
恩 低功耗系统设计 LiXi Computer Applications Lab CS Department,USTC
低功耗系统设计 Li Xi Computer Applications Lab CS Department, USTC

小米手机(MU),双核 USTC 主屏分辨率 480×854像素 自动 高 一低 42.0 主屏色彩 1600万色 40.7 30.9 网络模式 GSM,WCDMA 操作系统 MIUI+原生Android(基于Android OS v2.3.5) 核心数 双核 40.2 CPU型号 高通snapdragon QSD8260 CPU频率 1536MHZ GPU型号 高通Adreno220 29.0 机身内存 1GB RAM+4GB ROM 08129/2011 003751 存储卡 MicroSD卡 自动 扩展容量 32GB 高 低 °C44.0 42.1日30.9 电池容量 1930mAh 40.4 ·高温处? -MSM8260 29.0 08129/2011 00:42:59
小米手机(MIUI),双核 • 高温处? – MSM8260
Outline ·The Effects of Power ·Low Power Design -DPM based low power optimization -DVS based low power optimization ex:Program-level optimization for multimedia ACPI:OS supported PM 一软硬件协同低功耗设计 Power model:Power Analysis/Estimation Tek Tools Temperature Aware Design ·Leakage Power ·Case Study -Cache、Memory、Data Center、Handheld 。Conclusion llxx@ustc.edu.cn 3/62
Outline • The Effects of Power • Low Power Design – DPM based low power optimization – DVS based low power optimization • ex: Program-level optimization for multimedia – ACPI:OS supported PM llxx@ustc.edu.cn 3/62 – ACPI:OS supported PM – 软硬件协同低功耗设计 • Power model: Power Analysis/Estimation Tek & Tools • Temperature Aware Design • Leakage Power • Case Study – Cache、Memory、Data Center、Handheld • Conclusion

参考文献 POWER AWARE Power Aware Design Methodologies DESIGN METHODOLOGIES edited by M.Pedram and J.Rabaey, Kluwer Academic Publishers,2002. ●( Compilers and Operating Systems for uu=一 Low Power Compilers and Operating Systems for Low Power Benini,Luca;Kandemir,Mahmut; Ramanujam,J.(Eds.),Springer,2003, 246 p.,Hardcover Advanced Memory Optimization ck toLOOK INSIDE目 Techniques for Low-Power Embedded Processors Advanced Memory Jptimizanon lechniques Manish Verma,Peter Marwedel,Springer; or Low-Power Embedded Processors 1st edition (May 8,2007) llxx@ustc.edu.cn 4/62
