
计算机组成原理 第5章层次化存储 概述,Cache llxx@ustc.edu.cn
计算机组成原理 第5章 层次化存储 概述,Cache llxx@ustc.edu.cn
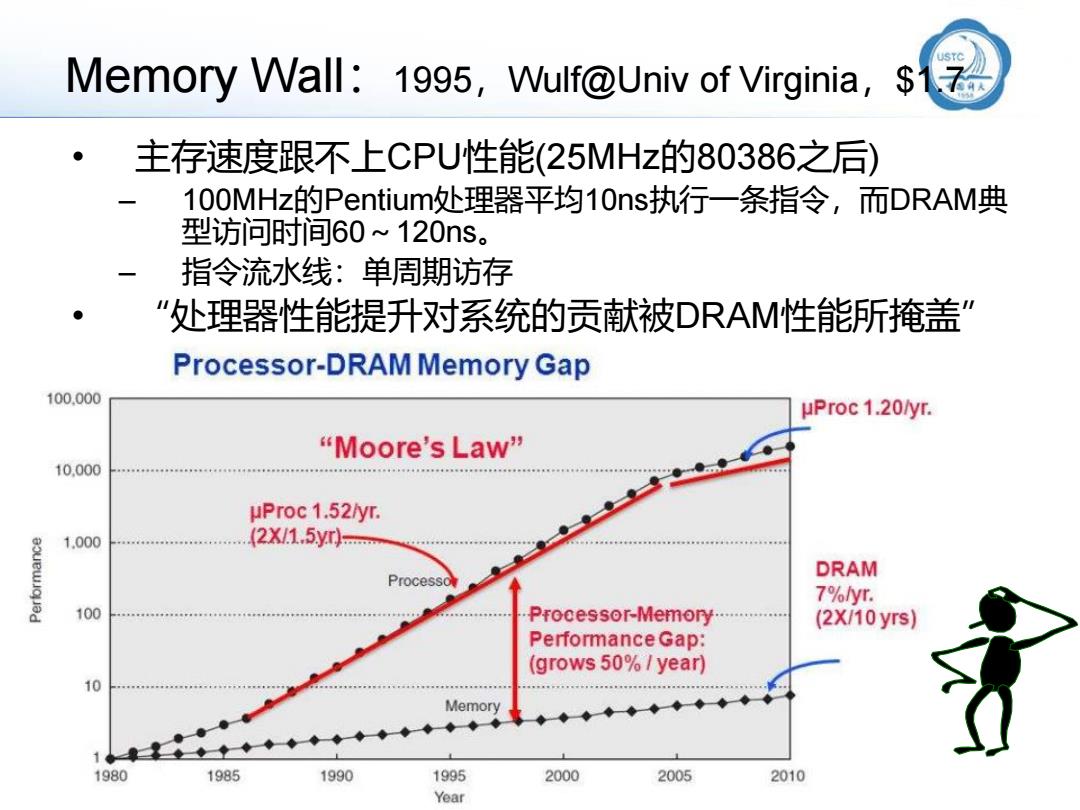
STC Memory Wall:1995,Wulf@Univ of Virginia,S $ 1 主存速度跟不上CPU性能(25MHz的80386之后) 100MHz的Pentium处理器平均10ns执行一条指令,而DRAM典 型访问时间60~120ns。 指令流水线:单周期访存 ● "处理器性能提升对系统的贡献被DRAM性能所掩盖” Processor-DRAM Memory Gap 100.000 μProc1.20y “Moore'sLaw" 10.000 uProc 1.52/yr. 1.000 (2X115yr DRAM Processo 7%yt. 100 Processor-Memory (2X/10yrs) Performance Gap: (grows 50%/year) 10 Memory 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Year
