
Anaerobic Digestion By Niu Dongjie
Anaerobic Digestion By Niu Dongjie

Biogas -a way to solve sanitation problems Anaerobic fermentation is a natural and unavoidable How much biogas can be produced from excreta and biomass? process How safe is the process and its sludge?? Learning objectives:to know about the fundamental processes in biogas production Jam-Olof Drangert,Linkoping university.Sweden
Biogas – a way to solve sanitation problems Learning objectives: to know about the fundamental processes in biogas production Anaerobic fermentation is a natural and unavoidable process Jam-Olof Drangert, Linköping university, Sweden
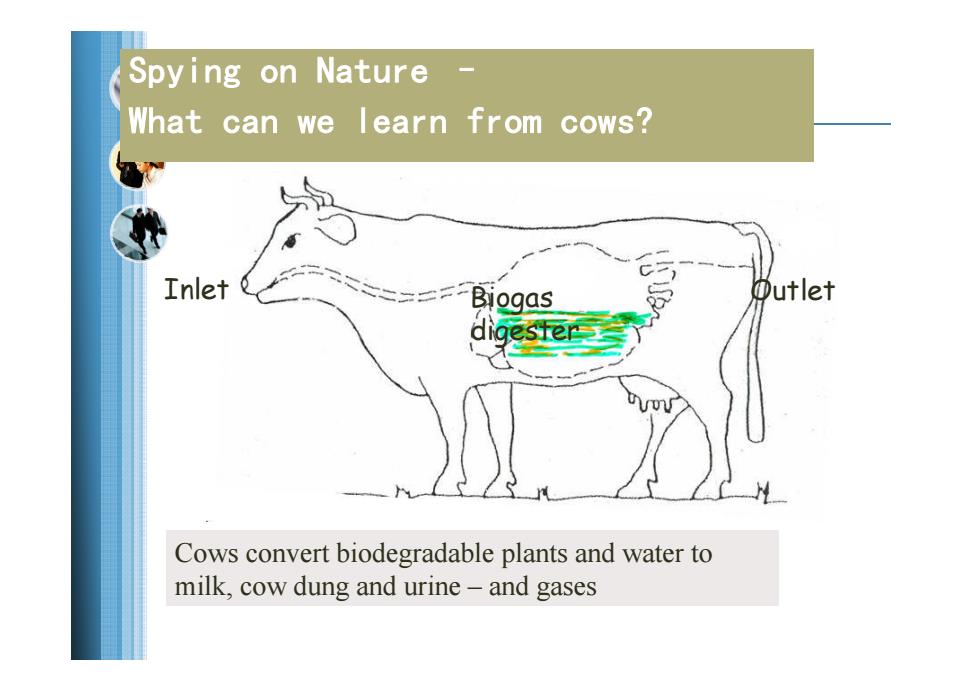
Spying on Nature What can we learn from cows? Inlet Outlet digeste三 Cows convert biodegradable plants and water to milk,cow dung and urine-and gases
Spying on Nature – What can we learn from cows? Inlet Biogas Outlet digester Cows convert biodegradable plants and water to milk, cow dung and urine – and gases
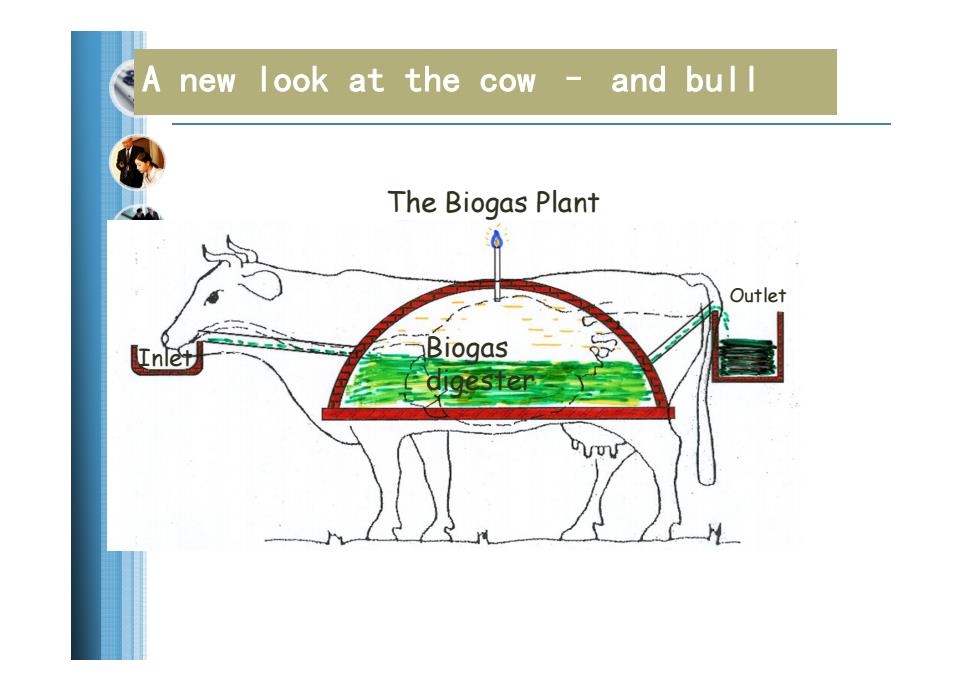
A new look at the cow- and bul l The Biogas Plant 0 Outlet Inlet Biogas digester
A new look at the cow – and bull Inlet Outlet Biogas digester The Biogas Plant
