
Incineration,pyrolysis gasification Niu Dongjie niudongjie@tongji.edu.cn
Incineration, pyrolysis & gasification Niu Dongjie niudongjie@tongji.edu.cn
Table of content ODefinitions o Incineration systems oPyrolysis systems oGasification systems
Table of content Definitions Incineration systems Pyrolysis systems Gasification systems

Definition o Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of organic substances contained in waste materials.[11 "thermal treatment". o Incineration of waste materials converts the waste into ash,flue gas,and heat. o The ash is mostly formed by the inorganic constituents of the waste,and may take the form of sol id lumps or particulates carried by the flue gas
Definition Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of organic substances contained in waste materials.[1] "thermal treatment". Incineration of waste materials converts the waste into ash, flue gas, and heat. The ash is mostly formed by the inorganic constituents of the waste, and may take the form of solid lumps or particulates carried by the flue gas
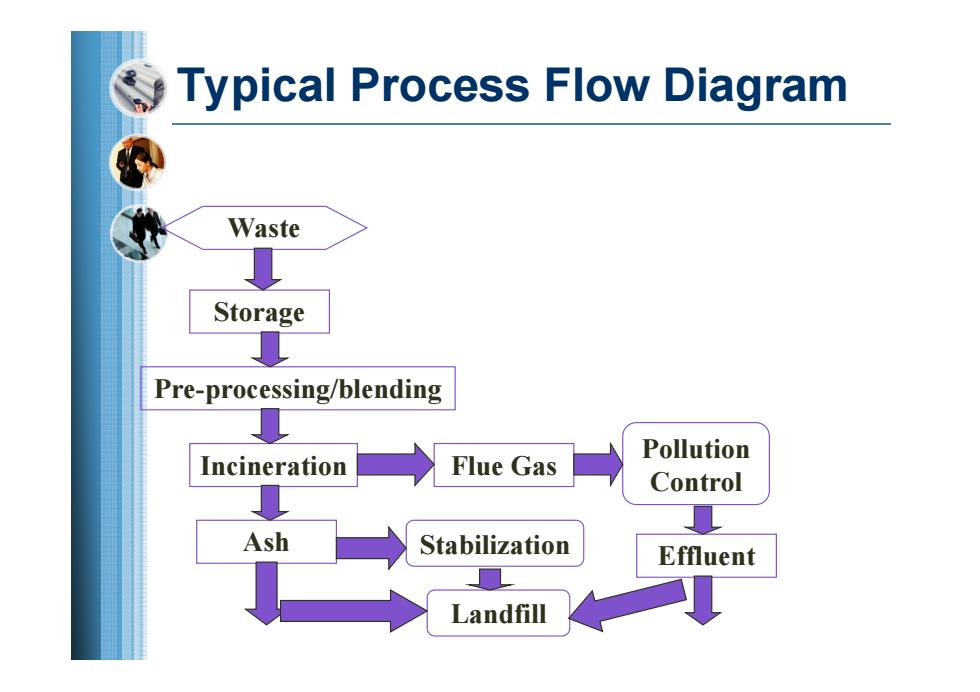
Typical Process Flow Diagram Waste Storage Pre-processing/blending Pollution Incineration Flue Gas Control Ash Stabilization Effluent Landfill
Typical Process Flow Diagram Waste Storage Pre-processing/blending Incineration Flue Gas Pollution Control Ash Stabilization Landfill Effluent

Heating value oThe heating value or calorific value of a substance, usual ly a fuel or food (see food energy),is the amount of heat released during the combustion of a specified amount of it. oa characteristic for each substance. ounits kcal/kg,kJ/kg,J/mol
Heating value The heating value or calorific value of a substance, usually a fuel or food (see food energy), is the amount of heat released during the combustion of a specified amount of it. a characteristic for each substance. units : kcal/kg, kJ/kg, J /mol

Heating value Heating value is commonly determined by use of a bomb calor imeter. OThe heat of combustion for fuels is expressed as the HHV,LHV,or GHV
Heating value Heating value is commonly determined by use of a bomb calorimeter. The heat of combustion for fuels is expressed as the HHV, LHV, or GHV

Higher heating value odetermined by bringing all the products of combustion back to the or iginal pre-combustion temperature, and in particular condensing any vapor produced. 25°C. 1 o hhV assumes all the water component is in liquid state at the end of combustion (in product of combust ion)
Higher heating value determined by bringing all the products of combustion back to the original pre-combustion temperature, and in particular condensing any vapor produced. 25 °C. HHV assumes all the water component is in liquid state at the end of combustion (in product of combustion)

