
® 实时系统设计(DRE系统) 李曦 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 计算机系计算机应用研究室
实时系统设计(DRE系统) 李曦 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 计算机系计算机应用研究室

内容提要 ·分布式实时系统 Leslie Lamport "A system is distributed if the message transmission delay is not negligible compared to the time between events in a single process."[Lam78b]. Real-Time Systems and Dependable Systems Temporal properties Timing constraints on interface,including ordering restrictions ·分布式通信协议 OSI collapsed model LIN/CAN 。 时间同步 ·TTP协议 ·H.Kopetz. Real-Time Systems:Design Principles for Distributed Embedded Applications.Kluwer Academic Publishers.1997. P.Verissimo and L.Rodriguez. Distributed Systems for System Architects.Kluwer Academic Publishers.2001
内容提要 • 分布式实时系统 – Leslie Lamport • “A system is distributed if the message transmission delay is not negligible compared to the time between events in a single process.” [Lam78b]. • Real-Time Systems and Dependable Systems – Temporal properties • Timing constraints on interface, including ordering restrictions • 分布式通信协议 – OSI collapsed model – LIN/CAN • 时间同步 • TTP协议 • H. Kopetz. – Real-Time Systems: Design Principles for Distributed Embedded Applications. Kluwer Academic Publishers. 1997. • P. Veríssimo and L. Rodríguez. – Distributed Systems for System Architects. Kluwer Academic Publishers. 2001
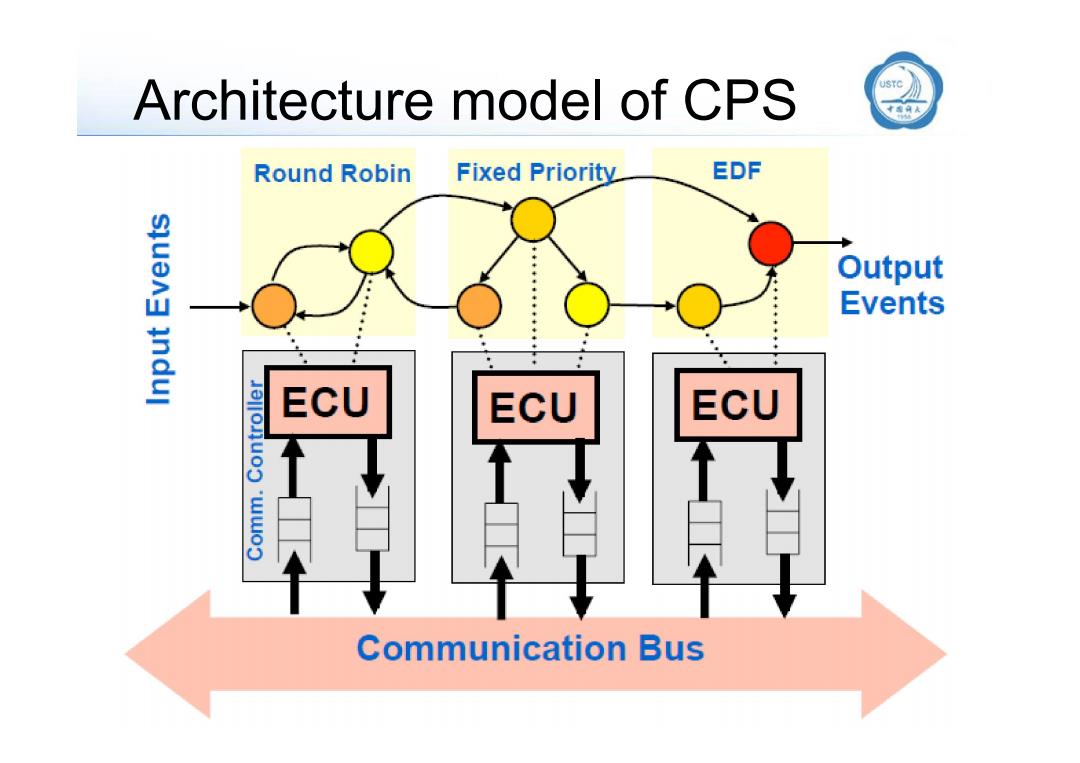
Architecture model of CPS Round Robin Fixed Priority EDF Output Events ECU ECU ECU Communication Bus
Architecture model of CPS
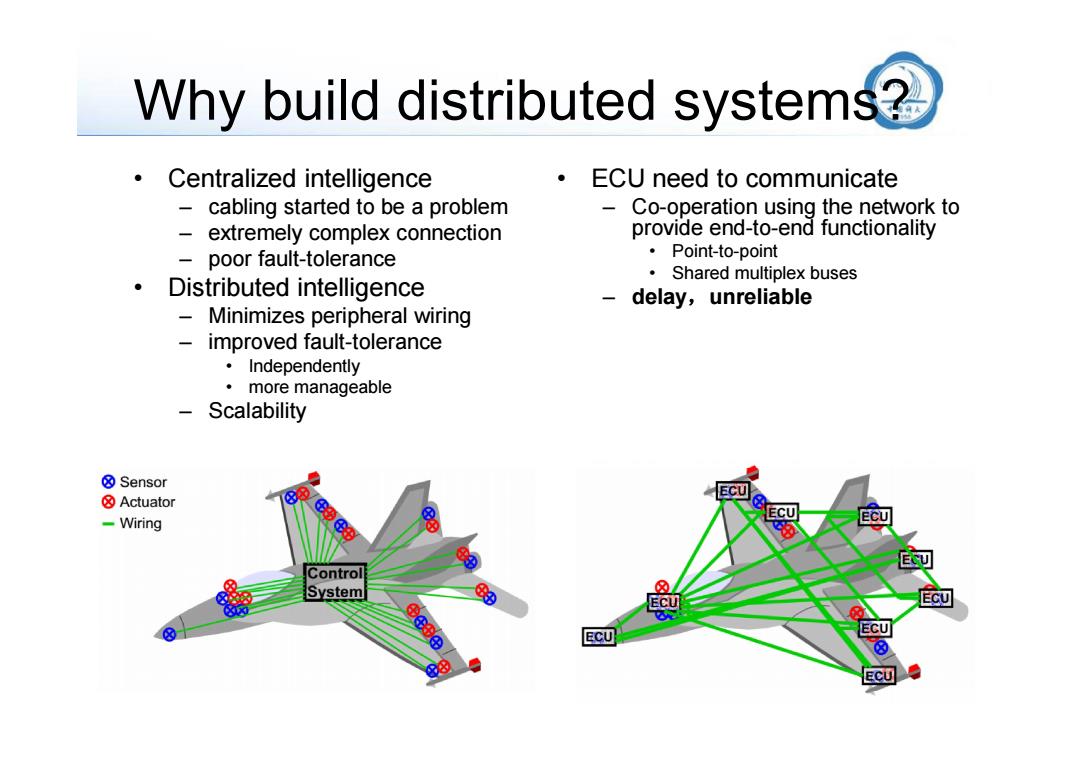
Why build distributed systems? Centralized intelligence ECU need to communicate - cabling started to be a problem Co-operation using the network to extremely complex connection provide end-to-end functionality poor fault-tolerance ·Point-to-point Shared multiplex buses 。 Distributed intelligence delay,unreliable - Minimizes peripheral wiring improved fault-tolerance ·Independently ·more manageable Scalability ⑧Sensor ☒Actuator ECU -Wiring ☒ Control System Ec可 ECU
