
第二章细胞生理 Centrioles Cell Membrane Lysosome Smooth E.R Golgi Body Nucleus Mitochondrion Rough E.R. Chloroplast Ribosome
第二章 细胞生理
主要内容 细胞膜的结构与功能 细胞的兴奇与生物电现象 3 兴春的传递 4 肌肉收缩
1 细胞膜的结构与功能 2 细胞的兴奋与生物电现象 3 兴奋的传递 4 肌肉收缩 主 要 内 容
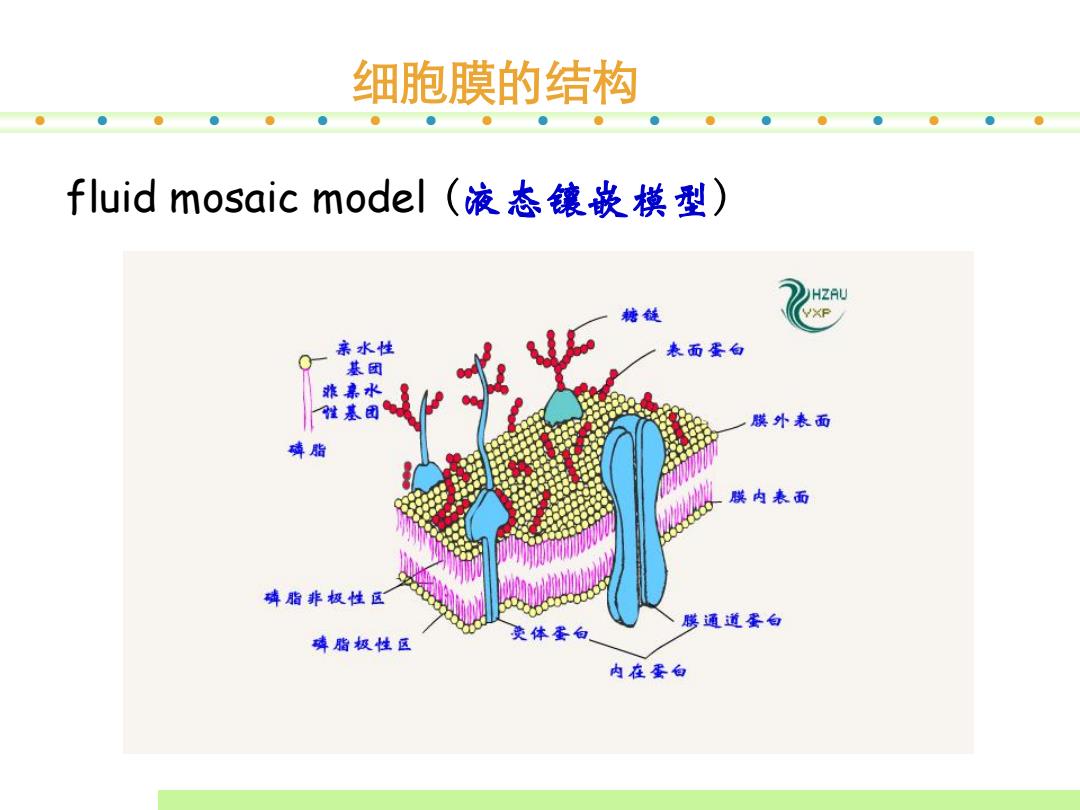
细胞膜的结构 fluid mosaic model(液态镶嵌模型) HZAU 糖链 YXP 亲水性 表面蛋白 基团 水 基团 熊外表面 磷脂 膜内表面 磷脂非极性区 膳通道蛋白 磷脂极性区 荧体蛋向 内在蛋白
细胞膜的结构 fluid mosaic model (液态镶嵌模型)

膜蛋白的功能 Transport (a)A protein that spans the membrane may provide a hydrophillc channel across the membrane that is selective for a particular solute.(b)Some transport proteins hydrolyze ATP as an energy source to actively pump substances across the membrane. Signal transduction A membrane protein may have a binding site with a specific shape that fits the shape of a