Memory Wall:1995,Wulf@Univ of Virginia,$1.7 • 主存速度跟不上CPU性能(25MHz的80386之后) – 100MHz的Pentium处理器平均10ns执行一条指令,而DRAM典 型访问时间60~120ns。 – 指令流水线:单周期访存 • “处理器性能提升对系统的贡献被DRAM性能所掩盖
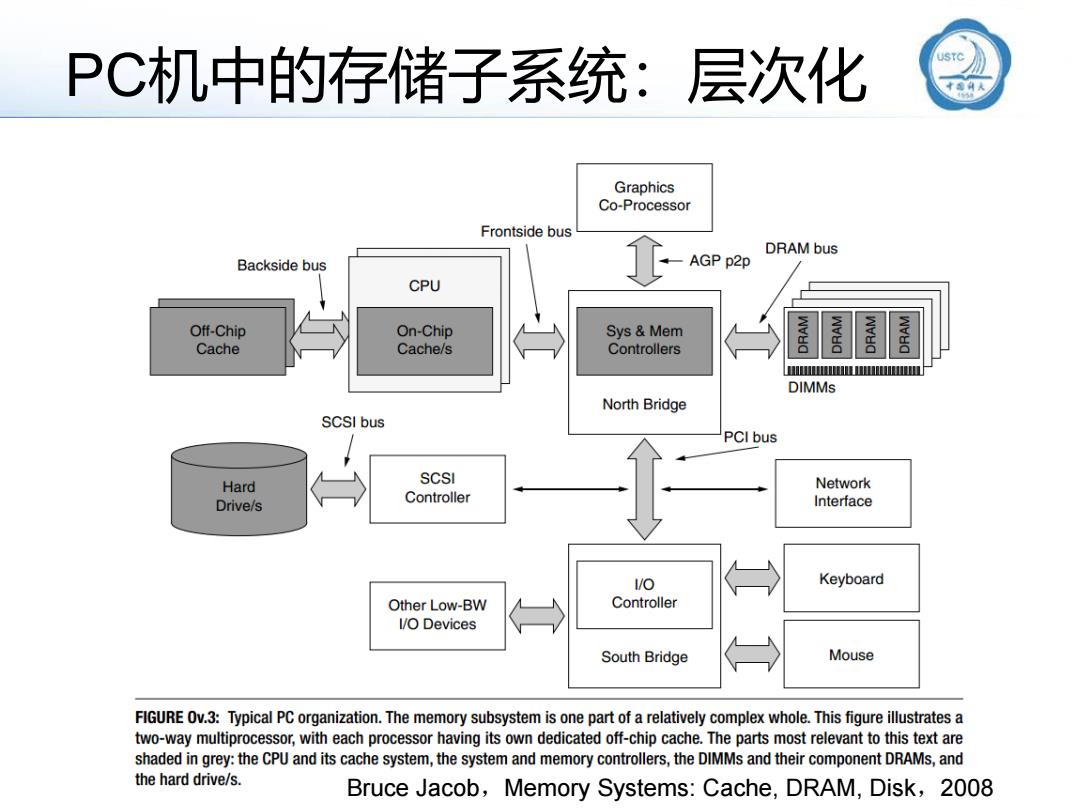
PC机中的存储子系统:层次化 JSTC Graphics Co-Processor Frontside bus DRAM bus Backside bus AGP p2p CPU Off-Chip On-Chip Sys Mem Cache Cache/s Controllers DIMMs North Bridge SCSI bus PCI bus Hard SCSI Network Drive/s Controller Interface 1/O Keyboard Other Low-BW Controller 1/O Devices South Bridge Mouse FIGURE Ov.3:Typical PC organization.The memory subsystem is one part of a relatively complex whole.This figure illustrates a two-way multiprocessor,with each processor having its own