
中围种学技本大学 嵌入式系统形式化规范与建模 李曦 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 计算机系、计算机应用研究室
嵌入式系统形式化规范与建模 李曦 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 计算机系、计算机应用研究室
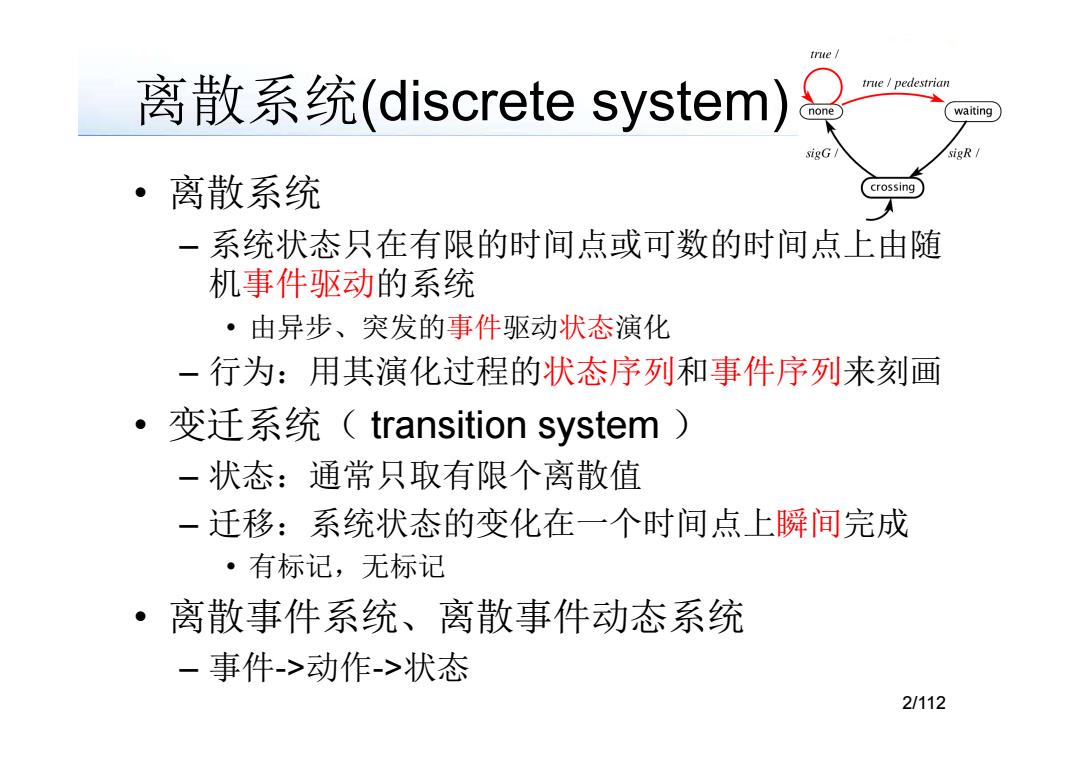
true 离散系统(discrete system) true /pedestrian waiting sigG sigR ·离散系统 crossing 一系统状态只在有限的时间点或可数的时间点上由随 机事件驱动的系统 ·由异步、突发的事件驱动状态演化 一行为:用其演化过程的状态序列和事件序列来刻画 。7 变迁系统(transition system) 一状态:通常只取有限个离散值 一迁移:系统状态的变化在一个时间点上瞬间完成 ·有标记,无标记 ·离散事件系统、离散事件动态系统 一事件->动作->状态 2/112
离散系统(discrete system) • 离散系统 – 系统状态只在有限的时间点或可数的时间点上由随 机事件驱动的系统 • 由异步、突发的事件驱动状态演化 – 行为:用其演化过程的 用其演化过程的状态序列和事件序列来刻画 • 变迁系统( transition system ) – 状态:通常只取有限个离散值 – 迁移:系统状态的变化在一个时间点上瞬间完成 • 有标记,无标记 • 离散事件系统、离散事件动态系统 – 事件->动作->状态 2/112
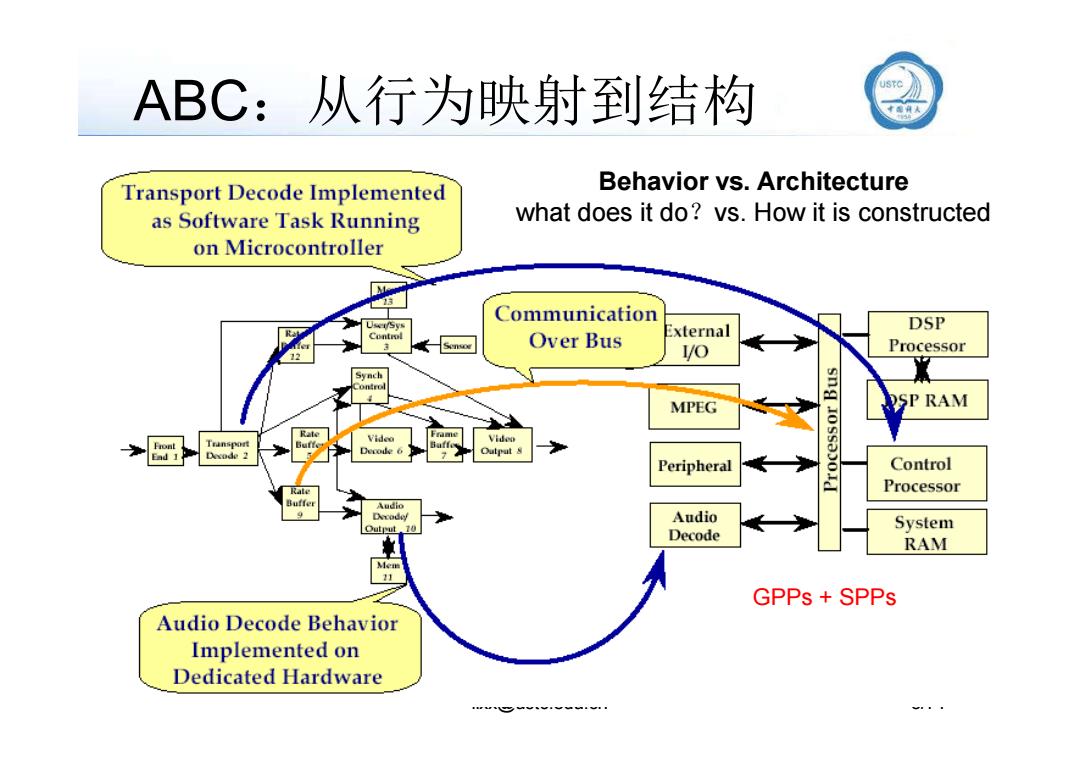
ABC:从行为映射到结构 Transport Decode Implemented Behavior vs.Architecture as Software Task Running what does it do?vs.How it is constructed on Microcontroller Communication External DSP Over Bus Processor 12 lo Synch onrol