
IESD Students 2006-2017:118 Chinese students +284 international students >From 80 countries
IESD Students ➢ 2006-2017: 118 Chinese students +284 international students ➢ From 80 countries

General Introduction to water resources
General Introduction to water resources

Outline -1.1 Water resources -1.2 Win-win solutions to mitigate water scarcity -1.3 Climate Change and Water Scarcity -1.4 Solutions to reduce water consumption -1.5 Sustainable water use -1.6 Sustainable water resources management
– 1.1 Water resources – 1.2 Win-win solutions to mitigate water scarcity – 1.3 Climate Change and Water Scarcity – 1.4 Solutions to reduce water consumption – 1.5 Sustainable water use – 1.6 Sustainable water resources management Outline

1.1 Water Resources
1.1 Water Resources

Properties of Water ● Composed of 2 Hydrogen and (a) 1 Oxygen Exists as solid,liquid or gas (b) ·High heat capacity 。Polar -One end has (+charge,one end has (-)charge ·Forms Hydrogen bond between 2 water molecules -H-bonds define water's physical properties
Properties of Water • Composed of 2 Hydrogen and 1 Oxygen • Exists as solid, liquid or gas • High heat capacity • Polar – One end has (+) charge, one end has (-) charge • Forms Hydrogen bond between 2 water molecules – H-bonds define water’s physical properties

Definition Water resources Water resources are sources of water that are potentially useful -Wikipedia Water resources management Water resource management is the activity of planning, developing,distributing and managing the optimum use of water resources It is a sub-set of water cycle management. Ideally,water resource management planning has regard to all the competing demands for water and seeks to allocate water on an equitable basis to satisfy all uses and demands. As with other resource management,this is rarely possible in practice
Definition Water resources • Water resources are sources of water that are potentially useful. - Wikipedia Water resources management • Water resource management is the activity of planning, developing, distributing and managing the optimum use of water resources. • It is a sub-set of water cycle management. • Ideally, water resource management planning has regard to all the competing demands for water and seeks to allocate water on an equitable basis to satisfy all uses and demands. • As with other resource management, this is rarely possible in practice