Lower heating value odetermined by subtracting the heat of vaporization of the water v vapor from the higher heating value. OThis treats any H20 formed as a vapor. OThe energy required to vaporize the water therefore is not real ized as heat
Lower heating value determined by subtracting the heat of vaporization of the water vapor from the higher heating value. This treats any H 2O formed as a vapor. The energy required to vaporize the water therefore is not realized as heat

Heating value w=r-2Ho4-8】 式中LHV一低位热值,kJkg: HHV一高位热值,kJkg; H,O一焚烧产物中水的质量百分率,%; H、C、F一分别为废物中氢、氯、氟含量的质量 百分率,%
Heating value 式中 LHV—低位热值,kJ/kg; HHV—高位热值,kJ/kg; H2O—焚烧产物中水的质量百分率, %; H、Cl、F—分别为废物中氢、氯、氟含量的质量 百分率,%。 35.5 19 2420 2 9 Cl F LHV HHV H O H
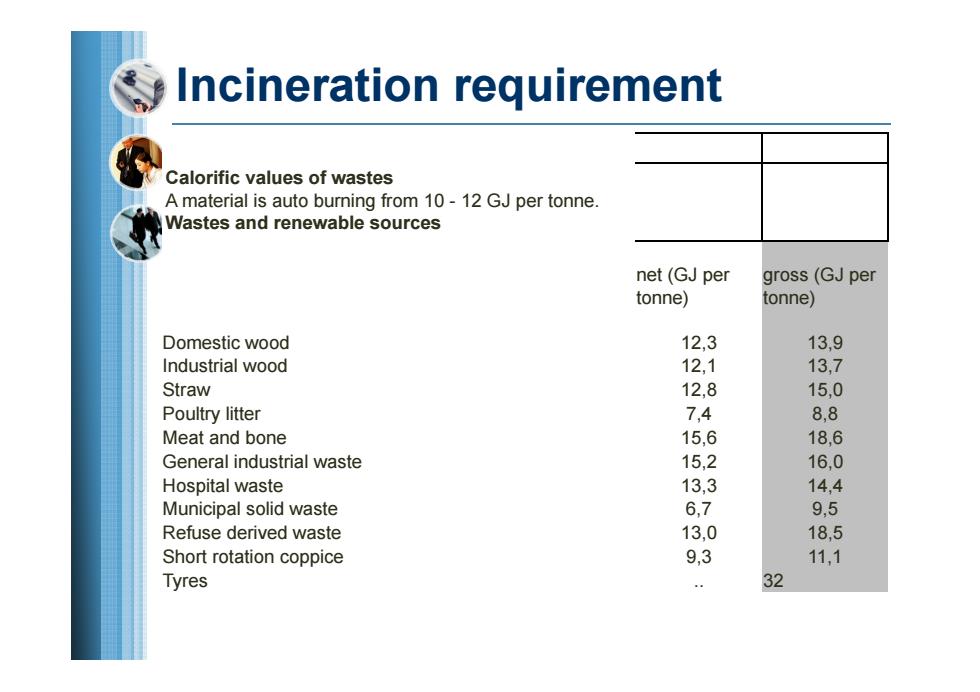
Incineration requirement Calorific values of wastes A material is auto burning from 10-12 GJ per tonne. Wastes and renewable sources net(GJ per gross(GJ per tonne) tonne) Domestic wood 12,3 13,9 Industrial wood 12,1 13,7 Straw 12,8 15,0 Poultry litter 7,4 8,8 Meat and bone 15,6 18,6 General industrial waste 15,2 16,0 Hospital waste 13,3 14,4 Municipal solid waste 6,7 9,5 Refuse derived waste 13,0 18,5 Short rotation coppice 9,3 11,1 Tyres … 32
Incineration requirement Calorific values of wastes A material is auto burning from 10 - 12 GJ per tonne. Wastes and renewable sources net (GJ per tonne) gross (GJ per tonne) Domestic wood 12,3 13,9 Industrial wood 12,1 13,7 Straw 12,8 15,0 Poultry litter 7,4 8,8 Meat and bone 15,6 18,6 General industrial waste 15,2 16,0 Hospital waste 13,3 14,4 Municipal solid waste 6,7 9,5 Refuse derived waste 13,0 18,5 Short rotation coppice 9,3 11,1 Tyres .. 32