are leachate and landfill gas?

Leachate
Leachate

General definition >"Leachate is the term used for any liquid produced by the action of leaching which occurs when water percolates through any permeable material." >"Leachate is the liquid that drains or 'leaches'from a landfill;it varies widely in composition regarding the age of the landfill and the type of waste that it contains.It usually contains both dissolved and suspended material
“Leachate is the term used for any liquid produced by the action of leaching which occurs when water percolates through any permeable material.” “Leachate is the liquid that drains or ‘leaches’ from a landfill; it varies widely in composition regarding the age of the landfill and the type of waste that it contains. It usually contains both dissolved and suspended material.” General definition
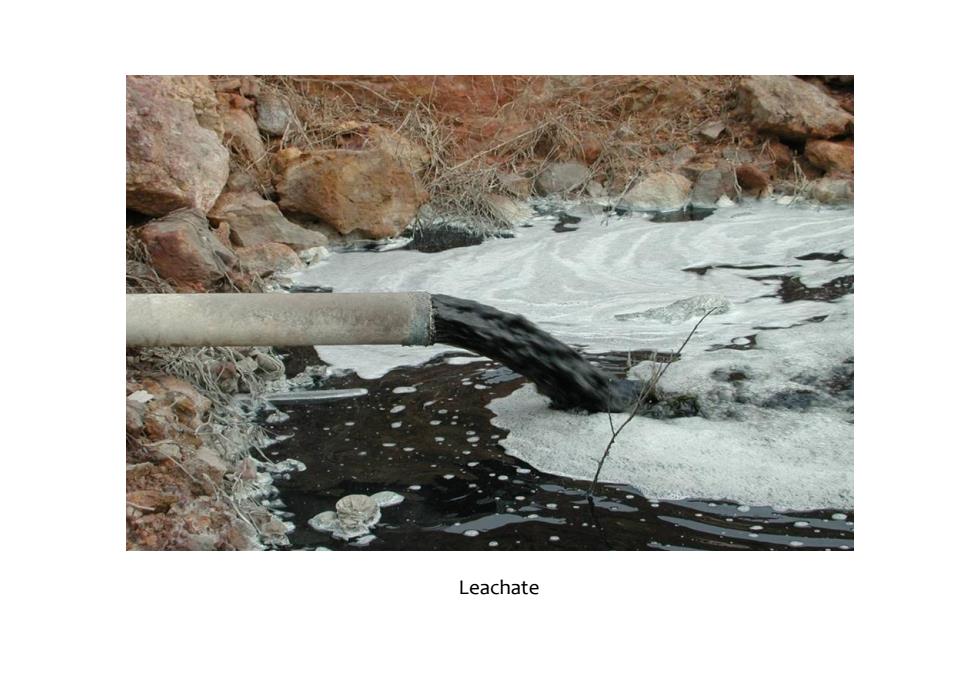

Leachate
Leachate

Origin composition Water rainfall Decomposition >An important contributor to the >Some liquids exist already before water generation of leachate leakage in the landfill:inside garbage,food products and chemical waste. >Goes through the landfill and collects contaminants. Decomposition of material produces "Contaminants are leached from solid some water and a wide range of additional wastes” materials:methane,carbon dioxide,acids, -Leaching of inherent soluble materials in sugars,iron,heavy metals,pesticides,etc. the wastes -Leaching of soluble products of chemical >They produce a small quantity of reactions created by decomposition leachate by themselves,which,will be -Washout of fines and colloids collected by water,which,in turn,creates further leachate. >Aids bacteria in the process of decomposition:When organic matter decomposes it needs oxygen.Adding water to wastes makes the process faster
Water rainfall Decomposition An important contributor to the generation of leachate Goes through the landfill and collects contaminants. “Contaminants are leached from solid wastes” ‐Leaching of inherent soluble materials in the wastes ‐Leaching of soluble products of chemical reactions created by decomposition ‐Washout of fines and colloids Aids bacteria in the process of decomposition: When organic matter decomposes it needs oxygen. Adding water to wastes makes the process faster. Some liquids exist already before water leakage in the landfill: inside garbage, food products and chemical waste. Decomposition of material produces some water and a wide range of additional materials: methane, carbon dioxide, acids, sugars, iron, heavy metals, pesticides, etc. They produce a small quantity of leachate by themselves, which, will be collected by water, which, in turn, creates further leachate. Origin & composition