Global Water resources Total amount of water at the Earth's surface:1408.7X 106 km3 unevenly distribution of fresh water in the world. China with 21%of world's population has only 7%of the water resources. ● However,Canada,with only 0.5%of the world population,has 20% of world's fresh water. The world's fresh water supply is continuously collected,purified, recycled,and distributed in the solar powered hydraulic cycle
• Total amount of water at the Earth’s surface: 1408.7×106 km3 • unevenly distribution of fresh water in the world. • China with 21% of world’s population has only 7% of the water resources. • However, Canada, with only 0.5% of the world population, has 20% of world’s fresh water. • The world’s fresh water supply is continuously collected, purified, recycled, and distributed in the solar powered hydraulic cycle. Global Water Resources
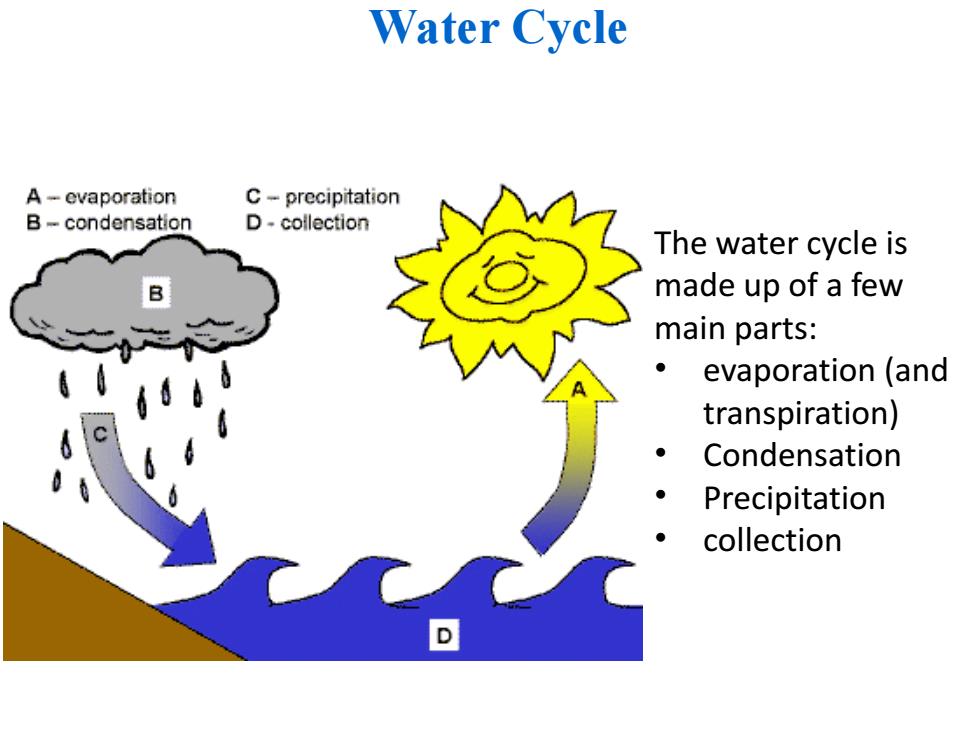
Water Cycle A-evaporation C-precipitation B-condensation D-collection The water cycle is made up of a few main parts: ● evaporation (and transpiration) ● Condensation Precipitation collection
Water Cycle The water cycle is made up of a few main parts: • evaporation (and transpiration) • Condensation • Precipitation • collection
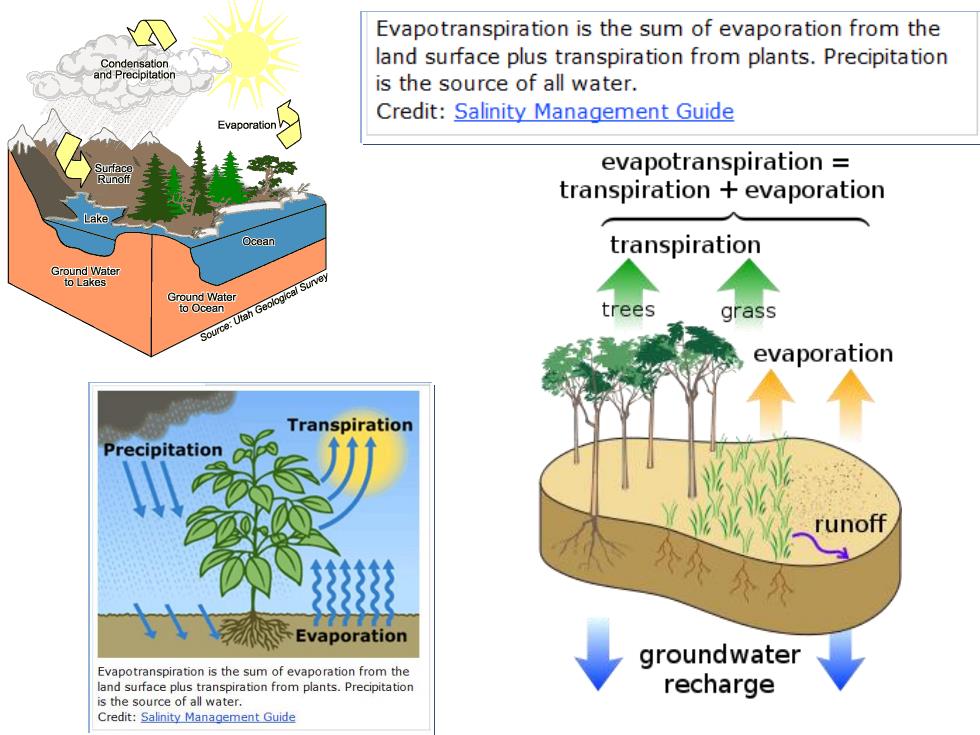
公 Evapotranspiration is the sum of evaporation from the land surface plus transpiration from plants.Precipitation is the source of all water. Credit:Salinity Management Guide Evaporation evapotranspiration transpiration evaporation ake Ocean transpiration Source:Utah Geologicai Survey trees grass evaporation Transpiration Precipitation runoff 公外分公 泰Evaporation groundwater Evapotranspiration is the sum of evaporation from the land surface plus transpiration from plants.Precipitation recharge is the source of all water. Credit:Salinity Management Guide

Water Cycle-continuously collected, purified,recycled and distributed Flowing artesian well Precipitation Evaporation and transpiration Well requiring a pump Confined Evaporation Recharge Area Runoff Aquifer Stream Infiltration Water table Lake Infiltration Unconfined aquifer ole Confined aquifer Less permeable material such as clay Confirming permeable rock layer 2002 Brooks
Evaporation and transpiration Evaporation Stream Infiltration Water table Infiltration Unconfined aquifer Confined aquifer Lake Well requiring a pump Flowing artesian well Runoff Precipitation Confined Recharge Area Aquifer Less permeable material such as clay Confirming permeable rock layer Water Cycle – continuously collected, purified, recycled and distributed