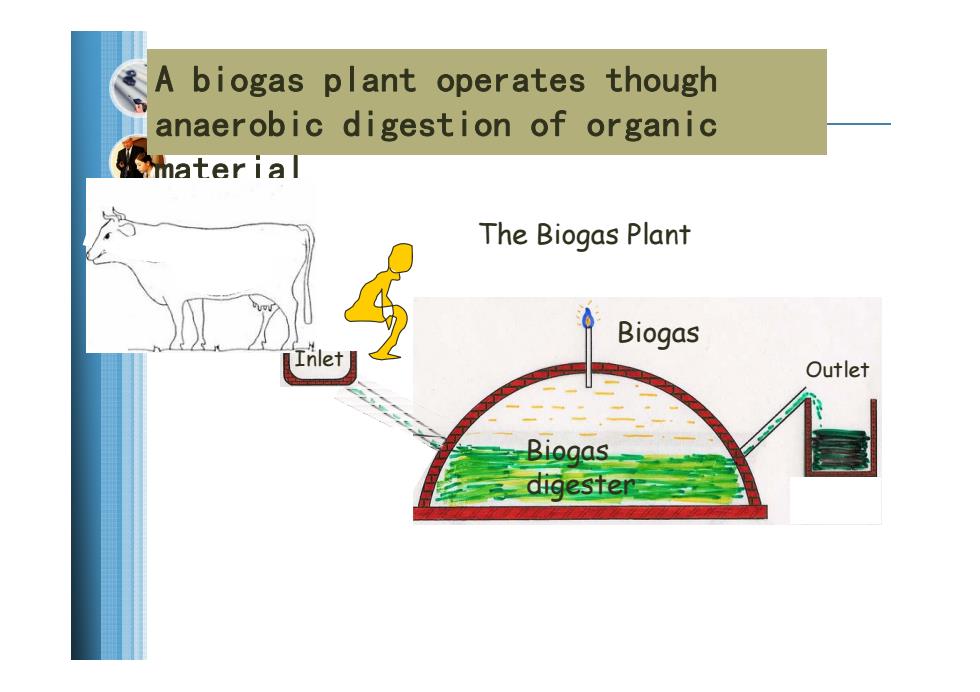
A biogas plant operates though anaerobic digestion of organic mater ial The Biogas Plant Biogas Outlet Biogas digester
A biogas plant operates though anaerobic digestion of organic material The Biogas Plant Inlet Outlet Biogas digester Biogas
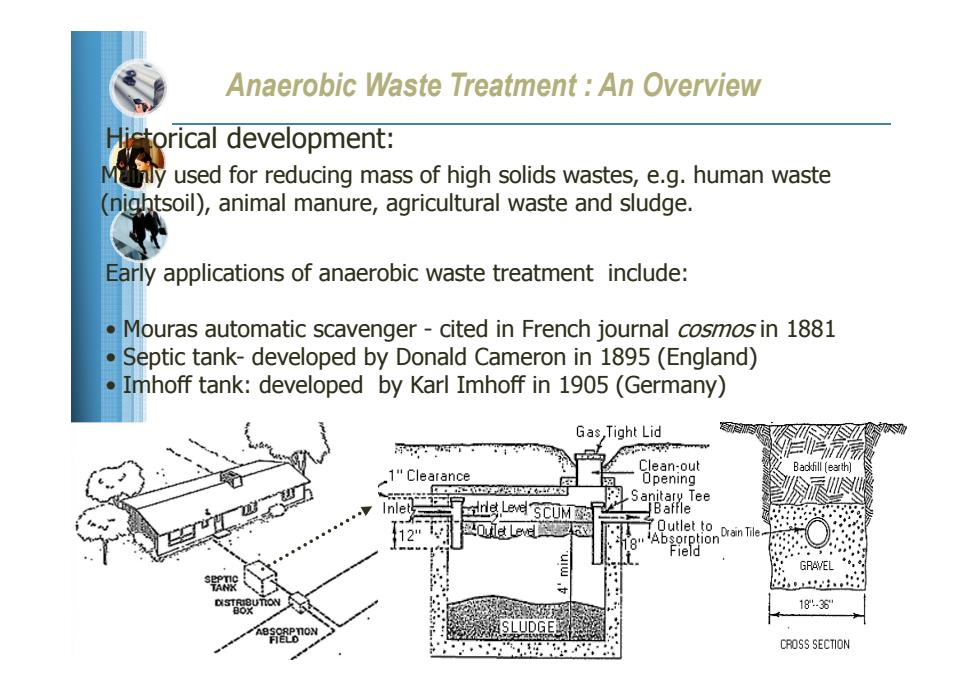
Anaerobic Waste Treatment An Overview Hictorical development: Mly used for reducing mass of high solids wastes,e.g.human waste (nightsoil),animal manure,agricultural waste and sludge. Early applications of anaerobic waste treatment include: Mouras automatic scavenger-cited in French journal cosmos in 1881 Septic tank-developed by Donald Cameron in 1895 (England) Imhoff tank:developed by Karl Imhoff in 1905 (Germany) Gas ,Tight Lid Clean-out Backfill [earth] 1"Clearance Opening Sanitar以Tee nle ne Leve SCUM Baffle Outlet to Absorption Drain Tile Field GRAVEL 18.3 CROSS SECTION
Anaerobic Waste Treatment : An Overview Historical development: Mainly used for reducing mass of high solids wastes, e.g. human waste (nightsoil), animal manure, agricultural waste and sludge. Early applications of anaerobic waste treatment include: • Mouras automatic scavenger - cited in French journal cosmos in 1881 • Septic tank- developed by Donald Cameron in 1895 (England) • Imhoff tank: developed by Karl Imhoff in 1905 (Germany)
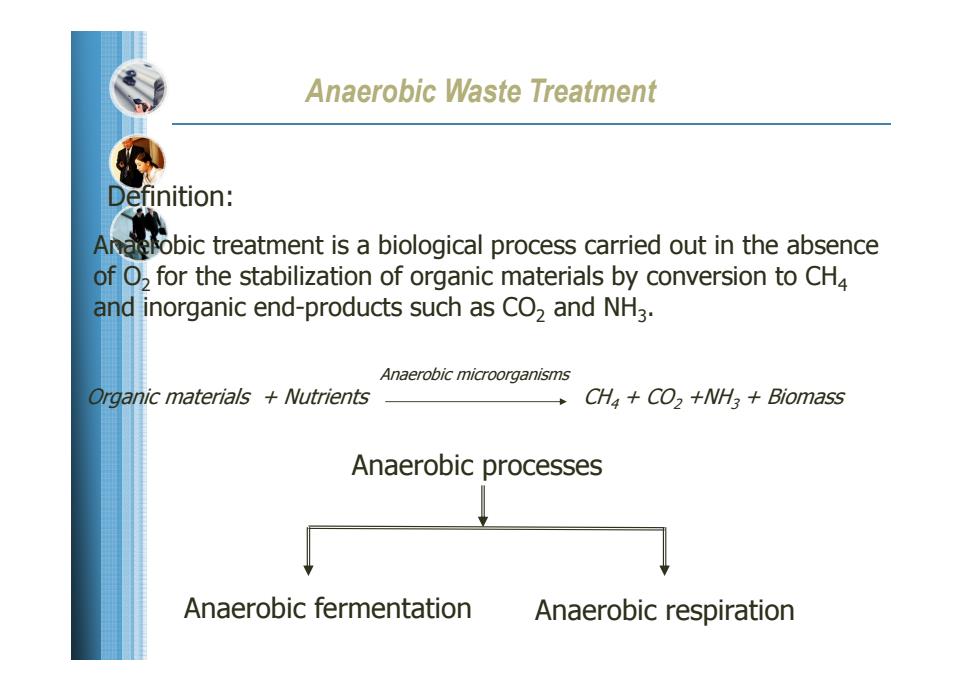
Anaerobic Waste Treatment Definition: Analobic treatment is a biological process carried out in the absence of O,for the stabilization of organic materials by conversion to CH4 and inorganic end-products such as CO2 and NH3. Anaerobic microorganisms Organic materials Nutrients CH CO2 +NH3 Biomass Anaerobic processes Anaerobic fermentation Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Waste Treatment Definition: Anaerobic treatment is a biological process carried out in the absence of O2 for the stabilization of organic materials by conversion to CH 4 and inorganic end-products such as CO 2 and NH 3. Organic materials + Nutrients CH4 + CO2 +NH3 + Biomass Anaerobic microorganisms Anaerobic processes Anaerobic fermentation Anaerobic respiration
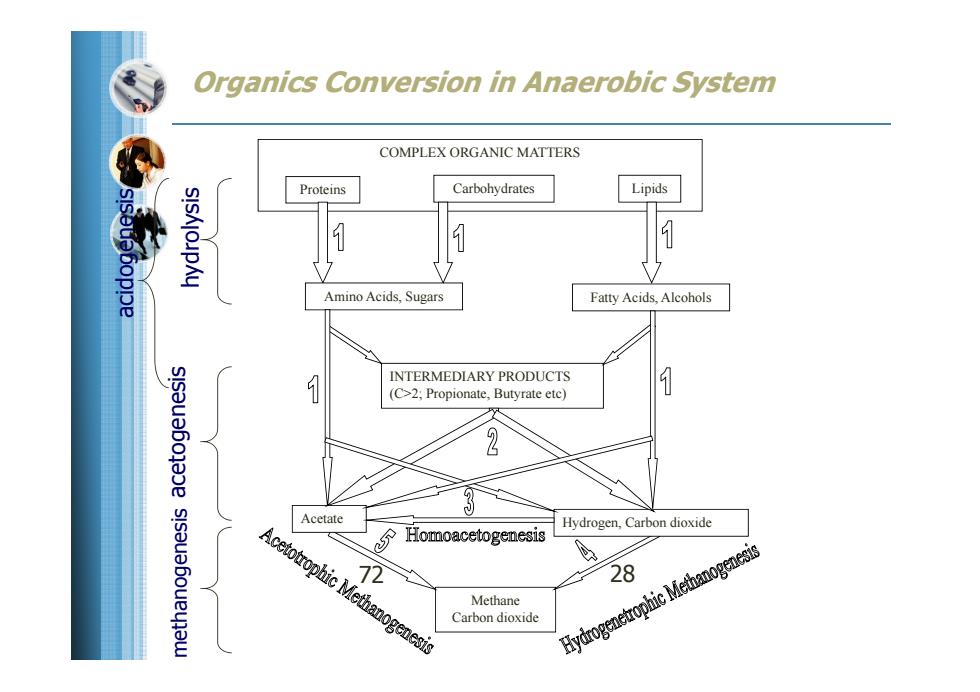