Factors influencing its composition >The characteristics of leachate are influenced by a wide range of factors: Composition of waste(e.g:batteries) Climate/season/Precipitations Site hydrology and soil composition Waste age Landfill design,cover design,sampling way,age of the landfill
The characteristics of leachate are influenced by a wide range of factors: ‐ Composition of waste (e.g: batteries) ‐ Climate / season /Precipitations ‐ Site hydrology and soil composition ‐ Waste age ‐ Landfill design, cover design, sampling way, age of the landfill Factors influencing its composition

Leachate escape >"Field capacity":the maximum moisture the soil can retain >In the unfinished landfill:When a landfill layer reaches its field capacity,more moisture will displace the moisture in the soil.The water will drop in the landfill the leachate will drop to the next lowest soil and refuse layer. >In the finished landfill:If the field capacity of the soil covering waste is exceeded,the water percolates through the soil and into the buried solid waste.If the field capacity of waste is exceeded,leachate flows into the collection system/into the ground
“Field capacity”: the maximum moisture the soil can retain In the unfinished landfill: When a landfill layer reaches its field capacity, more moisture will displace the moisture in the soil. The water will drop in the landfill & the leachate will drop to the next lowest soil and refuse layer. In the finished landfill: If the field capacity of the soil covering waste is exceeded, the water percolates through the soil and into the buried solid waste. If the field capacity of waste is exceeded, leachate flows into the collection system / into the ground. Leachate escape
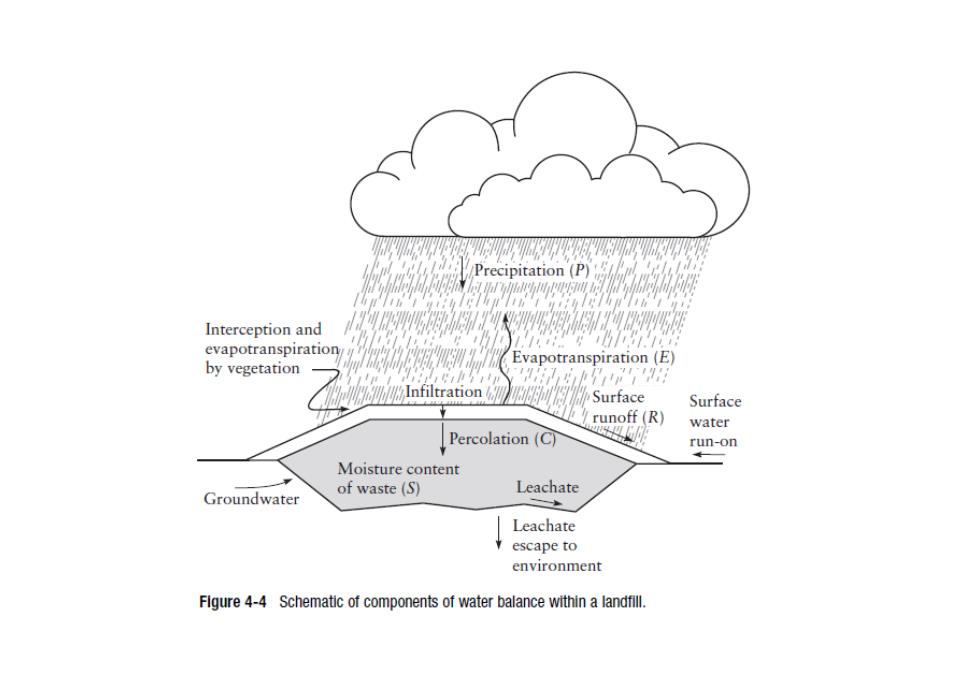
% Precipitation (P) Interception and evapotranspiration Evapotranspiration(E) by vegetation Infiltration Surface Surface runoff(R) 明 water Percolation(C】 run-on Moisture content of waste (S) Leachate Groundwater Leachate escape to environment Flgure 4-4 Schematic of components of water balance within a landfill