chemical messenger,such as a hormone.The external messenger(signal)may cause a conformational change in the protein that relays the message to the inslde of the cell. Adhesion Some ghycoproteins attach to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix. Cell-cell recognition Some glycoproteins(proteins with short chains of sugars)serve as identification tags that are specifically recognized by other cells
膜蛋白的功能
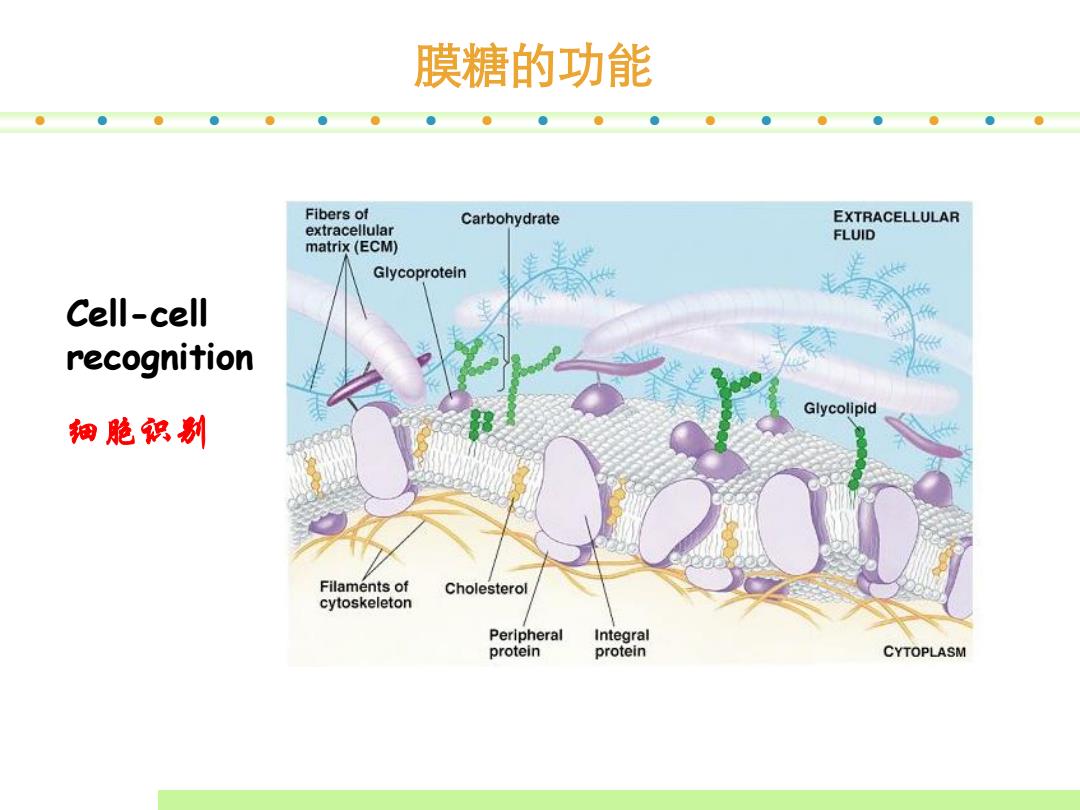
膜糖的功能 Fibers of Carbohydrate EXTRACELLULAR extracellular FLUID matrix (ECM) Glycoprotein Cell-cell 板 recognition Glycolipid 细胞积制 Filaments of Cholesterol cytoskeleton Peripheral Integral protein protein CYTOPLASM
膜糖的功能 Cell-cell recognition 细胞识别
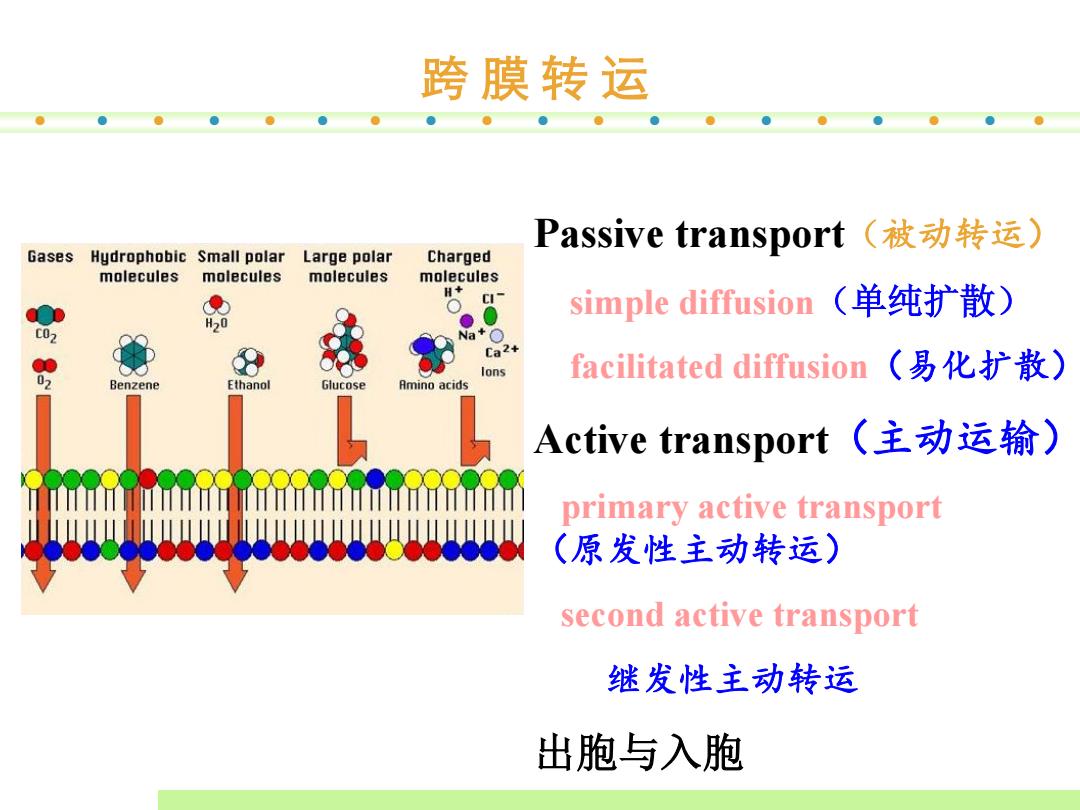