MPEG SP RAM Rate Video Frame Video Front Ead 1 Decode 6 Outpat 8 Peripheral Control Processor Audio Derode Audio Decode System RAM 11 GPPs SPPs Audio Decode Behavior Implemented on Dedicated Hardware
ABC:从行为映射到结构 Behavior vs. Architecture what does it do?vs. How it is constructed llxx@ustc.edu.cn 3/71 GPPs + SPPs
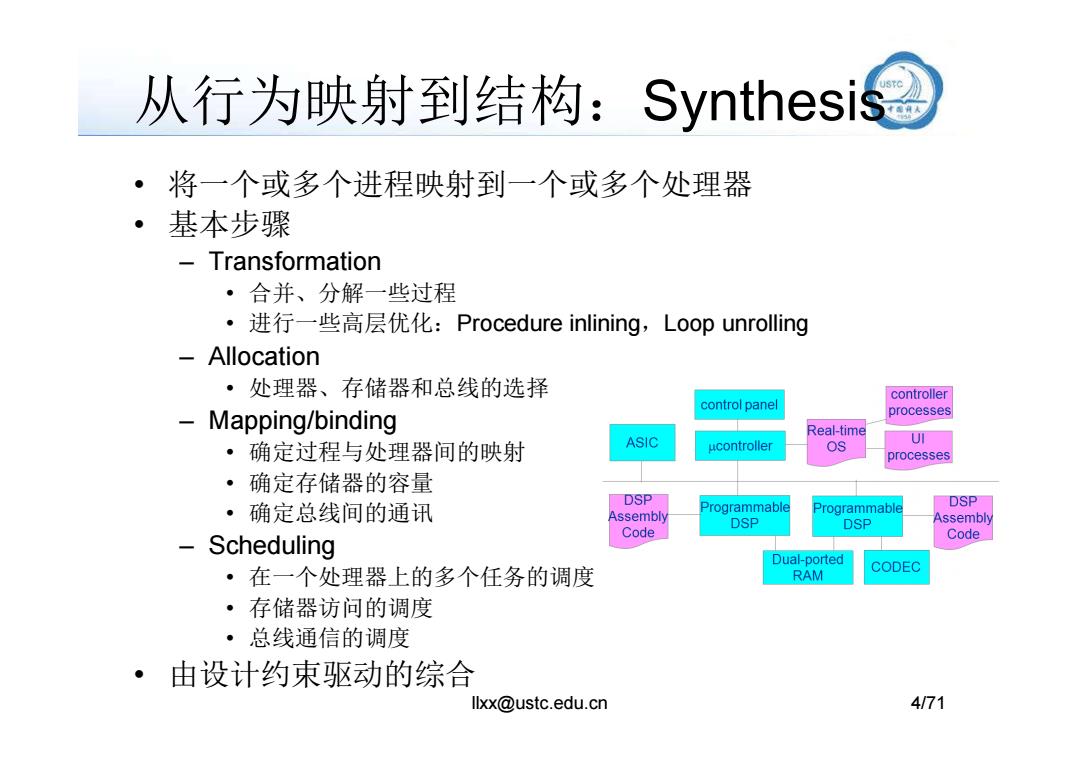
从行为映射到结构:Synthesis悬 ·将一个或多个进程映射到一个或多个处理器 基本步骤 Transformation ·合并、分解一些过程 ·进行一些高层优化:Procedure inlining,Loop unrolling Allocation ·处理器、存储器和总线的选择 controller control panel -Mapping/binding processes Real-time ASIC ucontroller OS UI ·确定过程与处理器间的映射 processes ·确定存储器的容量 DSP ·确定总线间的通讯 Programmable Programmable DSP Assembly DSP DSP Assembly Code - Scheduling Code Dual-ported ·在一个处理器上的多个任务的调度 CODEC RAM ·存储器访问的调度 ·总线通信的调度 ·由设计约束驱动的综合 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 4/71