参考文献 • Power Aware Design Methodologies – edited by M. Pedram and J. Rabaey, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2002. • Compilers and Operating Systems for Low Power – Benini, Luca; Kandemir, Mahmut; llxx@ustc.edu.cn 4/62 Ramanujam, J. (Eds.) , Springer, 2003, 246 p., Hardcover • Advanced Memory Optimization Techniques for Low-Power Embedded Processors – Manish Verma, Peter Marwedel, Springer; 1st edition (May 8, 2007)

Power Constraint:heat dissipation limited systems High-end systems,e.g.servers,stations and desktops Cooling and packaging cost Reliability requires System Power Consumption evey10℃increase on Athion 64 3500+90nm Athlon 64 3500+130nm relative operating temperature ■Pentium43.4GHz90nn MTBF double failure rate for the 112 131 1下 components 151 0.8 151 Sphinx 179 0.6 233 0.4 146 Moldyn 175 0.2 230 0 151 Xmpeg 179 707580859095100105 236 source:Intel Components Quality Temp 50 100 150 200 250 and Reliability Handbook Watts llxx@ustc.edu.cn 5/62
Power Constraint:heat dissipation limited systems • High-end systems, e.g. servers, stations and desktops – Cooling and packaging cost – Reliability requires relative MTBF every 10℃ increase on operating temperature double failure rate for the llxx@ustc.edu.cn 5/62 Temp MTBF 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 source: Intel Components Quality and Reliability Handbook double failure rate for the components