dedicated off-chip cache.The parts most relevant to this text are shaded in grey:the CPU and its cache system,the system and memory controllers,the DIMMs and their component DRAMs,and the hard drive/s. Bruce Jacob,Memory Systems:Cache,DRAM,Disk,2008
PC机中的存储子系统:层次化 Bruce Jacob,Memory Systems: Cache, DRAM, Disk,2008
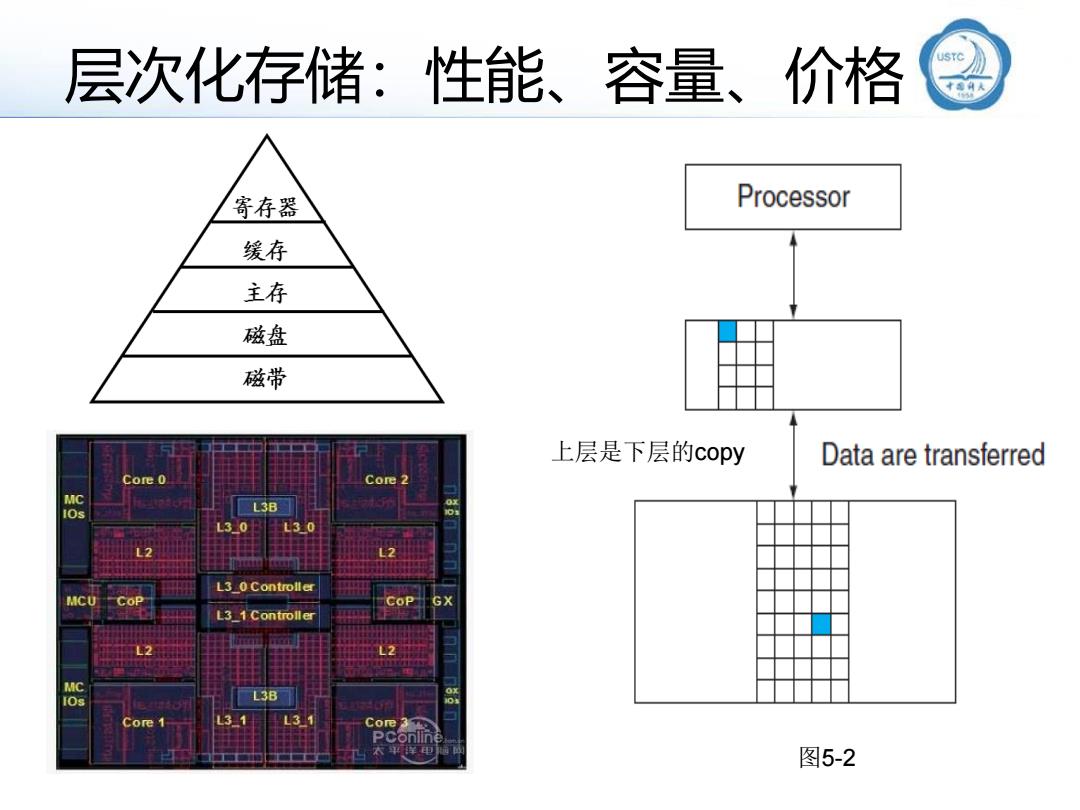
层次化存储:性能、容量、价格 寄存器 Processor 缓存 主存 磁盘 磁带 上层是下层的copy Data are transferred Core 0 Core 2 MC os L3 30 L30 3 0 Controller MCU GX L2 MC L3B Core 1 Core 3 本电 图5-2
层次化存储:性能、容量、价格 上层是下层的copy 图5-2
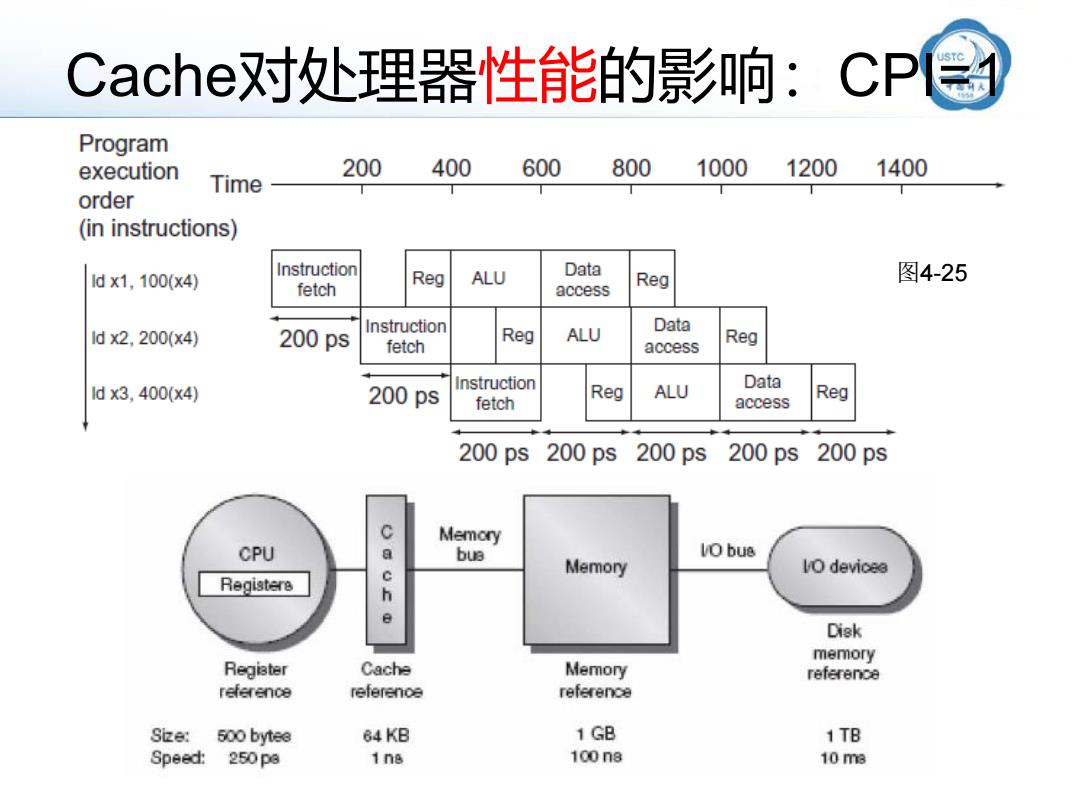