从行为映射到结构:Synthesis • 将一个或多个进程映射到一个或多个处理器 • 基本步骤 – Transformation • 合并、分解一些过程 • 进行一些高层优化:Procedure inlining,Loop unrolling – Allocation • 处理器、存储器和总线的选择 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 4/71 • 处理器、存储器和总线的选择 – Mapping/binding • 确定过程与处理器间的映射 • 确定存储器的容量 • 确定总线间的通讯 – Scheduling • 在一个处理器上的多个任务的调度 • 存储器访问的调度 • 总线通信的调度 • 由设计约束驱动的综合
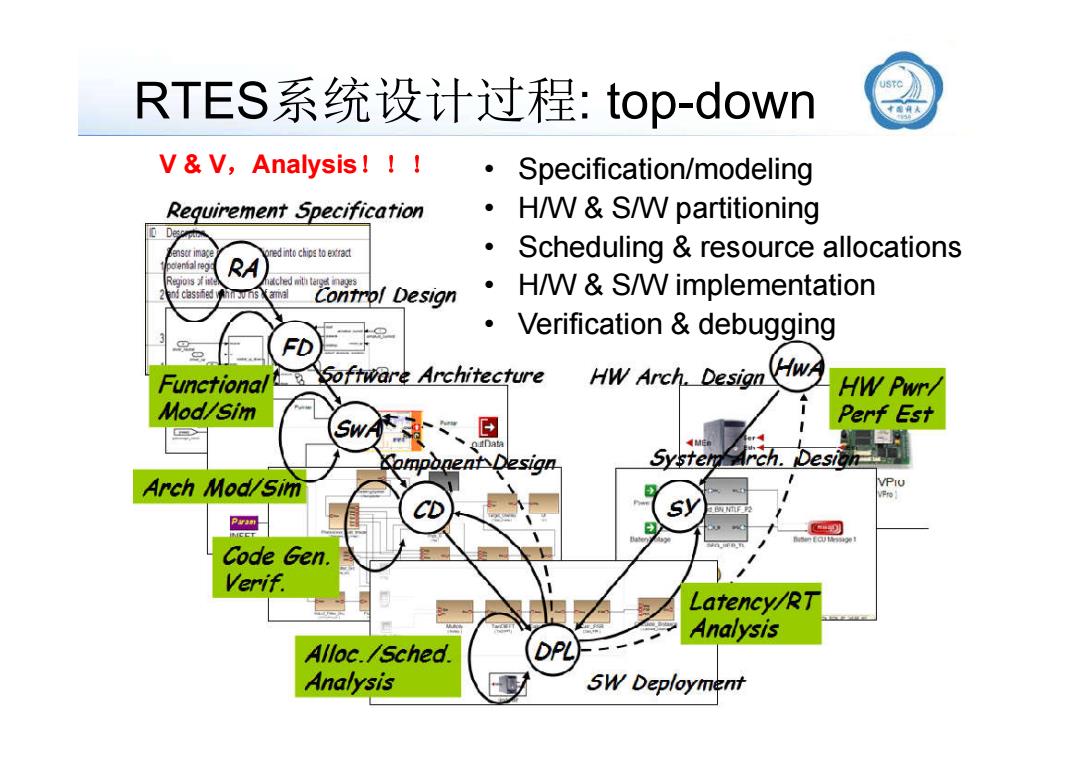
RTES系统设计过程:top-down USTC V&V,Analysis! Specification/modeling Requirement Specification H/W&S/W partitioning De ned into chins to extract Scheduling resource allocations reg Reg0si Control Design H/W&S/W implementation Verification debugging FD (HwA Functional Software Architecture HW Arch.Design HW Pwr/ Mod/sim w、旦 Perf Est Somponent Design Arch Mod/Sim Paran Code Gen. Verif. Latency/RT Analysis Alloc./Sched Analysis 5W Deployment
RTES系统设计过程: top-down • Specification/modeling • H/W & S/W partitioning • Scheduling & resource allocations • H/W & S/W implementation • Verification & debugging V & V,Analysis!!!