HPC:风冷 Evaluating the Intel MIC Architecture Arndt Bode Leibniz Supercomputing Centre,Germany with input from Iris Christadler,Alexander Heinecke and Volker Weinber June 2011,ISC,Hamburg m TECHNSCHE 人5 MONCHEN
HPC:风冷
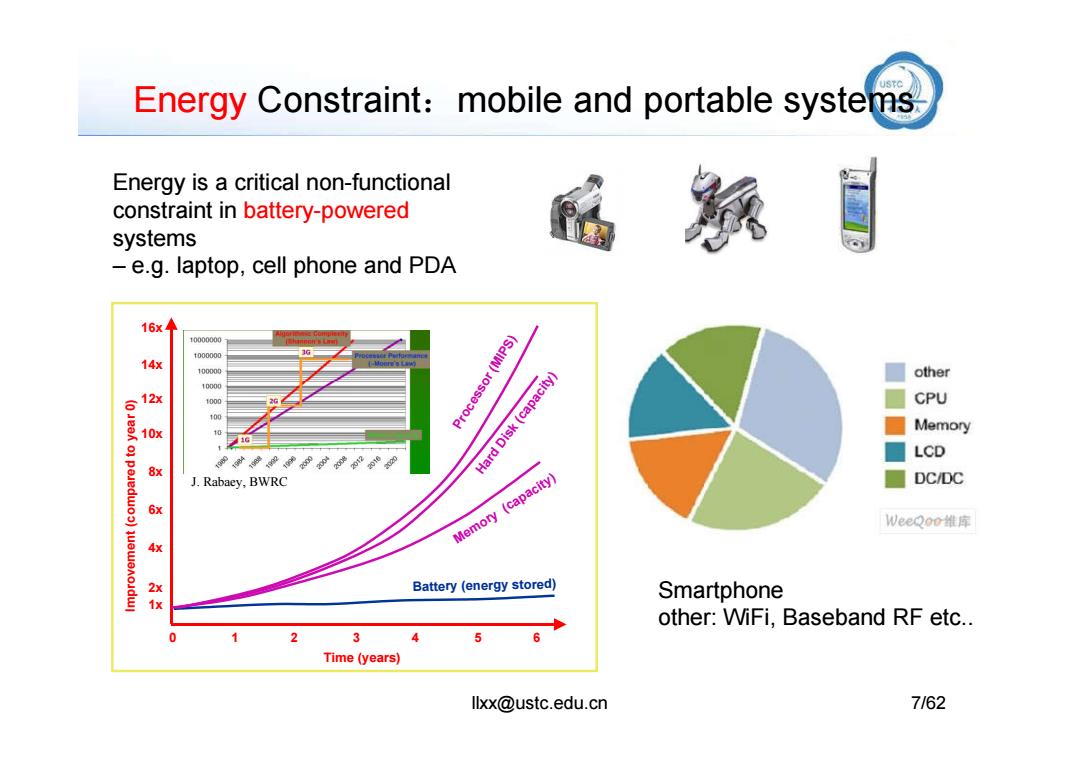
C Energy Constraint:mobile and portable systems Energy is a critical non-functional constraint in battery-powered systems -e.g.laptop,cell phone and PDA 16x◆ 10000000 1000000 14X 10000 other 1000g 6 12x 1000 Processor(MIPS) Hard Disk(capacity) CPU 100 10X Memory LCD o]peiedwo) 8x J.Rabaey.BWRC DC/DC 6x Memory(capacity】 VeeQoo锥库 4x 2x Battery (energy stored) Smartphone other:WiFi,Baseband RF etc.. 2 Time(years) llxx@ustc.edu.cn 7162
Energy Constraint:mobile and portable systems Processor (MIPS) Hard Disk (capacity) 16x 14x Energy is a critical non-functional constraint in battery-powered systems – e.g. laptop, cell phone and PDA llxx@ustc.edu.cn 7/62 Processor (MIPS) Hard Disk (capacity) Memory (capacity) Battery (energy stored) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 12x 10x 8x 6x 4x 2x Improvement (compared to year 0) 1x Time (years) J. Rabaey, BWRC Smartphone other: WiFi, Baseband RF etc
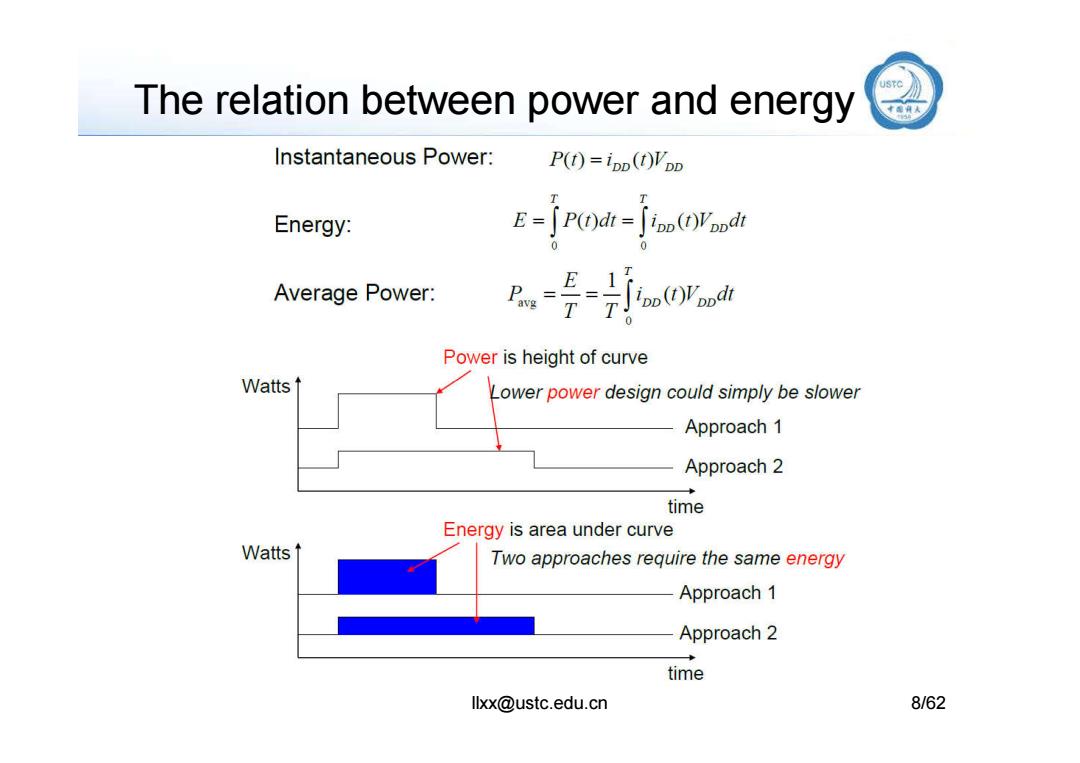
The relation between power and energy Instantaneous Power: P(t)=ipD(t)VDD EP(d (d T Energy: Average Power: Power is height of curve Watts Lower power design could simply be slower Approach 1 Approach 2 time Energy is area under curve Watts Two approaches require the same energy Approach 1 Approach 2 time llxx@ustc.edu.cn 8/62
The relation between power and energy llxx@ustc.edu.cn 8/62