Cache对处理器性能的影响:CP Program execution 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 Time order (in instructions) 1dx1,100(x4) Instruction Reg ALU Data Reg 图4-25 fetch access Data 1dx2,200(x4) 200ps Instruction fetch Reg ALU access Reg Data 1dx3.400(x4) 200ps Instruction fetch Reg ALU access Reg 200ps200ps200ps 200ps200ps Memory CPU 9 bu3 VO bue Memory Vo devicea Registere h Disk memory Regiater Cache Memory reference reference referenoe reference Size:500 bytee 64KB 1 GB 1TB Speed: 250pa 1n8 100n8 10 me
Cache对处理器性能的影响:CPI=1 图4-25
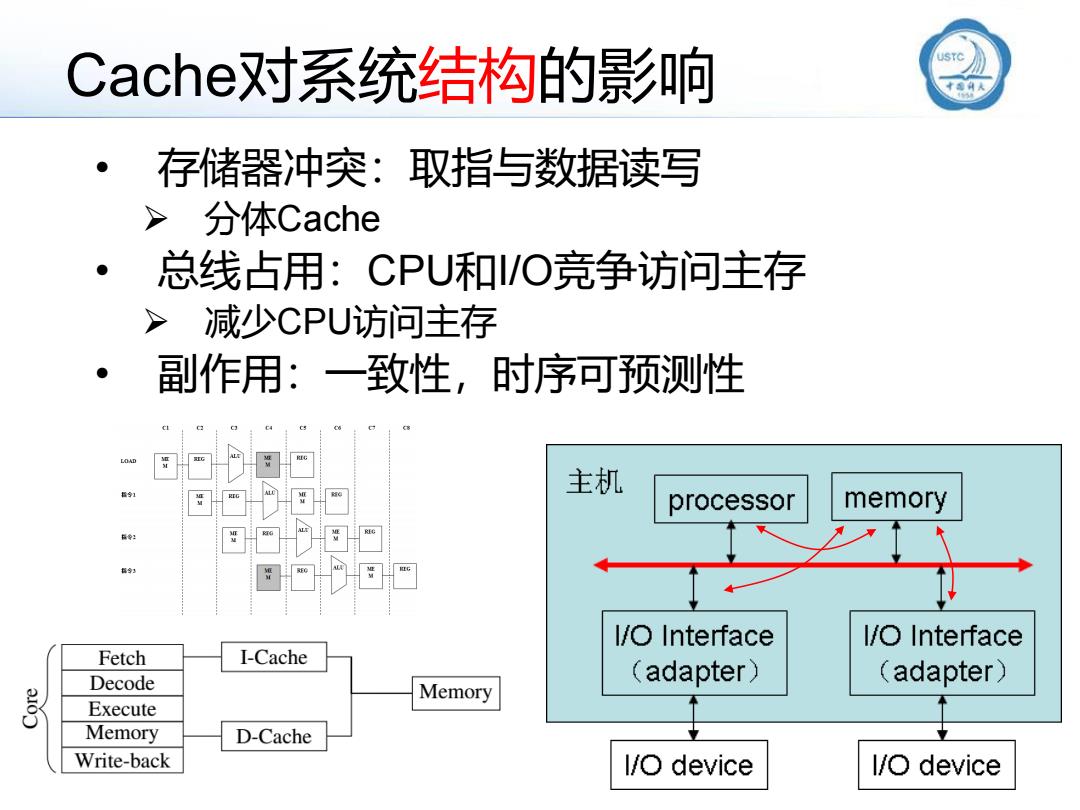