V&V 。验证Verification vs.确认Validation -验证:Design=Specification? ·保证设计是正确的和完备的 -正确:指精确地实现了SPEC定义的功能、性能等要求 -完备性:描述与所有输入相关的输出 -确认:Design==Requirement? ·形式化验证(Formal verification) 一困难:仅适合于小的设计,或验证某些关键的属性 。 模拟(Simulation)与测试(Testing) 一大多数情况下都采用这种方法 -仅增加了正确性和完备性的可信度 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 6/71
V&V • 验证Verification vs. 确认Validation – 验证:Design == Specification? • 保证设计是正确的和完备的 – 正确:指精确地实现了SPEC定义的功能、性能等要求 – 完备性:描述与所有输入相关的输出 – 确认: Design == Requirement? llxx@ustc.edu.cn 6/71 – 确认: Design == Requirement? • 形式化验证(Formal verification) – 困难:仅适合于小的设计,或验证某些关键的属性 • 模拟(Simulation)与测试(Testing) – 大多数情况下都采用这种方法 – 仅增加了正确性和完备性的可信度
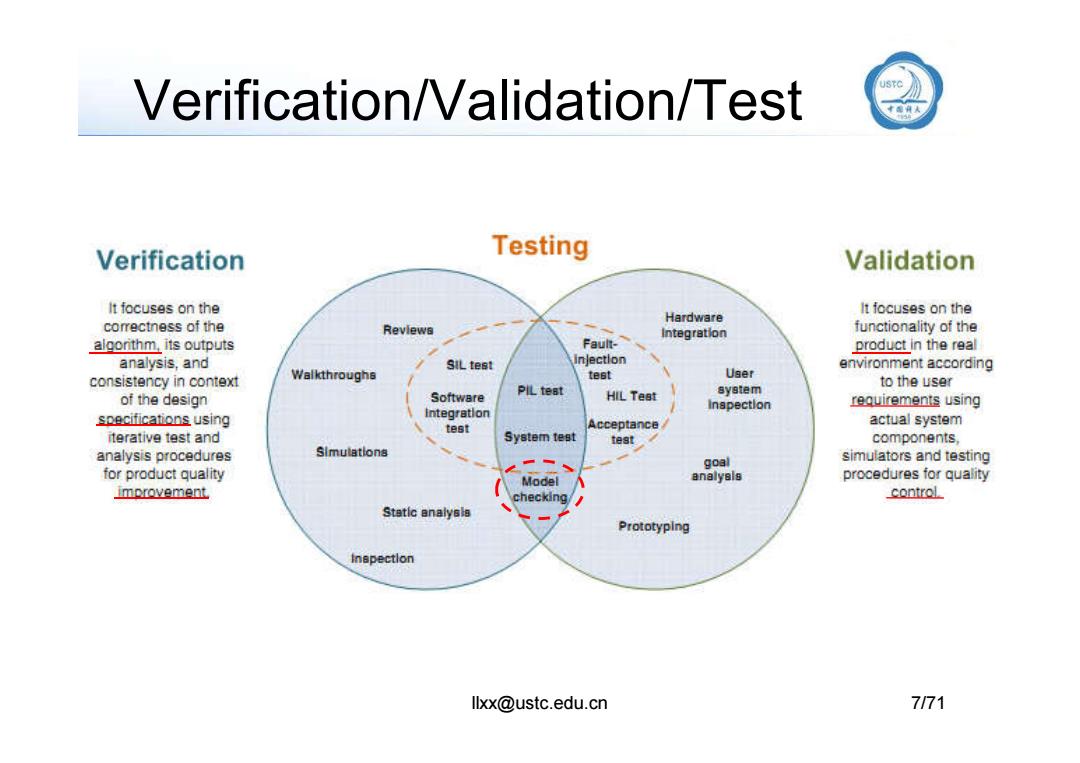
Verification/Validation/Test USTC Verification Testing Validation It focuses on the Hardware It focuses on the correctness of the Revlews Integration functionality of the algorithm,its outputs Fault. product in the real analysis,and SILtest inJection environment according consistency in context Walkthroughs test Uaer to the user of the design Software PiL test HIL Test