跨膜转运 Passive transport(被动转运) Gases Hydrophobic Small polar Large polar Charged molecules molecules molecules molecules H+ ci- simple diffusion(单纯扩散) C07 Ca2+ facilitated diffusion(易化扩散) 02 Benzene Ethanol Glucose Amino acids Active transport(主动运输) primary active transport (原发性主动转运) second active transport 继发性主动转运 出胞与入胞
跨 膜 转 运 Passive transport(被动转运) simple diffusion(单纯扩散) facilitated diffusion(易化扩散) Active transport(主动运输) primary active transport (原发性主动转运) second active transport 继发性主动转运 出胞与入胞

被动转运Passive Transport The movement of substances across the membrane by down their concentration or electrochemical gradient without consumption of energy. 指物质顺电位或化学梯度通过细胞膜的转 运过程,不需消耗能量 分类: simple diffusion(单纯扩散) facilitated diffusion(易化扩散)
被动转运 Passive Transport The movement of substances across the membrane by down their concentration or electrochemical gradient without consumption of energy. 指物质顺电位或化学梯度通过细胞膜的转 运过程,不需消耗能量 分类: simple diffusion(单纯扩散) facilitated diffusion (易化扩散)
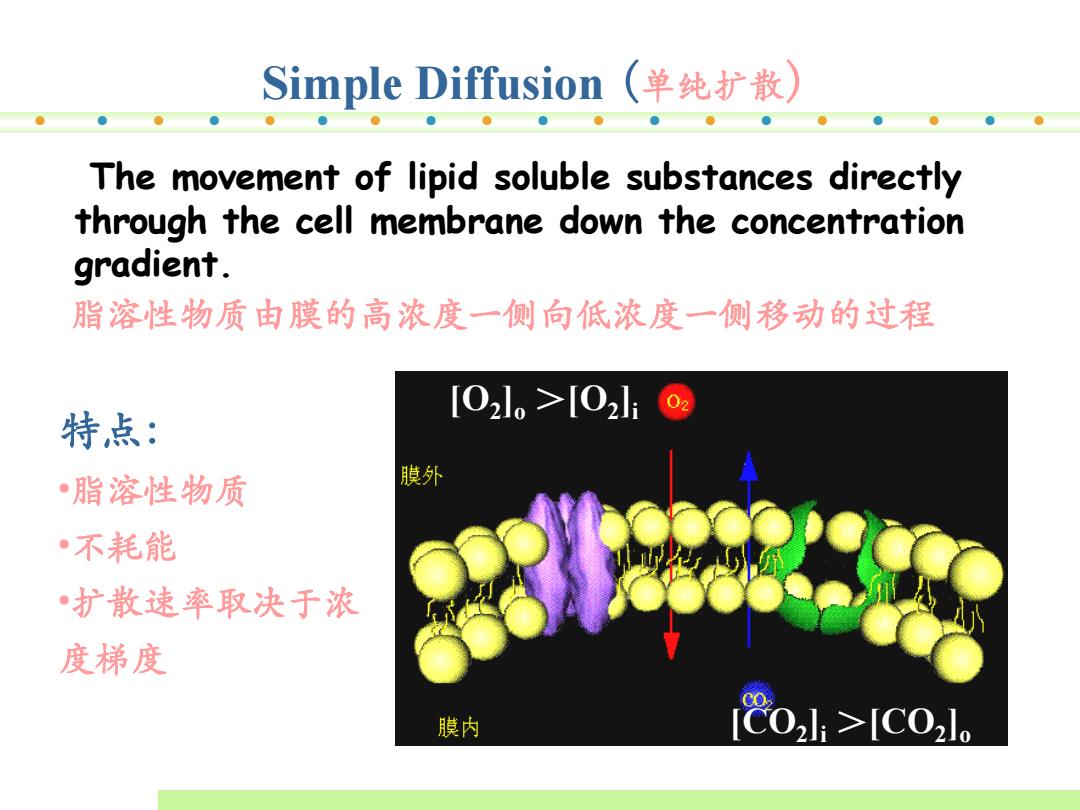
Simple Diffusion 单纯扩散 The movement of lipid soluble substances directly through the cell membrane down the concentration gradient. 脂溶性物质由膜的高浓度一侧向低浓度一侧移动的过程 [02l。>[02l1 02 特点: •脂溶性物质 膜外 •不耗能 ·扩散速率取决于浓 度梯度 膜内 80,l>IC02l
[CO2 ]i >[CO2 ]o [O2 ]o >[O2 ]i Simple Diffusion (单纯扩散) The movement of lipid soluble substances directly through the cell membrane down the concentration gradient. 脂溶性物质由膜的高浓度一侧向低浓度一侧移动的过程 特点: •脂溶性物质 •不耗能 •扩散速率取决于浓 度梯度
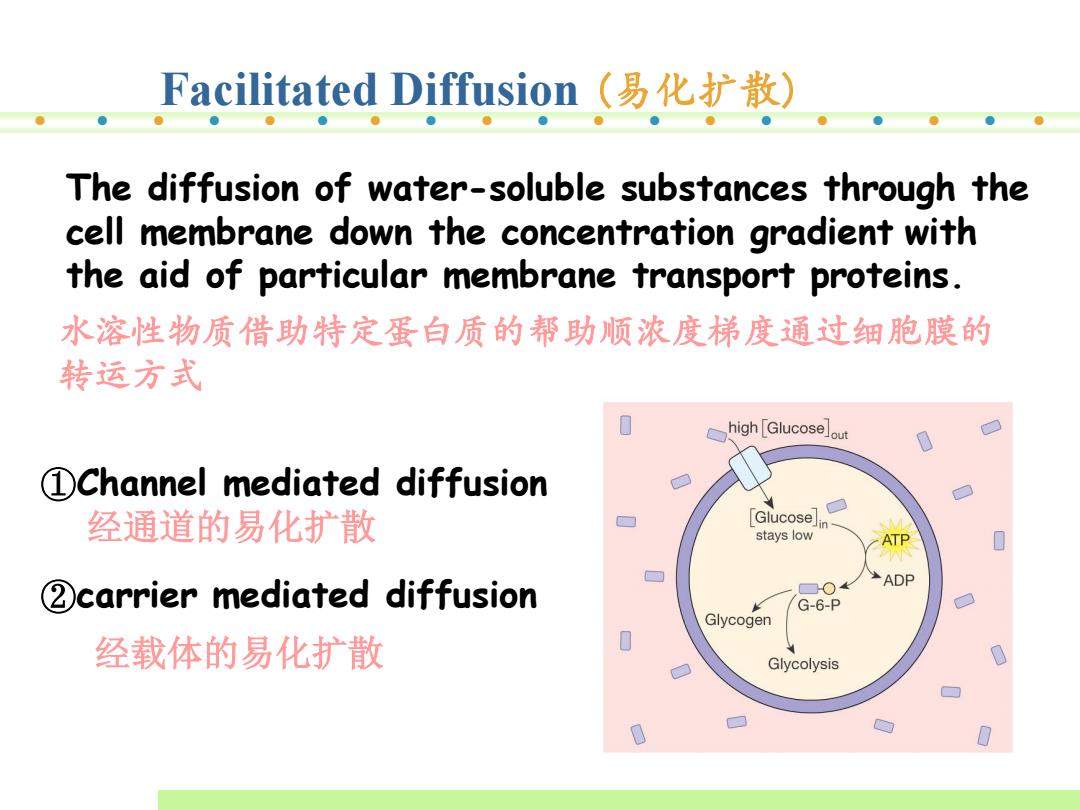