Cache对系统结构的影响 存储器冲突:取指与数据读写 >分体Cache ●】 总线占用:CPU和I/O竞争访问主存 减少CPU访问主存 副作用:一致性,时序可预测性 主机 processor memory I/O Interface I/O Interface Fetch I-Cache Decode (adapter) (adapter) Memory Execute Memory D-Cache Write-back l/O device I/O device
Cache对系统结构的影响 • 存储器冲突:取指与数据读写 ➢ 分体Cache • 总线占用:CPU和I/O竞争访问主存 ➢ 减少CPU访问主存 • 副作用:一致性,时序可预测性
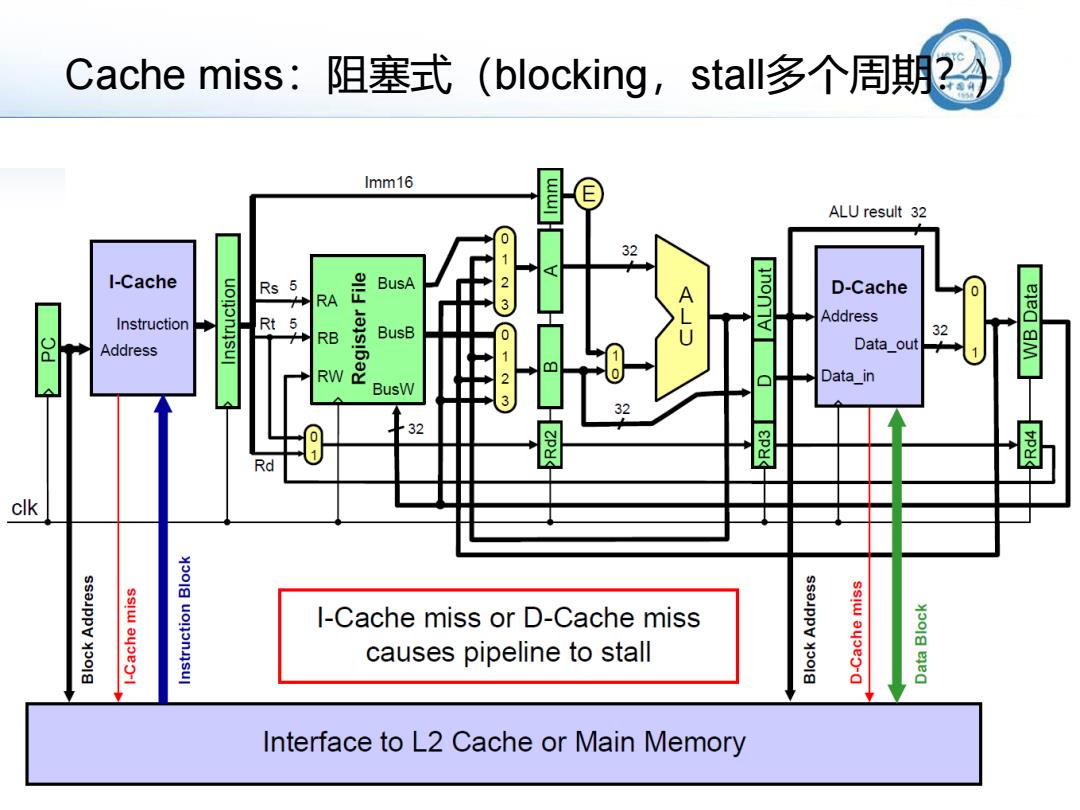
Cache miss:阻塞式(blocking,stall多个周期 2 Imm16 E ALU result 32 32 I-Cache Rs BusA 0123 inon7 D-Cache RA Instruction Rt 5 Address RB BusB 32 Address Data_out 1 RW BusW 23 Data_in 32 32 01 Rd clk I-Cache miss or D-Cache miss causes pipeline to stall Interface to L2 Cache or Main Memory
Cache miss:阻塞式(blocking,stall多个周期?)