Power and Energy ·Circuit level view -dynamic(transistor switching),short circuit,leakage current P=Pan +Pe+Pu =0.5CLVDD Af +IsV DDA+IRVDD Voo:supply voltage; CL:node capacitance; Capacitive(Dynamic)Power Static (Leakage)Power Vdd f.clock frequency; A:activity factor: n Vout Isc:Short circuit current; lIk:leakage current .Dynamic power is the dominant source now. .Static power is growing faster Higher Architecture level view -Datapath Power,Memory System Power,Bus Power,etc llxx@ustc.edu.cn 9/62
Power and Energy • Circuit level view — dynamic (transistor switching), short circuit, leakage current dyn sc lk L DD sc DD lkVDD P P P P C V Af I V A I 2 0.5 VDD: supply voltage; CL: node capacitance; f: clock frequency; A: activity factor; llxx@ustc.edu.cn 9/62 A: activity factor; Isc:Short circuit current ; Ilk: leakage current • Architecture level view —Datapath Power, Memory System Power, Bus Power,etc •Dynamic power is the dominant source now. •Static power is growing faster Higher
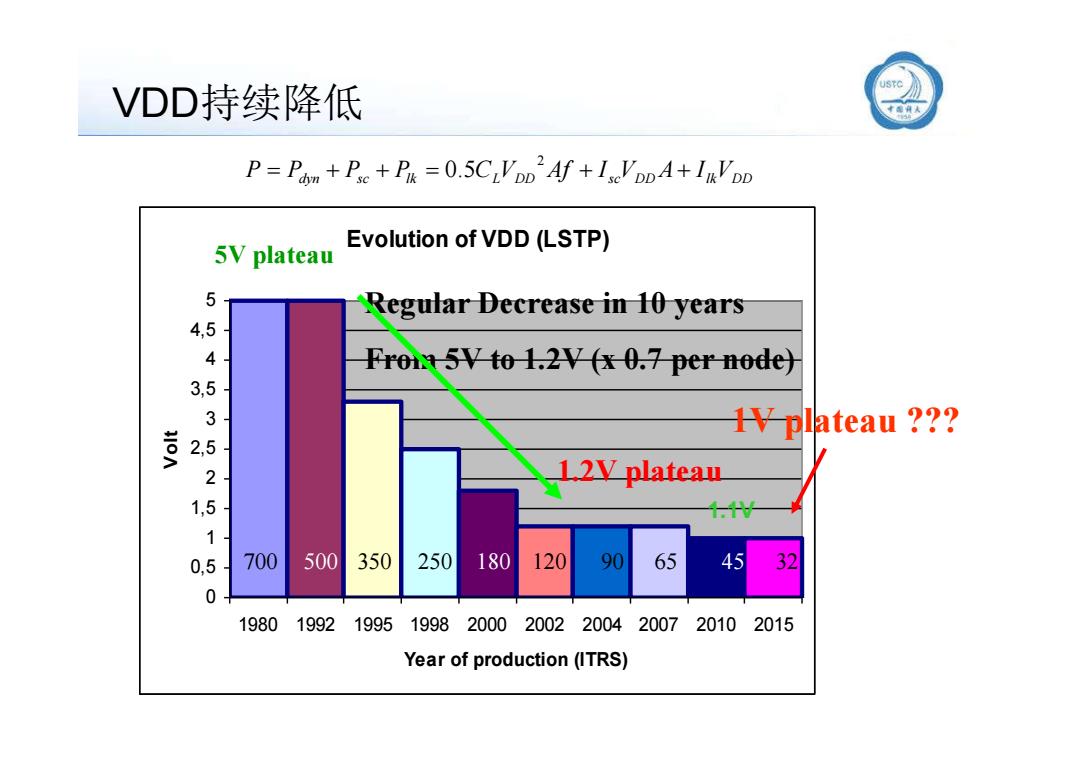
VDD持续降低 P=Pam +Pse+P=0.5CLVDD'Af +IsVDDA+InVDD Evolution of VDD(LSTP) 5V plateau 5 Regular Decrease in 10 years 433525 Froi 5V to 1.2V (x 0.7 per node) HVplateau ?? 12V plateau 0,5 700 500 350 250 180 120 90 65 45 0 1980 1992 1995 1998 20002002 2004 20072010 2015 Year of production(ITRS)
VDD持续降低 Evolution of VDD (LSTP) 3,5 4 4,5 5 5V plateau Regular Decrease in 10 years From 5V to 1.2V (x 0.7 per node) dyn sc lk L DD sc DD lkVDD P P P P C V Af I V A I 2 0.5 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 2,5 3 3,5 1980 1992 1995 1998 2000 2002 2004 2007 2010 2015 Year of production (ITRS) Volt 1V plateau ??? 1.2V plateau 700 350 250 120 90 65 45 32 1.1V 500 180