Why build distributed systems? • Centralized intelligence – cabling started to be a problem – extremely complex connection – poor fault-tolerance • Distributed intelligence – Minimizes peripheral wiring – improved fault-tolerance • Independently • more manageable – Scalability • ECU need to communicate – Co-operation using the network to provide end-to-end functionality • Point-to-point • Shared multiplex buses – delay,unreliable

Reactive,real-time and distributed S 前端模块 风精雨副罗 音响/信息损乐 MB90495G Me89215 系镜 HB90540 Me89935B MB90340 MB90590 MB90390 坐调面饭 MB90430 后裤棋典 终端电用 4B89215 MB90540G 电动座精 MB90385 MB39935B 1B90590G NB90385 4B90495G LIN MB90495G MB90545G 高逃CAN Bus 发动机 ABS 兼客检测 低速CAN 位表同关 电动门 MB90385 Bus MB90340 4B90385 MB90495G Me90390 4B90495G MB90420G Me90440G 后规镜 方向控 门禁系统 Me90540G Me89215 MB90385 MB90495G M890590G Me899358 MB90495
Reactive, real-time and distributed ES
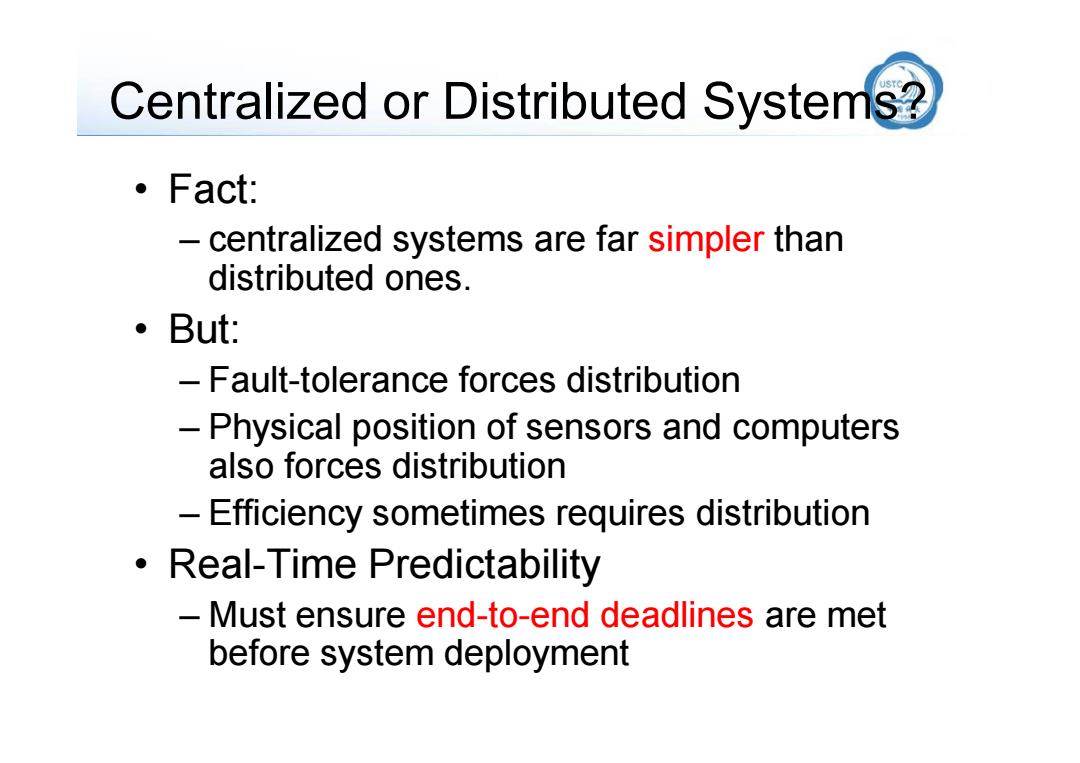
Centralized or Distributed Systems? ·Fact: 一 centralized systems are far simpler than distributed ones. But: -Fault-tolerance forces distribution -Physical position of sensors and computers also forces distribution -Efficiency sometimes requires distribution Real-Time Predictability Must ensure end-to-end deadlines are met before system deployment
Centralized or Distributed Systems? • Fact: – centralized systems are far simpler than distributed ones. • But: – Fault-tolerance forces distribution – Physical position of sensors and computers also forces distribution – Efficiency sometimes requires distribution • Real-Time Predictability – Must ensure end-to-end deadlines are met before system deployment