Organics Conversion in Anaerobic System COMPLEX ORGANIC MATTERS Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids sisouebopppe Amino Acids,Sugars Fatty Acids,Alcohols INTERMEDIARY PRODUCTS (C>2;Propionate,Butyrate etc) 2 Acetate Hydrogen,Carbon dioxide Homoacetogenesis Acetotrophic Methanogenesis 72 Methane Carbon dioxide Hydrogenetrophic Methanogs 28
Methane Carbon dioxide COMPLEX ORGANIC MATTERS Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids Amino Acids, Sugars Fatty Acids, Alcohols hydrolysis INTERMEDIARY PRODUCTS (C>2; Propionate, Butyrate etc) acidogenesis Acetate Hydrogen, Carbon dioxide acetogenesis Organics Conversion in Anaerobic System methanogenesis 72 28
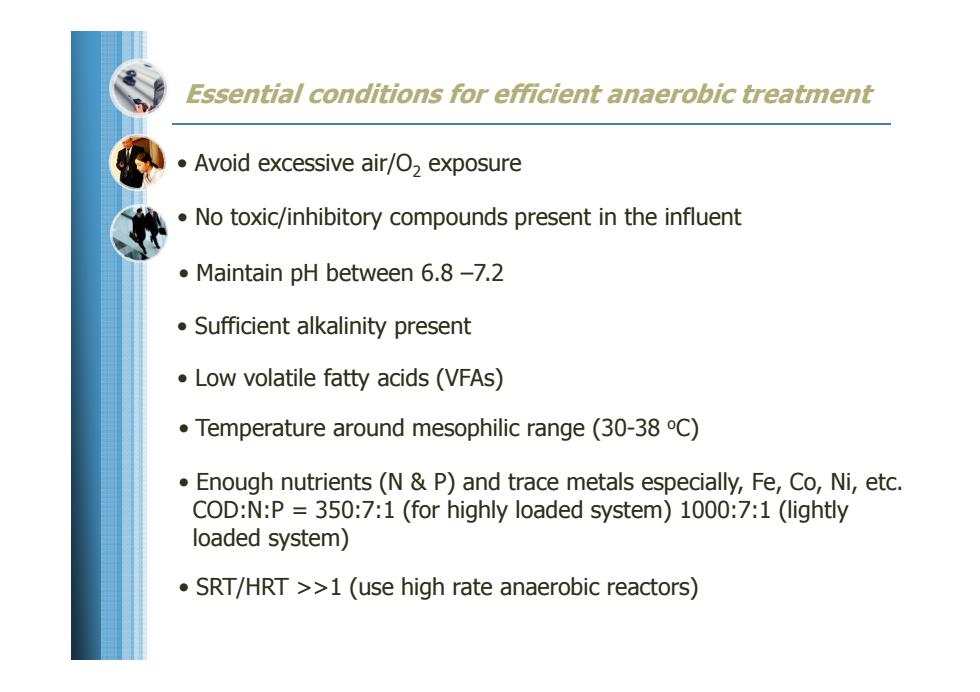
Essential conditions for efficient anaerobic treatment Avoid excessive air/O,exposure No toxic/inhibitory compounds present in the influent Maintain pH between 6.8-7.2 Sufficient alkalinity present Low volatile fatty acids(VFAs) Temperature around mesophilic range(30-38 C) Enough nutrients(N P)and trace metals especially,Fe,Co,Ni,etc. COD:N:P 350:7:1 (for highly loaded system)1000:7:1 (lightly loaded system) SRT/HRT >>1(use high rate anaerobic reactors)
Essential conditions for efficient anaerobic treatment • Enough nutrients (N & P) and trace metals especially, Fe, Co, Ni, etc. COD:N:P = 350:7:1 (for highly loaded system) 1000:7:1 (lightly loaded system) • Avoid excessive air/O 2 exposure • No toxic/inhibitory compounds present in the influent • Maintain pH between 6.8 –7.2 • Sufficient alkalinity present • Low volatile fatty acids (VFAs) • Temperature around mesophilic range (30-38 oC) • SRT/HRT >>1 (use high rate anaerobic reactors)

Environmental factors The successful operation of anaerobic reactor depends on maintaining the environmental factors close to the comfort of the microorganisms involved in the process. Temperature Anaerobic processes like other biological processes strongly depend on temperature. In anaerobic system:three optimal temperature ranges; Psychrophilic(5-15C) > Mesophilic (35-40 C) Thermophilic (50-55 C)
Environmental factors The successful operation of anaerobic reactor depends on maintaining the environmental factors close to the comfort of the microorganisms involved in the process. Temperature Anaerobic processes like other biological processes strongly depend on temperature. In anaerobic system: three optimal temperature ranges; Psychrophilic (5 - 15 oC) Mesophilic (35 – 40 C) Thermophilic (50-55 oC)