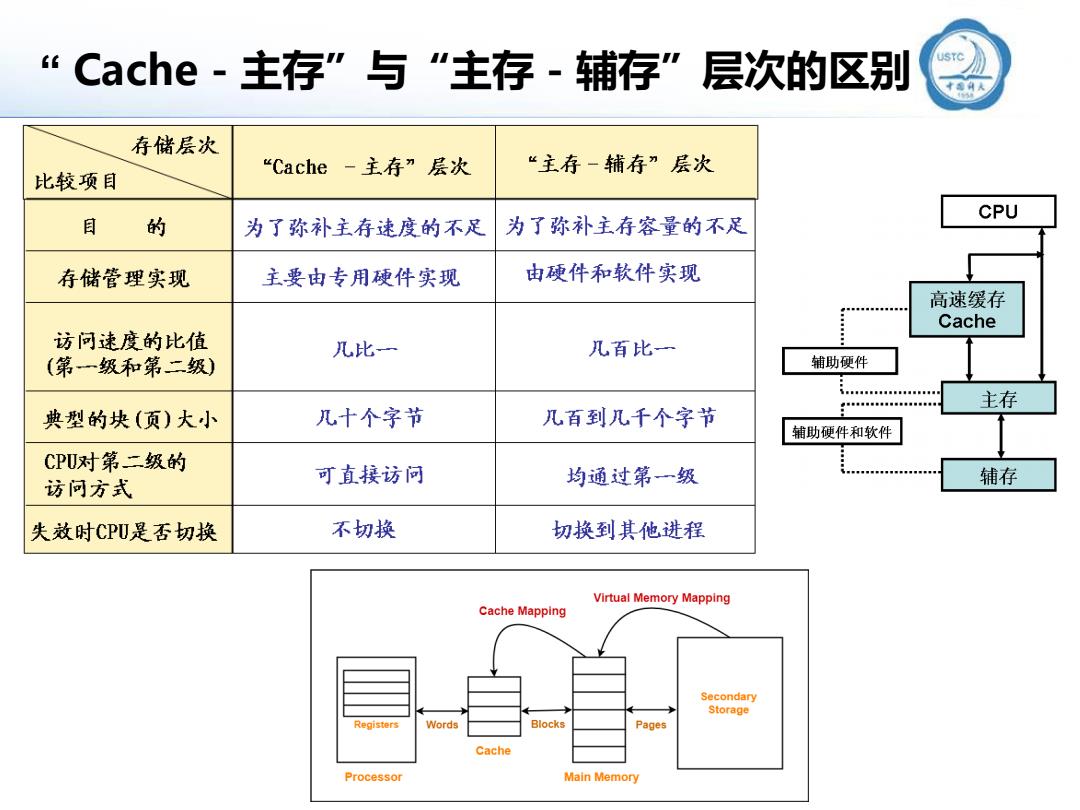
Cache-主存”与“主存-辅存”层次的区别 sc》 存储层次 “Cache-主存”层次 “主存一辅存”层次 比较项目 CPU 目 的 为了弥补主存速度的不足 为了弥补主存容量的不足 存储管理实现 主要由专用硬件实现 由硬件和软件实现 高速缓存 Cache 访问速度的比值 几比一 几百比一 (第一级和第二级) 辅助硬件 飞84■88■88588 主存 典型的块(页)大小 几十个字节 几百到几千个字节 辅助硬件和软件 CPU对第二级的 访问方式 可直接访问 均通过第一级 辅存 失效时CPU是否切换 不切换 切换到其他进程 Virtual Memory Mapping Cache Mapping Secondary Storage Registers Words Blocks Pages Cache Processor Main Memory
“ Cache-主存”与“主存-辅存”层次的区别
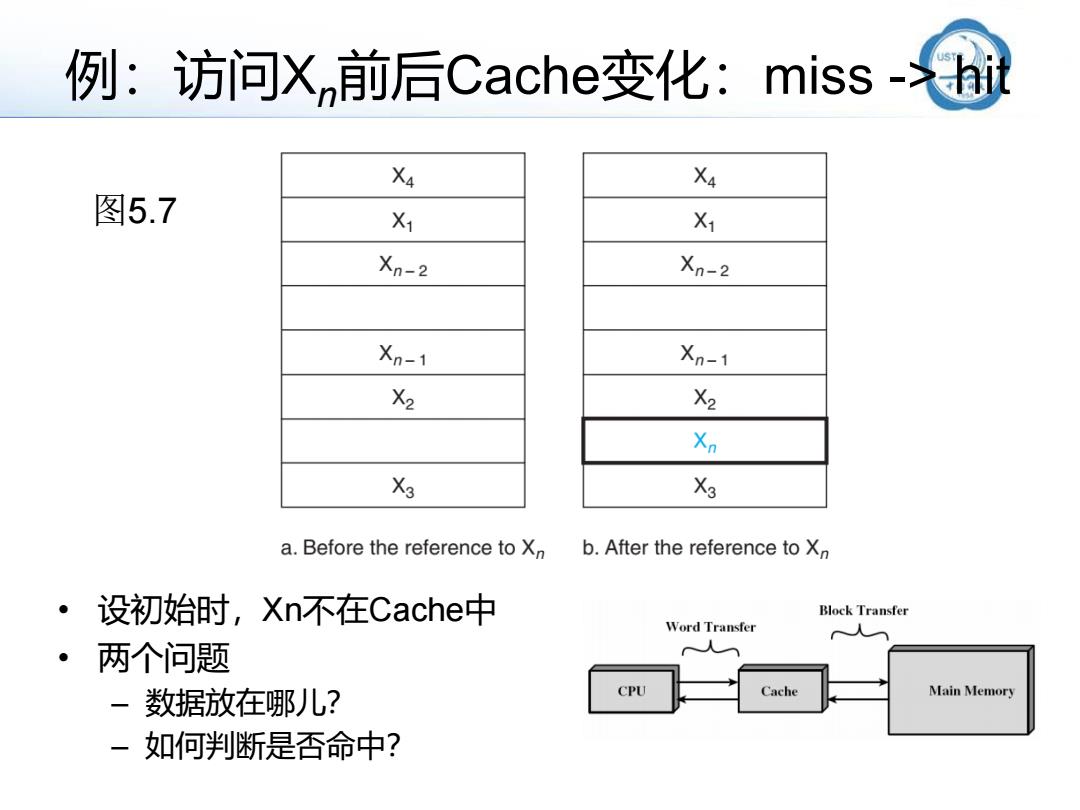
例:访问X前后Cache变化:miss-hit X4 X4 图5.7 X1 X1 Xn-2 Xn-2 Xn-1 Xn-1 X2 X2 Xn X X3 a.Before the reference to X b.After the reference to Xn ·设初始时,Xn不在Cache中 Block Transfer Word Transfer 人 ·两个问题 人 一数据放在哪儿? CPU Cache Main Memory 一如何判断是否命中?
例:访问Xn前后Cache变化:miss -> hit • 设初始时,Xn不在Cache中 • 两个问题 – 数据放在哪儿? – 如何判断是否命中? 图5.7

本讲内容:Cache系统(单处理器) ·为什么需要Cache? 一性能、结构 三个关键问题:PWR 。 Cache?有效性的理论基础 the mapping function(映射) -局部性原理:时间,空间 the link between a block's address ·影响Cache命中率的因素 in memory and its location in the cache; Cache的基本结构,5.3 Block Placement Schemes Cache的读写操作过程,5.3,5.8 o the write policy Cache-一致性 