Distributed architecture USTC Temporal contracts Node Both the network and ECU resources are shared - Placing deadlines on each component network arbitration scheme Event Static(cyclic)scheduling Processing Message Message occurs begins generated ready for ·LIN ◆transmission Node response time Priority-based arbitration CAN(Controller Area Network) Network Source Event Node Node Destination Node Node Node Response Network Response Node Response End-to-End Deadline
Distributed architecture • Temporal contracts – Both the network and ECU resources are shared – Placing deadlines on each component • network arbitration scheme – Static (cyclic) scheduling • LIN – Priority-based arbitration • CAN (Controller Area Network) Source Node Destination Node
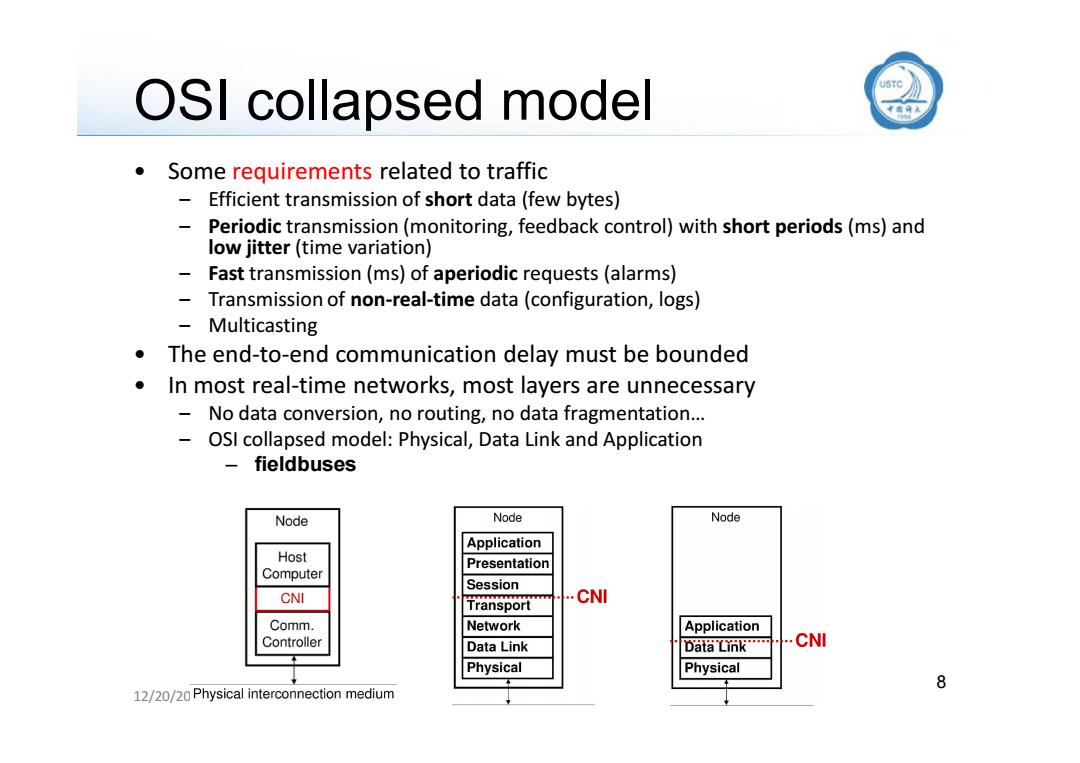
OSI collapsed model sc》 Some requirements related to traffic Efficient transmission of short data(few bytes) Periodic transmission(monitoring,feedback control)with short periods(ms)and low jitter(time variation) Fast transmission(ms)of aperiodic requests(alarms) Transmission of non-real-time data(configuration,logs) - Multicasting The end-to-end communication delay must be bounded In most real-time networks,most layers are unnecessary No data conversion,no routing,no data fragmentation... OSI collapsed model:Physical,Data Link and Application fieldbuses Node Node Node Application Host Presentation Computer Session CNI Transport CNI Comm. Network Application Controller Data Link Data Link CNI Physical Physical 8 12/20/20 Physical interconnection medium
8 12/20/2016 OSI collapsed model • Some requirements related to traffic – Efficient transmission of short data (few bytes) – Periodic transmission (monitoring, feedback control) with short periods (ms) and low jitter (time variation) – Fast transmission (ms) of aperiodic requests (alarms) – Transmission of non-real-time data (configuration, logs) – Multicasting • The end-to-end communication delay must be bounded • In most real-time networks, most layers are unnecessary – No data conversion, no routing, no data fragmentation… – OSI collapsed model: Physical, Data Link and Application – fieldbuses