Facilitated Diffusion(易化扩散) The diffusion of water-soluble substances through the cell membrane down the concentration gradient with the aid of particular membrane transport proteins. 水溶性物质借助特定蛋白质的帮助顺浓度梯度通过细胞膜的 转运方式 high [Glucoseout 1Channel mediated diffusion 经通道的易化扩散 Glucose],□ stays low ATP 2carrier mediated diffusion ☐O ADP G-6-P Glycogen 经载体的易化扩散 Glycolysis
Facilitated Diffusion (易化扩散) ②carrier mediated diffusion 经载体的易化扩散 ①Channel mediated diffusion 经通道的易化扩散 The diffusion of water-soluble substances through the cell membrane down the concentration gradient with the aid of particular membrane transport proteins. 水溶性物质借助特定蛋白质的帮助顺浓度梯度通过细胞膜的 转运方式
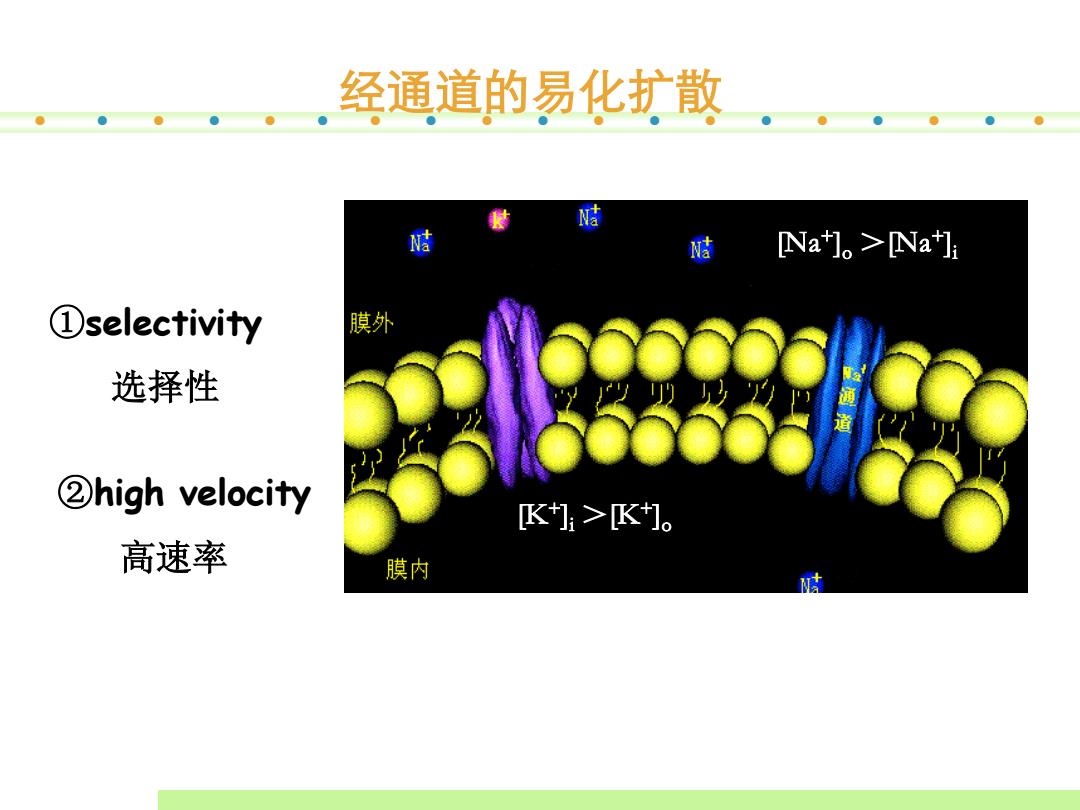
经通道的易化扩散 kN洁 Nah]。>Na]i ①selectivity 膜外 选择性 通道 ②high velocity K]:>K]。 高速率 膜内
[K+] i >[K+]o [Na+]o >[Na+] i 经通道的易化扩散 ①selectivity 选择性 ②high velocity 高速率