system Inspection requirements using specifications using Integration Acceptance actual system test iterative test and System test Simulations test components analysis procedures goal simulators and testing for product quality Model analyels procedures for quality improvement checking/ control Static analysls Prototyping Inspectlon llxx@ustc.edu.cn 7/71
Verification/Validation/Test llxx@ustc.edu.cn 7/71

“Y-Chart”Approach for Model--Based Analysis Applications,Platform,Allocation Application Platform Model Model Applic.Constraints Resources QoS .Environment Params .Capacity,speed.etc. .Quality Requirements Reliability(avallabillty .Design Constraints fault tolerance,etc.) Allocation Alloc.Information put Files for .Applic.to Platform Analysis mapping .Allocation-specific properties Analysis Tools Analysis Results Specification of Non-Functional Properties! Generated Code
“Y-Chart” Approach for Model-Based Analysis • Applications,Platform,Allocation
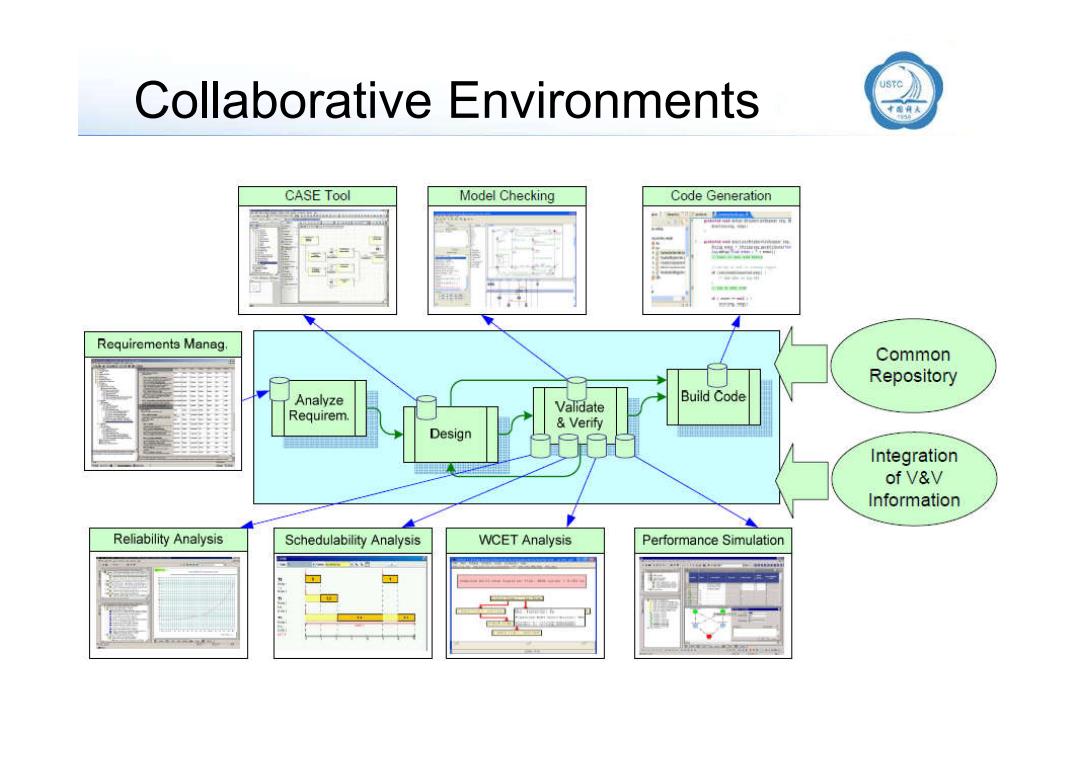
Collaborative Environments CASE Tool Model Checking Code Generation 44 Requirements Manag. Common Repository Analyze Build Code Validate Requirem. Verify Design Integration of V&V Information Reliability Analysis Schedulability Analysis WCET Analysis Performance Simulation
Collaborative Environments

内容提要 Modeling Design Analysis ·系统规约、建模、实现、分析方法:ABC -CBD:分治,结构 -MBD:抽象,分析 Integrate Models to DESIGN-BUILD-VALIDATE-VERIFY 。可视化模型语言 -变迁系统:FSM/HCFSM,Timed Automata -数据流系统:CDFG,数据流进程网络(KPN,SDF) ·应用与工具 到 ·Peter Marwedel,.TU Dortmund教授 战入式系统设计一入式 信息物理系统基础■ -《嵌入式系统设计,嵌入式CPS系统基础》,第2版2011 -第二章:规范与建模 llxx@ustc.edu.cn
内容提要 • 系统规约、建模、实现、分析方法:ABC – CBD:分治,结构 – MBD:抽象,分析 • Integrate Models to DESIGN-BUILD-VALIDATE-VERIFY • 可视化模型语言 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 10/71 – 变迁系统:FSM/HCFSM,Timed Automata – 数据流系统:CDFG,数据流进程网络(KPN,SDF) • 应用与工具 • Peter Marwedel,TU Dortmund教授 – 《嵌入式系统设计·嵌入式CPS系统基础》,第2版2011 – 第二章:规范与建模