Physical Layer features 》 In many cases low cost of the cabling scheme is fundamental! Is simplifies cabling Makes unnecessary for the protocol to perform routing -It facilitates a consistent reception of the same information in broadcast mode It facilitates the achievement of a consistent order in the reception of the messages. 9 12/20/2016
9 12/20/2016 Physical Layer features • In many cases low cost of the cabling scheme is fundamental! – Is simplifies cabling – Makes unnecessary for the protocol to perform routing – It facilitates a consistent reception of the same information in broadcast mode – It facilitates the achievement of a consistent order in the reception of the messages
Data Link Layer features USTC ·Addressing Direct addressing:The sender and receiver(s)are explicitly identified in every transaction,using physical addresses (as in Ethernet) - Indirect(source)addressing:The message contents are explicitly identified(e.g.temperature of sensor X).Receivers that need the message,retrieve it from the network(as in CAN and WorldFIP) Indirect(time-based)addressing:The message is identified by the time instantat which it is transmitted(as in TTP) Logical Link Control (LLC) transmission error control Medium Access Control (MAC) -Which is fundamental for RT response 10 12/20/2016
10 12/20/2016 Data Link Layer features • Addressing – Direct addressing: The sender and receiver(s) are explicitly identified in every transaction, using physical addresses (as in Ethernet) – Indirect (source) addressing: The message contents are explicitly identified (e.g. temperature of sensor X). Receivers that need the message, retrieve it from the network (as in CAN and WorldFIP) – Indirect (time-based) addressing: The message is identified by the time instantat which it is transmitted (as in TTP) • Logical Link Control (LLC) – transmission error control • Medium Access Control (MAC) – Which is fundamental for RT response