how the processor writes data to ·阻塞式Cache the cache so that main memory eventually gets updated; Cache-MEM映射机制,5.4,5.8 the replacement algorithm ·块放哪儿? - the method used to figure out Cachel的替换策略,5.4,5.8 which block to remove from the cache in order to free up a line. Cache控制器:5.9,5.12 Cache性能分析 COD5 ·主要见体系结构课 5.3,5.4,5.8,5.9,5.12 Cache Coherence,5.10 唐:4.3,附录4A ·见体系结构课
本讲内容:Cache系统(单处理器) • 三个关键问题:PWR • the mapping function(映射) – the link between a block's address in memory and its location in the cache; – Block Placement Schemes • the write policy – how the processor writes data to the cache so that main memory eventually gets updated; • the replacement algorithm – the method used to figure out which block to remove from the cache in order to free up a line. • COD5 – 5.3, 5.4, 5.8, 5.9, 5.12 • 唐:4.3,附录4A • 为什么需要Cache? – 性能、结构 • Cache有效性的理论基础 – 局部性原理:时间,空间 • 影响Cache命中率的因素 • Cache的基本结构,5.3 • Cache的读写操作过程,5.3,5.8 • Cache一致性 • 阻塞式Cache • Cache-MEM映射机制,5.4,5.8 • 块放哪儿? • Cache的替换策略,5.4,5.8 • Cache控制器:5.9,5.12 • Cache 性能分析 • 主要见体系结构课 • Cache Coherence,5.10 • 见体系结构课